Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCP
Încărcat de
dericTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCP
Încărcat de
dericDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Student Nurses Community
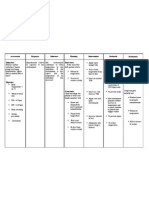
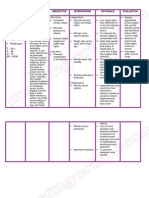
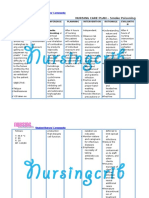
NURSING CARE PLAN Pedia TB Meningitis
ASSESSMEN
T
SUBJECTIVE:
Nilalagnat
ang
anak ko as
verbalized by
the
mother.
OBJECTIVE:
Flushed
skin,
warm to
touch.
Increased
respiratory
rate.
V/S taken as
follows:
T: 37.8
P: 110
R: 45
DIAGNOSIS
INFERENCE
Hyperthermia
related to
infectious
process and
dehydration.
Tuberculosis
meningitis is
the most
severe form of
tuberculosis.
It causes
severe
neurologic
deficits or
death in more
than half of
cases.
Tuberculois
meningitis
begins
insidiously
with a gradual
fluctuating
fever, fatigue,
weight loss,
behavior
changes,
headache,
and vomiting.
This early
phase is
PLANNING
INTERVENTIO
N
RATIONALE
After 4 hrs. of
Independent:
Dysrhythmias
nursing
and ECG
interventions, Monitor heart
changes are
the client will
rate and
common
maintain core
rhythm.
due to
temperature Record all
electrolyte
within normal
sources of
imbalance
range.
fluid loss such
and
as urine,
dehydration
vomiting.
and direct
Promote surface
effect of
cooling by
hyperthermi
means of
a on blood
tepid sponge
and cardiac
bath.
tissues.
Wrap
To monitor or
extremities
potentiates
with cotton
fluid and
blankets.
electrolyte
Provide
loses.
supplemental To decrease
oxygen.
temperatur
Administer
e by means
replacement
through
fluids and
evaporation
electrolytes.
and
EVALUATIO
N
After 4 hrs.
of nursing
intervention
s, the client
was able
maintain
core
temperatur
e within
normal
range.
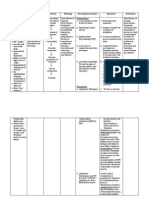
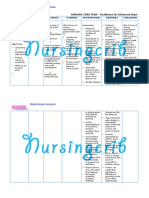
Student Nurses Community
followed by
neurologic
deficits, loss
of
consciousness
, or
convulsions. A
dense
gelatinous
exudates
(outpouring)
forms and
envelops the
brain arteries
and cranial
nerves. It
creates a
bottleneck in
the flow of the
cerebrospinal
fluid, which
leads to
hydrocephalu
s.
conduction.
Maintain bed
To minimize
rest.
shivering.
Provide high
To offset
calorie diet,
increased
tube feedings,
oxygen
or parenteral
demands
nutrition.
and
Administer
consumptio
antipyretics
n.
orally or
To support
rectally as
circulating
prescribed by
volume and
the physician.
tissue
perfusion.
To reduce
metabolic
demands
and oxygen
consumptio
n.
To increased
metabolic
demands.
To facilitate
fast
recovery.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument3 paginiHyperthermia NCPJayr DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newborn Careplan 9-15-2011Document17 paginiNewborn Careplan 9-15-2011Brittany Wood100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiIneffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanJose Mari F. Esguerra0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Pedia TB MeningitisDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Pedia TB Meningitisderic100% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan of MeningitisDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan of MeningitisŦỏṯặ Łaẕỗzą100% (7)
- Urinary Tract Infection - NCPDocument2 paginiUrinary Tract Infection - NCPIssa Farne0% (1)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 paginăNCP HyperthermiaPastor James PacadaljenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan JaundiseDocument1 paginăNursing Care Plan Jaundisearif aimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 paginăHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument28 paginiNursing Care PlanChristine Karen Ang Suarez67% (3)
- Bronchopneumonia Care PlanDocument6 paginiBronchopneumonia Care PlanAbhijit Soundade0% (1)
- Neonatal Jaundice and Ineffective Breundiceeding Nursing Care PlanDocument3 paginiNeonatal Jaundice and Ineffective Breundiceeding Nursing Care Planpapadaad100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM)Document1 paginăDiabetes Mellitus (DM)Bheru LalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS HIVDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For AIDS HIVFARAH MAE MEDINA100% (2)
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument4 paginiNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityElgie SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- HyperthermiaDocument2 paginiHyperthermiapamgee100% (11)
- Hyperbilirubinemia Case PresentationDocument25 paginiHyperbilirubinemia Case PresentationEricka B. Banaszczuk100% (3)
- NURSING CARE PLAn-Imbalance NutritionDocument2 paginiNURSING CARE PLAn-Imbalance NutritionJoan Parlan100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiNursing Care PlanKath RubioÎncă nu există evaluări
- CJ C J CJ CJ Cî CJ CJ C C ! "! Cî C Ë # C Ë # CJ$ C C 0 "% C C & C C C Ë Î C "' (C Ëj "ËjDocument105 paginiCJ C J CJ CJ Cî CJ CJ C C ! "! Cî C Ë # C Ë # CJ$ C C 0 "% C C & C C C Ë Î C "' (C Ëj "ËjShirin Forbes Aquino100% (2)
- NCP Proper 1Document6 paginiNCP Proper 1Noreen PinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Age Case PresentationDocument21 paginiAge Case PresentationDev AakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASSESSMENT HEALTH NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATIONDocument3 paginiASSESSMENT HEALTH NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATIONtflorenzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Post-Surgical Pain ReliefDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan for Post-Surgical Pain ReliefAdelaine LorestoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For PediaDocument10 paginiNCP For PediavonkinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plans For UTIDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plans For UTIHannah Pin67% (3)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 paginăNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for GastroenteritisDocument7 paginiNursing Care Plan for GastroenteritisChris Denver BancaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument4 paginiNCPEugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP SepsisDocument6 paginiNCP SepsisgopscharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infection NCPDocument1 paginăInfection NCPMsOrangeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acc Phu Case NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 paginăAcc Phu Case NCP Hyperthermiamacy_bautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan NephritisDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Nephritisderic82% (17)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 paginiNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lanjutan NCP DMDocument14 paginiLanjutan NCP DMVera Andri YaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFFARAH MAE MEDINA100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 paginiNursing Care PlanZerica Andaca83% (6)
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 paginiNCP HemothoraxMichael John F. NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument15 paginiNCPCamille PinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing care plan for client with UTI and feverDocument3 paginiNursing care plan for client with UTI and feverTheresa AbrilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Bronchiolitis 1Document2 paginiChild Bronchiolitis 1sarooah1994100% (2)
- Body Weakness NCPDocument1 paginăBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care for Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument7 paginiNursing Care for Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverjoycevillamorÎncă nu există evaluări
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 paginiCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Billy Admitted with Ear and Throat InfectionsDocument6 paginiNursing Care Plan for Billy Admitted with Ear and Throat InfectionsNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Care Plan Redo For NeonateDocument2 paginiCare Plan Redo For NeonateIris Lopez100% (6)
- NCP PTBDocument2 paginiNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For FT, SGADocument7 paginiNCP For FT, SGAJule Santoya80% (5)
- NCP PancreatitisDocument2 paginiNCP PancreatitisJeanelle GenerosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Measles Case PresDocument1 paginăNCP Measles Case PresFranz RolfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 paginiDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care of HyperbilirubinemiaDocument12 paginiNursing Care of HyperbilirubinemiaFri-fri Manila67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Patiients With MeningitisDocument35 paginiNursing Care Plan For Patiients With Meningitisixa_morales67% (6)
- Tuberculous Meningitis Nursing AssessmentDocument1 paginăTuberculous Meningitis Nursing AssessmentMark Adrian D. DizorÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP With LogoDocument2 paginiNCP With LogoRhea ArriesgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing care of pediatric dengue patientsDocument11 paginiNursing care of pediatric dengue patientsMike Faustino SolangonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rheumatic FeverDocument46 paginiRheumatic FeverAbinaya RanganathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For HemodialysisDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Hemodialysisderic80% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPderic88% (40)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPderic79% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For AmputationDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Amputationderic80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Glaucomaderic79% (28)
- Nursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPderic100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPderic100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPderic100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPderic100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- Nursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPderic82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPderic100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic71% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPderic67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPderic88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPDocument8 paginiNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic87% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument14 paginiNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPderic92% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPderic71% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPderic100% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPderic83% (23)