Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Hobbes, Locke and Rousseau Comparison Grid
Încărcat de
d-fbuser-3672746988%(24)88% au considerat acest document util (24 voturi)
49K vizualizări2 paginiThe document discusses Thomas Hobbes, John Locke, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau's views on the state of nature and social contract theory. Hobbes saw the state of nature as a state of war where life is solitary, poor, nasty, brutish and short. Locke believed the state of nature was not necessarily bad, and that people are born free and equal with natural rights. Rousseau saw the state of nature as one without laws or morality, but with potential for goodness. They all argued that people form social contracts and governments to escape the state of nature, but differed on people's natural state and the government formed.
Descriere originală:
a comparison grid among philosophers hobbes, locke and rousseau
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe document discusses Thomas Hobbes, John Locke, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau's views on the state of nature and social contract theory. Hobbes saw the state of nature as a state of war where life is solitary, poor, nasty, brutish and short. Locke believed the state of nature was not necessarily bad, and that people are born free and equal with natural rights. Rousseau saw the state of nature as one without laws or morality, but with potential for goodness. They all argued that people form social contracts and governments to escape the state of nature, but differed on people's natural state and the government formed.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
88%(24)88% au considerat acest document util (24 voturi)
49K vizualizări2 paginiHobbes, Locke and Rousseau Comparison Grid
Încărcat de
d-fbuser-36727469The document discusses Thomas Hobbes, John Locke, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau's views on the state of nature and social contract theory. Hobbes saw the state of nature as a state of war where life is solitary, poor, nasty, brutish and short. Locke believed the state of nature was not necessarily bad, and that people are born free and equal with natural rights. Rousseau saw the state of nature as one without laws or morality, but with potential for goodness. They all argued that people form social contracts and governments to escape the state of nature, but differed on people's natural state and the government formed.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
THOMAS HOBBES JOHN LOCKE JEAN- JACQUES ROUSSEAU
Violent place, people live in constant fear
Is NOT equal to a state of war A primitive condition without law or morality
Like a state of war (not necessarily fighting but the
It is actually chaotic but neither it is good nor bad “uncorrupted moral” prevails
inclination to fight and take pre-emptive measures
People are equal and free to do whatever they want Mean are ignorant and innocent
against each other)
STATE OF but are bound by the law of nature Men are free and equal
“The condition of man... is a condition of war of
People have stronger moral limits Men are born with the potential of goodness
NATURE everyone against everyone”
When there is no government Men are just like any other animals
People think of their own interests over others’
“want [lack] of a common judge, with authority, puts People don’t interact much but Interaction and
No morality
all persons in a state of nature” competition are unavoidable
Solitary, poor, nasty, brutish and short life
When there is no government
When there is no government
fundamental law of nature is that as much as
Natural law is morality
Man may do whatever he sees fit to protect his interests, possible mankind is to be preserved
Morality is preservation of self without causing harm
especially his life men are free and equal
LAW OF “A man cannot lay down the right of resisting them that Single absolute law regardless of where people live
to others
Morality is a natural repugnance at seeing other
NATURE assault him by force, to take away his life.” (applies to all)
humans suffer
Men are equal Can be discovered by reason alone
Rousseau does not agree of causing pain to others in
Different from divine law
order to preserve oneself.
Right to life (to live); to liberty (to do anything they
Right to life/ preservation of life
want with respect to the right of others to life); to whatever you need to survive is good but as musch
Right of a person to everything
RIGHT OF Right of a person to do whatever is necessary to
property (to own all they create or acquire with as possible, not in the extent of harming others
respect to others’ life and liberty rights) Natural rights are on the principles of pity and self-
NATURE preserve his interests, especially his life
All people have natural rights preservation
Right to equality
These are privileges or claims to which people are These rights make men unequal
entitled
Persons collectively agree to give up all their freedom
Social contract is made among all people of that
and power to a sovereign (ruler)
society to bring them in harmony
“That a man be willing, when others are so too, as far Governments exist by of the consent of people to
A general will is made, and agreed by the people to
forth as for peace and defence of himself he shall think it protect their natural rights and promote public good
abide by it
SOCIAL necessary, to lay down this right to all things; and be The right of revolution is exercised when the
“Each of us puts his person and all his power in
contented with so much liberty against other men, as he government fails (people may rebel to redress the
CONTRAC common under the supreme direction of the general
would allow other men against himself. “ government)
T Absolute control (authoritarian monarchy) where all There is the principle of the rule of majority where
will; and in a body we receive each member as an
indivisible part of the whole”
powers and laws are by that sovereign things are decided by the greater public (liberal
Direct rule by the people (republicanism/democracy)
Government imposes laws and order to prevent the monarchy)
“Whoever refuses to obey the general will shall be
state of war
compelled to do so by the whole body.”
MARIANO, KEITH RICHARD D.
2010-78830, BA JOURNALISM
6 October 2010
Prof. JAIME NAVAL
SOC SCI 2, CSSP
Sources: http://seop.leeds.ac.uk/, http://www.blackwellreference.com/, http://www.brainyquote.com/, http://www.wikipedia.org/
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Why Fascism Is Considered To Be The Child of First Half of 20th Century Events To Place in EuropeDocument4 paginiWhy Fascism Is Considered To Be The Child of First Half of 20th Century Events To Place in EuropeMuhammad Umair Afzal89% (9)
- Hobbes Locke RousseauDocument5 paginiHobbes Locke RousseauMarnie TonsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rise of Muslim Nationalism in South Asia With Special Reference To The Role of Sir Syed AhmadDocument5 paginiRise of Muslim Nationalism in South Asia With Special Reference To The Role of Sir Syed AhmadasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSS Gender StudiesDocument19 paginiCSS Gender StudiesM Faadi Malik100% (2)
- Democracy in Pakistan Hopes and Hurdles - Jahangir's World TimesDocument4 paginiDemocracy in Pakistan Hopes and Hurdles - Jahangir's World TimesAnonymous 8Jhnaab2z33% (3)
- Sir Syed NOT Pro BritishDocument3 paginiSir Syed NOT Pro BritishNatashashafi75% (4)
- Salient Features of French Judicial SystemDocument2 paginiSalient Features of French Judicial SystemHamza Bilal60% (5)
- Is Sex Socially DeterminedDocument3 paginiIs Sex Socially Determinedwaleed33% (3)
- Ideology of PakistanDocument5 paginiIdeology of PakistanSyed Hafeez ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Political Science Paper 2 NotesDocument58 paginiPolitical Science Paper 2 NotesKhanzada Afridi100% (1)
- Democracy and Illiteracy Cannot Move TogetherDocument6 paginiDemocracy and Illiteracy Cannot Move Togethergodic100% (2)
- Organismic and Social Contract Theory Comparison For CSS Aspirants (Sociology)Document26 paginiOrganismic and Social Contract Theory Comparison For CSS Aspirants (Sociology)Freedom WritersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Will Rule of Law Always Be An Impracticable Myth in Our CountryDocument3 paginiWill Rule of Law Always Be An Impracticable Myth in Our CountryArshad Usman100% (2)
- CSS Essay DemocracyDocument24 paginiCSS Essay DemocracyAtta Dhaku100% (2)
- Universal Human Equality Is Utopic.: Case in PointDocument7 paginiUniversal Human Equality Is Utopic.: Case in PointDuaa’s CreativityÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSS Forum OutlineDocument10 paginiCSS Forum Outlinewaqar hattar0% (1)
- CSS Essay - Free Speech Should Have LimitationsDocument4 paginiCSS Essay - Free Speech Should Have LimitationsAnaya Rana100% (1)
- Ir Notes Css ForumDocument19 paginiIr Notes Css ForumGPS218 Narwala MarkazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Political ScienceDocument252 paginiPolitical ScienceMuhammad AslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corruption in Pakistan Mother of All Ills - Essay by DR Quratulain (PAS)Document4 paginiCorruption in Pakistan Mother of All Ills - Essay by DR Quratulain (PAS)Abdullah Bhatti100% (1)
- British History NOtesDocument15 paginiBritish History NOtesM Faadi Malik100% (1)
- Literary Essay Failure of Democracy in Pakistan PDFDocument8 paginiLiterary Essay Failure of Democracy in Pakistan PDFilyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSS 2014 Solved Paper of English Precis and Composition PDFDocument7 paginiCSS 2014 Solved Paper of English Precis and Composition PDFservices be100% (1)
- Causes of Failure of Democracy in Pakistan PDFDocument9 paginiCauses of Failure of Democracy in Pakistan PDFZeshan AzeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes Ghazali Theory of KhilafatDocument6 paginiLecture Notes Ghazali Theory of KhilafatBilal AkhterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of Military in Turkish PoliticsDocument5 paginiRole of Military in Turkish PoliticsHamza Bilal100% (1)
- Functions and Responsibilities of Juvenile Justice SystemDocument2 paginiFunctions and Responsibilities of Juvenile Justice SystemChanesar Khan Baloch63% (8)
- 00 CSS European History NotesDocument107 pagini00 CSS European History NotesFareed Shahwani100% (1)
- Pol Science Paper 1Document150 paginiPol Science Paper 1sadayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fascism Generally Flourishes in Countries With Strong Nationalism and Weak DemocraciesDocument2 paginiFascism Generally Flourishes in Countries With Strong Nationalism and Weak DemocraciesEhsas ScholarshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Democracy Has Failed To Deliver in Pakistan! (Essay For CSS)Document10 paginiDemocracy Has Failed To Deliver in Pakistan! (Essay For CSS)Basheer AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Democracy in PakistanDocument37 paginiDemocracy in Pakistananfal azamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theories of Nature of State: Assistant Professor Hidayatullah National Law University Raipur, ChhattisgarhDocument15 paginiTheories of Nature of State: Assistant Professor Hidayatullah National Law University Raipur, ChhattisgarhOnindya Mitra100% (2)
- PS - 14 - Rise of Muslim Nationalism in South Asia and Pakistan MovementDocument31 paginiPS - 14 - Rise of Muslim Nationalism in South Asia and Pakistan MovementBali Gondal100% (2)
- Plato's Ideal State: Features of An Ideal State 1.rule of PhilosophyDocument6 paginiPlato's Ideal State: Features of An Ideal State 1.rule of PhilosophyRAJVEER PARMAR100% (2)
- Failure of Democracy in PakistanDocument2 paginiFailure of Democracy in Pakistanaamer4u20% (1)
- W PoliticalDocument69 paginiW PoliticalNAYYAR MUMTAZ100% (2)
- Probation and Parole in Pakistan PDFDocument6 paginiProbation and Parole in Pakistan PDFUmair MahmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Notes For CSS General Science and Ability Paper PDFDocument108 paginiShort Notes For CSS General Science and Ability Paper PDFAbdullah Khan67% (3)
- Assignment On: Ibn Khaldun's Theory of "Asabiyah"Document12 paginiAssignment On: Ibn Khaldun's Theory of "Asabiyah"Md Fahim100% (1)
- Causes of Delay in Constitution Making of PakistanDocument6 paginiCauses of Delay in Constitution Making of PakistanHamza ShahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Criminology Notes by Ali Hameed KhanDocument25 paginiCriminology Notes by Ali Hameed KhanFakhra Rajpoot100% (1)
- M.G.M Law College: Plato'S Theory of Ideal StateDocument14 paginiM.G.M Law College: Plato'S Theory of Ideal StatePrisha BauskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Iqbal Concept On IjtehadDocument6 pagini2 - Iqbal Concept On Ijtehadkstaley7323100% (1)
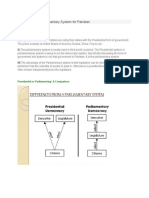
- Presidential or Parliamentary System For PakistanDocument2 paginiPresidential or Parliamentary System For PakistanSamina Haider100% (1)
- Q.18 Case Studies. (PR) FinitoDocument21 paginiQ.18 Case Studies. (PR) FinitoHassan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes of Crimes in PakistanDocument3 paginiCauses of Crimes in Pakistanyusha habib89% (9)
- Salient Features of British ConstitutionDocument4 paginiSalient Features of British ConstitutionBilal akbar100% (2)
- Lecture Aristotle Father of Politcal ScienceDocument9 paginiLecture Aristotle Father of Politcal ScienceBilal Akhter100% (2)
- Main Features of 18th Amendment - CSS Online AcademyDocument7 paginiMain Features of 18th Amendment - CSS Online AcademyHamza Azhar100% (1)
- Probation and Parole in PakistanDocument6 paginiProbation and Parole in Pakistanfaryal67% (3)
- Constitutional Development of Pakistan-2Document19 paginiConstitutional Development of Pakistan-2Basharat Aslam100% (1)
- Political Science Notes For CssDocument36 paginiPolitical Science Notes For Cssjunaidammar83% (6)
- American Revolution and Ideas of EnlightenmentDocument15 paginiAmerican Revolution and Ideas of EnlightenmentAnonymous PjzAdj0% (1)
- PhilosophyDocument4 paginiPhilosophyrose SeparaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Similarities Differences Contrast AnalogyDocument2 paginiSimilarities Differences Contrast AnalogyLance AngeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social Contract Theory ActivityDocument1 paginăSocial Contract Theory ActivityFritz Roynore RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Freedom Is The Power To Choose Our Own Chains.": Jean-Jacques RousseauDocument7 pagini"Freedom Is The Power To Choose Our Own Chains.": Jean-Jacques RousseauMERBUEN BACUSÎncă nu există evaluări
- "All Persons Are Born Free and Equal in Dignity and Rights Without Any Distinction S To Race, Color, Sex, Religion, Origin, and Social StatusDocument3 pagini"All Persons Are Born Free and Equal in Dignity and Rights Without Any Distinction S To Race, Color, Sex, Religion, Origin, and Social StatusJedaia Balugo100% (1)
- Hobes, Locke and RousseauDocument4 paginiHobes, Locke and RousseauMiya NaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viernes vs. People of The Philippines G.R. No.156643 FactsDocument6 paginiViernes vs. People of The Philippines G.R. No.156643 FactsAngeline De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Administrative and Judicial Protest For Tax - Gantt Chart ProcessDocument13 paginiAdministrative and Judicial Protest For Tax - Gantt Chart Processshie_fernandez9177Încă nu există evaluări
- Marriage ApplicationDocument2 paginiMarriage ApplicationTanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Byu Dailyunivmag Nov23 pgs4-7Document4 paginiByu Dailyunivmag Nov23 pgs4-7api-663826938Încă nu există evaluări
- Revue Des Études Juives. 1880. Volume 51.Document410 paginiRevue Des Études Juives. 1880. Volume 51.Patrologia Latina, Graeca et OrientalisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Cumulative Record Guidelines: Saskatchewan - CaDocument19 paginiStudent Cumulative Record Guidelines: Saskatchewan - CaMark Lemuel Layones ArceoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts Rule StatementsDocument40 paginiTorts Rule Statementskoreanman100% (1)
- National Labor Relations Board v. International Brotherhood of Boilermakers, Iron Shipbuilders, Blacksmiths, Forgers and Helpers, Local Lodge No. 338, Afl-Cio, 409 F.2d 922, 10th Cir. (1969)Document4 paginiNational Labor Relations Board v. International Brotherhood of Boilermakers, Iron Shipbuilders, Blacksmiths, Forgers and Helpers, Local Lodge No. 338, Afl-Cio, 409 F.2d 922, 10th Cir. (1969)Scribd Government DocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 12 Employer Liability in Negligence - Learning ActivitiesDocument3 paginiTopic 12 Employer Liability in Negligence - Learning ActivitiesOnyee FongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Law of Torts - LLB - Study Notes PDFDocument126 paginiLaw of Torts - LLB - Study Notes PDFSwastik Grover100% (2)
- U.S. v. Thomas CooperDocument1 paginăU.S. v. Thomas CooperLaw&CrimeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cralaw Virtua Law Lib RaryDocument5 paginiCralaw Virtua Law Lib RaryTaga BukidÎncă nu există evaluări
- UnitDocument48 paginiUnitapi-373488523Încă nu există evaluări
- Waiver, Release and Quitclaim SAMPLE 2019Document2 paginiWaiver, Release and Quitclaim SAMPLE 2019Alado LawÎncă nu există evaluări
- PIL Ch10-End (FINALS)Document12 paginiPIL Ch10-End (FINALS)Katrina Hirang OlaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 PDFsam CompStat Public 2020 Week 50Document1 pagină1 PDFsam CompStat Public 2020 Week 50Ann DwyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treatise On Equity Jurisprudence Vol I - Pomeroy - 1918 PDFDocument1.060 paginiTreatise On Equity Jurisprudence Vol I - Pomeroy - 1918 PDFAkil Bey100% (4)
- Problem 13Document4 paginiProblem 13Ashley CandiceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alberto Vs Dela CruzDocument3 paginiAlberto Vs Dela CruzRolando ReubalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 Del Rosario vs. MeralcoDocument5 pagini03 Del Rosario vs. Meralcorodel talabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mattel Inc vs. FranciscoDocument1 paginăMattel Inc vs. FranciscoEderic ApaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appearance and Non-Appearance of The PartyDocument16 paginiAppearance and Non-Appearance of The PartySlim ShadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digest Legal EthicsDocument48 paginiDigest Legal EthicsMary Joessa Gastardo AjocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teenage Drug Abuse AlarmingDocument6 paginiTeenage Drug Abuse AlarmingSang PengembaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pretrial Memorandum - LMSDDocument9 paginiPretrial Memorandum - LMSDLMVUEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Criminal Law SummaryDocument97 paginiCriminal Law SummaryJordan ParkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Afulgencia Vs Metrobank G.R. No. 185145Document7 paginiAfulgencia Vs Metrobank G.R. No. 185145Newbie KyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- City of Angeles Vs CADocument2 paginiCity of Angeles Vs CAMaria Cecilia OlivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Co Kim Cham vs. Valdez Tan Keh, 75 Phil 113Document2 paginiCo Kim Cham vs. Valdez Tan Keh, 75 Phil 113Arnel Pablo100% (2)
- Civics SummaryDocument69 paginiCivics SummaryJupis Sengo100% (1)