Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Rotating Biological Contactor
Încărcat de
Dr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
934 vizualizări10 paginiRotating biological contactors (RBCs) are used for wastewater treatment. They consist of disks on a horizontal shaft that support a microbial film. Wastewater flows through a tank and is exposed alternately to the disk surface and atmosphere as the disks rotate. Microbes in the film absorb and break down organic matter. RBCs can remove biochemical oxygen demand and nitrify wastewater. They are simple to operate and use little energy but may develop odor or sloughing issues if overloaded. RBC design considers the disk material and area, shaft, tank size, and drive system. Disk area requirements depend on wastewater strength and treatment goals.
Descriere originală:
deals with the basics of rotating biological contactor reactors for the wastewater treatment.
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentRotating biological contactors (RBCs) are used for wastewater treatment. They consist of disks on a horizontal shaft that support a microbial film. Wastewater flows through a tank and is exposed alternately to the disk surface and atmosphere as the disks rotate. Microbes in the film absorb and break down organic matter. RBCs can remove biochemical oxygen demand and nitrify wastewater. They are simple to operate and use little energy but may develop odor or sloughing issues if overloaded. RBC design considers the disk material and area, shaft, tank size, and drive system. Disk area requirements depend on wastewater strength and treatment goals.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
934 vizualizări10 paginiRotating Biological Contactor
Încărcat de
Dr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyRotating biological contactors (RBCs) are used for wastewater treatment. They consist of disks on a horizontal shaft that support a microbial film. Wastewater flows through a tank and is exposed alternately to the disk surface and atmosphere as the disks rotate. Microbes in the film absorb and break down organic matter. RBCs can remove biochemical oxygen demand and nitrify wastewater. They are simple to operate and use little energy but may develop odor or sloughing issues if overloaded. RBC design considers the disk material and area, shaft, tank size, and drive system. Disk area requirements depend on wastewater strength and treatment goals.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 10
Rotating Biological Contactors
Dr. Akepati S. Reddy
Associate Professor, Thapar University
Adjunct Scientist, TCIRD
Patiala (PUNJAB) -147 004
Rotating biological contactor (RBC)
• Series of closely spaced polystyrene/polyvinyl chloride
circular disks on horizontal shaft constitute RBC unit
• Standard RBC unit includes
– 3.5 m dia disks with total disk area of 9300 m2/unit to support
microbial film
– A shaft of 8.23 m length (of this 7.23 m is occupied by disks)
• RBC unit is placed in a 45 m3 capacity tank
– Shaft orientation is either perpendicular to or parallel to the
wastewater flow
• RBC unit is usually provided with an enclosure
– Prevents algal growth
– Discs are protected from sunlight (UV light)
– Prevents heat loss and exposure to cold weather
RBC
Treatment process (sec. or advanced level)
• Treatment is for BOD removal, or nitrification, or both, or
for pretreatment of higher strength industrial effluent
• Wastewater clarified in primary clarifier or fine screened is
fed to the reactor
• 40% of disc surface is submerged in wastewater
maintained in a 45 m3 tank
• Disk surface is alternatively brought in contact with
wastewater and atmosphere by rotating at 1 to 1.6 rpm
rate either mechanical or pneumatically
• Treatment occurs through bio-sorption of organic matter of
wastewater into bio-film and aerobic biooxidation of the
sorbed matter when bio-film is exposed to atmospheric air
• Bio-film as it thickens and looses its ability to cling to disc
surface due to hydrodynamic shears sloughs off
• Treated effluent needs secondary clarification
RBC
• A number of RBC units may be operated in series to
form a process train
– Exploit the benefits of staged biological reactor design –
facilitates maintaining different conditions in different stages
– For reliability two or more parallel flow trains are employed
– 2-4 units in series are used for BOD removal
≥ 6 units are used for combined BOD removal & nitrification
– To avoid overloading on initial stages, stepped feed or
tapered systems are opted
– RBC units decrease as one moves to higher stages
• RBC units are of low, medium and high density types
– Low density or standard type units are used for initial stages
– Medium and high density units (11000 and 16,700 m2 area)
are used in the mid and final stages
RBC
Simple to operate and involves low energy costs
Performance is related to specific surface loading of
BOD and/or NH4-N
– For first stage it is 12-20 g/m2.day of soluble BOD (as total
BOD it is 24-30 g/m2.day)
– For nitrification maximum loading rate is 1.5 g/m2.day
Associated with odor and bio-film sloughing problems
– Occurs when oxygen demand exceeds supply
– Sulfur oxidizing bacteria form tenacious whitish film and
prevent sloughing off
Structural failure of shafts, disks and disk support
systems can occur
– Excessive bio-film growth and sloughing problems cause it
RBC design considerations
Principal elements of RBC
• Disc material and configuration
– HDPE of different configurations or corrugation patterns
– Corrugation increases available surface area and enhances
structural stability
• Shaft
– Shape is square, round or octagonal
– Steel shafts coated for protection against corrosion of 13-30
mm thickness are used
• Tankage
– Requirement is 0.0049 m3/m2 film area
– Typical side wall depth is 1.5 m
– At 0.08 m3/m2 day hydraulic loading rate HRT is 1.44 hrs
RBC design considerations
Drive system
– Mechanical or pneumatic drives are used for shaft rotation
– Mechanical drive capacity is 3.7 or 5.6 kW per unit
– Deep plastic cups are attached to the perimeter of the disks
and compressed air is released into the cups for rotation
– Air requirement is 5.3 m3/min for standard density shaft and
7.6 m3/min for high density shaft
Enclosures
– Segmented fiberglass reinforced plastic enclosures are used
RBC design
First stage RBC disk area is determined by using 12-15
g/m2.day sBOD loading
Disk area of subsequent stages is found by second order
model by Opatken
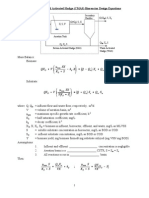
− 1 + 1 + 4 × 0.00974 × ( As / Q ) × S n −1
Sn =
2 × 0.00974 × ( As / Q)
Sn is soluble BOD concentration in mg/l
As is disk surface area for stage-n (in m2)
Q is flow rate in m3/day
Here sBOD/BOD is taken as
0.5 for secondary clarified effluent
0.5 to 0.75 for primary clarified effluent
RBC design
For nitrification stages area required is found by using
maximum nitrification rate (rn.max ) as 1.5 g/m2.day
– Applicable if sBOD of wastewater is <10 to 15 mg/l -
otherwise rn.max should be corrected by:
Frx = 1.0 − 0.1× sBOD
Here Frx is fraction of nitrification rate possible
sBOD is soluble BOD loading in g/m2.day
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Rotating Biological ContactorDocument17 paginiRotating Biological Contactormikelycan100% (2)
- Rotating Biological ContactorsDocument11 paginiRotating Biological ContactorsDevendra SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trickling FilterDocument34 paginiTrickling FilterDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (9)
- Biotower FundamentalsDocument40 paginiBiotower Fundamentalsram1987_rajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rotating Biological ContactorDocument6 paginiRotating Biological ContactorDebasish NayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nitrification and Denitrification in the Activated Sludge ProcessDe la EverandNitrification and Denitrification in the Activated Sludge ProcessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sanitary Engineer II: Passbooks Study GuideDe la EverandSanitary Engineer II: Passbooks Study GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reaction Mechanisms in Environmental Engineering: Analysis and PredictionDe la EverandReaction Mechanisms in Environmental Engineering: Analysis and PredictionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinetics of Wastewater Treatment: Proceedings of a Post-Conference Seminar Held at the Technical University of Denmark, Copenhagen, 1978De la EverandKinetics of Wastewater Treatment: Proceedings of a Post-Conference Seminar Held at the Technical University of Denmark, Copenhagen, 1978S. H. JenkinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waste Treatment: Proceedings of the Second Symposium on the Treatment of Waste WatersDe la EverandWaste Treatment: Proceedings of the Second Symposium on the Treatment of Waste WatersPeter C. G. IsaacEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Liquid Membranes: Principles and Applications in Chemical Separations and Wastewater TreatmentDe la EverandLiquid Membranes: Principles and Applications in Chemical Separations and Wastewater TreatmentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Wastewater Treatment III - MBR Processes R1Document26 paginiBiological Wastewater Treatment III - MBR Processes R1NUR ASYIQIN BINTI AZAHARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uasb/egsb Applications For Industrial Wastewater TreatmentDocument10 paginiUasb/egsb Applications For Industrial Wastewater Treatmentalberto_03Încă nu există evaluări
- Activated Sludge ProcessDocument10 paginiActivated Sludge ProcessSai Raghava Rajeev100% (1)
- Activated Sludge Calcs With ExcelDocument22 paginiActivated Sludge Calcs With ExcelsahatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 - Rotating Biological Contactor-ProcessDocument55 pagini12 - Rotating Biological Contactor-ProcessMohammed Barni100% (1)
- Municipal Wastewater Treatment: Evaluating Improvements in National Water QualityDe la EverandMunicipal Wastewater Treatment: Evaluating Improvements in National Water QualityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chief Water Treatment Plant Operator: Passbooks Study GuideDe la EverandChief Water Treatment Plant Operator: Passbooks Study GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trickling FilterDocument7 paginiTrickling FilterTasirmistÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shortcut Nitrogen Removal-Nitrite Shunt and DeammonificationDe la EverandShortcut Nitrogen Removal-Nitrite Shunt and DeammonificationÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBBR TechnologyDocument5 paginiMBBR Technologymsajidfcc100% (2)
- Anaerobic ReactorsDocument21 paginiAnaerobic ReactorsManish Kumar GhoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Water: Advances in Treatment, Remediation and RecyclingDe la EverandEnvironmental Water: Advances in Treatment, Remediation and RecyclingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Treatment of WastewaterDocument64 paginiBiological Treatment of WastewaterDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (7)
- Electrochemical Water Treatment Methods: Fundamentals, Methods and Full Scale ApplicationsDe la EverandElectrochemical Water Treatment Methods: Fundamentals, Methods and Full Scale ApplicationsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (4)
- ENVI Trickling FiltersDocument23 paginiENVI Trickling FiltersbaBy daBy AnNetTeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clarifier Settling Tank PDFDocument25 paginiClarifier Settling Tank PDFvenustasiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 17 - MathematicsDocument13 paginiChapter 17 - MathematicsLivingston JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conversion Table For Wastewater TreatmentDocument5 paginiConversion Table For Wastewater TreatmentAG-Metal /Tretman Otpadnih Voda/Wastewater TreatmentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activated SludgeDocument17 paginiActivated SludgeAquasoul Co100% (1)
- Chapter-14 Final Aerobic-DigestionDocument18 paginiChapter-14 Final Aerobic-DigestionIrvin joseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physicochemical Methods for Water and Wastewater TreatmentDe la EverandPhysicochemical Methods for Water and Wastewater TreatmentEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Activated Sludge Process Design2Document2 paginiActivated Sludge Process Design2Vipin YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- UASB-Process Design For Various Types of WastewatersDocument21 paginiUASB-Process Design For Various Types of WastewatersapitbhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines for Grit Sampling and CharacterizationDe la EverandGuidelines for Grit Sampling and CharacterizationÎncă nu există evaluări
- 77 Two Stage Uasb Treatment of Industrial Wastewater With Internal CirculationDocument10 pagini77 Two Stage Uasb Treatment of Industrial Wastewater With Internal CirculationngocdungmtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of DesalinationDe la EverandPrinciples of DesalinationK SpieglerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turning Sewage into Reusable Water: Written for the LaypersonDe la EverandTurning Sewage into Reusable Water: Written for the LaypersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7-Trickling Filter F11Document31 pagini7-Trickling Filter F11Jon Bisu Debnath100% (1)
- Activated Sludge Design EquationsDocument5 paginiActivated Sludge Design EquationsKenny Then Soon Hung100% (2)
- The Removal of Nitrogen Compounds from WastewaterDe la EverandThe Removal of Nitrogen Compounds from WastewaterEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Applications of New Concepts of Physical-Chemical Wastewater Treatment: Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee September 18-22, 1972De la EverandApplications of New Concepts of Physical-Chemical Wastewater Treatment: Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee September 18-22, 1972Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Electrochemical Water and Wastewater TreatmentDe la EverandElectrochemical Water and Wastewater TreatmentCarlos Alberto Martínez-HuitleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low Cost Wastewater Bioremediation Technology: Innovative Treatment of Sulfate and Metal-Rich WastewaterDe la EverandLow Cost Wastewater Bioremediation Technology: Innovative Treatment of Sulfate and Metal-Rich WastewaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment: Emerging Green Chemical TechnologyDe la EverandAdvanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment: Emerging Green Chemical TechnologyEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- Adsorption Column Design PDFDocument58 paginiAdsorption Column Design PDFCharles John Catan100% (1)
- Cost Analysis of Activated Sludge ProcessDocument19 paginiCost Analysis of Activated Sludge ProcessDevendra Sharma100% (1)
- Concept of Zero DischargeDocument4 paginiConcept of Zero DischargeShesharam Chouhan67% (3)
- Advanced Activated Sludge ProcessDocument5 paginiAdvanced Activated Sludge ProcessDileep C DileepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sequence Batch ReactorDocument4 paginiSequence Batch ReactorKwang Je LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solar PV CourseDocument126 paginiSolar PV CourseDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (3)
- Sewerage SystemDocument66 paginiSewerage SystemDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (10)
- IEE EnMS Practical Guide PDFDocument78 paginiIEE EnMS Practical Guide PDFDr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC ThaparDocument8 paginiEC ThaparDr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sewerage and Sewage Treatment - 2014 - Solutions For End Semester ExaminationDocument16 paginiSewerage and Sewage Treatment - 2014 - Solutions For End Semester ExaminationDr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sewage Treatment: Primary TreatmentDocument81 paginiSewage Treatment: Primary TreatmentDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (7)
- Sewage Treatment OverviewDocument13 paginiSewage Treatment OverviewDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (3)
- Water Transmission and Distribution SystemsDocument71 paginiWater Transmission and Distribution SystemsDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (6)
- Sewerage and Sewage Treatment - Tutorials 1 To 8Document13 paginiSewerage and Sewage Treatment - Tutorials 1 To 8Dr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy0% (1)
- Sewage Treatment: Priliminary Treatment UnitsDocument56 paginiSewage Treatment: Priliminary Treatment UnitsDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy50% (2)
- Water Treatment QuizDocument3 paginiWater Treatment QuizDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (4)
- Hardness, Water Softening - Lime-Soda Ash ProcessDocument22 paginiHardness, Water Softening - Lime-Soda Ash ProcessDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (8)
- Water Supply Engineering Quiz-1Document3 paginiWater Supply Engineering Quiz-1Dr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (1)
- Water and Wastewater Treatment Quiz-1Document3 paginiWater and Wastewater Treatment Quiz-1Dr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (6)
- Water Treatment PlantDocument100 paginiWater Treatment PlantDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy96% (23)
- 01 Water QualityDocument25 pagini01 Water QualityDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (3)
- Water Supply Engineering Tutorials 4 To 7Document5 paginiWater Supply Engineering Tutorials 4 To 7Dr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Note Address, National Conference On Preservation of Environment: Challenges Before HumanityDocument8 paginiKey Note Address, National Conference On Preservation of Environment: Challenges Before HumanityDr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10-Taxonomy and Major Groups of BacteriaDocument84 pagini10-Taxonomy and Major Groups of BacteriaDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (7)
- Development and Implementation of Environmental Management SystemDocument53 paginiDevelopment and Implementation of Environmental Management SystemDr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Properties: Dr. Akepati S. Reddy Thapar University Patiala (PUNJAB) - 147 004 IndiaDocument29 paginiFluid Properties: Dr. Akepati S. Reddy Thapar University Patiala (PUNJAB) - 147 004 IndiaDr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Wastewater Treatment (UPO-2) - Question PapersDocument22 paginiBiological Wastewater Treatment (UPO-2) - Question PapersDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (1)
- Stormwater HydrologyDocument124 paginiStormwater HydrologyDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (4)
- IsO 14000 Family of StandardsDocument116 paginiIsO 14000 Family of StandardsDr. Akepati Sivarami ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- End of Pipe Approach To EMS ApproachDocument49 paginiEnd of Pipe Approach To EMS ApproachDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (1)
- MCQ-Water Supply and Wastewater EngineeringDocument11 paginiMCQ-Water Supply and Wastewater EngineeringDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy79% (33)
- Organic Matter, BOD and BOD KineticsDocument90 paginiOrganic Matter, BOD and BOD KineticsDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (6)
- UPO-1: Unit Processes and Operations (Physico-Chemical) - Question PapersDocument20 paginiUPO-1: Unit Processes and Operations (Physico-Chemical) - Question PapersDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (2)
- Drinking Water MOHDocument3 paginiDrinking Water MOHNur Amanina OmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Certi Ficate 1Document5 paginiCerti Ficate 1ANJANI KUMAR SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Management Plan - BU1 - Jan 19Document19 paginiEnvironmental Management Plan - BU1 - Jan 19vigor.hairulÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChemistryDocument22 paginiChemistryChinmay JenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Souvenir Volume-9 Issue-2S2 December 2019 PDFDocument161 paginiSouvenir Volume-9 Issue-2S2 December 2019 PDFprashanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waste Water Engineering: Dr. Mahbuboor Rahman ChoudhuryDocument17 paginiWaste Water Engineering: Dr. Mahbuboor Rahman ChoudhuryMisbah MostaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- UWW PRTR Electronic Toolset V5.0Document31 paginiUWW PRTR Electronic Toolset V5.0Galih SaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preliminary Study of The Efficiency of Ultrafiltration Treatment of Poultry Slaughterhouse WastewaterDocument5 paginiPreliminary Study of The Efficiency of Ultrafiltration Treatment of Poultry Slaughterhouse WastewaterДинкоЙорданов0% (1)
- TL 829 Cert New 2 AlcanceDocument39 paginiTL 829 Cert New 2 AlcanceEve Maldonado FDÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 +Randy+Ramadani PDFDocument11 pagini2 +Randy+Ramadani PDFErni DepayaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Report On TGR - Volume-1Document342 paginiFinal Report On TGR - Volume-1Hem Prakash SanchetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid Waste Management in The PhilippinesDocument26 paginiSolid Waste Management in The PhilippinesRyan Alinab50% (2)
- Effect of Untreated Brewery Wastewater On The Physicochemical Properties of Agricultural Soil and Crop YieldDocument12 paginiEffect of Untreated Brewery Wastewater On The Physicochemical Properties of Agricultural Soil and Crop YieldEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- Watertreatmentproceeding SMALLSIZE PDFDocument565 paginiWatertreatmentproceeding SMALLSIZE PDFmarc ugoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Sugar-Mill Liquid Effluent To Z PDFDocument10 paginiManaging Sugar-Mill Liquid Effluent To Z PDFLuu TonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clean Water ActDocument17 paginiClean Water ActDaniel Naoe FestinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Year Project Chapter 1,2,3,4,5Document55 paginiFinal Year Project Chapter 1,2,3,4,5Noraini Rosman78% (36)
- Introduction To Waste Water Treatment by Root Zone TechniqueDocument4 paginiIntroduction To Waste Water Treatment by Root Zone TechniqueAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Environmental Hydrogeochemistry PDFDocument106 paginiIntroduction To Environmental Hydrogeochemistry PDFJuan-CarlosPeroniZamudioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cluster Development India - Diagnostic StudyDocument19 paginiCluster Development India - Diagnostic StudyAtul KhichariyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Envi. Data AcquisitionDocument10 paginiEnvi. Data AcquisitionDexter John Gomez JomocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hernandez-Padilla Etal 2017Document15 paginiHernandez-Padilla Etal 2017Mohsin ModiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised Effluent Regulations of 1990 - EMB-DeNRDocument8 paginiRevised Effluent Regulations of 1990 - EMB-DeNRmcdaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceng 426 Project FinalDocument23 paginiCeng 426 Project FinalDuaa SalehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Quality Modelling Qual 2KW For River Tungabhadra (India) .Document4 paginiWater Quality Modelling Qual 2KW For River Tungabhadra (India) .Ranjith ShepurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decom Manual: Maintenance of Uasb FOR Domest C Manual For The Design, Construction, Operation, Treatm Ent WastewaterDocument304 paginiDecom Manual: Maintenance of Uasb FOR Domest C Manual For The Design, Construction, Operation, Treatm Ent WastewaterMaku RajkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Water Quality Index-Crashing The Psychological BarrierDocument10 paginiA Water Quality Index-Crashing The Psychological BarriernoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sugar Industry Wastewater TreatmentDocument20 paginiSugar Industry Wastewater TreatmentAditi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)Document2 paginiBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)ke20% (1)
- Contact Session Slides Rubber Manufacture, Processing and Value Addition - 2015Document27 paginiContact Session Slides Rubber Manufacture, Processing and Value Addition - 2015Chathura Thennakoon100% (1)