Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Che 1
Încărcat de
vkkaliaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Che 1
Încărcat de
vkkaliaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
--
\ c;{t-.,I
10\ ::;
fb.t -=-
Section B (60 marIr~)
Answer any four questions in this section.
5. (a) (i) Define relative atomic mass.
(ii) The relative atomic mass of X is 30.97. By how many times is an atom of
X heavier than one atom of carbon-l 2.
(ill) Naturally occurring sulphur consists of four isotopes with relative
abundance as given in the table below.
Relative isotopic mass Relative abundance(%) 1
31.97 95.02
32.97 0.75
33.96 4.21
35.96 0.02
1\.1\1 t... CI,,>-01 l' ..
Calculate the relative atomic mass of sulphur. - ',' - --
\11'\) -;. 11.0"\ (6)
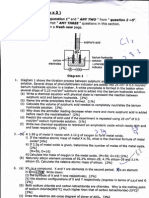
(a) Element Y is a gas at room conditions. The density ofY is 1.11g dm-3at 25°C ~~/,
and 86.1 kPa
(i) Using the ideal gas equation, calculate the relative molecular mass ofY and ~' ~.J~'
determine the identity of y~ 1 "
-Q.
(ii) Name the allotrope of.Y, give its molecular formula, and draw its Lewis
structure. (9)
6. (a)(i) Define buffer solution.
(ii) A mixture of aqueous ammonia, NH3 , and aqueous ammonium chloride, NH4CIis
an example of a buffer solution. Using suitable equations, explain how the buffer
v solution functions. (7)
0-'
~ ~
(b) (i) Calculate the pH of 1.0 dm3of a buffer solution prepared by dissolving 1.0 mol
of CH3COOHand 1.0 mol of CH3COONain sufficient amount of water.
'-1
+ [The acid dissociation constant, Kaof CH3COOHis 1.8 xl0-5 mol dm-3]
(ii) Calculate the pH of the buffer solution in (i) above when 0.1 mol of calcium tSrll
hydroxide is added to it. Write an equation for the reaction (8)
7 (a) Aluminium oxide and aluminium chloride have different chemical properties . \r:,~\
With reference to the bonding in the aluminium oxide and aluminium chloride, explain j 110.~
(i) the amphotheric nature of aluminium oxide
(ii) the reaction between aluminium chloride and water (8)
(b) Explain the following statements.
(i) Nitrogen is inert
(ii) Carbon dioxide is a gas while silicon dioxide is a solid under normal room conditions ( 1)
M."O)
, j:\, !J.
\
0 CI 6
~ 0
~
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Choi E Q Estions With Only One - Answer: Multiple (B) KhcoDocument7 paginiChoi E Q Estions With Only One - Answer: Multiple (B) Khcohrishik guptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 10: Section V AtmosphereDocument12 paginiTopic 10: Section V AtmosphereRobin KosasihÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPP Chemical BondingDocument69 paginiDPP Chemical BondingAmar SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Reactions and Equations S ChandDocument2 paginiChemical Reactions and Equations S ChandNishtha poptani50% (2)
- E - Valuat, - Can Every T T: SectionDocument9 paginiE - Valuat, - Can Every T T: SectionAlok ChoubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Transfer & CalorimetryDocument35 paginiHeat Transfer & CalorimetrySanskruti GokhaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSEC Chemistry-2010-P2Document20 paginiCSEC Chemistry-2010-P27Timothy hnÎncă nu există evaluări
- PYQs Chemistry 2017-18Document20 paginiPYQs Chemistry 2017-18avika.thapliyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adobe Scan 04 Mar 2023Document14 paginiAdobe Scan 04 Mar 2023officialfarmaan1009Încă nu există evaluări
- TTTTDocument1 paginăTTTTAnonymous BT988qyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mbabwe Schoo: ZI LEDocument9 paginiMbabwe Schoo: ZI LEwb4qv7yzvzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Document PDF 493Document10 paginiDocument PDF 493Vandita KumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Model Paper 1Document9 paginiChemistry Model Paper 1MemoursÎncă nu există evaluări
- SECTION A (15 Marks) Answer ALL Questions in This SectionDocument15 paginiSECTION A (15 Marks) Answer ALL Questions in This SectionFazliawati MahayuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- S.5 ChemistryDocument5 paginiS.5 ChemistryAnthony AndyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11.0. Electrochemistry ProbsDocument8 pagini11.0. Electrochemistry ProbskabengejericorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry PackageDocument6 paginiChemistry Packagepetermyonga3516Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry 12Document3 paginiChemistry 12ABHIGYANÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1999-AL-Chem 2Document21 pagini1999-AL-Chem 2LokChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volumetric Effects of Ion Salt InteractionDocument6 paginiVolumetric Effects of Ion Salt InteractionVempati Rahul KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChemistyDocument5 paginiChemistyjembemojaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moorebank Preliminary HARDDocument21 paginiMoorebank Preliminary HARDjordanochanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy Moctet3Document12 paginiPhy Moctet3KIEN NGUYENDACCHIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scan 0002Document12 paginiScan 0002api-3696136Încă nu există evaluări
- Chem 1002 DR Aung Kyaw Swar General Chemistry (For Zool, Bot, Geol, Phys)Document3 paginiChem 1002 DR Aung Kyaw Swar General Chemistry (For Zool, Bot, Geol, Phys)YU TAÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALEVELREVISIONQUESTIONSDocument7 paginiALEVELREVISIONQUESTIONSAnthony AndyÎncă nu există evaluări
- P42 Feb 2021Document8 paginiP42 Feb 2021Aini Munirah Muhamad ShudÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Kerala Bhavans Chemistry 2010Document16 paginiAll Kerala Bhavans Chemistry 2010SajeevÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPP - LT - CHE - 08-07-21: SR - Physical Chemistry Revision Work SheetDocument13 paginiDPP - LT - CHE - 08-07-21: SR - Physical Chemistry Revision Work SheetShivakumar SomanapallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Testbank 1 1 PDFDocument7 paginiTestbank 1 1 PDFMyk AbayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Img 0002Document1 paginăImg 0002ANDREWLAWZHÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 1 (Malacca)Document14 paginiSTPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 1 (Malacca)sherry_christyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry F3 MS1Document14 paginiChemistry F3 MS1Okumu KevinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 12 MidDocument15 paginiYear 12 MidKissiedu YirenkyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09 Gaseous State EngDocument5 pagini09 Gaseous State EngMr XÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 3 Chemistry Assignment (WK 7)Document5 paginiForm 3 Chemistry Assignment (WK 7)JOSEPH MWANGIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gr. 11U Review - D2L VersionDocument2 paginiGr. 11U Review - D2L Versionsar2005Încă nu există evaluări
- C3Document2 paginiC3Varun LâlwáñíÎncă nu există evaluări
- KMPK Sk015 2324 (Question)Document6 paginiKMPK Sk015 2324 (Question)Ahya NatasyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSEC Chemistry June 2006 P1 PDFDocument9 paginiCSEC Chemistry June 2006 P1 PDFLaimen ReveskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry PSPM 1 2008/2009Document3 paginiChemistry PSPM 1 2008/2009Viknish Arumugam50% (2)
- Adobe Scan 20 Jan 2024Document8 paginiAdobe Scan 20 Jan 2024adityasethy47Încă nu există evaluări
- Chem Cgce 2011 A/lDocument9 paginiChem Cgce 2011 A/lmengotÎncă nu există evaluări
- SECTION A (15 Marks) Answer ALL Questions in This SectionDocument15 paginiSECTION A (15 Marks) Answer ALL Questions in This SectionFazliawati MahayuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSEJS Previous Year Question PaperDocument16 paginiNSEJS Previous Year Question PaperUS CREATIONSÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEMISTRYDocument6 paginiCHEMISTRYSharif KavumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soalan Ala PSPM Set 2 PDFDocument3 paginiSoalan Ala PSPM Set 2 PDFMOHAMAD AIMAN MOHAMAD ZAKIÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 Chemistry Standardised Test For Science Stream (SPM)Document7 pagini2018 Chemistry Standardised Test For Science Stream (SPM)carnationÎncă nu există evaluări
- KTESP SEM 1 TRIAL 2017 With AnswerDocument7 paginiKTESP SEM 1 TRIAL 2017 With AnswerShima SenseiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- S.5 P525 Chemistry 2 EOT1-2Document6 paginiS.5 P525 Chemistry 2 EOT1-2Talemwa ALFRED KAKORAKIÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gaseous State - JEE Mains PYQ 2020-2022Document73 paginiThe Gaseous State - JEE Mains PYQ 2020-2022pankaj baidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two On A Follow: A Olution 1 GM: So I S S S S S)Document6 paginiTwo On A Follow: A Olution 1 GM: So I S S S S S)Mohit SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ElectrolysisDocument8 paginiElectrolysisTanviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem Class 11th JsdjsjhbsDocument1 paginăChem Class 11th JsdjsjhbsPratham DesaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- GVSX DiagramsDocument18 paginiGVSX DiagramsSatyam vankayalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ngatataek Mixed Secondary School Chemistry (Theory) Paper 1 Form 3 Mid-Term Exam NAME ..ADM CLASS . Time: 2 HoursDocument10 paginiNgatataek Mixed Secondary School Chemistry (Theory) Paper 1 Form 3 Mid-Term Exam NAME ..ADM CLASS . Time: 2 HoursDavyieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chmistry HissanDocument2 paginiChmistry HissanVaskar Humagain100% (1)
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsDe la EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiDe la EverandTables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding, Periodic TableDocument5 paginiAtomic Structure and Chemical Bonding, Periodic TableVideo uploadingÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 02Document27 paginiCH 02Aaron GuralskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZCT+533 4+Dosimetry+and+Radiation+ProtectionDocument21 paginiZCT+533 4+Dosimetry+and+Radiation+ProtectionXeniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acid Bases Salt Important QuestionsDocument8 paginiAcid Bases Salt Important Questionslegal eagleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inconel 625Document6 paginiInconel 625heanjiametalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1920 F3 Chem First Exam AnswerDocument2 pagini1920 F3 Chem First Exam AnswerElsaaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Level Chemistry Edexcel FACER SampleDocument36 paginiA Level Chemistry Edexcel FACER SampleHuy Tran60% (5)
- Cah2 + 2 H2O - 2 H2 + Ca (Oh) 2: Sig FigDocument4 paginiCah2 + 2 H2O - 2 H2 + Ca (Oh) 2: Sig FigDennis KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Elemental Analysis of Various Classes of Chemical Compounds Using CHNDocument6 paginiThe Elemental Analysis of Various Classes of Chemical Compounds Using CHNMariam IshtiaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSS Chemistry Part 12 Patterns in Chemical WorldDocument7 paginiNSS Chemistry Part 12 Patterns in Chemical WorldFelix YueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument18 paginiBalancing Chemical EquationscedrickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valuable Metals Recovery and Recycling - Angewandte PDFDocument37 paginiValuable Metals Recovery and Recycling - Angewandte PDFEduardo RuedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 9 WorksheetsDocument5 paginiCH 9 Worksheetsadaglio001100% (1)
- Formation of Light and Heavy Elements: Prepared By: Jerome A. Bigael, Leyte Progressive High SchoolDocument17 paginiFormation of Light and Heavy Elements: Prepared By: Jerome A. Bigael, Leyte Progressive High Schoolshermaine geniston100% (1)
- Electrolyte and Non-Electrolyte SolutionsDocument14 paginiElectrolyte and Non-Electrolyte SolutionsSuwahono, M.PdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Previous Year (Chemistry)Document5 paginiPrevious Year (Chemistry)Khushi ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Science Week 2Document7 paginiPhysical Science Week 2ruel rinconadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 7 General Chapter 191 UpdateDocument23 paginiModule 7 General Chapter 191 UpdatesreekanthsharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concepts of Chemical Bonding: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument45 paginiConcepts of Chemical Bonding: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenBoNwoawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChloroformDocument1 paginăChloroformSesha Sai KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENG2000 Chapter 2 Atoms and Bonding: ENG2000: R.I. Hornsey Atom: 1Document29 paginiENG2000 Chapter 2 Atoms and Bonding: ENG2000: R.I. Hornsey Atom: 1Manuel Tutacha ™Încă nu există evaluări
- Answers To Mixed Stoichiometry Practice Review Problems-2Document2 paginiAnswers To Mixed Stoichiometry Practice Review Problems-2Jacqueline GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edgcse TTPP cc5-7 SB AnswersDocument6 paginiEdgcse TTPP cc5-7 SB Answersegcarty10090% (1)
- Chemistry 17 (Second Long Sample Exam)Document2 paginiChemistry 17 (Second Long Sample Exam)Nyka C.Încă nu există evaluări
- Acids, Bases and Salts: Chemistry Cambridge OL DR - Amira AhmedDocument23 paginiAcids, Bases and Salts: Chemistry Cambridge OL DR - Amira AhmedMoh AmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amount of Substance That Contain As Many Particle As The Number of Atoms Is Exactly 12g of CarbonDocument4 paginiAmount of Substance That Contain As Many Particle As The Number of Atoms Is Exactly 12g of CarbonnssÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch1 MCQ Sheet PadhleDocument7 paginiCh1 MCQ Sheet PadhleAmit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9H Using Chemistry SATS QDocument15 pagini9H Using Chemistry SATS QAnna CortiÎncă nu există evaluări
- JIS G0321 - 2010, Product Analysis and Its Tolerance For Wrought Steel PDFDocument13 paginiJIS G0321 - 2010, Product Analysis and Its Tolerance For Wrought Steel PDFRolando Castillo100% (1)
- WO2014188453A2Document43 paginiWO2014188453A2Dr-Nilesh SalunkheÎncă nu există evaluări