Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Nursing Care Plans Schiz
Încărcat de
Clariza CastroDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Nursing Care Plans Schiz
Încărcat de
Clariza CastroDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
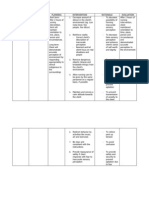
Assessment S:
Nursing Diagnosis Risk for injury: self
Scientific explanation Schizophrenia is a mental illness in which patients experience symptoms such as delusions, (mistaken beliefs) hallucinations, and disorganized behavior. Hallucinations are sounds or other sensations experienced as real when they exist only in the person's mind. While hallucinations can involve any of the five senses, auditory hallucinations (e.g. hearing voices or some other sound) are most common in schizophrenia. Visual
Planning Short Term: After 4 hours of NI the patient will not harm himself
Nursing Interventions Observe patients behaviour during routine patient care.
Rationale Close observation is necessary to protect from self harm. To determine the need for prompt intervention Such behaviours are critical clues regarding risk for self harm. To improved self esteem and avoid risk for suicidal ideations
Expected Outcome Short Term: After the NI the patient shall not have harmed himself Long Term: After the NI the patient shall have refrained from suicidal threats or behaviour gestures.
O: patient manifested:
directed r/t command hallucinations
Patient may manifest: Restlessness Panic Delirium Self mutilation
Long Term: After 2 days of NI the patient will refrain from suicidal threats or behaviour gestures.
Assess the congruency of behaviors Listen carefully suicidal statements and observe for non-verbal indications of suicidal intent. Self esteem enhancement-self esteem journal, give positive feedback, Hallucination managementassess, help client describe needs that might be reflected
To determine the need for prompt
hallucinations are also relatively common. Research suggests that auditory hallucinations occur when people misinterpret their own inner selftalk as coming from an outside source. People with schizophrenia have a high risk of attempting suicide. Any suicidal talk, threats, or gestures should be taken very seriously. People with schizophrenia are especially likely to commit suicide during psychotic episodes, during periods of depression, and in the first six months after
in the content of the hallucination, identify triggers of hallucinations
intervention
Ask direct questions to determine suicidal intent , plans for suicide, and means to commit suicide .
Suicide risk increases when plans and means exists
theyve started treatment thus confirming the diagnosis.
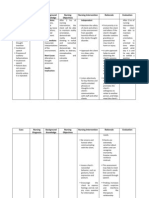
Assessment S:
Nursing Diagnosis
Disturbed sensory
Scientific explanation
Planning
Nursing Interventions
Rationale
Expected Outcome
Schizophrenia is a Short Term: mental illness in which patients experience symptoms such as delusions, (mistaken beliefs) hallucinations, and disorganized behavior. It is the
change in the amount or patterning of incoming stimuli accompanied by a diminished, exaggerated, distorted, or impaired response
Continuously orient Brief,
frequent Short Term:
the client to actual orientation helps
O: patient manifested:
y Auditory
perception related to alteration in
and visual function of hallucinati brain tissue ons y Misinterpr ets actions of others y Inability to make
After 2 hours of NI the pt will demonstrate accurate perception of the environment by responding appropriately to stimuli in the surroundings Long Term: After 2 days of NI the pt has
lessened visual and auditory hallucinations
environmental
to present reality Long Term:
events or activities to the client with in a nonchallenging sensoryway. perception disturbance Working with Reinforce and focus reality lessens on reality. Talk patients initiation of his about real events hallucinations. and real people. Use real situations and events client tedious, to from divert long,
simple decisions y Inappropri ate responses
repetitive of
verbalizations false ideas
Patient may
to such stimuli.
client's Explanation of, and participation description of in, real situations and Correct
manifest: Restlessness Panic Delirium Self mutilation
inaccurate
real activities interferes with perception, and the ability to describe the respond to hallucinations. situation as it exists in reality the Explore the content Exploring of hallucinations to content of the the hallucination helps the nurse possibility to harm self, others or the identify if the determine environment sensoryperceptual disturbance threatening is or
dangerous to the client, such as a command type
of hallucination that may be
telling the client to harm or kill the client or The
others.
nurse can then reinforce treatment safety precautions. and
Use clear, direct, Unclear directions or verbal instructions can communication confuse the rather than unclear client and promote or nonverbal distorted perceptions or gestures misinterpretatio ns of reality.
TIME AND DATE Januar y 21, 2009 @ 7:00 A.M
CUES
NEED
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
GOAL OF CARE
INTERVENTIONS
EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE Magpatambal ko. Kani man gud akong utok, naa niy grasa. as verbalized by the patient
C O G N I T I
Disturbed thought process related to disintegration thinking.
At the end of 2 hours of nursing care, the patient will be able to y Maintain reality
1. Be
sincere
and January 21, 2009 when @ 12:30 PM
honest
communicating with the client. GOAL PARTIALLY Clients are MET y The client
It is the disruption in cognitive operations and activities. Cognitive processes include those mental processes by which knowledge is acquired. These mental y y
orientation; Demonstrat e reality
extremely sensitive about others and can recognize
OBJECTIVE y Delusion persecution y Delusion paranoia y y y Thought insertion Incoherent speech Demonstrates disturbance sleep pattern y Presence auditory hallucinations
V of E of P E R C
was able to maintain reality orientation. He is
based thinking in verbal and nonverbal behavior; and Demonstrat e the ability to abstract, conceptuali ze, reason
insincerity. Evasive remarks mistrust. reinforce
oriented to 2. Assess clients time when nonverbal behavior, such as gestures, facial expression
a E in P T of U A L
asked what day it is.
But he is still preoccupied
and posture.
This
assessment
with
his
processes P A T T E R N include reality orientation, comprehension, awareness, and judgment. A disruption in these mental processes may lead to inaccurate interpretations of the environment and may result in an inability to evaluate reality accurately. Alterations in thought processes are not limited to any one age
and calculate consistent with ability to
may help to meet the clients needs that cannot be
delusions about being jealous him to his
conveyed speech.
through
3. Encourage client to
the express
The
client
was not able to demonstrate realitybased
feelings and do not pry cross examine for information
Probing increases clients suspicion
thinking in verbal and
and interferes with the therapeutic
nonverbal responses. His mannerism
relationship
4. Show empathy to the feelings, clients reassure
is
largely
observed and he
the client of your presence and
wasnt able to establish
group, gender, or clinical problem. (http://www1.us. elsevierhealth.c om/MERLIN/Gu lanick/Construct or/index.cfm?pl an=53.01)
acceptance
eye contact with any of
The
clients
the interviewer. y However, he was able to exhibit a positive abstract, reason,
experiences can be distressing. Empathy conveys
acceptance of the client your caring and interest.
5. Avoid
laughing, or quietly
judgment and calculation abilities.
whispering, talking
where client can see but not hear what is being said.
Suspicious clients often believe others are discussing
them, and secretive behaviors reinforce the paranoid
feelings.
6. Give directions short
simple using and
words
simple sentences.
Giving simple directions lessen or prevent confusion
of the patient
7. Never convey to the client that his delusions hallucinations real and are
The delusion or hallucination would be reinforce if its accepted.
8. Maintain oriented relationship environment
reality
and
reality
Maintaining based and lets
relationship environment
the patient know that the relationship is temporary and prevents separation anxiety
9. Give feedbacks
positive and the
acknowledge client
Positive feedback enhances sense of well-being and
makes positive
more situation
for the client.
10. Do not judge or belittle beliefs. clients
What the client feels or thinks is not funny for him. The client may feel rejected approached if by
attempts of humor.
TIME AND DATE .Janua ry 21, 2010 @ 12 :30 PM
CUES
NEED
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
GOAL OF CARE
INTERVENTIONS
EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE: Maulaw man gyud ko basta ing-ana
S E L F
Situational low self-esteem related to cognitive impairment
At the end of 2 hours of nursing care, will: the patient
1. Encourage client to express honest
January 21, 2010 @ 2:30 PM
feelings in relation to loss of prior level of functioning. y The patient GOAL UNMET
OBJECTIVE: y Lacking contact y Lack interaction y
eye P E social R C
y It is the state in which an individual who previously had positive selfesteem experience a negative feeling towards self due to a certain situation y
Verbalize understandi ng of things that precipitate current situation; and Demonstrat e behaviors that show
Acknowledge pain of loss. Support through
was unable to verbalize understanding of things that
client
process of grieving. Client may be fixed in anger stage of grieving process, which is turned inward on the self, resulting in diminished selfesteem. 2. Devise methods for assisting client to
Has little interest E P in activities Talks only when T I asked O N
lead to current situation y The patient
was unable to demonstrate behaviors show that
positive self-esteem
positive as by
self-esteem evidenced
Handbook of Nursing
inability to have
Diagnosis by Lynda Juall CarpenitoMuyet
express properly..
feelings
an eye-contact as well as
looking down at To explore the feelings of the client thereby allowing him to acknowledge his own strength and weakness. 3. Encourage client's attempts communicate. verbalizations to If are during interview. the
not understandable, express to client
what you think he or she intended to say. It may be to client
necessary reorient frequently.
The ability to communicate effectively with others may enhance self-esteem. 4. Encourage reminiscence and
discussion of life review. Also
discuss present-day events. Sharing
picture albums, if possible, is
especially good. Reminiscence and life review help the client resume
progression through the grief process associated disappointing with life
events and increase
self-esteem successes reviewed. 5. Encourage participation group
as are
in
activities.
Caregiver may need to accompany client at first, until he or she feels secure that the group members will be accepting, regardless of
limitations in verbal communication. Positive feedback from group members will increase selfesteem. 6. Offer support and empathy when
client
expresses at to people,
embarrassment inability remember
events, and places. Focus on
accomplishments to lift self-esteem. 7. Encourage client to be as independent as possible in selfcare activities. The ability to perform independently preserves selfesteem. 8. Listen to patients concerns verbalizations without comment and
or judgment. It enables the client to develop trust and thereby establish communication 9. Provide feedback to clients feelings. To allow the client experience a different view. negative
TIME AND DATE January 21, 2010 @12:30 PM
CUES
NEED
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
GOAL OF CARE
INTERVENTIONS
EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE: The clarified when exactly was the 2 months he was referring about his last used of marijuana, he verbalized Kadtong 2007 man to, aw 2008 diay
C O G N I T I V E
Impaired memory related to neurological disturbances Impaired memory is directly related to effects of general medical condition or ongoing effects of substance. Depending o n the areas of the brain, the client are unable to recall information, either remote or recent. The
At the end of 3 day nursing care, the patient will be able to: y Verbalize awareness of memory problems; and y Accept limitations of current
1. Provide opportunities reminiscence recall past events Long-term memory may
January 21, 2010 for @ 2:30 PM or GOAL MET y The patient was able to verbalize awareness of memory problems as he
persist after loss of recent memory. is an activity
Reminiscence usually enjoyable
OBHECTIVE: y
Disorientation to P time E R of C E
for the client.
verbalized Usahay the
Observed experience forgetting
condition 2. Encourage client to use written cues such as or y
gyud makalimot na ko The patient was able to
his P head when he is T unable to recall U Scratches information A to L
calendars notebooks Written decrease
cues the
verbalize acceptance
Inability
determine if a behavior performe is
client may confabulate to fill in those lost memories.
clients recall
need
to
of
his
activities,
limitations due to his conditions
plans and so on from memory. 3. Encourage ventilation feelings frustration, helplessness, and so forth. Refocus of of
attention to areas of focus and progress. To lessen feelings of powerlessness/hope lessness 4. Provide for proper pacing of activities and having
appropriate rest To avoid fatigue 5. Allow the client to do tasks on his
own, but do not rush him to do it. Make the client feel that he can still do things independently. It is important to maximize independent function, assist the client memory when has
deteriorated further. 6. Assist the client
deal with functional limitations and
identify resources. To individual maximizing independence. 7. Provide single step instructions when meet needs,
instructions needed. Client memory
are
with
impairment cannot remember multistep instructions 8. Do not contradict the client who an Instead, explain and find
experiences illusion. simply reality, some solutions problem Therapeutic
practical to the
responses promote reality offering while solutions
that help enhances the clients sense and may reduce
fear, anxiety, and confusion. 9. Monitor clients
behavior and assist in use of stressmanagement techniques To frustration 10. Determine clients response medication medications prescribe to to reduce
improve attention, concentration, memory process
and to lift spirits and emotional responses. Helpful deciding in whether modify
quality of life is improved using medications prescribed. TIME AND DATE January 21, 2010 @ 12:30 P.M. SUBJECTIVE: Makatamad usahay maligo. Wala pa gani ko ligo ron. Kapoy pud manlimpyo ug kuko, as verbalized by the patient. OBJECTIVE: Unkempt hair noted food stains visible on clothing untrimmed fingernails and toenails with visible dirt noted A C T I V I T Y E X E R C I Self care deficit: bathing / hygiene related to lack of motivation The patient has an impaired ability to provide self care requisites due to environmental and psychological factors. After 2 hours of nursing care, the client will be able to: a) verbalize self need b) Demonstrat e techniques to meet care 1. Establish rapport. R: to gain clients trust and facilitate a good working relationship. 2. Identify reason for difficulty in selfcare. R: underlying cause affects choice of interventions/ strategies. 3. Determine hygienic needs and provide assistance needed as with After 2 hours of nursing care, the client was able to: a) verbalize self need b) but unable was to care January 21, 2009 @ 2:30 PM CUES NEED NURSING DIAGNOSIS GOAL OF CARE INTERVENTIONS EVALUATION when the
GOAL PARTIALLY MET
self-care needs
S E
activities like care of nails and
demonstrate techniques to meet selfcare needs.
brushing teeth. P A T T E R N R: basic hygienic needs may be forgotten. 4. Discuss importance hygiene. R: makes client aware of how hygiene is vital in caring for oneself. 5. Orient client to on of
different equipment for self-care like various toiletries. R: increases the clients awareness of different materials for self-care. 6. Let the patient enumerate his ideas on the importance of hygiene. R: Encourages the
patient to understand the need for hygiene. 7. Discuss the possible negative
implications of not taking a bath such as infections and odor. R: Broadens the
patients idea about the problem and
encourages him to meet the need. 8. Encourage client to perform self-care to the maximum of ability as defined by the client. Do not rush client. R: promotes independence and sense of control, may decrease feelings of
helplessness. 9. Allot plenty of time to perform tasks. R: cognitive impairment may interfere with ability to manage even simple activities. 10. Assist with
dressing neatly or provide clothes. R: Enhances esteem and convey aliveness. colorful
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- NCP PsychosisDocument3 paginiNCP Psychosisinagasi100% (7)
- NCP PsychDocument8 paginiNCP Psychjmanipon_1100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaDocument9 paginiNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Schizophreniaاسيرالاحزان100% (1)
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocument3 paginiDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJames Lozano83% (6)
- Crisis Intervention: Psychiatric Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocument13 paginiCrisis Intervention: Psychiatric Nursing Nursing Care PlanKatherine 'Chingboo' Leonico Laud100% (4)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiNursing Care PlanJewelyn Bronda100% (2)
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument4 paginiSchizophrenia NCPGladys Barcelona91% (55)
- Nursing Care Plans For Delusional DisorderDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plans For Delusional Disorderkirill61195% (22)
- Nursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob76% (46)
- Care Plan For SchizophreniaDocument6 paginiCare Plan For SchizophreniaAllea Likestolaugh Brown100% (2)
- Altered Sensory and Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument4 paginiAltered Sensory and Disturbed Thought ProcessRosecinie Torrente100% (2)
- Xi. Nursing Care PlansDocument4 paginiXi. Nursing Care PlansNic Ji100% (1)
- NCP Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument2 paginiNCP Disturbed Thought ProcessCesara Lacorte80% (5)
- A NCP SchizoDocument5 paginiA NCP SchizoJoseph Wilson Macasa50% (4)
- Disturbed Thought Processes DescribeDocument2 paginiDisturbed Thought Processes DescribePRINCESS LARA CASILAOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paranoid Schizophrenia NCPDocument8 paginiParanoid Schizophrenia NCPCherubim Lei DC Flores67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Paranoid SchizophreniaDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan For Paranoid SchizophreniaAyra Batore Laguitao88% (17)
- NCP For SchizoDocument5 paginiNCP For SchizoRichelene Mae Canja100% (2)
- Schizophrenia NCP and DrugstudyDocument11 paginiSchizophrenia NCP and DrugstudyElle Monge100% (2)
- NCP Violence - OtherDocument2 paginiNCP Violence - OtherRosean Venus SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument4 paginiDisturbed Thought ProcessJessieRamosAnicetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- N C PDocument3 paginiN C PTrixia Diaz100% (1)
- NCP SchizophreniaDocument2 paginiNCP Schizophreniajoshua canja100% (5)
- NCPDocument1 paginăNCPNneka Andrea Datiles0% (2)
- NCP FinalDocument22 paginiNCP FinalAlmira Ahamad100% (1)
- Disturbed Thought Process NCP Gallano May 22 2018Document3 paginiDisturbed Thought Process NCP Gallano May 22 2018Charles Mallari ValdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schizophrenia NCPDocument2 paginiSchizophrenia NCPNicole cuencos100% (2)
- Care Plan For Schizoaffective DisorderDocument2 paginiCare Plan For Schizoaffective DisorderThalia Peart100% (13)
- Disturbed Thought ProcessesDocument2 paginiDisturbed Thought ProcessesJason Avellano100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob80% (5)
- 4 NCP SchizophreniaDocument9 pagini4 NCP SchizophreniaHazel Banday100% (4)
- NCP DisturbedThoughtProcessesDocument1 paginăNCP DisturbedThoughtProcessesJoan KarlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jean Pearl R. Caoili Bsn3 NCB Diagnosis: Paranoid Schizophrenia Psychiatric Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals/ Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument9 paginiJean Pearl R. Caoili Bsn3 NCB Diagnosis: Paranoid Schizophrenia Psychiatric Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals/ Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluationpj casteÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCHIZOPHRENIA Nursing Care PlanDocument1 paginăSCHIZOPHRENIA Nursing Care Planrinkai130% (1)
- NCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardDocument9 paginiNCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardMary Margarett BoadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For Bipolar DisorderDocument1 paginăNCP For Bipolar DisorderJohn Carlo Santos100% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan For DepressionDocument7 paginiNursing Care Plan For DepressionCatherineÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP SchizDocument12 paginiNCP SchizKristine Reyes - MerleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disturbed Thought Process NCPDocument2 paginiDisturbed Thought Process NCPreneighd100% (7)
- NCP Psyche2Document6 paginiNCP Psyche2Nica RTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Thought ProcessesDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Thought Processesrinkai1377% (13)
- ND - Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument2 paginiND - Disturbed Thought ProcessHu DawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Impaired Social InteractionDocument2 paginiNCP Impaired Social Interactionzenzamora87% (31)
- Nursing CARE PLAN PsychDocument7 paginiNursing CARE PLAN Psychtiptopyo100% (1)
- NCP For SchizoDocument6 paginiNCP For SchizoGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEAÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PsychDocument2 paginiNCP PsychJray Inocencio50% (4)
- NCP-Disturbed Thought ProcessesDocument3 paginiNCP-Disturbed Thought ProcessesAlexis Abigail de Leon75% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan For DepressionDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For DepressionCyrus De Asis87% (69)
- Bipolar NCPDocument2 paginiBipolar NCPGenevieve VLs100% (1)
- Dementia Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiDementia Nursing Care Planmp175767% (3)
- ND - Impaired Social InteractionDocument2 paginiND - Impaired Social InteractionHu Dawi67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For SchizophreniformDocument8 paginiNursing Care Plan (NCP) For SchizophreniformRisa Sol AriasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.D Ndera CaseDocument9 pagini2.D Ndera CaseNsengimana Eric MaxigyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategies For Working With DelusionsDocument4 paginiStrategies For Working With DelusionsHannah Grace Protasio LumongsodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scizophrenia NCP2Document12 paginiScizophrenia NCP2Kholid Abu Mohammad AlfaizinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schizo2 2017Document40 paginiSchizo2 2017maha abdallahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study Evaluation Sheet @@Document14 paginiCase Study Evaluation Sheet @@Mahammad Abd ElkarimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Status Assessment: A. General Appearance The Patient Grooming WasDocument4 paginiMental Status Assessment: A. General Appearance The Patient Grooming Wassandyzgurl100% (3)
- Case Study of PhobiasDocument8 paginiCase Study of PhobiasNsengimana Eric MaxigyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCHIZODocument25 paginiSCHIZOQuinonez Anna MarieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimizing Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy For Social Anxiety Disorder and Understanding The Mechanisms of ChangeDocument9 paginiOptimizing Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy For Social Anxiety Disorder and Understanding The Mechanisms of Changedinda septia ningrumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triage NurseDocument1 paginăTriage NurseJeyser T. GamutiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- COUN 506 Article ReviewDocument7 paginiCOUN 506 Article ReviewMaLinda DiTonnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abrams Annotated BibliographyDocument6 paginiAbrams Annotated BibliographyBenjamin AbramsÎncă nu există evaluări
- H & Mse of SunandaDocument12 paginiH & Mse of SunandaamitÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBT ReviewDocument1 paginăCBT ReviewBeyza Gül100% (1)
- (Relational Perspectives Book Series) Peter L. Rudnytsky - Mutual Analysis - Ferenczi, Severn, and The Origins of Trauma Theory-Routledge (2021)Document367 pagini(Relational Perspectives Book Series) Peter L. Rudnytsky - Mutual Analysis - Ferenczi, Severn, and The Origins of Trauma Theory-Routledge (2021)hugoarce100% (1)
- Initial Trauma Review: Adolescent/Young Adult Version (ITR-A)Document6 paginiInitial Trauma Review: Adolescent/Young Adult Version (ITR-A)belmarinagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social Work Creative WritingDocument8 paginiSocial Work Creative WritingRenz AntonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sigmund Freud Psychoanalytical Theory 11122020 045404pmDocument38 paginiSigmund Freud Psychoanalytical Theory 11122020 045404pmAbdul SamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bates Chapter 3 Flashcards - QuizletDocument8 paginiBates Chapter 3 Flashcards - Quizletaznknight323Încă nu există evaluări
- DiassDocument8 paginiDiassssukye1994Încă nu există evaluări
- Diass 6c Methods and Tools in CounselingDocument16 paginiDiass 6c Methods and Tools in CounselingKaela Llagas MarillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Some Psychopaths Make Great CEOsDocument4 paginiWhy Some Psychopaths Make Great CEOsalexandru_gheoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activities For AdolescentsDocument3 paginiActivities For AdolescentsLilithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tip Sheet: Functional Behavior Assessment and Function-Based InterventionsDocument8 paginiTip Sheet: Functional Behavior Assessment and Function-Based InterventionsMei MeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Major Depressive Disorder Concept PaperDocument8 paginiMajor Depressive Disorder Concept PaperCharles Señedo100% (1)
- Albert EllisDocument8 paginiAlbert EllisGaurish SalgaocarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skin ShamingDocument4 paginiSkin Shamingcedrick abalosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Empathy Map Canvas 006 PDFDocument1 paginăEmpathy Map Canvas 006 PDFAdam LenaartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stress & Burnout SyndromeDocument16 paginiStress & Burnout Syndromejh_ajjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychological Report of SR - DeseoDocument3 paginiPsychological Report of SR - DeseoRommel SarjÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Ryan Case StudyDocument6 paginiA Ryan Case StudycryziaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OniomaniaDocument25 paginiOniomaniaSobana RajandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ma Cristy L. Exconde, MD, FPOGSDocument62 paginiMa Cristy L. Exconde, MD, FPOGSCAROL ANN PATITICO100% (1)
- Assessing PersonalityDocument8 paginiAssessing PersonalityRajat ╚╝╔╗ NarangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approaches To Music TherapyDocument31 paginiApproaches To Music TherapyLuis AlbertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rizvi, S.L. - Treatment Failure in Dialectical Behavior TherapyDocument10 paginiRizvi, S.L. - Treatment Failure in Dialectical Behavior TherapyAlvaro Paredes RiveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmnesiaDocument4 paginiAmnesiaapi-351680270Încă nu există evaluări
- EmdrDocument6 paginiEmdrsabetÎncă nu există evaluări