Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Digital Synopsis
Încărcat de
Sunny KumarDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Digital Synopsis
Încărcat de
Sunny KumarDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SYNOPSIS OF ECE202
TOPIC:- SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORIES
To be submitted by: SUNNY KUMAR SEC: -RE3008A28 REG.NO. -11007230
Submitted to:MR. GAGANDEEP MEENA
INTRODUCTION:Semiconductor memory is an electronic data storage device which is often used as computer memory, implemented on a semiconductor-based integrated circuit. Example-ROM, RAM, FLASH MEMORY Data storage is essential for processing Data storage capacity available on a single integrated circuit Grows exponentially being doubled approximately every two years. Capacity of the dynamic read/write memory (DRAM) chip Exceeds now 1 Gigabit. Data transfer speed of a standard DRAM is at the level of 200Mb/sec/pin. Mask programmed ROM. The required contents of the memory is programmed during fabrication, Programmable ROM (PROM). The required contents is written in a permanent way by burning out internal interconnections (fuses). It is a oneoff procedure. Erasable PROM (EPROM). Data is stored as a charge on an isolated gate capacitor (floating gate). Data is removed by exposing the PROM to the ultraviolet light. Electrically Erasable PROM (EEPROM) also known as Flash Memory. It is also base on the concept of the floating gate. The contents can be re-programmed by applying a suitable voltages to the EEPROM pins.
Semiconductor Memories are classified according to the type of data storage and the type of data access mechanism into the following two main groups:
Non-volatile Memory (NVM) also known as Read-Only Memory (ROM) which retains information when the power supply voltage is off. With respect to the data storage mechanism NVM are divided into the following groups:
Static RAM:- where data is retained as long as there is power supply on.
The Flash Memories are very important data storage devices for mobile applications. Read/Write (R/W) memory, also known as Random Access Memory (RAM). From the point of view of the data storage mechanism RAM are divided into two main groups: Dynamic RAM:-where data is stored on capacitors and requires a periodic refreshment..
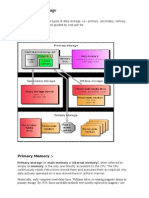
organization of a single chip semiconductor memory:-
Semiconductor Memory Classification
Read-Write Memory Non-Volatile Read-Write Memory EPROM E PROM SRAM DRAM FIFO LIFO Shift Register CAM FLASH
2
Read-Only Memory
Random Access
Non-Random Access
Mask-Programmed Programmable (PROM)
Digital Integrated Circuits2nd
Memories
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Phison Flash IdDocument2 paginiPhison Flash Idclaudi branÎncă nu există evaluări
- En Tia L: SM3281AB Test Program and ISP Release NoteDocument3 paginiEn Tia L: SM3281AB Test Program and ISP Release NotekhalibandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tabela de Chips BoschDocument4 paginiTabela de Chips BoschDanny EversonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Main Memory: 1-Read-Write or Random Access Memory (RAM)Document4 paginiTypes of Main Memory: 1-Read-Write or Random Access Memory (RAM)Sarmad Salih Jawad AlkodaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Unit 5Document21 paginiDC Unit 5thiruct77Încă nu există evaluări
- Explain in Detail Memory Classification. (Summer-2016, Summer-2015)Document19 paginiExplain in Detail Memory Classification. (Summer-2016, Summer-2015)yashuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selection - Memory - DR Monika - 22.03.23Document8 paginiSelection - Memory - DR Monika - 22.03.23Prof.Monika JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- T.Y. E.I. /2 / 1 Memories N.KapoorDocument5 paginiT.Y. E.I. /2 / 1 Memories N.KapoorNeelam KapoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Memory Operation: Static RAM, SRAM: An SRAM Is More Expensive and Less Dense Than DRAM. It Uses ADocument3 paginiBasic Memory Operation: Static RAM, SRAM: An SRAM Is More Expensive and Less Dense Than DRAM. It Uses AmadesrrrrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Microprocessor - Software Architecture: The MemoryDocument22 paginiBasic Microprocessor - Software Architecture: The MemoryMim FauziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory: Mohana S.H, Usmrfg College, Kuvempu UniversityDocument6 paginiMemory: Mohana S.H, Usmrfg College, Kuvempu UniversityMohana KurubaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ram, RomDocument12 paginiRam, Romheanyvoskowskyl.ar.sy.9.48.6Încă nu există evaluări
- Memory System Design PDFDocument13 paginiMemory System Design PDFNISHANT395Încă nu există evaluări
- CP and I Assing.Document12 paginiCP and I Assing.Aditya YewleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hierarchy of Storage: Primary MemoryDocument7 paginiHierarchy of Storage: Primary MemorySambit12Încă nu există evaluări
- "Memory Interface" in (Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing)Document22 pagini"Memory Interface" in (Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing)MUHAMMAD ABDULLAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Memory Interface" in (Microprocessor and Assembly Language)Document22 pagini"Memory Interface" in (Microprocessor and Assembly Language)MUHAMMAD ABDULLAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- FRAM - Semiconductor Memory TypesDocument5 paginiFRAM - Semiconductor Memory TypesMehmet KırgözoğluÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study About Non-Volatile MemoriesDocument11 paginiA Study About Non-Volatile MemoriesDileep KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory DevicesDocument19 paginiMemory DevicesMst. Najnin SultanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicroprocessorsDocument4 paginiMicroprocessorsleoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory Devices JayjeetDocument53 paginiMemory Devices JayjeetmansurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No.01Document2 paginiAssignment No.01Rizwan AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory 2Document21 paginiMemory 2Manish JangidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 (Csa)Document25 paginiUnit 5 (Csa)Bindu VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory OrganizationDocument70 paginiMemory OrganizationrahqansayeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- MICRO PROCESSOR UNIT (MPU) MEMORY SPECIaLIZATIONDocument6 paginiMICRO PROCESSOR UNIT (MPU) MEMORY SPECIaLIZATIONJoseph KimaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3.3Document4 paginiChapter 3.3OzzyÎncă nu există evaluări
- COA-Unit 4 Memory OraganizationDocument60 paginiCOA-Unit 4 Memory Oraganizationtanuja rajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-IV & V Course MaterialDocument31 paginiUnit-IV & V Course MaterialAbdul Wahid NohriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Organization & Architecture: Lalit Sharma, MCA IIDocument76 paginiComputer Organization & Architecture: Lalit Sharma, MCA IImutha123Încă nu există evaluări
- Css Abrico Primary MemoryDocument13 paginiCss Abrico Primary MemoryJohn Grande SepulvidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ram RomDocument24 paginiRam RomYatin Kshirsagar87% (15)
- Chapter 22Document23 paginiChapter 22Midhun LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Disk Memory Storage DevicesDocument74 paginiOptical Disk Memory Storage DevicesM.WASEEM YOUSAF100% (2)
- Lecture 6 PDFDocument14 paginiLecture 6 PDFtestscribd9898Încă nu există evaluări
- Memory Morgan Is at IonDocument2 paginiMemory Morgan Is at IonMukesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Names: Rafal Hassan Ali, Supervised By: Sadiq H. Abdulhussain Goulshin Adnan Fadhil, Edia Nail Saeed, Zainab Haidar HafedDocument9 paginiNames: Rafal Hassan Ali, Supervised By: Sadiq H. Abdulhussain Goulshin Adnan Fadhil, Edia Nail Saeed, Zainab Haidar Hafedرفل حسن عليÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer PresentationDocument33 paginiComputer PresentationGagandeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory HierarchyDocument12 paginiMemory Hierarchysinmayank31Încă nu există evaluări
- THE Rom and Ram: Technical Vocational & Livelihood Computer Systems Servicing 12 First QuarterDocument4 paginiTHE Rom and Ram: Technical Vocational & Livelihood Computer Systems Servicing 12 First QuarterbogusbaikawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defination of ROMDocument4 paginiDefination of ROMshubham shakyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMTS Handout 4Document6 paginiCMTS Handout 4Tolosa TafeseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compu Ter: Aima Tallat C1-ADocument4 paginiCompu Ter: Aima Tallat C1-AaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity No. 2 Computer Architecture ICS 222 (LAB) : Submitted byDocument4 paginiActivity No. 2 Computer Architecture ICS 222 (LAB) : Submitted byJasmine Mycarl MananganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory Selection of ESDocument37 paginiMemory Selection of ESAravind YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- 409 Part 2Document30 pagini409 Part 2omotoso femiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MemoryDocument22 paginiMemoryMd. Masum Latif Chowdhury (201016006)Încă nu există evaluări
- Read-Only Memory (Usually Known by ItsDocument18 paginiRead-Only Memory (Usually Known by ItsAnonymous 04kV8baÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - III Concept of Memory PDFDocument13 paginiUnit - III Concept of Memory PDFxsaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit4 Notes ADC DAC and MemoriesDocument13 paginiUnit4 Notes ADC DAC and Memoriesgoshika venkateshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group Members: Karnail Katoch Vishal Mahant Archana Kahrinar Mohammad Pisavadi Kashyap BaradDocument55 paginiGroup Members: Karnail Katoch Vishal Mahant Archana Kahrinar Mohammad Pisavadi Kashyap BaradpRiNcE DuDhAtRaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer MemoryDocument4 paginiComputer MemoryRVRM1995Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of RAM and ROMDocument6 paginiTypes of RAM and ROMTinu Elza Vinu100% (1)
- RAM and RomDocument4 paginiRAM and Rommanoj22490Încă nu există evaluări
- Primary Memory FinalDocument24 paginiPrimary Memory FinalRavikiranSharmaSrkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q9 Bes AssignmentDocument7 paginiQ9 Bes AssignmentMilind Lawande.Încă nu există evaluări
- Ict Assignment# 01Document7 paginiIct Assignment# 01ibrarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semiconductor MainMemoryDocument18 paginiSemiconductor MainMemoryShruti ChandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esd Unit II Part3Document14 paginiEsd Unit II Part3Manoj GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Test Methods for SRAMs: Effective Solutions for Dynamic Fault Detection in Nanoscaled TechnologiesDe la EverandAdvanced Test Methods for SRAMs: Effective Solutions for Dynamic Fault Detection in Nanoscaled TechnologiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gain-Cell Embedded DRAMs for Low-Power VLSI Systems-on-ChipDe la EverandGain-Cell Embedded DRAMs for Low-Power VLSI Systems-on-ChipÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.De la EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.Încă nu există evaluări
- Essay of AngerDocument2 paginiEssay of AngerBalram JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synopsis On Signal and SystemsDocument2 paginiSynopsis On Signal and SystemsSunny KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synopsis On Signal and SystemsDocument2 paginiSynopsis On Signal and SystemsSunny KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combinational Devices and ASM ChartsDocument10 paginiCombinational Devices and ASM ChartsSunny KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18 AsmDocument22 pagini18 AsmHarold WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- BJT CircuitsDocument4 paginiBJT CircuitsRahul RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security Issues in Wireless NetworkDocument50 paginiSecurity Issues in Wireless NetworkdeardestinyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition - What Does Cellular Network Mean?Document2 paginiDefinition - What Does Cellular Network Mean?Sunny KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carduri Memorie: Office@gimex - Ro WWW - GimexDocument3 paginiCarduri Memorie: Office@gimex - Ro WWW - GimexofficeintrocarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Memory PDFDocument13 paginiComputer Memory PDFRamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flash Memory - Cache MemoryDocument3 paginiFlash Memory - Cache MemoryIsham IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psa Modules Wiring Diagrams: Obd2 DB9Document9 paginiPsa Modules Wiring Diagrams: Obd2 DB9Hlias AlafogiannisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogo Reclamos Publicitarios by ARTWORK ESTUDIOSDocument675 paginiCatalogo Reclamos Publicitarios by ARTWORK ESTUDIOSARTWORK ESTUDIOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUMMER OFFER Truck ExplorerDocument2 paginiSUMMER OFFER Truck ExplorerJoel AgbekponouÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC574Document1 paginăEC574utkarsh rajwanshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Android TCBDocument9 paginiAndroid TCBandymustopaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mask MotorolaDocument54 paginiMask Motorolazoki100% (2)
- DP CardReaders Wnt6-x64 1112 Vista-7-X64Document101 paginiDP CardReaders Wnt6-x64 1112 Vista-7-X64blindangleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dell Vflash SD Card With 100 OPDocument5 paginiDell Vflash SD Card With 100 OPmatkoshyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psa Modules Wiring Diagrams: Obd2 DB9Document9 paginiPsa Modules Wiring Diagrams: Obd2 DB9Fhertronics AutotronicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSD Buying Guide - List July 21, 2020Document19 paginiSSD Buying Guide - List July 21, 2020MJ ServaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lista Roy MemoryDocument12 paginiLista Roy Memoryazteca68Încă nu există evaluări
- H4nPro Compatible Cards E3Document2 paginiH4nPro Compatible Cards E3José ArceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet SU630 EN 20190619 PDFDocument2 paginiDatasheet SU630 EN 20190619 PDFHávila CorreiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ferroelectric RAMDocument7 paginiFerroelectric RAMSwayams MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Onf Ide Ntia L: SM3267AC/AE Test Program and ISP Release NoteDocument6 paginiOnf Ide Ntia L: SM3267AC/AE Test Program and ISP Release NoteRaul Trujillo PÎncă nu există evaluări
- AH 480 DeviceList 20210719Document456 paginiAH 480 DeviceList 20210719Yu FelixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selecting A SSD: Sata (2.5" or M.2) Nvme (Pcie M.2)Document1 paginăSelecting A SSD: Sata (2.5" or M.2) Nvme (Pcie M.2)conceptÎncă nu există evaluări
- Support Device ListDocument60 paginiSupport Device Listfox7878Încă nu există evaluări
- Nor - Nand Flash Guide: Selecting A Flash Memory Solution For Embedded ApplicationsDocument8 paginiNor - Nand Flash Guide: Selecting A Flash Memory Solution For Embedded ApplicationsDANIEL-COSTEL PETCUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cm3panel Schematic PDFDocument6 paginiCm3panel Schematic PDFDiep Ha100% (1)
- Embedded System of Shibu K VDocument10 paginiEmbedded System of Shibu K Vshahebgoudahalladamani0% (1)
- GL827 Usb 2.0Document47 paginiGL827 Usb 2.0oyoveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psa Modules Wiring Diagrams: Obd2 DB9Document9 paginiPsa Modules Wiring Diagrams: Obd2 DB9Oscar GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSD A100 DatasheetDocument2 paginiSSD A100 Datasheetrute silvaÎncă nu există evaluări