Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Seizure Pathophysiology
Încărcat de
Paula Nantes NazarethDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Seizure Pathophysiology
Încărcat de
Paula Nantes NazarethDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
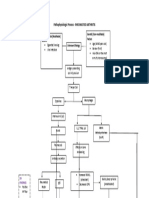
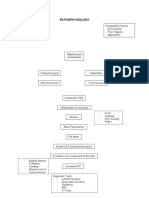
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF SEIZURE:
NERVOUS SYSTEM
ETIOLOGY PREDISPOSING
FACTORS
- an electrical disturbance - idiopathic (genetic,
in the nerve cells in one developmental defects)
section of the brain, causing - acquired
(hypoxemia,
them to emit abnormal, vascular insufficiency,
recurring, uncontrolled, fever (childhood), head
injury,
electrical discharges hypertension, CNS
infections,
metabolic and toxic
conditions,
brain tumor, drug and
alcohol
withdrawal, and allergies)
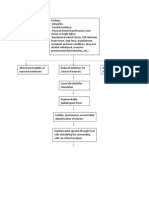
CELLULAR/ METABOLIC CHANGES GROSS ANATOMICAL PHYSICAL CHANGES
PHYSIOLOGIC MANIFESTATION
- when the integrity of the neuronal cell - involuntary movements may spread - epigastric
sensations, pallor,
membrane is altered, the cell begins firing centrally and involve the entire limb, including sweating,
flushing, goose flesh
with increased frequency and amplitude. one side of the face and lower extremities. (piloerection),
pupillary dilation,
When the intensity discharges reaches the the client also may exhibit changes in posture tachycardia,
and tachypnea.
threshold, the neuronal firing spreads to or spoken utterances
adjacent neurons, ultimately resulting to
seizure. Inhibitory neurons in epilepsy have
slow neuronal firing in the cortex, anterior
thalamus, and basal ganglia. Once the
inhibitory processes develop or the
epileptogenic neurons are exhausted, the
seizure stops then later events depress the
CNS activity and impair consciousness
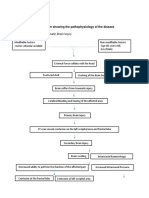
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS LABORATORY FINDINGS
TONIC PHASE:
- fall, loss of consciousness, yell or “tonic cry”, - MRI may detect lesions in the brain,
focal abnormalities,
extension of arms, legs, and/or face, fingers and cerebral degenerative changes
and jaw clenched. AUTONOMIC SYMPTOMS - EEG may allow diagnosis of the type and
location of the
include increase in blood pressure, heart rate occurring seizure.
and bladder pressure, flushing, sweating, - SPECT may identify the epileptogenic zone
so that the
increased salivation and bronchial secretion, area in the brain giving rise to seizures can
be removed
and apnea surgically.
CLONIC PHASE:
- muscles relax completely, then muscle tone
returns which causes rhythmic jerking of head
and body.
POST-ICTAL PHASE:
- biting of the tongue, cheek or lip, and
urinary incontinence are common
SEIZURE
COMPLICATIONS
- Hypoxic brain damage and mental retardation may follow repeated seizures
- Depression and anxiety may develop. Long-term social isolation may also occur
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 5 NCPDocument3 pagini5 NCPAllord Lacanilao Bungay0% (1)
- Child Behavior Checklist - WikipediaDocument7 paginiChild Behavior Checklist - WikipediaAdarsh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Epilepsy: Causes, Types, and TreatmentDocument51 paginiUnderstanding Epilepsy: Causes, Types, and TreatmentDeepa SeiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple SclerosisDocument21 paginiMultiple Sclerosisjhodane100% (1)
- Ischemic Stroke Pathophysiology and Principles of Localization (1) G PDFDocument16 paginiIschemic Stroke Pathophysiology and Principles of Localization (1) G PDFGina Ayudia PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chiropractic Day: A Historical Review of A Day Worth CelebratingDocument10 paginiChiropractic Day: A Historical Review of A Day Worth CelebratingcdjohnsondcÎncă nu există evaluări
- TAHBSODocument3 paginiTAHBSOakatzkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dave Mearns - Person-Centred Counselling Training-SAGE (1997)Document247 paginiDave Mearns - Person-Centred Counselling Training-SAGE (1997)dd1335100% (4)
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument8 paginiMental Status ExaminationanisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Undifferentiated SchizophreniaDocument26 paginiUndifferentiated SchizophreniaVictor Shon100% (1)
- Encephalitis PathophysiologyDocument19 paginiEncephalitis PathophysiologyHeron Bayanin80% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Potts DiseaseDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Potts DiseaseJoanna Marie M. dela Cruz100% (5)
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument11 paginiMental Status ExaminationIman TawasilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poc Pott's DiseaseDocument8 paginiPoc Pott's Diseasealsbeth50% (4)
- Colloid Nodular GoiterDocument37 paginiColloid Nodular GoiterLori GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology - Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument1 paginăPathophysiology - Rheumatoid ArthritisAngel FiloteoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cva-Hypertension-Case-Analysis-Group-I FinalDocument59 paginiCva-Hypertension-Case-Analysis-Group-I FinalVhince Norben PiscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument12 paginiNCPJonathan Liscano100% (3)
- EpilepsyDocument36 paginiEpilepsypodki gurungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Rheumatoid ArthritisGerardeanne ReposarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chi Gong - Chunyi Lin Ebook IntroDocument51 paginiChi Gong - Chunyi Lin Ebook IntroGreg Wolfe100% (4)
- Seizure PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiSeizure Pathophysiologyqwertyuiop60% (10)
- Seizure PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiSeizure PathophysiologyqwertyuiopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peat 1Document42 paginiPeat 1Steve Colbert100% (3)
- A Beautiful Mind XDocument7 paginiA Beautiful Mind XAnn Desamito100% (1)
- Seizure DisordersDocument12 paginiSeizure Disordersmardsz83% (6)
- Multiple Sclerosis PathoDocument1 paginăMultiple Sclerosis PathoAleli DoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Cushing's SyndromeDocument2 paginiNCP Cushing's SyndromeChristine LebicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Acute PainDocument2 paginiNCP Acute PainMimi Nacor100% (3)
- Case Study 1Document67 paginiCase Study 1Herbie SoÎncă nu există evaluări
- EmpyemaDocument11 paginiEmpyemaJoha_AdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guillain BarreDocument42 paginiGuillain BarreKeeshia Magbanua100% (3)
- Patho of Pott's DiseaseDocument2 paginiPatho of Pott's DiseaseIris Balino100% (1)
- PathoConceptMap AIDSDocument3 paginiPathoConceptMap AIDSKristen Babauta50% (2)
- El Exprime Hombres 2Document11 paginiEl Exprime Hombres 2Carlos GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Findings: Small Cell CarcinomaDocument4 paginiLaboratory and Diagnostic Findings: Small Cell CarcinomaTheresa Sombilla FacunlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Context and Counseling BasicsDocument49 paginiContext and Counseling BasicsJohn Paul BrionesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case of Febrile SeizuresDocument2 paginiCase of Febrile SeizuresAzizan HannyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Meniere FinalDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Meniere Final1S VILLEGAS GabrielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schizophrenia ParanoidDocument129 paginiSchizophrenia ParanoidhjhjhjkjkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology: Bipolar DisorderDocument3 paginiPathophysiology: Bipolar DisorderPae EdejerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagram Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument1 paginăCarpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagram Pa Tho PhysiologyLJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rabies: A Deadly Viral Disease Spread by Animal BitesDocument3 paginiRabies: A Deadly Viral Disease Spread by Animal BitesDavid CalaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostics - Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument9 paginiDiagnostics - Nursing ResponsibilitiesCarmellaDawn100% (3)
- Potts Disease NCP .. JustificationDocument8 paginiPotts Disease NCP .. JustificationMicah SalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing case study on EncephalitisDocument7 paginiNursing case study on EncephalitisJitendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burns - Skin Integrity, ImpairedDocument2 paginiBurns - Skin Integrity, Impairedmakyofrancis20Încă nu există evaluări
- PPPDocument3 paginiPPPJack BangcoyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study: Christine Joy P. de Chavez, SNDocument23 paginiCase Study: Christine Joy P. de Chavez, SNHELLOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joelle Maze M. de Belen & Iyah Clarisse RetondaDocument1 paginăJoelle Maze M. de Belen & Iyah Clarisse RetondaDE BELEN JOERES SHENNEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiNursing Care Planrexale riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meniere's DiseaseDocument57 paginiMeniere's DiseasejohannesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Bipolar DisorderDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Bipolar DisorderbeshyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Client with Altered Thought ProcessDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan for Client with Altered Thought ProcessOphelia Ross Omaña TutanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocument7 paginiDrug Study - IbuprofenajÎncă nu există evaluări
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of NeurocysticercosisDocument6 paginiPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of Neurocysticercosisteddydeclines14100% (3)
- HNP PathoDocument1 paginăHNP PathoYrban GuyuranÎncă nu există evaluări
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Bacterial Meningitis 2Document2 paginiPATHOPHYSIOLOGY Bacterial Meningitis 2Luis Leh100% (2)
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocument3 paginiDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJoenna GaloloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obsessive Compulsive DisorderDocument14 paginiObsessive Compulsive Disorderfrancis00090100% (1)
- EpilepsyDocument37 paginiEpilepsyMakojoa KatisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- EpilepsyDocument19 paginiEpilepsyJashwanth KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epilepsy Sa 1Document33 paginiEpilepsy Sa 1Kishan GoyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epilepsy-Students 2016Document85 paginiEpilepsy-Students 2016Alberto MayorgaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seizures in Childhood: For C-1Document50 paginiSeizures in Childhood: For C-1Yemata HailuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding the Causes and Classification of SeizuresDocument106 paginiUnderstanding the Causes and Classification of SeizuresLife PediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuropathy: Departemen Neurologi FK Usu/ Rsup H. Adam Malik MedanDocument41 paginiNeuropathy: Departemen Neurologi FK Usu/ Rsup H. Adam Malik MedanHatta Diana TariganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intensive Management of Status EpilepticusDocument41 paginiIntensive Management of Status EpilepticussnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Culinary Terms Related To Sandwiches-Lesson3Document55 paginiCulinary Terms Related To Sandwiches-Lesson3John Rey Tresbe100% (1)
- Torts Project NervousShockDocument21 paginiTorts Project NervousShockShivam PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nurse-Patient Family CommunicationDocument2 paginiNurse-Patient Family CommunicationYULLIANTI 43Încă nu există evaluări
- Graph Data Analysis AEUK ExampleDocument8 paginiGraph Data Analysis AEUK ExampleHuỳnh Xuân NhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulation of Accident Prevention ProgrammeDocument24 paginiFormulation of Accident Prevention ProgrammeCHANDUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Manuscript of Group 1Document104 paginiFinal Manuscript of Group 1AYLEYA L. MAGDAONGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 47Document11 paginiChapter 47Aziil LiizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood MealDocument3 paginiBlood MealAnggaVaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerebral Palsy Assessment Form: History: VisionDocument16 paginiCerebral Palsy Assessment Form: History: VisionRupam KanungoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cholera: Key FactsDocument9 paginiCholera: Key FactsDennis NjorogeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pain - FDocument22 paginiPain - FmadvincyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braverman Personality Type Assessment - Online TestDocument16 paginiBraverman Personality Type Assessment - Online TestKomkor GuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mario and Bowsette in The Blazes of Love - ComicsNixDocument1 paginăMario and Bowsette in The Blazes of Love - ComicsNixBryan DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychology For PhysiotherapyDocument404 paginiPsychology For PhysiotherapybptcomsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accuracy Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniques For Patient Liver DiseaseDocument15 paginiAccuracy Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniques For Patient Liver DiseaseManoj Kumar100% (1)
- Polyshield: (Bituminous Damp Proof Membrane)Document31 paginiPolyshield: (Bituminous Damp Proof Membrane)Mathikumar Melur MelurÎncă nu există evaluări
- (PDF) Mesure Du Stress en Milieu de Travail Par Autoquestionnaires Validés en Français - Revue de La LittératureDocument10 pagini(PDF) Mesure Du Stress en Milieu de Travail Par Autoquestionnaires Validés en Français - Revue de La LittératureAdouahiri Matthieu ZongobouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parents Evaluation of Aural Performance of Children (PEACH) v.4Document2 paginiParents Evaluation of Aural Performance of Children (PEACH) v.4Gwyneth PañaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LKJHHDocument5 paginiLKJHHVishnu SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auriculotherapy For Stress Management As Self Help in Isolation Situations Covid 19Document3 paginiAuriculotherapy For Stress Management As Self Help in Isolation Situations Covid 19Miki ShimizuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physicochemical and Biological Properties of Drugs For CRDDSDocument29 paginiPhysicochemical and Biological Properties of Drugs For CRDDSNirali DongaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Citrate Anticoagulation During CRRTDocument12 paginiCitrate Anticoagulation During CRRTpmunizÎncă nu există evaluări