Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Biology Form 4 Short Notes (2.2) - Part 1
Încărcat de
incognito278Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Biology Form 4 Short Notes (2.2) - Part 1
Încărcat de
incognito278Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Biology Form 4 short notes
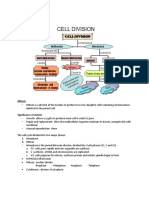
Chapter 2- Cell Structure and Cell Organisation
2.2 Cell Organisation
Cell organisation in unicellular organisms.
-Unicellular organisms consist of one cell.
-The structure is very simple.
-These organisms can feed, respire, excrete and move. They also respond
to external stimuli.
-Examples of unicellular organisms are Amoeba sp. and Paramecium sp.
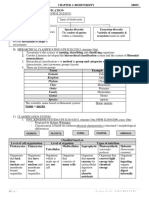
Amoeba sp.
-Amoeba lives in freshwater lakes and ponds.
-The cytoplasm is enclosed by a plasma membrane.
-Changes shape when meets stimuli and obstacle.
-The outer part is called ectoplasm and the inner part is endoplasm
-Amoeba moves and feeds by using pseudopodia. Also called as ‘false feet’.
The locomotion is called as ‘ameboid movement’.
-Amoeba reproduces by binary fission (asexual reproduction).
-Grows by synthesising new cytoplasm.
Paramecium sp.
-Has fixed slipper-like shape.
-The surface is covered by tiny hair projection called cilia.
-Has two nuclei- macronucleus- for metabolism control and asexual
reproduction. –Micronucleus- for sexual reproduction.
-It moves by beating the cilia.
-Feeds on microscopic organisms.
-Reproduces asexually and sexually. In favourable condition, could
reproduce rapidly by binary fission. Sexual reproduction, also known as
conjugation takes place when condition is not favourable.
-Also grows by synthesising new cytoplasm.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 2Document12 paginiNota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 2Firas Muhammad100% (2)
- Bio ACE Form 4Document3 paginiBio ACE Form 4Myramel KlarisÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Answer SPM Biology Paper 1 2 3 by Kenneth NG Edited May 2009Document20 paginiHow To Answer SPM Biology Paper 1 2 3 by Kenneth NG Edited May 2009Boon Kiat Teh90% (10)
- Biology Paper 3 Experiment Checklists: Num. Form Activity NotesDocument1 paginăBiology Paper 3 Experiment Checklists: Num. Form Activity Notesdebbycley70% (10)
- Experiment BioDocument29 paginiExperiment BioQin Jamil100% (1)
- SPM Physics Terms and DefinitionDocument12 paginiSPM Physics Terms and Definitionnursuhailah100% (3)
- Electrical Conductivity: Revision Notes On The Topic 'Electrical Conductivity' For Edexcel IGCSE ChemistryDocument16 paginiElectrical Conductivity: Revision Notes On The Topic 'Electrical Conductivity' For Edexcel IGCSE ChemistryDANSTAN GISOREÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.8 Transport in PlantsDocument26 pagini1.8 Transport in PlantsHema LataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 2Document93 paginiBiology Form 4 Chapter 2leelijye100% (1)
- Active N Passive ImmuityDocument13 paginiActive N Passive ImmuityeffadilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Updated 2 Iza and IkmalDocument25 paginiBiology Updated 2 Iza and IkmalEva WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 5 Cell DivisionDocument7 paginiBiology Form 4 Chapter 5 Cell Divisiongelgaban67% (3)
- Koleksi Eksperimen Biologi SPMDocument39 paginiKoleksi Eksperimen Biologi SPMMohd Raimi Rahim80% (5)
- SPM Biology Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Cell Structures and Functions (ALL 12 Structures of Plant Cell and Animal Cell)Document4 paginiSPM Biology Form 4 Chapter 2.1 Cell Structures and Functions (ALL 12 Structures of Plant Cell and Animal Cell)Felicia LingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 4-ProteinDocument1 paginăBiology Form 4 Chapter 4-ProteinFarain Rashdi75% (4)
- BIO - SPM 2020 Model Answers - Predicted QuestionsDocument33 paginiBIO - SPM 2020 Model Answers - Predicted QuestionskumarantuitionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio NotesDocument19 paginiBio NotesMyramel KlarisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell (Organelle and Non-Organelle)Document10 paginiCell (Organelle and Non-Organelle)ridwan80% (5)
- Biology Module Chap 8Document37 paginiBiology Module Chap 8Faida Hamid100% (4)
- Interaction Between Living OrganismsDocument27 paginiInteraction Between Living Organismsaiyriss100% (2)
- Chemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Document2 paginiChemistry (Chapter 3 - Notes)Daniel Wong Sai Meng100% (1)
- 1 Compressed Notes BioDDocument23 pagini1 Compressed Notes BioDLIM ZHI SHUENÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2017 SPM BIOLOGY Trial PaperDocument10 pagini2017 SPM BIOLOGY Trial PaperV. SundrramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9Document24 paginiChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9dinda syi100% (18)
- Science F4 Chapter 3 3.1Document40 paginiScience F4 Chapter 3 3.1KSSM TSE100% (1)
- SOLAF 2014 Biologi SPM Modul 3: JPN Perak 1Document7 paginiSOLAF 2014 Biologi SPM Modul 3: JPN Perak 1AZIANA YUSUFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Properties of Group 18, Group 1 and Group 17 ElementsDocument2 paginiPhysical Properties of Group 18, Group 1 and Group 17 ElementsJames Chua Hong KhengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 6Document9 paginiChemistry Form 4 Chapter 6Steven Wong50% (2)
- Biology Chapter 2 Topical ExerciseDocument3 paginiBiology Chapter 2 Topical ExerciseAlan WangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry SPMDocument20 paginiChemistry SPMJacob ChowÎncă nu există evaluări
- WORKSHEET 15.1 Comparing Continuous and Discontinuous VariaDocument2 paginiWORKSHEET 15.1 Comparing Continuous and Discontinuous VariaSiti Nor Aishah100% (1)
- Chapter 2 (Cell Organisation)Document3 paginiChapter 2 (Cell Organisation)Danial AsyraafÎncă nu există evaluări
- f4 Chapter 2 Cell Ion NotesDocument2 paginif4 Chapter 2 Cell Ion NotesVimal RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 2Document23 paginiBiology Form 4 Chapter 2Thiyaku MaruthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Form 4 Notes 2.3Document2 paginiBiology Form 4 Notes 2.3gelgabanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Form 4Document23 paginiSPM Form 4tqahazliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unicellular (Single-Celled) Protists - Eukaryotic Protozoan: EuglenaDocument3 paginiUnicellular (Single-Celled) Protists - Eukaryotic Protozoan: EuglenaEGSRHEtjykudli.u;Încă nu există evaluări
- What Are Cells?: Biology Form 4 Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation Subtopic 2.1: Cell Structure & FunctionDocument13 paginiWhat Are Cells?: Biology Form 4 Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation Subtopic 2.1: Cell Structure & FunctionyayeetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Morphology and Physiology of Living Things: National Diploma in Science Laboratory TechnologyDocument99 paginiMorphology and Physiology of Living Things: National Diploma in Science Laboratory Technologyogbonna ebuka innocent100% (1)
- Biology PlantsDocument7 paginiBiology PlantsSoumya RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phylum Protozoa Classification: Elementary IdeaDocument3 paginiPhylum Protozoa Classification: Elementary IdeaSudesh RathodÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Protista (15p)Document15 pagini2 Protista (15p)Olanrewaju AgodirinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - NotesDocument6 paginiSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Notessundarchoudhary2020Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is AmoebaDocument12 paginiWhat Is AmoebaAssaf KamaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 4 Animl KingdomDocument12 paginiCHAPTER 4 Animl KingdomAnushka MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProtzoologyDocument37 paginiProtzoologyhumanupgradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- GenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2Document7 paginiGenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2The GreatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genbio ReviewerDocument3 paginiGenbio ReviewerAnne Carmel PinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 15-23 SUMMARY UpdatedDocument7 paginiActivity 15-23 SUMMARY UpdatedZoe Kristeun GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Ii - BSWDocument30 paginiUnit Ii - BSWAshwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio F4 KSSM Chapter 2-DLPDocument102 paginiBio F4 KSSM Chapter 2-DLPNurasyikin SaidinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells & MicroorganismDocument3 paginiCells & Microorganismkimmiefisher23Încă nu există evaluări
- 2.2.1 Cell OrganisationDocument15 pagini2.2.1 Cell Organisationche salÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organ System: Kingdom AnimaliaDocument18 paginiOrgan System: Kingdom AnimaliaTanishq AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity No.1 Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument4 paginiActivity No.1 Cell and Molecular Biologyjocelynmillano115100% (1)
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants NotesDocument7 paginiReproduction in Flowering Plants NotesUthara UmeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 2. Plant Cell Vs Animal CellDocument5 paginiActivity 2. Plant Cell Vs Animal CellMary Joyce BonayonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal KingdomDocument35 paginiAnimal KingdomSuresh KuppananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Words To Know: Amoeba Proteus. (Reproduced by Permission ofDocument3 paginiWords To Know: Amoeba Proteus. (Reproduced by Permission ofMary JinuÎncă nu există evaluări