Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
DSP and Microprocessor 1 PDF
Încărcat de
shyam_krishnan_160 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
77 vizualizări3 paginiA DSP processor is a specialized type of microprocessor optimized for digital signal processing tasks like modifying signals. While microprocessors are general purpose processors used for tasks like computation, a DSP processor aims to measure, filter, and compress analog and digital signals. The main difference is that DSP processors have features designed to efficiently perform numerically intensive tasks like complex arithmetic calculations used for applications such as image and speech processing.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
DSP and Microprocessor 1.pdf
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentA DSP processor is a specialized type of microprocessor optimized for digital signal processing tasks like modifying signals. While microprocessors are general purpose processors used for tasks like computation, a DSP processor aims to measure, filter, and compress analog and digital signals. The main difference is that DSP processors have features designed to efficiently perform numerically intensive tasks like complex arithmetic calculations used for applications such as image and speech processing.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
77 vizualizări3 paginiDSP and Microprocessor 1 PDF
Încărcat de
shyam_krishnan_16A DSP processor is a specialized type of microprocessor optimized for digital signal processing tasks like modifying signals. While microprocessors are general purpose processors used for tasks like computation, a DSP processor aims to measure, filter, and compress analog and digital signals. The main difference is that DSP processors have features designed to efficiently perform numerically intensive tasks like complex arithmetic calculations used for applications such as image and speech processing.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
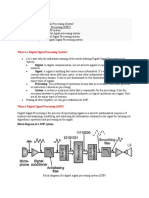
Difference between DSP and
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions
of a computer's central processing unit (CPU) on a single or few integrated
circuits (IC). The purpose of a microprocessor is to accept digital data as
input, process it as per the instructions, and then provide the output. This is
known as sequential digital logic. The microprocessor has internal memory
and operates basically on the binary system.
Most general purpose microprocessors are present in personal computers.
They are often used for computation, text editing, multimedia display, and
communication over a network. Other microprocessors are part of
embedded systems. These provide digital control over practically any
technology, such as appliances, automobiles, cell phones, industrial process
control, etc.
The DSP processor, on the other hand, is a particular type of
microprocessor. DSP stands for digital signal processing. It is basically any
signal processing that is done on a digital signal or information signal. A DSP
processor is a specialized microprocessor that has an architecture optimized
for the operational needs of digital signal processing.
DSP aims to modify or improve the signal. It
is characterized by the representation of discrete units, such as discrete
time, discrete frequency, or discrete domain signals. DSP includes subfields
like communication signals processing, radar signal processing, sensor array
processing, digital image processing, etc.
The main goal of a DSP processor is to measure, filter and/or compress
digital or analog signals. It does this by converting the signal from a realworld analog signal to a digital form. In order to convert the signal it uses a
digital-to-analog converter (DAC). However, the required output signal is
often another real-world analog signal. This is turn also requires a digital-toanalog converter.
Digital signal processing algorithms run on various platforms, such as general
purpose microprocessors and standard computers; specialized processors
called digital signal processors (DSPs); purpose-built hardware such as
application-specific integrated circuit (ASICs) and field-programmable gate
arrays (FPGAs); Digital Signal Controllers; and stream processing for
traditional DSP or graphics processing applications, such as image, video.
The main difference between a DSP and a microprocessor is that a DSP
processor has features designed to support high-performance, repetitive,
numerically intensive tasks. DSP processors are designed specifically to
perform large numbers of complex arithmetic calculations and as quickly as
possible. They are often used in applications such as image processing,
speech recognition and telecommunications. As compared to general
microprocessors, DSP processors are more efficient at performing basic
arithmetic operations, especially multiplication.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument1 paginăDigital Signal ProcessingsenthilkumarmvnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To DSP ProcessorsDocument15 paginiIntroduction To DSP ProcessorsParesh SawantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiements (Using DSP Kit) Introduction To DSP Processors: MicroprocessorDocument9 paginiExperiements (Using DSP Kit) Introduction To DSP Processors: Microprocessorshiksha singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 ComputingDocument69 pagini3 Computinggülsüm önalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appl of DSPDocument7 paginiAppl of DSPeswarnageswarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igital Ignal Rocessing: at SivagangaiDocument21 paginiIgital Ignal Rocessing: at SivagangaidhivakargunalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP NotesDocument6 paginiDSP NotesSringaSyamÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP CasestudyDocument23 paginiDSP CasestudyShayani BatabyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To DSP ProcessorDocument4 paginiIntroduction To DSP ProcessorAye BihariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar Report DSPDocument34 paginiSeminar Report DSPwmallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Signal Processing Definition of A Digital Signal ProcessorDocument18 paginiDigital Signal Processing Definition of A Digital Signal ProcessorAnil YarlagaddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rtes 6713Document9 paginiRtes 6713Bharath Prabhu PÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Choosing The Right DSP Processor: 4.1 Digital Signal ProcessingDocument14 pagini4 Choosing The Right DSP Processor: 4.1 Digital Signal ProcessingShavel KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Signal Processing TutorialsDocument17 paginiDigital Signal Processing TutorialsNikhil PathakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument1 paginăDigital Signal ProcessingMaha RajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSPPDocument2 paginiDSPPPrithvirajKshatriya-BadgujarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP Based Electrical Lab: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering & Technology (Autonomous)Document77 paginiDSP Based Electrical Lab: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering & Technology (Autonomous)P Praveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Digital Signal ProcessingDocument5 paginiIntroduction To Digital Signal ProcessingmailmeasddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real Time Special Effects Generation AND Noise Filtration OF Audio Signal Using Matlab GUIDocument17 paginiReal Time Special Effects Generation AND Noise Filtration OF Audio Signal Using Matlab GUIAnonymous lVQ83F8mCÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP ProcessorDocument12 paginiDSP ProcessorselimohapatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital System Design Assign 1Document7 paginiDigital System Design Assign 1arsalan amjadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Digital Signal Processing (ADSP) For Decreasing Power DissipationDocument4 paginiAdvanced Digital Signal Processing (ADSP) For Decreasing Power DissipationSindhu V MÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Digital Signal Processing System?Document4 paginiWhat Is A Digital Signal Processing System?nazmulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Voice EnhancementDocument10 paginiDigital Voice EnhancementNaresh KnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Signal Processor: ArchitectureDocument3 paginiDigital Signal Processor: ArchitectureSanthosh Kumar ChittipoluÎncă nu există evaluări
- With The Block Diagram Explain Basic Elements of DSPDocument4 paginiWith The Block Diagram Explain Basic Elements of DSPAnil Shrestha100% (3)
- ProcessorsDocument26 paginiProcessorsNavi KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To DSPDocument59 paginiIntroduction To DSPSiony BelloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sanjay - High Performance DSP ArchitecturesDocument38 paginiSanjay - High Performance DSP Architecturesapi-3827000Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument4 paginiChapter 1 IntroductionRajesh BnÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP SmartDocument91 paginiDSP SmartNishanth NissanÎncă nu există evaluări
- By Rodger H. Hosking: Reprinted From Vmebus Systems / June 2000Document4 paginiBy Rodger H. Hosking: Reprinted From Vmebus Systems / June 2000Abhilasha MathurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tiger SHARC ProcessorDocument35 paginiTiger SHARC ProcessorSurangma ParasharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tiger SHARC ProcessorDocument36 paginiTiger SHARC ProcessorChintan PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use A Microprocessor, A DSP, or BothDocument11 paginiUse A Microprocessor, A DSP, or Bothnqdinh100% (2)
- Ask Me For Signal ProcessingDocument2 paginiAsk Me For Signal ProcessingHudaa EltÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit IvDocument72 paginiUnit Ivfishatsion09Încă nu există evaluări
- IntrDocument18 paginiIntrTarun HuiremÎncă nu există evaluări
- Search Results: People Also AskDocument3 paginiSearch Results: People Also AskGhepo GhoruiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Signal Processing (DSP)Document5 paginiDigital Signal Processing (DSP)abdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 2Document59 paginiCH 2gcrossnÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP Lab Manual DSK Technical Programming With C, MATLAB Programs 2008 B.Tech ECE IV-I JNTU Hyd V1.9Document52 paginiDSP Lab Manual DSK Technical Programming With C, MATLAB Programs 2008 B.Tech ECE IV-I JNTU Hyd V1.9Chanukya Krishna Chama80% (5)
- Image Processing Using FPGADocument12 paginiImage Processing Using FPGAMehanathan Maggie MikeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application Specific ProcessorsDocument8 paginiApplication Specific ProcessorsCnellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Batch 7Document74 paginiBatch 7kota naikÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP Unit-5 FinalDocument97 paginiDSP Unit-5 FinalreventhhuntÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1Document30 paginiUnit 1prabhavathysund8763Încă nu există evaluări
- Microprocessor and InterfaceDocument16 paginiMicroprocessor and InterfaceMajid MehmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examination Based On RfidDocument62 paginiExamination Based On Rfidsudhakar5472100% (2)
- Application of Digital Signal Processing ON TMS320C6713 DSKDocument21 paginiApplication of Digital Signal Processing ON TMS320C6713 DSKlakshamanaraoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document24 paginiChapter 1Ken MutaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Embedded Systems Three Types of Embedded Systems AreDocument24 paginiClassification of Embedded Systems Three Types of Embedded Systems Arekartika_krazeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP ProcessorsDocument9 paginiDSP Processorsatharv musaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embedded and Real-Time Operating Systems: Course Code: 70439Document76 paginiEmbedded and Real-Time Operating Systems: Course Code: 70439SrikanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digi Sign ProcDocument40 paginiDigi Sign Procgkk_143Încă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Embedded SystemsDocument13 paginiApplications of Embedded Systemssandeepsandy07Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit-1 Introduction To Digital Signal ProcessingDocument3 paginiUnit-1 Introduction To Digital Signal Processingpratik2882002Încă nu există evaluări
- Digital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesDe la EverandDigital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color Profile: Exploring Visual Perception and Analysis in Computer VisionDe la EverandColor Profile: Exploring Visual Perception and Analysis in Computer VisionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spen Eaflet: Transformer Damage Curve Made EasyDocument2 paginiSpen Eaflet: Transformer Damage Curve Made Easyshyam_krishnan_16Încă nu există evaluări
- FIGURE 10. The Effects of Voltage and Frequency Variation On Induction-Motor CharacteristicsDocument2 paginiFIGURE 10. The Effects of Voltage and Frequency Variation On Induction-Motor Characteristicsshyam_krishnan_16Încă nu există evaluări
- 6211 ProtectingPower AK 20050916 WebDocument8 pagini6211 ProtectingPower AK 20050916 Webshyam_krishnan_16Încă nu există evaluări
- Trans ProtDocument45 paginiTrans Protshyam_krishnan_16Încă nu există evaluări
- R4 Test Buttons (No Latching) and PlugsDocument1 paginăR4 Test Buttons (No Latching) and Plugsshyam_krishnan_16Încă nu există evaluări
- Relpol R4 Miniature RelaysDocument1 paginăRelpol R4 Miniature Relaysshyam_krishnan_16Încă nu există evaluări
- R4 Relay Coil DataDocument1 paginăR4 Relay Coil Datashyam_krishnan_16Încă nu există evaluări
- R4 Relay DimentionsDocument1 paginăR4 Relay Dimentionsshyam_krishnan_16Încă nu există evaluări
- Motor Differential Protection Using Flux BalancingDocument1 paginăMotor Differential Protection Using Flux Balancingshyam_krishnan_16Încă nu există evaluări
- Digsilent PDFDocument1 paginăDigsilent PDFshyam_krishnan_16Încă nu există evaluări
- ALSTOM Check Synchronising Relays SKD, SKE High Res PDFDocument4 paginiALSTOM Check Synchronising Relays SKD, SKE High Res PDFshyam_krishnan_16100% (1)
- Motor Start Detection: 19.4.3 Number of Starts LimitationDocument1 paginăMotor Start Detection: 19.4.3 Number of Starts Limitationshyam_krishnan_16Încă nu există evaluări
- Analog Devices - MT-016Document6 paginiAnalog Devices - MT-016ModyKing99Încă nu există evaluări
- Subho Soren Hardware Component Chatper 1Document10 paginiSubho Soren Hardware Component Chatper 1Kaushik ChoudhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogo Varco BJDocument56 paginiCatalogo Varco BJJhon CastRo78% (9)
- Owner'S Manual: Operation Maintenance Parts ListDocument126 paginiOwner'S Manual: Operation Maintenance Parts ListDmitryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Table of Content S.N0. Topic: Page NoDocument2 paginiTable of Content S.N0. Topic: Page NoRajat SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Documentation - Regulation (EU) N. 2281 - 2016 - NECS 1314 - 3218 SEERDocument59 paginiTechnical Documentation - Regulation (EU) N. 2281 - 2016 - NECS 1314 - 3218 SEERAlexandru GÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3bhs107542e01 AbbDocument14 pagini3bhs107542e01 Abbsabah nooriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Request Letter For Training NC 2 EimDocument6 paginiRequest Letter For Training NC 2 EimMohammmad Habibolla Ibon EsmaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- L6.01 Abrasive Blasting Check ListDocument3 paginiL6.01 Abrasive Blasting Check ListNATIONAL BASICS COMPANY100% (1)
- Smardt Catalogue V-ClassDocument14 paginiSmardt Catalogue V-ClassAldifirÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATS - EnGDocument4 paginiATS - EnGRamires AdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topical Test Chapter 18: AC Circuits Section A: Objective (10 Marks)Document4 paginiTopical Test Chapter 18: AC Circuits Section A: Objective (10 Marks)Wong Chai YenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 300nb Fire Water Line - BEEL - 071953Document2 pagini300nb Fire Water Line - BEEL - 071953irshadiiitÎncă nu există evaluări
- BANSHEE EXCEL LITE IP66 SpecificationDocument1 paginăBANSHEE EXCEL LITE IP66 SpecificationVladimir BukaricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯ ವಿಜ್ಞಾನ ಮತ್ತು ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನ K M ಸುರೇಶ್Document592 paginiಸಾಮಾನ್ಯ ವಿಜ್ಞಾನ ಮತ್ತು ತಂತ್ರಜ್ಞಾನ K M ಸುರೇಶ್Manjushree Megharaj100% (1)
- M52TU Throttle Valve CodesDocument3 paginiM52TU Throttle Valve Codeswicka3Încă nu există evaluări
- User Manual 2555737Document116 paginiUser Manual 2555737Cristian Dante CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Z30UMEUR (En) 02Document2 paginiZ30UMEUR (En) 02zeljavalybiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eve Online Manufacturing SheetDocument19 paginiEve Online Manufacturing SheetradubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jeff Shoemaker - "Introduction To BLDC Motor Control"Document26 paginiJeff Shoemaker - "Introduction To BLDC Motor Control"Cătălin MănăilăÎncă nu există evaluări
- DataSheet SRS50-HFA0-K21 1037067 enDocument6 paginiDataSheet SRS50-HFA0-K21 1037067 enHAMOUM LounisÎncă nu există evaluări
- D) AUMA MATIC - O&M Manual For Electric Actuators (English) PDFDocument68 paginiD) AUMA MATIC - O&M Manual For Electric Actuators (English) PDFwiyatnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 (Basic Principles of Protective Relays and Circuit Breaker Operations)Document11 paginiLesson 1 (Basic Principles of Protective Relays and Circuit Breaker Operations)kelotvÎncă nu există evaluări
- 32pfl5605 98 Dfu EngDocument36 pagini32pfl5605 98 Dfu EngMiki MikicÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Universal Gauge For Machine ToolsDocument12 paginiThe Universal Gauge For Machine ToolsFabrizio AugustoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Argus C3 Service ManualDocument6 paginiArgus C3 Service ManualRicardo Luis AbboudÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.2 The Main Components of Computer Systems: ICT IGCSE Theory - Revision PresentationDocument9 pagini1.2 The Main Components of Computer Systems: ICT IGCSE Theory - Revision PresentationNermeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual de Peças 545D SkidderDocument723 paginiManual de Peças 545D SkidderPaulo RobertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Provision Stock ListDocument59 paginiProvision Stock Listapi-234089277Încă nu există evaluări
- Fuji Igbt Application ManualDocument95 paginiFuji Igbt Application Manualramon navaÎncă nu există evaluări