Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lubricate and Bleed Procedure Excel Calculation
Încărcat de
stevebeardsleyDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lubricate and Bleed Procedure Excel Calculation
Încărcat de
stevebeardsleyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
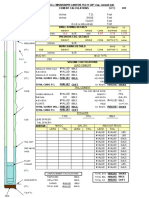
Name of Company:
Well Name & Number: Drilling Application
LUBRICATE
LUBRICATE &
& BLEED
BLEED
Microsoft Excel 97 Date: September 18, 2010 PROCEDURE
PROCEDURE
This method is used when the kick fluid nears the surface, circulation is not feasible,
and the surface pressures could possibly reach the pressure rating of the wellhead or the casing.
The method employs injecting a fluid into the well and allowing it to fall to start increasing the
hydrostatic pressure. Since this hydrostatic pressure is added to the well, a back pressure equal
to the gain in the hydrostatic pressure must be removed by bleeding through a control device.
INPUT INFORMATION MUD PUMP
Shut-in Casing Pressure, psi Stroke Length, in? =
Casing ID, in? = Liner Size, in? =
Pipe OD, in? = % Efficiency (1 - 100)? =
Density of Fluid in Well, ppg? = Pump Output, bbl/stk 0.0000
Number of pump strokes to increase the SCIP 200 psi? =
Start the pumping into well until the SICP has increased approximately ±200 psi. While waiting
for the fluid to fall through the gas to the top of the fluid column, the casing pressure can be bled
back to it's original pressure. Bleed off only gas, not the injected fluid. After a sufficient time, the
gain in hydrostatic can be bled off in "back" pressure.
LUBRICATE and BLEED PROCEDURE CALCULATIONS
Volume of fluid pumped, bbls H17 0.00
Annular volume, bbl/ft 0.0000
Height or space added fluid will occupy in wellbore, ft #DIV/0!
Gain in hydrostatic pressure due to added fluid, psi #DIV/0!
Value to bleed casing pressure down, psi #DIV/0!
The basic procedure is to inject fluid, wait for the pressure to stabilize, then bleed off
This procedure is repeated until the annulus is full of fluid. If the well was underbalanced, then the
gas space at the surface in the wellbore must be replaced with a fluid heavy enough to dominate
the pressure underbalance.
THE END
Reference: WCS Well Control School
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 13 3-8" Cementing Program ChecklistDocument2 pagini13 3-8" Cementing Program ChecklistYougchu LuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kirksey - Squeeze CementingDocument37 paginiKirksey - Squeeze CementingAquiles CarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Squeeze Cementing JobDocument1 paginăSqueeze Cementing JobstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drilling application evaluate design bit hydraulicsDocument1 paginăDrilling application evaluate design bit hydraulicsstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Level Cyber Security Assessment - Detailed ReportDocument57 paginiHigh Level Cyber Security Assessment - Detailed Reportdobie_e_martinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To ProtectorsDocument22 paginiIntroduction To ProtectorsMuhammad ShahrukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introspective Hypnosis Class - 052017 - Antonio Sangio (2745)Document62 paginiIntrospective Hypnosis Class - 052017 - Antonio Sangio (2745)sandra100% (4)
- Well Control Worksheet - Surface BOPDocument2 paginiWell Control Worksheet - Surface BOPstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Tips For Well Control Success: Aberdeen Drilling SchoolsDocument4 paginiEssential Tips For Well Control Success: Aberdeen Drilling SchoolsCerón Niño SantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evo-Trieve® EB0 Retrievable Straddle - HalliburtonDocument2 paginiEvo-Trieve® EB0 Retrievable Straddle - HalliburtonYovaraj KarunakaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drilling Application Hydraulics AnalyzedDocument1 paginăDrilling Application Hydraulics AnalyzedstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimize Fishing Operations with Decision Trees and CalculatorsDocument53 paginiOptimize Fishing Operations with Decision Trees and Calculatorsciucalata88100% (1)
- Wireline PCE PDFDocument56 paginiWireline PCE PDFMuhammad ShahrukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bop Test 1Document1 paginăBop Test 1asiraza100% (1)
- Rules of Thumb - Murchison School 2006 PDFDocument55 paginiRules of Thumb - Murchison School 2006 PDFReza BorahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Well Killing ProceduresDocument28 paginiWell Killing ProceduresYeho ShuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cement calculations for 20Document3 paginiCement calculations for 20stevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Stress Relief PrescriptionDocument8 paginiThe Stress Relief PrescriptionRajesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mud Engineer User ManualDocument48 paginiMud Engineer User ManualstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iwcf NotesDocument81 paginiIwcf NotesShraddhanand More100% (1)
- Fishing With CTDocument14 paginiFishing With CTMuhammad ShahrukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Completion EquipmentDocument41 paginiCompletion Equipmenteng20072007Încă nu există evaluări
- Bit RecordDocument1 paginăBit RecordstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wellcare Oil Tools Pvt Ltd Product IndexDocument33 paginiWellcare Oil Tools Pvt Ltd Product IndexBrahim LetaiefÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Fishing Operation ": Drilling EngineeringDocument28 pagini"Fishing Operation ": Drilling EngineeringLulav Barwary100% (1)
- CT Operations ExerciseDocument20 paginiCT Operations ExerciseMohammed Anis FortasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CT Ops Exercise - No AnswersDocument9 paginiCT Ops Exercise - No AnswersMohammed Anis FortasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 22CL 8.gas MigrationDocument48 pagini22CL 8.gas MigrationEslam Atif AzkolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drilling Tools - 1Document269 paginiDrilling Tools - 1berrouiÎncă nu există evaluări
- KickDocument22 paginiKickyarra suryatejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.5 - Blow-Out Prevention SystemDocument69 pagini3.5 - Blow-Out Prevention SystemSamuel OkezieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wellhead Completion Equipments 1689794492Document13 paginiWellhead Completion Equipments 1689794492Saeed AbdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tosin Mud Sce EffDocument593 paginiTosin Mud Sce Effstevebeardsley100% (1)
- Catalogue: Packer SystemDocument56 paginiCatalogue: Packer SystemChinmoyee Sharma100% (1)
- BOP test proceduresDocument7 paginiBOP test proceduresjvmspÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shut-In Procedures OverviewDocument71 paginiShut-In Procedures OverviewRichard Reiersen100% (3)
- Spot Heavy MudDocument1 paginăSpot Heavy MudstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 06 Section 06 - Well Control EquipmentDocument43 pagini06 Section 06 - Well Control Equipmentddrb23Încă nu există evaluări
- Kick-Off Techniques: Hassan AlemiDocument52 paginiKick-Off Techniques: Hassan Alemimagoankit50% (2)
- Drilling Day 3 Valve Wireline Bop Manual Hydraulic Slick Line and Multi StrandDocument132 paginiDrilling Day 3 Valve Wireline Bop Manual Hydraulic Slick Line and Multi Strandhosam aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- AVIARA ENERGY CORP Well Drilling ApplicationDocument1 paginăAVIARA ENERGY CORP Well Drilling ApplicationstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coiled Tubing Unit: ApplicationsDocument24 paginiCoiled Tubing Unit: Applicationswill castellanosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drilling EquipmentDocument63 paginiDrilling EquipmentYudha negaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coiled Tubing & SnubbingDocument4 paginiCoiled Tubing & SnubbingMichael LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Off-Bottom Drilling PracticesDocument3 paginiOff-Bottom Drilling PracticesAdel Ahmed AlkhaligyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leak-Off Test Analysis: Well: RigDocument5 paginiLeak-Off Test Analysis: Well: RigstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coiled Tubing CompletionDocument9 paginiCoiled Tubing Completionreborn2Încă nu există evaluări
- Measurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignDe la EverandMeasurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Danieli Danarc Plus M Furnace at Abs Meltshop: Aldo A. Fior Danieli C M - Process Engineer Buttrio, ItalyDocument6 paginiThe Danieli Danarc Plus M Furnace at Abs Meltshop: Aldo A. Fior Danieli C M - Process Engineer Buttrio, ItalyBrandon CoxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Swab and Surge Pressures SHBDocument1 paginăSwab and Surge Pressures SHBstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- DHSV Functions and Well Completion ComponentsDocument4 paginiDHSV Functions and Well Completion Componentsmissaoui0% (1)
- Stripping With Volumetric Control Steps and Example Calculations - Drilling Formulas and Drilling Calculations PDFDocument19 paginiStripping With Volumetric Control Steps and Example Calculations - Drilling Formulas and Drilling Calculations PDFAmine MimoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 05 Tripping Backreaming PracticesDocument68 paginiSection 05 Tripping Backreaming PracticesSpeculeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout Well Intervention Pressure ControlDocument208 paginiHandout Well Intervention Pressure Controlomar shahatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Well CompletionDocument26 paginiWell Completioneliud apindiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 63 Rig Train Wireline Fishing 5 DayDocument224 pagini63 Rig Train Wireline Fishing 5 DayTebengz Shakespear100% (4)
- Recommended Practice for Open Hole Sidetrack DrillingDocument5 paginiRecommended Practice for Open Hole Sidetrack DrillingAdel Ahmed AlkhaligyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pump Fit/Lot Weight Up Equivalent Circulating DensityDocument109 paginiPump Fit/Lot Weight Up Equivalent Circulating DensitynurmhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barrier (Well Control) 1Document13 paginiBarrier (Well Control) 1Zahraa AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stuck Pipe WorksheetDocument1 paginăStuck Pipe WorksheetMino MinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diaseal M PresentationDocument22 paginiDiaseal M PresentationstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Well Control - Combined Stripping and Volumetric MethodDocument3 paginiWell Control - Combined Stripping and Volumetric MethodAbdul Hameed Omar100% (1)
- Wireline Operations Techniques: Approach Into Slick, Braided & Electrical Line Equipment, Tools & ApplicationsDocument4 paginiWireline Operations Techniques: Approach Into Slick, Braided & Electrical Line Equipment, Tools & ApplicationsJerome LIKIBIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Casing Design PreliminaryDocument29 paginiCasing Design Preliminaryalizareiforoush100% (2)
- Optimizing ROP with Schlumberger TechniquesDocument14 paginiOptimizing ROP with Schlumberger TechniquesMaría MarquinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Well Control Checklist for Safe Drilling OperationsDocument14 paginiWell Control Checklist for Safe Drilling OperationsAdam InesÎncă nu există evaluări
- W181 - Preparation For The Wellsite CementingDocument31 paginiW181 - Preparation For The Wellsite Cementinghardrockgeo6088Încă nu există evaluări
- Gas MigrationDocument42 paginiGas Migrationmoussa mrzg100% (1)
- CTHBDocument543 paginiCTHBJose AcostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surface Kill Sheet Exercise 2Document3 paginiSurface Kill Sheet Exercise 2adeelsnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Well Control Pre-Kick Sheet CalculationsDocument4 paginiWell Control Pre-Kick Sheet CalculationsElrohirPendragonÎncă nu există evaluări
- IADC Well Intervention For Coil Tubing (English)Document2 paginiIADC Well Intervention For Coil Tubing (English)NguyễnTrườngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cabeza de Inyeccion de GrasaDocument100 paginiCabeza de Inyeccion de GrasaPierre MejiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Well Control Principles & Procedures Subsea BOPDocument5 paginiWell Control Principles & Procedures Subsea BOPKRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Low Choke High Quality PDFDocument4 paginiDynamic Low Choke High Quality PDFWCGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Coiled Tubing Fails and HowDocument56 paginiWhy Coiled Tubing Fails and HowArdita S IrwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medimurec Gaurina N Pasic B Simon K Matanovic D Malnar MDocument9 paginiMedimurec Gaurina N Pasic B Simon K Matanovic D Malnar MstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volumetric MethodDocument1 paginăVolumetric MethodstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pump Displacements and Hole CapacitiesDocument11 paginiPump Displacements and Hole CapacitiesstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- TVD NeededDocument2 paginiTVD NeededstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phone ListDocument29 paginiPhone ListstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Randy Smith KillDocument2 paginiRandy Smith KillstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nozzle SelectionDocument1 paginăNozzle SelectionstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Log and Geo ManualDocument87 paginiLog and Geo ManualstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maximum Casing Pressure and Pit GainDocument1 paginăMaximum Casing Pressure and Pit GainstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacity of HoleDocument1 paginăCapacity of HolestevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mud Solids AnalysisDocument1 paginăMud Solids AnalysisstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Freezing Weather ChecklistDocument1 paginăFreezing Weather CheckliststevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Casing Talley RPTDocument2 paginiCasing Talley RPTstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bop DrawingDocument9 paginiBop DrawingstevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation Fracture PressureDocument5 paginiFormation Fracture PressurestevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drill Pi Pet AlleyDocument9 paginiDrill Pi Pet AlleystevebeardsleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duration of LTMDocument3 paginiDuration of LTMsamueldaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baumann Forklift Dx50!14!40 S N 5361 Spare Parts CatalogueDocument22 paginiBaumann Forklift Dx50!14!40 S N 5361 Spare Parts Catalogueanneclark120297mgz100% (108)
- Toms2003 A Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of The Periodontal Ligament Under Orthodontic Tooth LoadingDocument9 paginiToms2003 A Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of The Periodontal Ligament Under Orthodontic Tooth LoadingPuttnaree NiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shell Donax TA Transmission Fluid TDS PDFDocument1 paginăShell Donax TA Transmission Fluid TDS PDFirwanbahrudin117134Încă nu există evaluări
- Design of A Neural Network Function Block For Insertion Into The Function Block Library of A Programmable Logic ControllerDocument4 paginiDesign of A Neural Network Function Block For Insertion Into The Function Block Library of A Programmable Logic ControllerArmando Fermin PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Load of Pedstrain On FobDocument26 paginiLoad of Pedstrain On FobPOOJA VÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS EN 50131-1998 Alarm Systems Intrusion Systems Part 6Document30 paginiBS EN 50131-1998 Alarm Systems Intrusion Systems Part 6Michael Camit EsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intermediate Financial Management 13th Edition Brigham Test BankDocument25 paginiIntermediate Financial Management 13th Edition Brigham Test BankMonicaHoustonwjtgz100% (56)
- NB-CPR 14-612r7 Issuance of Certificates Under CPRDocument13 paginiNB-CPR 14-612r7 Issuance of Certificates Under CPRÜmit BUCAKÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 & 6 Risk AssessmentDocument23 pagini5 & 6 Risk AssessmentAzam HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- No Curfew for College Dorm StudentsDocument2 paginiNo Curfew for College Dorm Students陳玟蓁Încă nu există evaluări
- Ropes and Wires: Malaysian Maritime Academy/Seamanship/May2003 1 of 6Document6 paginiRopes and Wires: Malaysian Maritime Academy/Seamanship/May2003 1 of 6Rohit SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annexure - Subject Wise IBDP Grade BoundariesDocument4 paginiAnnexure - Subject Wise IBDP Grade BoundariesazeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Resilience Philippines Urban PoorDocument16 paginiBuilding Resilience Philippines Urban PoorYasmin Pheebie BeltranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Let's Mingle Chat Invite ExamplesDocument22 paginiLet's Mingle Chat Invite ExamplesCarmen BalbuenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Directory StructureDocument47 paginiDirectory StructureStevenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet Chapter 50 Introduction To Ecology The Scope of EcologyDocument2 paginiWorksheet Chapter 50 Introduction To Ecology The Scope of EcologyFernando CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meinrad 2018 All Symbols With NumbersDocument4 paginiMeinrad 2018 All Symbols With NumbersXer N. AcostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spatial Personality For Human Space InteractionDocument10 paginiSpatial Personality For Human Space Interactionavijitsaha bornoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dav Public School, Berhampur, Odisha Summer Holiday HomeworkDocument3 paginiDav Public School, Berhampur, Odisha Summer Holiday HomeworkOmÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Overview PsasDocument19 pagini5 Overview Psasعلي صالحÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operator Interface SERIES 300 Device Platform EAGLE OS ET-316-TXDocument6 paginiOperator Interface SERIES 300 Device Platform EAGLE OS ET-316-TXDecoÎncă nu există evaluări
- KTO12 Curriculum ExplainedDocument24 paginiKTO12 Curriculum ExplainedErnesto ViilavertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Positive Leadership and Adding Value - A Lifelong Journey: June 2017Document7 paginiPositive Leadership and Adding Value - A Lifelong Journey: June 2017CescSalinasÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Membership Application GemsDocument5 paginiNew Membership Application Gemslaguila18Încă nu există evaluări
- OAF Hello Word Page PDFDocument20 paginiOAF Hello Word Page PDFNaveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări