Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
PHY3 CJune 2002
Încărcat de
api-3726022Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
PHY3 CJune 2002
Încărcat de
api-3726022Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
PHY3 JUNE 2002 - TOPIC C - NUCLEAR & PARTICLE PHYSICS 1
Topic C - Nuclear and Particle Physics
3. (a) A stationary neutron can decay to a proton and an electron. Use the data below to predict the maximum total
kinetic energy of the electron and the proton in MeV.
Data: mass of neutron = 1.008 665u; mass of proton = 1.007 276u;
mass of electron = 0.000 549u; lu = 930 MeV (3)
Explain why the principle of conservation of linear momentum tells
you that almost all this kinetic energy is given to the electron. (2)
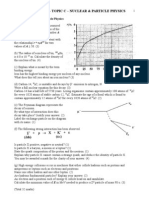
On the axes opposite sketch a graph showing the energy spectrum
for the β - particles produced during beta decay.
Add a scale to the horizontal axis. (3)
Explain why the shape of this graph led to the prediction of the existence
of neutrinos. You may be awarded a mark for the clarity of your answer. (3)
(b) State one similarity and one difference between a proton and an antiproton. (2)
Write down two particle-antiparticle pairs of leptons. (2)
What happens when a particle and its antiparticle collide? (1)
(c) Use the laws of conservation of charge and baryon number to decide whether the following interactions are possible
or not. In each case show how you applied the laws. (4)
These two decays are examples of strong interactions. What exchange particle is responsible for the decays? (1)
Delta particles are baryons consisting of u and d quarks only. Two more members of the delta particle family are the Δ+
and the Δ°. These are excited states of the proton and the neutron. State the quark composition of the Δ+ and the Δ°. (2)
(d) Read the short passage below and answer the questions about it.
What is a hadron? (1)
List all the leptons mentioned in the passage. (1)
Why are pions unable to decay by means of the strong interaction? (1)
Copy and complete the following sentence by circling the appropriate word inside the brackets.
Pions which decay by the weak interaction have a {shorter / similar / longer} lifetime than those which decay by the
electromagnetic interaction. (1)
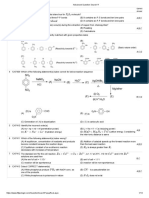
A positive pion π+ has a quark composition
State one possible quark composition of a neutral pion π°.
Draw a Feynman diagram showing the decay of a neutron to a proton,
(2)
Why must this be a weak interaction? (1)
Label the exchange particle on your Feynman diagram. (1)
(Total 32 marks)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cec 103. - Workshop Technology 1Document128 paginiCec 103. - Workshop Technology 1VietHungCao92% (13)
- Mass Defect and Binding EnergyDocument3 paginiMass Defect and Binding EnergyMark ProchaskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music GcseDocument45 paginiMusic GcseAimee DohertyÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide To The Preparation of Civil Engineering Drawing PDFDocument186 paginiA Guide To The Preparation of Civil Engineering Drawing PDFEraj100% (3)
- PHY3 CJanuary 2003Document1 paginăPHY3 CJanuary 2003api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Atoms & NucleiDocument15 paginiAtoms & NucleixkryxxzÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 CJanuary 2006Document1 paginăPHY3 CJanuary 2006api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 12 Physics: Atoms and Nuclei QuestionsDocument4 paginiCBSE Class 12 Physics: Atoms and Nuclei QuestionsBug LordÎncă nu există evaluări
- WS - Honors Atomic Theory WSDocument9 paginiWS - Honors Atomic Theory WSsquattingm0nkeysÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nuclei QB XiiDocument23 paginiNuclei QB XiiToshani GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xii-Board 3RD 33% Physics QP - 18.11.2023Document7 paginiXii-Board 3RD 33% Physics QP - 18.11.2023eashwarsiddhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 1002 Assn 1Document3 paginiCH 1002 Assn 1DorothyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Years of Atom&NucleiDocument4 pagini10 Years of Atom&NucleidipeshjoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 87 EssayDocument4 pagini87 EssaySam SamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Worksheet On Structure of Atom 2022-23Document2 paginiRevision Worksheet On Structure of Atom 2022-23Malolan SriramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Department: Topic 7.1 - Discrete Energy & Radioactivity Topic 7.2 - Nuclear Reactions 12 Grade (Physics SL)Document8 paginiScience Department: Topic 7.1 - Discrete Energy & Radioactivity Topic 7.2 - Nuclear Reactions 12 Grade (Physics SL)ananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cbse 12th Question Bank PhysicsDocument6 paginiCbse 12th Question Bank Physicsramayodi223Încă nu există evaluări
- Nuclear Tutorial SolutionDocument19 paginiNuclear Tutorial SolutionGordon GohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document3 paginiAssignment 1MainzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCT 131 General Chemistry CA1 CA2 Proper-1Document2 paginiSCT 131 General Chemistry CA1 CA2 Proper-1JensiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy 3 C SpecimenDocument1 paginăPhy 3 C Specimennahian_aziz9050Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics 222 - Test 3 - Spring 2011Document1 paginăPhysics 222 - Test 3 - Spring 2011eltytanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bangladesh Physics Olympiad 2015 (National)Document3 paginiBangladesh Physics Olympiad 2015 (National)Science Olympiad Blog100% (7)
- Atoms and NucleiDocument4 paginiAtoms and NucleiMishti GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 11 Problems 5th EditionDocument3 paginiCH 11 Problems 5th Editionnisannn0% (1)
- SAT Chemistry Eng-11-12 G AdvancedDocument80 paginiSAT Chemistry Eng-11-12 G AdvancedАрнур ОспановÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions on Fundamental Particles: Cs Cs Cs Cs β β β βDocument10 paginiQuestions on Fundamental Particles: Cs Cs Cs Cs β β β βjoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Provided:: A Formula Sheet and Table of Physical Constants Is Attached To This PaperDocument10 paginiData Provided:: A Formula Sheet and Table of Physical Constants Is Attached To This PaperSrinivas RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYSICS burdwan University question paperDocument2 paginiPHYSICS burdwan University question paperb718535740Încă nu există evaluări
- Phys 452, Summer 1444 H HW # 1Document2 paginiPhys 452, Summer 1444 H HW # 1SmoguherÎncă nu există evaluări
- ParticlePhysicsQuestions U4 Physics ALEVELDocument20 paginiParticlePhysicsQuestions U4 Physics ALEVELNMVRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atom ThryDocument6 paginiAtom ThrySumathi SrinivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure TutorialDocument3 paginiAtomic Structure Tutorialchong56Încă nu există evaluări
- Pyl 100 - Tutorial Sheet 5Document2 paginiPyl 100 - Tutorial Sheet 5HardeepSinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework (II) ForextrascoreDocument3 paginiHomework (II) Forextrascore張廷Încă nu există evaluări
- 14 SQPDocument8 pagini14 SQPdipanshu76612Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 CJanuary 2005Document1 paginăPHY3 CJanuary 2005api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure ExplainedDocument20 paginiAtomic Structure ExplainedAkhlak HossainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Atomic StructureDocument13 paginiChapter 2 Atomic StructureBetty BavorováÎncă nu există evaluări
- AS-Physics-Particles-Answers-AQA - QuarksDocument6 paginiAS-Physics-Particles-Answers-AQA - QuarksLuka BoyleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Ans CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level-2: (170 Marks)Document30 paginiShort Ans CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level-2: (170 Marks)Hiya ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic PhysicsDocument3 paginiAtomic Physicssikatlearning1Încă nu există evaluări
- Test Topic 2Document4 paginiTest Topic 2Ashutosh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bhavan's Netaji Subhash Physics Pre Board 1Document9 paginiBhavan's Netaji Subhash Physics Pre Board 1niladriputatunda1Încă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Dual Nature of Radiation Atoms and NucleiDocument4 paginiCBSE Class 12 Physics Dual Nature of Radiation Atoms and Nucleishanugamer0042Încă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class-12 PHYSICS (Theory) Outside Delhi Set-1Document8 paginiCBSE Class-12 PHYSICS (Theory) Outside Delhi Set-1Haarish KrishnamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms and Nuclei TestDocument2 paginiAtoms and Nuclei TestBee PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam 1 Extra Problems for 5.111Document9 paginiExam 1 Extra Problems for 5.111Truong Cai100% (1)
- PhotonDocument4 paginiPhotonSteveFarraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1Document9 paginiCBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1PallavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model Test Paper 2Document3 paginiModel Test Paper 2Aman bansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subatomic Problem Set 1: Radioactivity and Nuclear StabilityDocument32 paginiSubatomic Problem Set 1: Radioactivity and Nuclear StabilityDiego M GranziolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prestige Public School: Periodic Test - III (2021-22)Document3 paginiPrestige Public School: Periodic Test - III (2021-22)Lucifer GamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class XII 2023 2024 Prelims IDocument10 paginiClass XII 2023 2024 Prelims ITanishkha RaajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Physics - I - PH6151 Important 2 Marks With AnswersDocument23 paginiEngineering Physics - I - PH6151 Important 2 Marks With AnswersZaffu Zealy100% (4)
- PRE BOARD EXAM, 2020-21 Physics (Code No. 042) Class - XII: General InstructionsDocument10 paginiPRE BOARD EXAM, 2020-21 Physics (Code No. 042) Class - XII: General InstructionsRämíz MêmóñÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bolleballi Naganivrithi (Greendaless) - 1ENA - Chapter 8 Atoms & Molecules (Notes)Document25 paginiBolleballi Naganivrithi (Greendaless) - 1ENA - Chapter 8 Atoms & Molecules (Notes)B.NiviÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Atom &nucleiDocument2 pagini11 Atom &nucleivedantgupta249Încă nu există evaluări
- Gem Chem MidsemDocument2 paginiGem Chem MidsemRohan TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 5 Physics Chapter 5 - Teacher'sDocument12 paginiForm 5 Physics Chapter 5 - Teacher'sPavithiran100% (5)
- Chapter11: Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument23 paginiChapter11: Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterSANIKA VERMAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyDe la EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 2: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #2De la EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 2: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #2Încă nu există evaluări
- Biojan 2006 U4aqDocument20 paginiBiojan 2006 U4aqapi-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology Jan 2008 6101 QuestionDocument20 paginiBiology Jan 2008 6101 QuestionAdrees MeahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biojune 2002 U5bqDocument11 paginiBiojune 2002 U5bqapi-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Biojune 2008 U4aqDocument24 paginiBiojune 2008 U4aqapi-3726022100% (1)
- Unit 1 Exam Jan 2002Document16 paginiUnit 1 Exam Jan 2002Öykü TuralÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6102 01 Que 20080109Document20 pagini6102 01 Que 20080109Inas ManurungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biojan 2008 U3qDocument16 paginiBiojan 2008 U3qapi-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Biojan 2003 U4aqDocument11 paginiBiojan 2003 U4aqapi-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Biojune 2008 U3qDocument12 paginiBiojune 2008 U3qapi-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Biojune 2002 U2bqDocument10 paginiBiojune 2002 U2bqapi-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Biojune 2004 U3qDocument12 paginiBiojune 2004 U3qapi-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 DJune 2006Document1 paginăPHY3 DJune 2006api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Biojan 2005 U3qDocument16 paginiBiojan 2005 U3qapi-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Biojune 2008 U2bqDocument16 paginiBiojune 2008 U2bqapi-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Biojan 2004 U2bqDocument11 paginiBiojan 2004 U2bqapi-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Biojune 2008 U1qDocument16 paginiBiojune 2008 U1qapi-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 DJanuary 2006Document1 paginăPHY3 DJanuary 2006api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 DJune 2005Document1 paginăPHY3 DJune 2005api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 DJune 2002Document1 paginăPHY3 DJune 2002api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 DJanuary 2005Document1 paginăPHY3 DJanuary 2005api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Biojune 2003 U1qDocument12 paginiBiojune 2003 U1qapi-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 DJune 2004Document1 paginăPHY3 DJune 2004api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 DJanuary 2004Document1 paginăPHY3 DJanuary 2004api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 DJanuary 2003Document1 paginăPHY3 DJanuary 2003api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 DJanuary 2002Document1 paginăPHY3 DJanuary 2002api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 CJune 2006Document1 paginăPHY3 CJune 2006api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 CJune 2005Document1 paginăPHY3 CJune 2005api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 CJune 2003Document1 paginăPHY3 CJune 2003api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- PHY3 CJune 2004Document1 paginăPHY3 CJune 2004api-3726022Încă nu există evaluări
- Design Plan: A Performance Task in GeometryDocument12 paginiDesign Plan: A Performance Task in GeometryRobert Ryan SantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRM Institute of Science and Technology Department of Mathematics Probability and Queueing Theory Tutorial Sheet I2Document1 paginăSRM Institute of Science and Technology Department of Mathematics Probability and Queueing Theory Tutorial Sheet I2Cooldude 69Încă nu există evaluări
- 3RP15 05-1aDocument3 pagini3RP15 05-1atycristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nādatanumanisham Shankaram Namami Me Manasa ShirasaDocument12 paginiNādatanumanisham Shankaram Namami Me Manasa Shirasaveena murthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pragathi Full Test-6, Paper-2 (Qp+Key) - 18.07.22Document14 paginiPragathi Full Test-6, Paper-2 (Qp+Key) - 18.07.22Ganesan MuthukrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time TableDocument7 paginiTime TableChethan .H.GÎncă nu există evaluări
- QAF10A200S TheTimkenCompany 2DSalesDrawing 03 06 2023Document1 paginăQAF10A200S TheTimkenCompany 2DSalesDrawing 03 06 2023LeroyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wartsila CPP PaperDocument4 paginiWartsila CPP Papergatheringforgardner9550Încă nu există evaluări
- Metacentric Height: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 paginiMetacentric Height: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaВладимир ШевченкоÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xenomai 3 DocumentationDocument673 paginiXenomai 3 DocumentationGuile BonafiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excel 2007 Lesson 7 QuizDocument5 paginiExcel 2007 Lesson 7 Quizdeep72Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology - Physics Chemistry MCQS: Gyanm'S General Awareness - November 2014Document13 paginiBiology - Physics Chemistry MCQS: Gyanm'S General Awareness - November 2014santosh.manojÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICSE Mathematics X PapersDocument22 paginiICSE Mathematics X PapersImmortal TechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eltek PSR 327Document2 paginiEltek PSR 327fan liuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Displaymax JR 1500 SpecsDocument1 paginăDisplaymax JR 1500 SpecsFRANCISCOÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO 8243 2013 Cigarettes - SamplingDocument18 paginiISO 8243 2013 Cigarettes - SamplingEko YuliantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- e-GP System User Manual - Tender Evaluation Committee UserDocument82 paginie-GP System User Manual - Tender Evaluation Committee UserMd. Jakaria ApuÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTM D 1510 - 02 Carbon Black-Iodine Adsorption NumberDocument7 paginiASTM D 1510 - 02 Carbon Black-Iodine Adsorption Numberalin2005100% (1)
- LC IN SCIENCE and MathDocument14 paginiLC IN SCIENCE and MathCharity Anne Camille PenalozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operational Guidelines For VlsfoDocument2 paginiOperational Guidelines For VlsfoИгорьÎncă nu există evaluări
- Windows Mbox Viewer User Manual 1.0.3.4Document33 paginiWindows Mbox Viewer User Manual 1.0.3.4Billy NoelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution of Homework 4Document4 paginiSolution of Homework 4Kamalakar Reddy100% (2)
- Enzyme Inhibition and ToxicityDocument12 paginiEnzyme Inhibition and ToxicityDaniel OmolewaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eurotech IoT Gateway Reliagate 10 12 ManualDocument88 paginiEurotech IoT Gateway Reliagate 10 12 Manualfelix olguinÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSD - Assignment 1 2018Document3 paginiDSD - Assignment 1 2018Naveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- UG WeibullDocument776 paginiUG WeibullCharles GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction - Week 2Document37 paginiIntroduction - Week 2Tayyab AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări