Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pott's Disease
Încărcat de
Rheegell Ellar-FuertesDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pott's Disease
Încărcat de
Rheegell Ellar-FuertesDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
INTRODUCTION
Pott’s disease is a presentation of extrapulmonary tuberculosis that affects
the spine, a kind of tuberculous arthritis of the intervertebral joints. Scientifically,
it is called tuberculous spondylitis. Pott’s disease is the most common site of bone
infection in TB; hips and knees are also often affected. The lower thoracic and
upper lumbar vertebrae are the areas of the spine most often affected.
Pott's disease, which is also known as Pott’s caries, David's disease, and
Pott's curvature, is a medical condition of the spine. Individuals suffering from
Pott's disease typically experience back pain, night sweats, fever, weight loss, and
anorexia. They may also develop a spinal mass, which results in tingling,
numbness, or a general feeling of weakness in the leg muscles. Often, the pain
associated with Pott's disease causes the sufferer to walk in an upright and stiff
position.
Pott’s disease is caused when the vertebrae become soft and collapse as
the result of caries or osteitis. Typically, this is caused by mycobacterium
tuberculosis. As a result, a person with Pott's disease often develops kyphosis,
which results in a hunchback. This is often referred to as Pott’s curvature. In some
cases, a person with Pott's disease may also develop paralysis, referred to as
Pott’s paraplegia, when the spinal nerves become affected by the curvature.
The disease progresses slowly. Signs and symptoms include: back pain,
fever, night sweats, anorexia, weight loss, and easy fatigability. Diagnosis is based
on: blood tests - elevated ESR , skin tests ,radiographs of the spine , bone scan
,CT of the spine , and bone biopsy. Gibbus formation is the pathognomonic sign of
this disease. Gibbus formation refers to a sharply angled curvature of the
backbone, resulting from collapse of a vertebra or simply a hunchback.
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
Approximately 1-2% of total tuberculosis cases are attributable to Pott
disease. The incidence rate here in the Philippines is approximately 20-30% of all
the patient diagnosed to have Tuberculosis. Most of the cases of the Pott's disease
in the Philippines is caused by the non-compliance of the treatment regimen of
TB. Internationally, between 1993 and 2001, tuberculosis of the bone and joints
accounted for 3.5% of all tuberculosis cases (0.2-1.1% in patients of European
origin and 2.3-6.3% in patients of non-European origin) .
“21 nursing problems” according to Faye Glenn Abdellah could be best
adapted on this kind of case. She defined nursing as broadly grouped into the 21
nursing problem areas to guide care and promote the use of nursing judgement.
She also said that nursing is a service that is based on the art and science and
aims to help people, sick or well, cope with their health needs. The said disease
could lead to different problems that the patient can experince. It is the
responsibility of the nurse to meet the different needs of the client to achive the
optimum level of functioning. The researcher chose to discuss Pott's disease as
one of the requirement in the rotation. This study will help the researcher to
analyze and dig deeper and see a clearer picture, in response to our roles as
future registered nurses.
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
GENERAL OBJECTIVES:
To be able to develop a comprehensive case study that would focus on the chosen
case with regards to the pathology of the disease, its corresponding medical
actions and the associative function of client-based interventions which will be
used to facilitate the client’s health status which is aimed towards achieving
optimum level of functioning.
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES:
• To know the patho-physiologic mechanism of the disease process of Pott's
disease, placing emphasis on how the complications and the disease
etiology relate and sync with each other.
• To accurately explain the various laboratory examinations that require for
the detection of the disease and how the significant remarks or findings
relate to his disease.
• Cite various drugs required for the treatment of the disease in giving a
client based analysis on the said pharmacologic treatment.
• To be able to give health teachings regarding the prevention and cure of the
disease.
• To evaluate the presenting clinical manifestations based on the overall
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
condition with emphasis placed on the alterations.
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
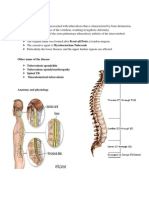
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
The spinal cord is the largest nerve in the body, and it is comprised of the
nerves which act as the communication system for the body. The nerve fibers
within the spinal cord carry messages to and from the brain to other parts of the
body. The spinal cord is surrounded by protective bone segments, called the
vertebral column. The vertebral column is comprised of seven cervical vertebrae,
twelve thoracic vertebrae, five lumbar vertebrae and five sacral vertebrae. The
vertebral column also provides attachment points for muscles of the back and
ribs. The vertebral disks serve as shock absorbers during activities such as
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
walking, running and jumping, they also allow the spine to flex and extend.
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
1. Tuberculin skin test (purified protein derivative [PPD])
results are positive in 84-95% of patients with Pott disease who are not infected
with HIV. A standard dose of 5 Tuberculin units (0.1 mL)(The standard Mantoux
test in the UK consists of an intradermal injection of 2TU of Statens Serum
Institute (SSI) tuberculin RT23 in 0.1ml solution for injection.) Injected
intradermally (between the layers of dermis) and read 48 to 72 hours later. This
intradermal injection is termed the mantoux technique. A person who has been
exposed to the bacteria is expected to mount an immune response in the skin
containing the bacterial proteins. The reaction is read by measuring the diameter
of induration (palpable raised hardened area) across the forearm (perpendicular
to the long axis) in millimeters. If there is no induration, the result should be
recorded as "0 mm". Erythema (redness) should not be measured. If a person has
had a history of a positive tuberculin skin test, or has not had a recent tuberculin
skin test (within one year), another skin test may be needed.
2. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) may be markedly elevated
(>100 mm/h).
ESR stands for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. It is a test that indirectly measures
how much inflammation is in the body. However, it rarely leads directly to a
specific diagnosis. This test can be used to monitor inflammatory or cancerous
diseases. It is a screening test, which means it cannot be used to diagnose a
specific disorder. However, it is useful in detecting and monitoring tuberculosis,
tissue death, certain forms of arthritis, autoimmune disorders, and inflammatory
diseases that cause vague symptoms.
3. Radiography
Radiographic changes associated with Pott disease present relatively late. The
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
following are radiographic changes characteristic of spinal tuberculosis on plain
radiography: visibly seen curvature of the spine or visible bone lesions on different
levels.
4. CT scanning
CT scanning provides much better bony detail of irregular lytic lesions, sclerosis,
disk collapse, and disruption of bone circumference. Low-contrast resolution
provides a better assessment of soft tissue, particularly in epidural and paraspinal
areas. CT scanning reveals early lesions and is more effective for defining the
shape and calcification of soft-tissue abscesses. In contrast to pyogenic disease,
calcification is common in tuberculous lesions.
5. MRI
MRI is the criterion standard for evaluating disk-space infection and osteomyelitis
of the spine and is most effective for demonstrating the extension of disease into
soft tissues and the spread of tuberculous debris under the anterior and posterior
longitudinal ligaments. MRI is also the most effective imaging study for
demonstrating neural compression.
MRI findings useful to differentiate tuberculous spondylitis from pyogenic
spondylitis include thin and smooth enhancement of the abscess wall and well-
defined paraspinal abnormal signal, whereas thick and irregular enhancement of
abscess wall and ill-defined paraspinal abnormal signal suggest pyogenic
spondylitis. Thus, contrast-enhanced MRI appears to be important in the
differentiation of these two types of spondylitis.
6. Bone biopsy
A bone biopsy is a procedure in which a small sample of bone is taken from the
body and looked at under a microscope for cancer, infection, or other bone
disorders.
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
Confirm the diagnosis of a bone disorder that was found by another test, such as
an X-ray, CT scan, bone scan, or a MRI. Tell the difference between a
noncancerous (benign) bone mass, such as a bone cyst, and bone cancer, such as
multiple myeloma. See what is causing a bone infection (osteomyelitis) or if an
infection is present. Find the cause of ongoing bone pain. Check bone problems
seen on an X-ray.
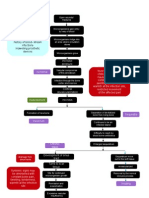
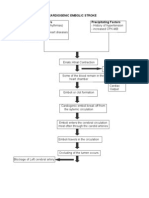
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
PRECIPITATING FACTORS
PREDISPOSING FACTORS
- Non-compliance to medicines - PTB diagnosed
- Continuous exposure to M.Tubeculosis
- Malnutrition
- Socio-economic status
Exposure to Mycobacterium Tubeculosis
MEDICATIONS:
HRZE
Primary Pulmonary Tuberculosis Intermittent fever,
upper back pain, night
sweats, poor appetite,
weight loss.
Spread of M. Tuberculosis
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
Infection spreads to the intervertebral disc
in the T7-T9 of the spine
Progressive bone destruction Persistent back
pain
Intervertebral Collapse Caseation takes place
Gibbus formation between T4-T7 or T7-T9
Spinal cord depression
Neurological effects and lower motor defficits Pott's parplegia
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
MEDICAL-SURGICAL-NURSING
MANAGEMENT
Since Pott's disease is caused by a bacterial infection, prevention is possible
through proper control. The best method for preventing the disease is reduce or
eliminate the spread of tuberculosis. In addition, testing for tuberculosis is an
important preventative measure, as those who are positive for purified protein
derivative (PPD) can take medication to prevent tuberculosis from forming. A
tuberculin skin test is the most common method used to screen for tuberculosis,
though blood tests , bone scans, bone biopsies, and radiographs may also be
used to confirm the disease.
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
• Before the advent of effective antituberculosis chemotherapy, Pott disease
was treated with immobilization using prolonged bed rest or a body cast.
• Studies performed by the British Medical Research Council indicate that
tuberculous spondylitis of the thoracolumbar spine should be treated with
combination chemotherapy for 6-9 months.
• According to the most recent recommendations issued in 2003 by the US
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Infectious Diseases Society
of America, and the American Thoracic Society, a 4-drug regimen should be
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
used empirically to treat Pott disease.
• Isoniazid and rifampin should be administered during the whole course of
therapy. Additional drugs are administered during the first 2 months of
therapy. These are generally chosen among the first-line drugs, which
include pyrazinamide, ethambutol, and streptomycin. The use of second-line
drugs is indicated in cases of drug resistance.
• Opinions differ regarding whether the treatment of choice should be
conservative chemotherapy or a combination of chemotherapy and surgery.
The treatment decision should be individualized for each patient.
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
• Indications for surgical treatment of Pott disease generally include the
following:
o Neurologic deficit (acute neurologic deterioration, paraparesis,
paraplegia)
o Spinal deformity with instability or pain
o No response to medical therapy (continuing progression of kyphosis or
instability)
o Large paraspinal abscess
o Nondiagnostic percutaneous needle biopsy sample
• Resources and experience are key factors in the decision to use a surgical
approach.
• The lesion site, extent of vertebral destruction, and presence of cord
compression or spinal deformity determine the specific operative approach
(kyphosis, paraplegia, tuberculous abscess).
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
• In Pott disease that involves the cervical spine, the following factors justify
early surgical intervention:
o High frequency and severity of neurologic deficits
o Severe abscess compression that may induce dysphagia or asphyxia
o Instability of the cervical spine
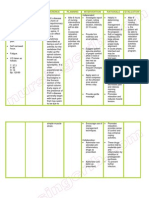
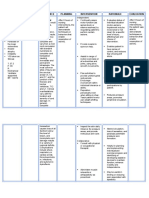
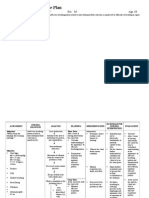
Nursing Diagnosis
• Acute pain related to inflammatory process
• Disturbed body image related to trauma/injury to spinal cord
• Self – bathing hygiene deficit related to musculoskeletal impairment
• Impaired physical mobility related to therapeutic restriction of movement
• Imbalance nutrition related to inadequate food intake
Nursing Responsibilities
• Drug treatment is generally sufficient for Pott’s disease, with spinal
immobilization if required.
• Surgery is required if there is spinal deformity or neurological signs of spinal
cord compression.
• Standard antituberculosis treatment is required. Duration of antituberculosis
treatment: If debridement and fusion with bone grafting are performed,
treatment can be for six months. If debridement and fusion with bone
grafting are NOT performed a minimum of 12 months’ treatment is required.
• It may also be necessary to immobilize the area of the spine affected by the
disease, or the person may need to undergo surgery in order to drain any
abscesses that may have formed or to stabilize the spine.
• Other interventions include application of knight/ taylor brace, head halter
traction.
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
PATIENT HEALTH TEACHING
P- atient should be reminded to attend check-ups at the nearest….
O- rthopedic center
T- reatment should be taken in a…..
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
T- imely manner
S- ight any symptoms other than the usual and report it to the
physician
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
Global City Innovative College
Bonifacio Global City, Taguig City
Philippines
In Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements in
Nursing Care Management 105
CASE STUDY
POTT'S DISEASE
Clinical Agency : Philippine Orthopedic Hospital
Submitted By:
FUERTES, Rheegell E.
N413 Group B Cluster 2
December 2010
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
Pott's Disease: A Case Report
Fuertes, Rheegell E. N413 POC
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- POTT's DISEASEDocument33 paginiPOTT's DISEASEJemimah A. Mangalindan100% (4)
- Pott's DiseaseDocument8 paginiPott's DiseaseLorebell100% (2)
- Pott's Disease Night SweatsDocument22 paginiPott's Disease Night SweatsjesuitkrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poc Pott's DiseaseDocument8 paginiPoc Pott's Diseasealsbeth50% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan: West Visayas State University College of NursingDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan: West Visayas State University College of NursingLizaEllaga100% (1)
- Case Study About Pott's DiseaseDocument7 paginiCase Study About Pott's Diseasebhy18190% (1)
- Case Study - Pott's Disease (Final)Document38 paginiCase Study - Pott's Disease (Final)Raymund Christopher Dela Peña60% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Potts DiseaseDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Potts DiseaseJoanna Marie M. dela Cruz100% (5)
- Common Cause or Etiology of Pott's DiseaseDocument5 paginiCommon Cause or Etiology of Pott's DiseaseStan Aves GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Potts DiseaseDocument5 paginiPotts Diseasemyla-elmarie100% (1)
- CASESTUDY Pott's DiseaseDocument27 paginiCASESTUDY Pott's Diseasemae_kel100% (45)
- Pott's DiseaseDocument30 paginiPott's DiseaseLucila Lugo100% (1)
- Potts DiseaseDocument3 paginiPotts DiseasePaul Stephen PinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PottsDocument3 paginiNCP PottsFenie Jane Quinlat LapastoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Potts Disease Case Study OLGCDocument15 paginiPotts Disease Case Study OLGChomermanlapaz100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Pott's DiseaseDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Pott's Diseasederic95% (21)
- Potts Disease NCP .. JustificationDocument8 paginiPotts Disease NCP .. JustificationMicah SalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseLeLi CortezÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - OsteosarcomaDocument5 paginiNCP - OsteosarcomaNelson Lacsamana100% (1)
- Pott's DiseaseDocument8 paginiPott's DiseaseBij HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of OsteomyelitisDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of OsteomyelitisKeith Madarang100% (2)
- CDH Treatment Depends on AgeDocument6 paginiCDH Treatment Depends on AgeLory LynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predisposing Factors and Stages of OsteomyelitisDocument1 paginăPredisposing Factors and Stages of OsteomyelitisKim Enrico JumarangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Potts Disease Case AnalysisDocument5 paginiPotts Disease Case AnalysisAdrian MallarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patho of Pott's DiseaseDocument2 paginiPatho of Pott's DiseaseIris Balino100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of OsteomyelitisDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of OsteomyelitisJhon Jerric Pante Aguinaldo100% (1)
- Casestudy Pott's DiseaseDocument36 paginiCasestudy Pott's DiseaseyasiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of POTT's DiseaseIJ Ayop86% (7)
- Gout Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument17 paginiGout Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentPaulette Olisco0% (1)
- PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăPathophysiologyRj MagpayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- OsteomyelitisDocument47 paginiOsteomyelitisArmand Al HaraaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology OsteosarcomaDocument4 paginiPathophysiology OsteosarcomaGladys Barcelona0% (1)
- Potts Disease NCPDocument6 paginiPotts Disease NCPDyanne BautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final NCP LeptospirosisDocument6 paginiFinal NCP LeptospirosisKeith Austin100% (1)
- pathoPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOMYELITIS (DIAGRAM)Document1 paginăpathoPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOMYELITIS (DIAGRAM)redhoney100% (5)
- Congenital Hip DislocationDocument5 paginiCongenital Hip DislocationMonica Aguirre QuilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PainDocument2 paginiNCP PainKarizza Reyes Mamaradlo100% (1)
- Spinal Cord Injury NCPDocument2 paginiSpinal Cord Injury NCPEmmanuelRodriguez100% (1)
- Pott's Disease NCPDocument7 paginiPott's Disease NCPkristel_nicole18yahoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital hip dysplasia diagnosis in under 40Document6 paginiCongenital hip dysplasia diagnosis in under 40Bek DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- HNP Case Scenario For Case StudyDocument2 paginiHNP Case Scenario For Case StudyDeinielle Magdangal RomeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP: FracturesDocument21 paginiNCP: FracturesJavie100% (1)
- POTT's DiseaseDocument3 paginiPOTT's DiseaseFema Jill AtrejenioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pott's Disease PDFDocument14 paginiPott's Disease PDFRaja RajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pott DiseaseDocument6 paginiPott DiseaseMicah TuringanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pott's Disease Is A Presentation of ExtrapulmonaryDocument13 paginiPott's Disease Is A Presentation of ExtrapulmonaryJc HarharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pott Disease (TB Spondylitis) (Emed)Document7 paginiPott Disease (TB Spondylitis) (Emed)Ali Al.JuffairiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attending Osteomyelitis ModuleDocument9 paginiAttending Osteomyelitis ModuleMrLarry DolorÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Case Report On Potts Spine Spinal TubeDocument3 paginiA Case Report On Potts Spine Spinal TubeyaneemayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Background (2003)Document8 paginiBackground (2003)Jessarene Verzosa Latiza RNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pott DiseaseDocument15 paginiPott DiseasejunkirinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pott'S Disease: Partial Fulfilment in Orthopaedic Nursing de Ramos, Mary Grace L. Bsn-Iii March 08, 2013Document6 paginiPott'S Disease: Partial Fulfilment in Orthopaedic Nursing de Ramos, Mary Grace L. Bsn-Iii March 08, 2013Mary Grace de RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Current Concept Review: Tuberculosis of HipDocument10 paginiA Current Concept Review: Tuberculosis of HipAnonymous gvVAzlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuberculous Spondylitis (TB Spine/pott's Disease)Document28 paginiTuberculous Spondylitis (TB Spine/pott's Disease)Divo Septian Zarwin100% (1)
- AJRM Sept 18-20Document3 paginiAJRM Sept 18-20Indah RismandasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuberculosis Spondylitis IIDocument40 paginiTuberculosis Spondylitis IICendraiin MinangkabauÎncă nu există evaluări
- tmp9968 TMPDocument3 paginitmp9968 TMPFrontiersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pott Disease: BackgroundDocument5 paginiPott Disease: BackgroundBj DuquesaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Os 15 1454Document14 paginiOs 15 1454tugas rendyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pott's Disease or Tuberculosis in The SpineDocument7 paginiPott's Disease or Tuberculosis in The SpineEjay Jacob RicamaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassRheegell Ellar-Fuertes100% (3)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument3 paginiActivity IntoleranceRheegell Ellar-Fuertes50% (2)
- PADocument3 paginiPARheegell Ellar-FuertesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument2 paginiPa Tho PhysiologyRheegell Ellar-FuertesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aseptic TechniqueDocument3 paginiAseptic TechniquedubhieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baby NamesDocument9 paginiBaby Namesppremamca_617705407Încă nu există evaluări
- HistorydylaneditDocument6 paginiHistorydylaneditapi-19858424Încă nu există evaluări
- SAFETY AND LOSS PREVENTION FOR CHEMICAL PROCESS FACILITIESDocument13 paginiSAFETY AND LOSS PREVENTION FOR CHEMICAL PROCESS FACILITIESKinosraj KumaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Production Management Midterm ReviewDocument21 paginiProduction Management Midterm Reviewielsiu21184Încă nu există evaluări
- Gravimetric Analysis Lab ReportDocument5 paginiGravimetric Analysis Lab Reportclaire_miller_16100% (1)
- JCB 532-120 PDFDocument4 paginiJCB 532-120 PDFSyazrur Syazmir0% (1)
- NNDC Planning Applications 4oct - 11 OctDocument4 paginiNNDC Planning Applications 4oct - 11 OctRichard SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- GreyFox Intercom Install GuideDocument12 paginiGreyFox Intercom Install GuideAbdallah HashemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Mechanics SolutionsDocument193 paginiAnalytical Mechanics SolutionsQuinton Boltin67% (9)
- 5.case Study: Effects of Homeopathic Medicines in AdultsDocument2 pagini5.case Study: Effects of Homeopathic Medicines in AdultsAMEEN ARTSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant LayoutDocument16 paginiPlant LayoutAli MahmoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Check Valves SlamDocument2 paginiWhy Check Valves SlamBramJanssen76Încă nu există evaluări
- ASME B31.4-2016 Pipeline Transportation Systems For Liquids and SlurriesDocument1 paginăASME B31.4-2016 Pipeline Transportation Systems For Liquids and SlurriesJose Rodrigo Salguero DuranÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Karnataka Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Rules 2019Document30 paginiThe Karnataka Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Rules 2019Manisha SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel PropertiesDocument26 paginiSteel PropertiesLutfy AzanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introducing Inspira's: Managed Noc & Itoc ServicesDocument2 paginiIntroducing Inspira's: Managed Noc & Itoc ServicesmahimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 History of OrthodonticsDocument11 pagini2 History of OrthodonticsMeiz JaleelÎncă nu există evaluări
- KTS - Sarao.bakus Temple of Eternal FiireDocument176 paginiKTS - Sarao.bakus Temple of Eternal FiireK.T.S. SaraoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.1-T.C.Dies PDFDocument6 pagini3.1-T.C.Dies PDFYahyaMoummouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Akshay 71 Seminar ReportDocument22 paginiAkshay 71 Seminar ReportSanket Yadav25% (4)
- Booster Pump Service ManualDocument11 paginiBooster Pump Service ManualSGI AUTOMOTIVE PVT LTDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Limbah PabrikDocument2 paginiLimbah Pabrikindar dewaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dod EngDocument2 paginiDod Engvk4415003Încă nu există evaluări
- Inkontinensia Urin: Dr. Adhi Permana, SPPDDocument35 paginiInkontinensia Urin: Dr. Adhi Permana, SPPDTiara KhairinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manoeuvrability Final EditedDocument12 paginiManoeuvrability Final EditedSaptarshi BasuÎncă nu există evaluări
- TICSA - Diesel Uno Petroleos Guatemala (13.01.23)Document1 paginăTICSA - Diesel Uno Petroleos Guatemala (13.01.23)Luis M LópezÎncă nu există evaluări
- MACRO XII Subhash Dey All Chapters PPTs (Teaching Made Easier)Document2.231 paginiMACRO XII Subhash Dey All Chapters PPTs (Teaching Made Easier)Vatsal HarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2009 ESC Guidelines On EndocarditisDocument45 pagini2009 ESC Guidelines On EndocarditisDaondy Friarsa SoehartoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vapour Bar Exchange IMFL PackageDocument4 paginiVapour Bar Exchange IMFL PackageNishank AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regular Manual Cleaning: Mimaki Printer Maintenance and Long-Term Storage OptionsDocument3 paginiRegular Manual Cleaning: Mimaki Printer Maintenance and Long-Term Storage OptionshumbyxÎncă nu există evaluări