Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
DPP - Solids & Fluids
Încărcat de
Mohammed Aftab AhmedTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
DPP - Solids & Fluids
Încărcat de
Mohammed Aftab AhmedDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
1
DPP 29
1.
2.
A uniform rod of length L is hanging from a ceiling. The variation of tensile stress with
distance X from the ceiling is best represented by
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
A uniform steel wire hangs from the ceiling and elongates due to
its own weight. The ratio of elongation of the upper half of the
wire to the elongation of the lower half of wire is
(a) 4 : 1
(b) 3 : 1
(c) 3 : 2
(d) None
3.
Select the correct statement on the basis of the given
graph
(a) Young's modulus of A is greater but it is less
ductile
(b) Young's modulus of A is greater and it is more
ductile
(c) Young's modulus of A is less and it is less ductile
(d) Young's modulus of A is less but it is more ductile
4.
A steel rope of length L, area of cross-section A, Youngs modulus Y, is hanging from a
celling in equilibrium. The elastic potential energy per unit volume at a point L/3 from
ceiling is [Density = d]
(a) 2(dgL)2/9Y
(b) (dgL)2/9Y
(c) 2(dgL)/9AY
(d) 2(dgL)2/3Y
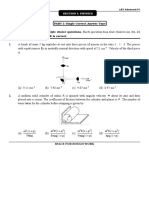
5.
Disk A of radius r moving on perfectly smooth surface at a speed v
collides elastically with an identical stationary disk B. If the impact
parameter is r/2 as shown, the velocity of the disk B after collision
will be
v 15
v
(a)
(b)
4
4
v
3
(c)
(d)
v
2
2
6.
A ring of radius r made of wire of density is rotated about a stationary
SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
vertical axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to the plane of
the ring as shown in figure. Determine the angular velocity (in rad /s) of
ring at which the ring breaks. The wire breaks at tensile stress . Ignore
gravity. (Take
= 4 and r = 1m)
7.
A wire having cross-sectional area S is attached to wall on one side and
a block of mass M on the other side which placed on a horizontal
surface having coefficient of friction as shown. Material of wire has
coefficient of thermal expansion and Young's modulus Y. At initial
temperature there is no stress in the wire. Now the wire is cooled.
Determine the decrease in temperature (in C) when the block will
begin to move (Take Mg = 4Y and S = 2 m2 )
8.
A ball is thrown from origin with a
velocity u (5i 15 j 10 k ) m/s . The
ball hits an inclined plane at point P as
shown. Find the time taken (in s) by the
ball to reach point P.
r P
45
SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
3
DPP 30
1.
A bucket contains water filled up to a height of 15 cm. The bucket is tied to a rope which is
passing over a frictionless light pulley and the other end of the rope is tied to a block whose
mass is half of that of the combined mass of bucket and water. If the system is released from
rest, the gauge pressure at the bottom of the bucket will be
(a) 0.5 kPa
(b) 1 kPa
(c) 5 kPa
(d) None of these
2.
A fire hydrant delivers water of density at a volume rate of L.
The water travels vertically upward through the hydrant and then
turns 90 turn to emerge horizontally at speed V. The pipe and
nozzle have uniform cross-section throughout. The force exerted
by the water on the corner of the hydrant is
(a) VL
(b) zero
(c) 2VL
(d) 2 VL
3.
A Newtonian fluid fills the clearance between a shaft and a sleeve. When a force of 800N is
applied to the shaft, parallel to the sleeve, the shaft attains a speed of 1.5 cm/sec. If a force
of 2.4 kN is applied instead, the shaft would move with a speed of
(a) 1.5 cm/sec
(b) 13.5 cm/sec
(c) 4.5 cm/sec
(d) None
4.
If the system is not in free fall, the correct statement about hydrostatic pressure is
(a) in a liquid, points at different depths can never be at same pressure.
(b) in a liquid, points at different depths may be at same pressure.
(c) in different liquids, points at same depth can never be at different pressure.
(d) in different liquids, points at same depth can be at same pressure.
5.
A particle moving with kinetic energy of 3 joule makes an elastic head on collision with a
stationary particle having twice its mass. The incorrect statement is
(a) The minimum kinetic energy of the system is 1 joule.
(b) The maximum elastic potential energy of the system is 2 joule.
(c) Momentum and total kinetic energy of the system are conserved at every instant.
(d) The ratio of kinetic energy to potential energy of the system first decreases and then
increases.
6.
A block of wood weighs 12 kg and has a relative density 0.6. It is to be in water with 0.9 of
its volume immersed. A metal of relative density 14 is attached below the block. Find the
weight (in N) of metal needed.
7.
A spherical tank of 1.2 m radius is half filled with oil of relative density 0.8 . If the
tank is given a horizontal acceleration of 10 m/s2. The maximum pressure on the tank
is 2 P pascal. Find the value of P.
SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
8.
A uniform cylindrical block of length l density d1 and area of cross
section A floats in a liquid of density d2 contained in a vessel (d2 > d1).
The bottom of the cylinder just rests on a spring of constant k. The other
end of the spring is fixed to the bottom of the vessel. Determine the
weight (in N) that may be placed on top of the cylinder such that the
cylinder is just submerged in the liquid. (Take l = 1m, d1 1200 kg/m 3 ,
d2 = 2000 kg/m3, K = 1000 N/m, A = 0.1 m2 and g = 10 m/s2)
9.
A plank OA rotates in vertical plane about a horizontal axis through
O with a constant counter clockwise angular velocity of 3 rad/sec. As
it passes the position = 0, a small mass m is placed upon it at a
radial distance (r) of 0.5 m. If the mass is observed to slip at = 37,
n
.
the coefficient of friction between the mass and the plank is
1000
Find the value of n.
SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
5
DPP 31
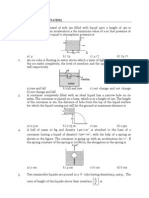
1.
The tank in fig discharges water at constant rate for all
water levels above the air inlet R. the heights above
datum to which water would rise in the manometer
tubes M and N is respectively
(a) 30cm, 60cm
(c) 20cm, 40cm
2.
3.
In the figure shown a particle P strikes the inclined
smooth plane horizontally and rebounds vertically.
If the angle is 60, then the coefficient of
restitution is:
(a) 1/3
(b) 1 / 3
(c) 1/2
(d) 1
A uniform aluminium ball of radius r is suspended through a
light string from the end of an uniform horizontal rod of mass
M placed horizontally on the edge of a container filled with
water. The system is under equilibrium and ball is half
submerged in water. Neglect surface tension of water. The ratio
y
4
M
will be (Given r 3
, density of ball = 2.7 103
x
3
100
kg/m3, density of water = 1 103 kg/m3).
(a) 40
4.
(b) 40cm, 60cm
(d) 20cm, 60cm
(b) 45
(c) 30
A cubical box of liquid has a small spout located in
one of the bottom corners. When the box is full and
placed on a level surface, opening the spout results in
the flow of liquid with an initial speed of v0 as shown
in figure. When the box is half empty, it is tilted at
45 so that the spout is at the lowest point. Now, the
opening of spout will allow the liquid to flow out
with a speed of
v
v
(a) v0
(b) 0
(c) 0
2
2
(d) 35
v0
(d)
v0
4
5.
A jug contains 15 glasses of orange juice. When you open the tap at the bottom it takes 12
sec to fill a glass with juice. If you leave the tap open. How long will it take (in s) to fill the
remaining 14 glasses and thus empty the jug? ( 15 3.9 , 14 3.7 )
6.
A large tank is filled with two liquids of specific gravities
2 and . Two holes are made on the wall of the tank as
shown. The ratio of the distances from O of the points on
the ground where the jets from holes A & B strike is
a : b . Find values of a and b.
SOLIDS AND FLUIDS
7.
The interface of two liquids of densities and 2 respectively lies at
the point A in a U tube at rest. The height of liquid column above A
is 8a/3 where AB = a. The cross sectional area of the tube is S. With
what angular velocity (in rad/s) the tube must be whirled about a
vertical axis at a distance a such that the interface of the liquids
180
shifts towards B by 2a/3. (Take a =
unit and g = 10 m/s2)
19
8.
A child of mass 4 kg jumps from cart B to cart A and then
immediately back to the cart B. The mass of each cart is 20kg and
they are initially at rest. In both cases the child jumps at 6m/s relative
to the cart. If the cart moves along the same line with negligible
friction with the final velocities of v B and v A respectively. Find the
ratio of 6v B and 5v A .
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Supplement Questions of FLUID MECHANICS: Paragraph For Question Nos. 1 To 3Document7 paginiSupplement Questions of FLUID MECHANICS: Paragraph For Question Nos. 1 To 3Tanuj Gupta0% (2)
- Mechanical Properties of Solids & FluidsDocument8 paginiMechanical Properties of Solids & FluidsShardaVermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Vertical Limbs of A U Shaped Tube Are Filled With A Liquid of DensityDocument14 paginiThe Vertical Limbs of A U Shaped Tube Are Filled With A Liquid of DensityUdeshaWickramaraachchi100% (1)
- Fluids Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument11 paginiFluids Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsHey Zac100% (1)
- Elasticity and Fluid Machanics-06 - Subjective Unsolved LevelDocument3 paginiElasticity and Fluid Machanics-06 - Subjective Unsolved LevelRaju SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics & ChemistryDocument15 paginiPhysics & ChemistryDexterMorgan007Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment ME401 For GATE PreparationDocument26 paginiAssignment ME401 For GATE Preparationhameem mohdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 2325 Exam 3-3 ReviewDocument11 paginiPhysics 2325 Exam 3-3 ReviewArvn Christian Santicruz FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment - Viscosity and Surface TensionDocument4 paginiAssignment - Viscosity and Surface TensionMayur Kumar GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8a-Fluids MC Practice ProblemsDocument8 pagini8a-Fluids MC Practice ProblemsUpeka WeerasinghaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harsh ADocument10 paginiHarsh AharshanauocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics Problems SolvedDocument10 paginiFluid Mechanics Problems SolvedGarlapati Srinivasa RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPP FiitjeeDocument18 paginiCPP FiitjeeAmey Kale0% (1)
- Chapter 7 ProblemsDocument3 paginiChapter 7 ProblemsLương Thị Quỳnh PhượngÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 SJPO-2013-GenDocument19 pagini4 SJPO-2013-Genronghui009Încă nu există evaluări
- MORSEL 20 (Fluid Statics)Document4 paginiMORSEL 20 (Fluid Statics)Lalitha RamakrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 11th Test-5 - 020241Document9 paginiClass 11th Test-5 - 020241Pushkar KirangeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYSICSDocument21 paginiPHYSICSdishugirdhar08100% (1)
- Forces on a rolling disc and particle SHM problemsDocument26 paginiForces on a rolling disc and particle SHM problemskeerthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- IIT JEE Fluid MechanicsDocument23 paginiIIT JEE Fluid MechanicsSherin ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluids SubjectiveDocument11 paginiFluids SubjectiveSayantan ChatterjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluids Practice Problems and SolutionsDocument10 paginiFluids Practice Problems and SolutionsLiam James Payne100% (1)
- Group Assignment II - FinalDocument7 paginiGroup Assignment II - Finallelisagetachew90Încă nu există evaluări
- Fluid ND ElasticityDocument54 paginiFluid ND ElasticityChhaya Sharma ce18b028Încă nu există evaluări
- FLUID MECHANICS MCQsDocument6 paginiFLUID MECHANICS MCQsPrashantcool1999Încă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics - Unit 4 - Justine T. SaldivarDocument9 paginiFluid Mechanics - Unit 4 - Justine T. SaldivarJustine Tizon SaldivarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 4 - HydrodynamicsDocument10 paginiAssignment 4 - HydrodynamicsluluÎncă nu există evaluări
- 流體力學Document30 pagini流體力學sonkuas100% (1)
- Ut2 XiDocument4 paginiUt2 Xivineet guptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eotvos Physics Competition 2017 2021Document8 paginiEotvos Physics Competition 2017 2021Marcus PoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- CP S HW CH 9 DetailedDocument6 paginiCP S HW CH 9 DetailedVei AdoptanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrostatics PDFDocument13 paginiHydrostatics PDFNsBhasinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wa0003.Document54 paginiWa0003.subhrojyoti balaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument6 paginiFluid Mechanics PDFmohapatramugdha99Încă nu există evaluări
- BPhO - AS - 2014 - QPDocument11 paginiBPhO - AS - 2014 - QPJakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Phy - Set B Ut-2Document4 pagini11 Phy - Set B Ut-2dikshachoud44Încă nu există evaluări
- SJPO Special Round 2009 Sample PDFDocument8 paginiSJPO Special Round 2009 Sample PDFziwei_from_chinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Objective Worksheet For Final Term 2023Document18 paginiObjective Worksheet For Final Term 2023SnowYTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actual 2009 STPMDocument16 paginiActual 2009 STPMtweihuai100% (1)
- AnnieDocument6 paginiAnnieAnnie Glorina LumauigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workbook FMDocument66 paginiWorkbook FMSubhash JhurawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhysicsDocument25 paginiPhysicsAdityaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 3Document3 paginiProblem Set 3sweet mondayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy 1231 SolutionDocument73 paginiPhy 1231 Solutionhusnerh musaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jee 2014 Booklet5 HWT LiquidsDocument10 paginiJee 2014 Booklet5 HWT LiquidsvarunkohliinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iit Jee Model Paper 4Document14 paginiIit Jee Model Paper 4studysteps.in67% (3)
- KCET MOCK TEST PHY Mock 2Document8 paginiKCET MOCK TEST PHY Mock 2VikashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sat-4 (Authentic) ViscosityDocument7 paginiSat-4 (Authentic) ViscosityLAKSHMI SUNEETAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 08.12.2022 OpenDocument15 pagini08.12.2022 OpenNaveen Raj VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics (QB) 13thDocument16 paginiFluid Mechanics (QB) 13thRaju SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHY11 Finals ReviewerDocument5 paginiPHY11 Finals ReviewerAylaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurDocument4 paginiIndian Institute of Technology KharagpurRohit TomarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IIT-JEE 2002 Mains Paper With Answer KeyDocument10 paginiIIT-JEE 2002 Mains Paper With Answer KeyNarmadha RameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Certificate of Education (Adv - Level) Examination, 2014Document12 paginiGeneral Certificate of Education (Adv - Level) Examination, 2014harshanauocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2 - Hydrostatic Pressure and Pascal - S LawDocument8 paginiAssignment 2 - Hydrostatic Pressure and Pascal - S LawluluÎncă nu există evaluări
- IIT-JEE-Physics-1997: Time: Three HourDocument9 paginiIIT-JEE-Physics-1997: Time: Three HourAdarsh UdayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slidewise Fundamentals of Radioactivity (B) 635610655961530298Document42 paginiSlidewise Fundamentals of Radioactivity (B) 635610655961530298Hrithik GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Nuclear Radioactivity PDF NotesDocument9 pagini3 Nuclear Radioactivity PDF NotesFatin IziantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PG Notes On Semiconductors (Part-3)Document31 paginiPG Notes On Semiconductors (Part-3)Mohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- JM FT 2Document18 paginiJM FT 2Mohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper - I (Question Paper)Document7 paginiPaper - I (Question Paper)Mohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- PG Notes on key aspects of p-n junction diodesDocument23 paginiPG Notes on key aspects of p-n junction diodesMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- PG Notes On Semiconductors (Part-1)Document12 paginiPG Notes On Semiconductors (Part-1)Mohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics: Space For Rough WorkDocument18 paginiMathematics: Space For Rough WorkMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set-A Test Series: JEE Main Full Test - 4 Hints & Solutions MathematicsDocument19 paginiSet-A Test Series: JEE Main Full Test - 4 Hints & Solutions MathematicsMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- JEE Main Full Test - 2 Hints & Solutions MathematicsDocument16 paginiJEE Main Full Test - 2 Hints & Solutions MathematicsMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- PT-1 - JEE AdvDocument18 paginiPT-1 - JEE AdvMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Answers & Hints) : JEE Adv. Part Test - 1Document12 pagini(Answers & Hints) : JEE Adv. Part Test - 1Mohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jee Main - CPT - IDocument31 paginiJee Main - CPT - IMohammed Aftab Ahmed0% (1)
- Work, Energy and Power ExplainedDocument6 paginiWork, Energy and Power ExplainedMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND MOTION OF RIGID BODIESDocument16 paginiSYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND MOTION OF RIGID BODIESMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work Energy and PowerDocument21 paginiWork Energy and PowerMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMPULSE AND MOMENTUMDocument6 paginiIMPULSE AND MOMENTUMMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinematics of Motion: Speed, Velocity, and AccelerationDocument10 paginiKinematics of Motion: Speed, Velocity, and AccelerationMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rotation Theory IDocument6 paginiRotation Theory IMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument8 paginiNewton's Laws of Motion ExplainedMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPP - 5 To 8Document20 paginiDPP - 5 To 8Mohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPP Nlm-IiDocument8 paginiDPP Nlm-IiMohammed Aftab Ahmed0% (1)
- DPP - 01 To 04Document23 paginiDPP - 01 To 04Mohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impulse N MomentumDocument11 paginiImpulse N MomentumMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Bank (S.C)Document54 paginiQuestion Bank (S.C)Mohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (1)
- Newtons Laws of Motion2 - 2Document10 paginiNewtons Laws of Motion2 - 2Mohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Rigid Body MotionDocument21 paginiUnderstanding Rigid Body MotionMohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newtons Laws of Motion2 - 1Document7 paginiNewtons Laws of Motion2 - 1Mohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newtons Laws of Motion - 1Document6 paginiNewtons Laws of Motion - 1Mohammed Aftab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRM in InfosysDocument11 paginiHRM in Infosysguptarahul27550% (4)
- Chain of Custody Requirement in Drug CasesDocument23 paginiChain of Custody Requirement in Drug CasesMiw CortesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4-23-18 DktEnt 138 Petitions Rehearing Enbanc PDFDocument103 pagini4-23-18 DktEnt 138 Petitions Rehearing Enbanc PDFArek FressadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 677 1415 1 SMDocument5 pagini677 1415 1 SMAditya RizkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAB REPORT-Osbourne Reynolds ApparatusDocument20 paginiLAB REPORT-Osbourne Reynolds Apparatusmizizasbonkure9055% (11)
- BCG X Meta India M&E 2023Document60 paginiBCG X Meta India M&E 2023Никита МузафаровÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP Question Paper April 2012Document2 paginiDSP Question Paper April 2012Famida Begam100% (1)
- Let's Meet Peter Conozcamos A PeterDocument4 paginiLet's Meet Peter Conozcamos A PeterJuan Felipe Restrepo MayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RICS Research On NECDocument9 paginiRICS Research On NECAhmad MajedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiotherapy's Role in Rehabilitation and Health Promotion Across the LifespanDocument3 paginiPhysiotherapy's Role in Rehabilitation and Health Promotion Across the LifespanMariana OspinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gen. Math TestDocument5 paginiGen. Math TestAlfred LabadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- FullertonDocument15 paginiFullertonSuman MandalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diffie Hellman WriteupDocument3 paginiDiffie Hellman WriteupSumitThoratÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.5 Inch 24.70 VX54 6625 4000 2 (Landing String)Document2 pagini5.5 Inch 24.70 VX54 6625 4000 2 (Landing String)humberto Nascimento100% (1)
- Motion For Reconsideration (Bolado & Aranilla)Document4 paginiMotion For Reconsideration (Bolado & Aranilla)edrynejethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Venous Access Devices (Cvads) andDocument68 paginiCentral Venous Access Devices (Cvads) andFitri ShabrinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mario, You Might Need ThisDocument436 paginiMario, You Might Need ThisJk McCreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Akhila-Rasamrta-Murtih Prasrmara-Ruci-Ruddha-Taraka-PalihDocument44 paginiAkhila-Rasamrta-Murtih Prasrmara-Ruci-Ruddha-Taraka-PalihSauri ChaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSEC Physics P2 2013 JuneDocument20 paginiCSEC Physics P2 2013 JuneBill BobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chromatography Viva Questions & Answers GuideDocument4 paginiChromatography Viva Questions & Answers GuidedhruvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calendar of ActivitiesDocument7 paginiCalendar of ActivitiesAries Robinson CasasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ais 9 ImDocument117 paginiAis 9 ImSimonNisjaPutraZai100% (1)
- DR Raudhah Ahmadi KNS1633 Engineering Mechanics Civil Engineering, UNIMASDocument32 paginiDR Raudhah Ahmadi KNS1633 Engineering Mechanics Civil Engineering, UNIMASAriff JasniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method in Dogmatic Theology: Protology (First Revelatory Mystery at Creation) To Eschatology (Last RedemptiveDocument62 paginiMethod in Dogmatic Theology: Protology (First Revelatory Mystery at Creation) To Eschatology (Last RedemptiveefrataÎncă nu există evaluări
- The US in WWII 1942 - 1944: The Outcome Is That We Were Able To Gain Sicily. We Got Into Italy Through SicilyDocument3 paginiThe US in WWII 1942 - 1944: The Outcome Is That We Were Able To Gain Sicily. We Got Into Italy Through SicilyVivian HartmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 13Document13 paginiActivity 13Lielannie CarasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benchmark Evidence BasedDocument11 paginiBenchmark Evidence BasedPeterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 504 Sample Accommodations and Modifications: Examples of General AccommodationsDocument16 paginiSection 504 Sample Accommodations and Modifications: Examples of General AccommodationsRukhsana KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Release Waiver and Quitclaim: Security Services IncDocument1 paginăRelease Waiver and Quitclaim: Security Services IncJobelle SaquitonÎncă nu există evaluări