Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Maths IGCSE Quick Revision
Încărcat de
farsxdchgDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Maths IGCSE Quick Revision
Încărcat de
farsxdchgDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
www.ciemathematics.blogspot.
com
IGCSE QUICK REVISION
Standard form:
a 10n
Where a one digit.
And n +ve
-ve
Simple Interest:
I=
Where
I : Interest.
P: Amount of Money.
T: Time Yearly.
R: Rate.
Compound Interest:
T = P(1+R/100)n
T: Total Amount of Money.
P: Amount of Money.
R: Rate.
n: Time Yearly.
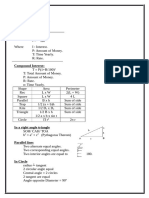
Shape
Area
Rec
LxW
Square
LxW
Parallel
Bxh
Trap
1/2 (a + b)h
Kite
1/2 D1 x D2
Triangle
1/2 B x h
1/2 a x b x sin t
Circle
r2
Perimeter
2(L + W)
4L
Sum of side
Sum of side
Sum of side
Sum of side
2 r
In a right angle triangle
SOH/ CAH/ TOA
b2 = a2 + c2 (Pythagoras Therom)
Parallel lines
Two alternate equal angles.
Two corresponding equal angles.
Two interior angles are equal to
In Circle
radius tangent
2 circular angle equal
Central angle = 2 circles
2 tangent are equal
180.
www.ciemathematics.blogspot.com
Angle opposite Diameter = 90
In cyclic opposite angle = 180
Arc length =
2
Sector area =
Volume = A x h
A = Base area.
Sum of interior = (n-2)180
(
Each angle in regular =
Sum of exterior = 360
In similarity
Angles equal
Sides proportional (equal ratio)
= ( )
= ( )
Direct Variation
xy
Inversely Variation
x
x=ky
x=
Indices
an x am = a n+m
an am = a n-m
(an)m = anm
=
=1
=
Inequality
-x < y
x > -y
Linear programming
Shade unrequired region after: Turn inequality
equation. (make y subject)
Draw equation of (straight line).
Shade over or under the line.
www.ciemathematics.blogspot.com
Bearing:
Angle measured
From
North
Clock Wise
Sine rule:
Given angle & opposite side
=
=
Cosine rule:
Given 3 sides or 2 sides and angle in bet.
a2 = b2 + c2 2bc cos A
cos A =
Limits of Accuracy:
nearest
2
result
Quadratic Equation:
Correct to 2 decimal place use
X=
where ax2 + bx + c = 0
Gradient:
Line touches the curve at point
Tan angle.
Diff of y / diff of x
Equation of straight line
y = mx + c
Where m = gradient , c = y intercept
Graphical soln:
Point of intersection of curve with x axis or line
Line cut x axis
y=0
Line cut y axis
x=0
In a speed time graph:
Distance = Area under graph.
Acceleration =
www.ciemathematics.blogspot.com
Sets:
AB
1A
1B
complement
not A
A
B
AB
all element
In Vector:
If you want resultant you must start with point and end by the other.
For example:
Column Vector:
Start with A 3 unit in +ve x
Then 2 unit in +ve y
Parallel Vector:
k //
Modulus Vector:
Length
If
magnitude
| |
Function:
To get the inverse make x subject.
Composed function substitute x by function.
Matrix:
Order R x C
M1 x M2
For multiply R1 x C1
Condition C1 = R2
R2 x C2
www.ciemathematics.blogspot.com
Inverse of matrix:
A=
1 0
-1
AA = I
0 1
I
Identity
A-1 =
Transformation:
G1 the size not change
Reflection
Distance from O to Mir = Distance from I to Mir
OI Mir
center ( Bisector of O & I)
Angle of rotation
Direction
column vector
Rotation
Translation
G2 the size changed (scale factor)
Enlargement
Scale factor
Center fenelayment
Scale Factor =
Shear
Scale factor
Invariant line
Scale Factor =
Stretch
Scale factor
Invariant line
Scale Factor =
www.ciemathematics.blogspot.com
Statistics
If histogram f.d =
If pie chart total frequency 360
Data
Ungrouped
Mean
Median
Middle after arrange
Mode
Most repeated
Median = 50% of frequency
Upper quartile = 75% of frequency
Lower quartile = 25% of frequency
Inter quartile = upper lower
Probability
P=
Sum of all probability = 1
For 2 events A & B
P (A and B) = P (A) x P (B)
P (A or B) = P (A) + P (B)
If we have 2 points
A (x1, y1)
A
Length of
= ( ) + (
Mid-point = (
,
)
Grad =
Middle class
2 and add till you get
highest frequency class
In cumulative frequency curve:
grouped
B(x2, y2)
B
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Standard mathematical formulas and concepts summaryDocument6 paginiStandard mathematical formulas and concepts summaryMahmoudsamir El Shazly100% (1)
- ZTZMGob JDocument7 paginiZTZMGob JObert MupomokiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALGEBRA 1 LOGARITHM ALGEBRA 2 UNIFORM MOTION PROBLEMS REMAINDER AND FACTOR THEOREMSDocument33 paginiALGEBRA 1 LOGARITHM ALGEBRA 2 UNIFORM MOTION PROBLEMS REMAINDER AND FACTOR THEOREMSLala Hala100% (3)
- MATH Formulas PDFDocument33 paginiMATH Formulas PDFAnonymous 0Mduljho100% (3)
- Maths IGCSE Quick Revision RecoveredDocument6 paginiMaths IGCSE Quick Revision RecoveredShifa RizwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CXC MATHS Formula SheetDocument7 paginiCXC MATHS Formula SheetEric D Medeci100% (1)
- CXC MATHS Formula SheetDocument7 paginiCXC MATHS Formula SheetSeleneGoberdhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATHS REVISION OF KEY FORMULAEDocument5 paginiMATHS REVISION OF KEY FORMULAEabhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Great Math Formula With ExamplesDocument37 paginiGreat Math Formula With Examplessandesh negi100% (1)
- All CE FormulasDocument131 paginiAll CE FormulasKathleen LacsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math Formula SheetDocument8 paginiMath Formula SheetHidayah TeacherÎncă nu există evaluări
- X y X Y: Ratio and Proportion A. Direct ProportionDocument11 paginiX y X Y: Ratio and Proportion A. Direct ProportionJerick Enrique FegaridoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic Field and Waves: EE 221 Spring 2004Document34 paginiElectromagnetic Field and Waves: EE 221 Spring 2004Ali Ahmad100% (1)
- Essential Trigonometry ConceptsDocument23 paginiEssential Trigonometry ConceptsTitis PohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric GraphsDocument1 paginăTrigonometric GraphsBlaine RogalskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAT II Math Level 2 Subject Test Notes: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument4 paginiSAT II Math Level 2 Subject Test Notes: Trigonometric Functionstomcantyyy100% (1)
- Co-Ordinate Geometry: Tests For Special QuadrilateralsDocument4 paginiCo-Ordinate Geometry: Tests For Special QuadrilateralskaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formula - by B B Susheel KumarDocument14 paginiFormula - by B B Susheel KumarB B Susheel KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ah FormulaeDocument5 paginiAh FormulaeVijay RajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Co-Ordinate Geometry: Tests For Special QuadrilateralsDocument4 paginiCo-Ordinate Geometry: Tests For Special QuadrilateralsCarla SassineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths Notes PT 4Document12 paginiMaths Notes PT 4kanisk4bÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Points and Formulae: Mathematics Grade 9 BmiDocument6 paginiImportant Points and Formulae: Mathematics Grade 9 BmiZulfiqar Ali MirÎncă nu există evaluări
- GMAT Math Formulas ListDocument3 paginiGMAT Math Formulas ListOlzhas BolatbekulyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algebra Geometry Statistics AllDocument26 paginiAlgebra Geometry Statistics AllDwin donever PacuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid Mensuration FormulasDocument2 paginiSolid Mensuration FormulasAllen Ang Naiba88% (69)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe la EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (8)
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionDe la EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (4)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDe la EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentDe la EverandMathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankDe la EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circles (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankDe la EverandCircles (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDe la EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesDe la EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tables of Racah Coefficients: Mathematical Tables SeriesDe la EverandTables of Racah Coefficients: Mathematical Tables SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe la EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsDe la EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankDe la EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Cambridge Mathematics AS and A Level Course: Second EditionDe la EverandCambridge Mathematics AS and A Level Course: Second EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge Mathematics A2 Level Course: Second EditionDe la EverandCambridge Mathematics A2 Level Course: Second EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsDe la EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- 0610 w07 QP 1Document20 pagini0610 w07 QP 1farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0610 w06 QP 3Document16 pagini0610 w06 QP 3farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0625 w06 QP 3Document16 pagini0625 w06 QP 3farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoverDocument1 paginăCoverfarsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0625 s12 QP 12Document20 pagini0625 s12 QP 12farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0625 s14 QP 12 PDFDocument20 pagini0625 s14 QP 12 PDFHaider AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Re Activity Series & Corrosion of MetalsDocument8 paginiRe Activity Series & Corrosion of MetalsAli MahadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0625 s11 QP 12Document20 pagini0625 s11 QP 12farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoverDocument1 paginăCoverfarsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0625 w10 QP 62Document12 pagini0625 w10 QP 62farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0625 s14 QP 12 PDFDocument20 pagini0625 s14 QP 12 PDFHaider AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0625 s15 QP 12Document20 pagini0625 s15 QP 12farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0625 s10 QP 12Document20 pagini0625 s10 QP 12farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0625 w05 QP 6Document12 pagini0625 w05 QP 6farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0625 w10 QP 62Document12 pagini0625 w10 QP 62farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0625 w06 QP 6Document12 pagini0625 w06 QP 6farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0625 w12 QP 62Document12 pagini0625 w12 QP 62farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crystallisation Techniques for X-Ray Quality CrystalsDocument11 paginiCrystallisation Techniques for X-Ray Quality CrystalsShafeeq AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crystallisation Techniques for X-Ray Quality CrystalsDocument11 paginiCrystallisation Techniques for X-Ray Quality CrystalsShafeeq AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igcse: PhysicsDocument1 paginăIgcse: PhysicsfarsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5-Homeostasis QuestionsDocument17 paginiUnit 5-Homeostasis Questionsareyouthere92Încă nu există evaluări
- 0417 s15 QP 12Document16 pagini0417 s15 QP 12farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0417 w13 QP 12Document16 pagini0417 w13 QP 12farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 paginiUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationKwadwo KankamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integration GCSE NoteDocument27 paginiIntegration GCSE NotebrianbobbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch16 Conversion To Linear FormDocument10 paginiCh16 Conversion To Linear FormDamien LeongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0417 Y16 SP 1Document14 pagini0417 Y16 SP 1farsxdchg0% (1)
- 0417 s15 QP 12Document16 pagini0417 s15 QP 12farsxdchgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Class X Areas Related To Circles Main1Document2 paginiAssignment Class X Areas Related To Circles Main1CRPF School100% (3)
- UTA015: Learn Engineering DrawingDocument2 paginiUTA015: Learn Engineering DrawingSHIVA THAVANIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics XI Numerical and MCQ's Motion in One DimensionDocument19 paginiPhysics XI Numerical and MCQ's Motion in One DimensionRehman khasÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Calcutta Faculty Academic Profile / CVDocument4 paginiUniversity of Calcutta Faculty Academic Profile / CVPrakash SardarÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Monograph Book) Jacques Hadamard - Lessons in Geometry, Vol. 1 - Plane Geometry (2008, American Mathematical Society) PDFDocument346 pagini(Monograph Book) Jacques Hadamard - Lessons in Geometry, Vol. 1 - Plane Geometry (2008, American Mathematical Society) PDFAlexandru Căliman100% (1)
- Coordinate Computation: Calculating Length, Bearing, Angles and CoordinatesDocument13 paginiCoordinate Computation: Calculating Length, Bearing, Angles and CoordinatesYoussif SedeakÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Introduction To NURBSDocument133 pagini1 Introduction To NURBSBala RanganathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imo Book 2012Document101 paginiImo Book 2012CNMarmo100% (1)
- Space Elevator TheoryDocument5 paginiSpace Elevator TheorympecthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution To Complex Analysis by SteinDocument15 paginiSolution To Complex Analysis by SteinRiteshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Drawing Lab ManualDocument52 paginiEngineering Drawing Lab ManualRAMAKANT RANA93% (15)
- Spherical TrigonometryDocument23 paginiSpherical TrigonometryPeejay Ollabrac100% (1)
- Surveying Defination of Terms PDFDocument89 paginiSurveying Defination of Terms PDFstanlee35Încă nu există evaluări
- Important geometry and calculus questionsDocument3 paginiImportant geometry and calculus questionsKampili akashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angular Projectile MotionDocument16 paginiAngular Projectile MotionwscienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics Surveying & Transportation Engineering: Prepared By: Rei Kevin C. TungcabDocument66 paginiMathematics Surveying & Transportation Engineering: Prepared By: Rei Kevin C. Tungcabjoshua remonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument23 paginiInverse Trigonometric FunctionsShruti GiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Add Maths Rev GuideDocument20 paginiAdd Maths Rev GuidesuperwebonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential and Integral Calculus Formulas, Concepts, ExamplesDocument6 paginiDifferential and Integral Calculus Formulas, Concepts, ExamplesDayLe Ferrer AbapoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP No. 1 Learning Area: Art Grade Level: 1 Quarter: 1 Duration: Learning Competency/ies: Key Concepts/ Understanding To Be Develop: I. DomainDocument4 paginiDLP No. 1 Learning Area: Art Grade Level: 1 Quarter: 1 Duration: Learning Competency/ies: Key Concepts/ Understanding To Be Develop: I. DomainPrincess Marisse Mañosa100% (5)
- Surfaces of The Second Order: Introductio in Analysin Infinitorum Vol. 2Document25 paginiSurfaces of The Second Order: Introductio in Analysin Infinitorum Vol. 2david.contatos4308Încă nu există evaluări
- IAS Mains Mathematics 2016 PDFDocument18 paginiIAS Mains Mathematics 2016 PDFshanmugamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 7 Yearly Exam 2015Document9 paginiYear 7 Yearly Exam 2015deborahmorton67% (3)
- Exercise: Short Answer Type QuestionsDocument3 paginiExercise: Short Answer Type QuestionsBharatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cyclic Quadrilaterals and Their PropertiesDocument2 paginiCyclic Quadrilaterals and Their Propertieskepler1729Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 14 Areas and Volumes (Word Problems)Document13 paginiUnit 14 Areas and Volumes (Word Problems)bemdasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS76-Computer Graphics LabDocument26 paginiCS76-Computer Graphics Labsathyalk81Încă nu există evaluări
- Analysis Manual for MIDAS/Gen Numerical ModelDocument323 paginiAnalysis Manual for MIDAS/Gen Numerical ModelNayeemuddin Khaja0% (1)
- Drafting ExercisesDocument12 paginiDrafting ExercisesJaime Andres Velez100% (3)
- Multi Variable Calculus NotesDocument105 paginiMulti Variable Calculus NotesmuhammadtalÎncă nu există evaluări































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)