Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Hypertension Mind Map
Încărcat de
Brett Dale0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
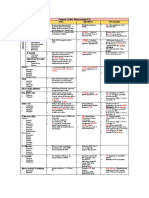
2K vizualizări1 paginăThis document outlines guidelines for diagnosing and treating hypertension. It defines normal blood pressure and stages of high blood pressure. First line drug treatments include ACE inhibitors, ARBs, calcium channel blockers, and thiazide diuretics. Lifestyle interventions such as diet, exercise, reducing alcohol and salt intake, and stopping smoking are also recommended treatments. Secondary causes of hypertension like renal, endocrine diseases, and drugs are investigated.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Hypertension mind map
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThis document outlines guidelines for diagnosing and treating hypertension. It defines normal blood pressure and stages of high blood pressure. First line drug treatments include ACE inhibitors, ARBs, calcium channel blockers, and thiazide diuretics. Lifestyle interventions such as diet, exercise, reducing alcohol and salt intake, and stopping smoking are also recommended treatments. Secondary causes of hypertension like renal, endocrine diseases, and drugs are investigated.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
2K vizualizări1 paginăHypertension Mind Map
Încărcat de
Brett DaleThis document outlines guidelines for diagnosing and treating hypertension. It defines normal blood pressure and stages of high blood pressure. First line drug treatments include ACE inhibitors, ARBs, calcium channel blockers, and thiazide diuretics. Lifestyle interventions such as diet, exercise, reducing alcohol and salt intake, and stopping smoking are also recommended treatments. Secondary causes of hypertension like renal, endocrine diseases, and drugs are investigated.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
Lowers arteriolar resistance and increases venous capacitance
Profound hypotension following first dose
Causes mild dry cough
ACE Inhibitor Contraindicated in bilateral renal artery stenosis (reduced renal
artery blood flow) - perform peripheral vascular exam
Check renal function after very change of dose
Directly causes vasodilation and reduce secretion of aldosterone
Preventable cause of Drugs
ARB / AT-II Used in patients who cannot tolerate ACE-I
premature morbidity and
mortality Major risk factor for CV disease
Causes arteriolar dilatation and reduces force of cardiac contraction
Often asymptomatic Calcium Channel Blocker SE: headaches, ankle swelling, sweating
Inhibits Na / Cl cotransporter
S/E: low K
<130 / <85 mmHg Thiazide Diuretic
Normal Affect serum cholesterol and glucose levels
Persistantly high BP > 160 / 100 mmHg
Persistantly BP > 140 / 100 mmHg + raised CV risk
High risk: FH, obesity, high LDL, impaired Diet and exercise
fasting glucose, south Asian, smoker Hypertension
Treat Decrease alcohol consumption
ACE Inhibitor < 55 yrs
Lifestyle Interventions Decrease caffine consumption
Thiazide diuretic or Drug therapy Decrease salt intake
calcium channel blocker > 55yrs / Black
Stop smoking
Urine dipstick Renal / renovascular disease
Serum creatine / electrolytes Investigations Endocrine disease
Secondary
Fasting glucose / cholesterol Pregnancy
Drugs
Hypertension.mmap - 07/09/2010 -
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- CVD and HTNDocument60 paginiCVD and HTNZsazsa100% (1)
- Product Manual ChronicDocument56 paginiProduct Manual ChronicsubhojitnayekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medications Doc XDocument4 paginiMedications Doc Xezinne obinna-umaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 5Document5 paginiWeek 5Joanna BakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treatment of CHF: Therapeutic UsesDocument2 paginiTreatment of CHF: Therapeutic UsesAsma AlfaouriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 8 & 9 - Cardiovascular and NSAIDsDocument29 paginiLect 8 & 9 - Cardiovascular and NSAIDsRaneem ShiferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Drugs HypertensionDocument5 paginiCardiac Drugs HypertensionEciOwnsMeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aldomet Altace Atenolol Verapamil: Medication Brand Name Drug ClassDocument11 paginiAldomet Altace Atenolol Verapamil: Medication Brand Name Drug Classshellyrn2010Încă nu există evaluări
- W3L1 Electrophysiology of The HeartDocument70 paginiW3L1 Electrophysiology of The HeartalfredÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 paginiPharmacology Summarysechzhen96% (46)
- Compiled PPT Angina FINALDocument25 paginiCompiled PPT Angina FINALMaverick LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diuretics Beta Blocker ACE Inhibitor Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Calcium Channel Blocker Alpha Blocker SympatholyticDocument2 paginiDiuretics Beta Blocker ACE Inhibitor Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Calcium Channel Blocker Alpha Blocker SympatholyticimperiouxxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Guide for NLN RN Pharmacology ExamDocument64 paginiStudy Guide for NLN RN Pharmacology Exammaniz442Încă nu există evaluări
- DRUGS USED IN HEART FAILURE 2016 ADocument36 paginiDRUGS USED IN HEART FAILURE 2016 ADeling ManuabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharm Exam 2 Drug Chart Pharm Exam 2 Drug ChartDocument20 paginiPharm Exam 2 Drug Chart Pharm Exam 2 Drug Chartminhmap90_635122804Încă nu există evaluări
- Sweet Glomerulus: A Case of Diabetic NephropathyDocument9 paginiSweet Glomerulus: A Case of Diabetic NephropathyRon OpulenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug ClassDocument13 paginiDrug ClassEdfren Salazar Colon100% (1)
- ANTIHYPERTENSIVEDocument32 paginiANTIHYPERTENSIVEKeziah TampusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antihypertensive Drugs: Dr. Dr. Nicolaski Lumbuun, SPFK Clinical Pharmacologist Faculty of MedicineDocument67 paginiAntihypertensive Drugs: Dr. Dr. Nicolaski Lumbuun, SPFK Clinical Pharmacologist Faculty of MedicineShally ChandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood and urine tests guideDocument3 paginiBlood and urine tests guidemayrzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7,8 - Antihypertensive DrugsDocument10 pagini7,8 - Antihypertensive DrugsHusniya MehamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Meds CompleteDocument3 paginiCardiac Meds CompleteDanielle100% (2)
- DRUG THERAPY FOR HEART FAILUREDocument40 paginiDRUG THERAPY FOR HEART FAILURENiteesh Kumar SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cardiovascular System: Classification of AntihypertensivesDocument57 paginiThe Cardiovascular System: Classification of AntihypertensivesDr. Hashibu SsekweyamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HYPERTENSIONSSSSDocument1 paginăHYPERTENSIONSSSSJulianne Jeamer FabroaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVS Drug TablesDocument12 paginiCVS Drug TablesSaajid AmraÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHARMACILOGY SUMMryDocument16 paginiPHARMACILOGY SUMMryKathy Real VillsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Pressure Cardiac Output X Peripheral ResistanceDocument52 paginiBlood Pressure Cardiac Output X Peripheral Resistancelourdes kusumadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology Cardiovascular DrugsDocument27 paginiPharmacology Cardiovascular DrugsMitzel AlvaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Classes, Mechanisms, Uses and Side EffectsDocument3 paginiDrug Classes, Mechanisms, Uses and Side EffectsWahaj MujahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 106 - Week 2 (Cardiovascular P1) (Midterm)Document7 paginiNCM 106 - Week 2 (Cardiovascular P1) (Midterm)MARIA KAWILANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacotherapy of Hypertention TerbaruDocument45 paginiPharmacotherapy of Hypertention TerbarulisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lizzie Heisler - Hypertension MedsDocument2 paginiLizzie Heisler - Hypertension MedsTricia Kaye IblanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal & Cardiovascular Drugs Lesson on RAAS InhibitorsDocument39 paginiRenal & Cardiovascular Drugs Lesson on RAAS InhibitorsJayla MarieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beta-Blockers in Heart Failure: What Will I Learn?Document5 paginiBeta-Blockers in Heart Failure: What Will I Learn?Sity DaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension: PharmacotherapyDocument23 paginiHypertension: Pharmacotherapytorr123Încă nu există evaluări
- PharmacologyDocument3 paginiPharmacologyDuy LuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- RenalDocument18 paginiRenallittle wordsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emergency Med ReviewDocument4 paginiEmergency Med ReviewviaereaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti HypertensionDocument4 paginiAnti HypertensionMuhammad Zeeshan AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic nitrates, calcium channel blockers, beta blockers, and alpha blockers for angina and hypertensionDocument29 paginiOrganic nitrates, calcium channel blockers, beta blockers, and alpha blockers for angina and hypertensionFluffy_iceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiology Review: HTN: Julia Akaah M.DDocument40 paginiCardiology Review: HTN: Julia Akaah M.DJose LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecular Pharmacology of AntihypertensivesDocument17 paginiMolecular Pharmacology of Antihypertensives백지원 (소네트리)Încă nu există evaluări
- Renal Guide and Charts: AlbuminDocument16 paginiRenal Guide and Charts: AlbuminYaima JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Condition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsDocument5 paginiCondition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsCasey Fioravante100% (1)
- 1CVS-2. ACEIs 1435 PDFDocument19 pagini1CVS-2. ACEIs 1435 PDFMuath AlqarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Drugs Used in The EmergencyDocument5 paginiCommon Drugs Used in The Emergencyhatem alsrour88% (25)
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs Class I Sodium Channel Blockers: Disopyramide (Norpace)Document5 paginiAntiarrhythmic Drugs Class I Sodium Channel Blockers: Disopyramide (Norpace)HannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension Rev 1Document38 paginiHypertension Rev 1endah ayunengrumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacotherapy of Hypertension: Dr. R. Jamuna Rani MD, Professor & HOD, Department of PharmacologyDocument24 paginiPharmacotherapy of Hypertension: Dr. R. Jamuna Rani MD, Professor & HOD, Department of PharmacologyshyamkattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- HF and CAD Case ScenarioDocument17 paginiHF and CAD Case ScenarioElla Neiza AngelesÎncă nu există evaluări
- PharmacologyDocument21 paginiPharmacologySophia Kyla AcerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesDe la EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- A Simple Guide to Hypertension and Heart DiseasesDe la EverandA Simple Guide to Hypertension and Heart DiseasesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Portal Hypertension, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandPortal Hypertension, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Artery Stenosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandRenal Artery Stenosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Pacemaker Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandPacemaker Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Otomicroscopy (Adult, Peds)Document4 paginiOtomicroscopy (Adult, Peds)Carmen EneaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OSPEDocument28 paginiOSPEsubashikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Personality DisorderDocument7 paginiLesson Plan Personality DisorderRaj MeghwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Clinical HematologyDocument42 paginiIntroduction To Clinical HematologyBishoy GalalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of Information Technology in Environment andDocument9 paginiRole of Information Technology in Environment andNithesh Chakravarthi Nekkanti100% (2)
- Depression Interview QuestionsDocument3 paginiDepression Interview QuestionsStarlin Vijay Mythri100% (1)
- Flea Allergy DermatitisDocument3 paginiFlea Allergy DermatitisDhea Febrianty OllybriieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vital Signs GuideDocument4 paginiVital Signs GuideellithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corneal Foreign Body: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument2 paginiCorneal Foreign Body: Causes, Symptoms & Treatmentmegayani santosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Risk Management ImplementationDocument38 paginiQuality Risk Management ImplementationAbdul NasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy & Physiology: Acute Otitis MediaDocument7 paginiAnatomy & Physiology: Acute Otitis MediaAbigael Patricia GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volume 15, Number 1 January 2011Document233 paginiVolume 15, Number 1 January 2011Nicolai BabaliciÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCPVDocument16 paginiCCPVdastgirrajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The All India Services (Med Att Rules) - Misc InstructionsDocument22 paginiThe All India Services (Med Att Rules) - Misc InstructionsJitendra Suraaj TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burn Workshop:: Splint and PositioningDocument31 paginiBurn Workshop:: Splint and Positioninganon_886804756Încă nu există evaluări
- NEDA Core Competencies With Cops Chart PDFDocument1 paginăNEDA Core Competencies With Cops Chart PDFskydivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 18 - PharmDocument35 paginiChapter 18 - PharmJames PerianayagamÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Elements of Success:: 21 Customer Stories On Achieving Autonomous TransformationDocument34 paginiThe Elements of Success:: 21 Customer Stories On Achieving Autonomous TransformationValenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nclex Hema and CardioDocument9 paginiNclex Hema and CardioDefensor Pison GringgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project of Shree Shivanand Mission Trust Hospital RajkotDocument22 paginiProject of Shree Shivanand Mission Trust Hospital RajkotDevvrat SukhwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- CetirizineDocument2 paginiCetirizinelintangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument30 paginiHemorrhagic StrokeAstrina SupandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Thinking Exercise NCM 106Document5 paginiCritical Thinking Exercise NCM 106Julienne Sanchez-SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traumatic Brain Injuries: Neuroimaging Findings and TreatmentDocument5 paginiTraumatic Brain Injuries: Neuroimaging Findings and TreatmentAudioBhaskara TitalessyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Copd (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)Document5 paginiCopd (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)Kirin JoiezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To AnaesthesiaDocument24 paginiIntroduction To AnaesthesiaDeobrat DwivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- UpdrsDocument3 paginiUpdrsfahlevyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stroke AccuDocument73 paginiStroke Accudeemoney3Încă nu există evaluări
- Apollo Hospitals - First-World Health Care at Emerging - Market PricesDocument3 paginiApollo Hospitals - First-World Health Care at Emerging - Market PricesNaveen Chander Dhar100% (1)
- Yale Insulin Drip Protocol (Target 100 139) PDFDocument2 paginiYale Insulin Drip Protocol (Target 100 139) PDFAprilia Christi SiwiÎncă nu există evaluări