Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Decreased Cardiac Output
Încărcat de
Chinita SangbaanDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Decreased Cardiac Output
Încărcat de
Chinita SangbaanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
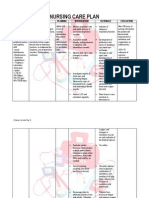
saNursing Care Plan Identified Problem: Decreased Cardiac Output Nursing Diagnosis: Decreased Cardiac Output r/t altered
afterload as evidenced by dyspnea and shortness of breath CUES Subjective: Murag hangakon mam ko uy, as verbalized by the client. Obective: Decreased peripheral pulses Edema on right lower leg S3 or S4 sounds Unstable VS: BP-130/90 mmHg RR-23 cpm PR-104 bpm T- 36.6 C OBJECTIVE STO: Within 8 hours of nursing care, patient will be able to participate in activities that reduce the workload of the heart such as therapeutic medication regimen, weight reduction, and balanced activity/rest plan. LTO: Within 3 days of nursing care, patient will be able to report or demonstrate decreased episodes of dyspnea. INTERVENTIONS Independent: Assess vital signs. Auscultate apical pulse; note heart sounds; and palpate peripheral pulses. RATIONALE EVALUATION Outcome met. Within 3 days of nursing care, the patient was able to report and demonstrate a decrease in episodes of dyspnea. T: 36. 3C P: 96 bpm R: 23 cpm BP: 120/90 mmHg
Check for calf tenderness; diminished pedal pulse; swelling, local redness, or pallor of extremity. Monitor urine output, noting decreasing output and dark/concentrated urine. Encourage rest, semirecumbent in bed or chair. Assist with physical care as indicated; elevate legs, avoiding pressure knee.
Collaborative: Monitor serial ECG, chest x-ray changes, laboratory studies (BUN, Creatinine)
Vital signs may be elevated because of increased SVR. The body may no longer be able to compensate and hypotension may occur. Reduced cardiac output, venous pooling/stasis, and enforced bed rest increases risk of thrombophlebitis. Kidneys respond to reduced cardiac output by retaining water and sodium. Physical rest should be maintained during acute or refractory HF to improve efficiency of cardiac contraction and to decrease to myocardial oxygen demand. ST segment depression and T wave flattening can develop because of increased myocardial oxygen demand. Chest xray may show enlarged heart and changes of pulmonary congestion. Elevation of BUN/creatinine reflects kidney hypoperfusion/failure. A variety of medications may be used to increase
Administer medications as indicated: diuretics, vasodilators, ACE inhibitors, Digoxin, inotropic agents, adlosterone
antagonist, anticoagulant Administer IV solutions, restricting total amount as indicated. Avoid saline solutions.
stroke volume, improve contractility, and reduce congestion. Because of existing elevated left ventricular pressure, client may not tolerate increased fluid volume.
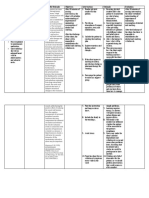
Nursing Care Plan Identified problem: Activity Intolerance Nursing Diagnosis: Activity Intolerance (level I) r/t imbalanced between oxygen supply and demand. CUES OBJECTIVE INTERVENTIONS Subjective: Independent: hangakon man gud ko usaahy pag STO: Check vital signs before galihok ko og todo, as verblaized Within 8 hours of nursing care, pt and immediately after by the pt. will be able to demonstrate a activity, especially if client decrease in physiologic signs of is receiving vasodilators, Objective: intolerance as evidenced by pulse, diuretics or B-blockers. respirations, and blood pressure Tachypneic within normal limits. Restless Document cardiopulmonary response to activity. Note Unstable VS: LTO: tachycardia, dysrhythmias, BP: 110/80 mmHg Within three days of nursing care, dyspnea, diaphoresis, RR: 30 cpm patient will be able to tolerate pallor. PR: 104 bpm. performance of ADLs as evidenced T: 36.0 C by absence of dyspnea upon exertion. Assess for other precipitators/causes of fatigue. Ex. Treatments, pain, medications. Evaluate accelerating activity intolerance. Provide assistance with self-care activities as indicated. Intersperse activity periods with rest periods. Collaborative: Implement graded cardiac rehabilitation/ activity program.
RATIONALE Orthostatic hypotension can occur with activity because of medication effect ( vasodilation), fluid shifts (diuresis), or compromised cardiac pumping function. Compromised myocardium/ inability to increase stroke volume during activity may cause an immediate increase in heart rate and oxygen demands, thereby aggravating weakness and fatigue. Fatigue is a side effect of medications. Pain and stressful regimens also extract energy and produce fatigue. May denote increasing cardiac decompensation rather than overactivity. Meets clients personal care needs without undue myocardial stress, excessive oxygen demands. Strengthens and improves cardiac function under stress if cardiac dysfunction is not irreversible.
EVALUATION Outcome met. Within three days of nursing care, the patient was able to tolerate ADLs as evidenced by vitals signs within normal normal vital signs and absence of dyspnea upon exertion. T: 36. 3C P: 70 bpm R: 16 cpm BP: 120/90 mmHg
Nursing Care Plan Identified problem: Excess fluid volume Nursing Diagnosis: Excess fluid volume r/t reduced glomerular filtration rate (decreased cardiac output)/ADH production, as evidenced by edema and hypertension. CUES Subjective: Day, ga hupong jud akong duha ka tiil.as verbalized by patient. Objective: Orthopnea +2 edema on both feet, +4 edema on right knee. Oliguria S3 heart sound Change in mental status/inconsistent with his answers Unstable VS T: 35.7 C P: 112 bpm R: 28 cpm Bp: 110/80 mmHg OBJECTIVE STO: Within 8 hours of nursing care, patient will be able to demonstrate understanding of individual dietary/ fluid restrictions as evidenced by a compliance towards fluid restriction therapy. LTO: Within 3 days of nursing care, patient will be able to stabilize fluid volume as evidenced by balanced intake and output and VS within normal range, and stable weight. INTERVENTIONS Monitor urine output, noting amount and color, as well as time of day when diuresis occurs. RATIONALE Urine output may be scanty and concentrated (especially during the day) because of reduced renal perfusion. Recumbency favors diuresis; therefore, urine output may be increased at night/ during bedrest. Diuretic therapy may result in sudden/ excessive fluid loss (circulating hypovolemia), even though edema/ ascites remains. Recumbency increases glomelular filtration and decreases production of ADH, thereby enhancing diuresis. Involving client in therapeutic regimen may enhance sense of control and cooperation with restriction. EVALUATION Outcome not met. Within 3 days of care, patient was not able to stabilize fluid volume as evidenced by unstable vital signs and imbalanced I/O. T: 36. 3C P: 70 bpm R: 16 cpm BP: 120/90 mmHg
Monitor/ calculate 24 hour intake and output (I/O) balanced. Maintain chair or bedrest in Semi- fowlers position during acute phase. Establish fluid intake schedule if fluids are medically restricted, incorporating beverage preference when possible. Give frequent mouth care/ ice chips as part of fluid allotment. Weighed daily.
Assess for distended neck and peripheral vessels. Inspect dependent body areas for edema with/
Documents changes in/ resolution of edema in response to therapy. A gain of 5 pounds represents approx. 2L of fluid. Conversely, diuretics can result in excessive fluid shifts and weight loss. Excessive fluid retention
without pitting; note presence of generalized body edema.
Change position frequently elevate feet when sitting, inspect skin surface, keep dry, and provide padding as indicated.
Auscultate breath sounds, noting decreased and/ or adventitious breath sounds: such as crackles, wheezes. Note prescence of increased dyspnea, tachypnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, persistent cough.
Collaborative: Maintain fluid/ sodium restrictions as indicated.
may be manifested by venous engorgement and edema formation. Peripheral edema in feet/ ankles and ascends as failure worsens. Pitting edema is generally obvious after retention of at least 10lbs of fluid. Edema formation, slowed circulation, altered nutritional intake, and prolonged immobility/ bedrest are cumulative stress source that affect skin integrity and require close supervision/ preventive interventions. Excess fluid volume often leads to pulmonary congestion symptoms of pulmonary edema may reflect acute left-sided HF. RHFs respiratory symptoms (dyspnea, cough, orthopnea) may have slower onset but are more difficult to reverse. Reduce total body water/ prevents fluid reaccumulation .
Nursing Care Plan Identified problem: Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Tissue perfusion related to third space fluid shift on both lower extremities CUES Subjective: day hubag lge jud akong duha ka tiil as client verbalized. Objective: +2 edema on both feet; +4 edema on right knee Delayed wound healing Skin discorations on lower extremities (blackened) Unstable VS: T: 35.7 C PR:112 bpm RR: 28 cpm BP: 110/80 mmHg OBJECTIVE STO: Within 8 hours of nursing care, patient will be able to demonstrate behaviors/lifestyle changes to improve circulation such as exercise/dietary program, relaxation techniques, cessation of smoking. LTO: Within 3 days of nursing care, patient will be able to demonstrate increased perfusion of lower extremities as evidence by peripheral pulses prescence, vital signs within clients normal range, absence of edema, and balance I/O. INTERVENTIONS Independent: Discuss the risk factors and potential outcomes of atherosclerosis. Encourage client to quit smoking. Discourage massaging of calf in prescence of varicose veins/ thrombophlebitis. Provide pillow and instruct the client to place it in between the knees. Encourage early ambulation when possible. Exercise caution in use of hot water bottles or heating pads. Monitor circulation in lower extremities. Apply ice and elevate limb as appropriate. Administer medication with caution (such as vasodilators, anticoagulants). Collaborative Administer IV fluids as indicated. Monitor laboratory studies, e.g.: Hct/ Hb; PT/ activated partial thromboplastin time. RATIONALE Information necessary for client to make informed choices and commit to lifestyle changes as possible. Smoking causes vasoconstriction and may further compromise perfusion. To prevent embolization. For comfort; to prevent the knees from rubbing each other creating friction which may lead to ulcerations. Enhances venous return. Tissues may have decreased sensitivity due to ischemia. Heat increases the metabolic demands of already compromised tissues. To reduce edema. Drug response, half-life, toxic levels may be altered by decreased tissue perfusion. Maintain circulating volume to maximize tissue perfusion. Indication of hypovolemia/ dehydration that can impair tissue perfusion. EVALUATION Outcome not met. Within 3 days of nursing care, patient was not able to demonstrate increased perfusion of lower extremities as evidenced by absence of peripheral pulses, and prescence of edema. Vital signs: T: 36. 3C P: 109 bpm R: 30 cpm BP: 110/90 mmHg
Nursing Care Plan Identified problem: Impaired Tissue Integrity Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Tissue Integrity r/t altered fluid status secondary to excess fluid volume. CUES Subjective: nasamad mani siya atong mi hupong ug ayo akong tuo nga tiil, as verbalized by client Objective: Lesion on right foot (epidermis), 1.5cm in diameter, edges white, hard to touch, without pain T: 35.7 C PR:112 bpm RR: 28 cpm BP: 110/80 mmHg OBJECTIVE STO: Within 8 hrs of nursing care, the patient will participate in prevention measures and treatment program such as leaving lesion open to air as much as possible LTO: Within 3 days of nursing care, patient will be able to display progressive improvement on the healing of skin lesion. INTERVENTIONS Discuss importance of early detection and reporting of changes in condition or any unusual physical discomforts/ changes. Record size (depth/width), temperature, texture, consistency of wounds/ lesions. Inspect lesions daily for changes. Promote good nutrition with adequate protein and calorie intake, vitamins/mineral supplements intake. Promote early mobility. Provide position changes, active/ passive and assistive exercises. Practice aseptic technique for cleansing, dressing, medicating lesions. Monitor laboratory studies (CBC and electrolytes). RATIONALE Promotes early detection of developing complications. Provides comparative baseline. Promotes timely intervention. To facilitate healing. EVALUATION Outcome partially met. Within 3 days of care, the patient was able to participate in prevention measure and treatment program such as leaving lesion open to air as much as possible, however, patient was not able to display full progressive improvement on healing of skin lesion. T: 36. 9C P: 104 bpm R: 24 cpm BP: 110/80 mmHg
To promote circulaton and prevent excessive tissue pressure. Reduces risk of cross contamination. For changes indicative of healing/infection/complications.
Nursing Care Plan Identified problem: Impaired gas exchange Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired gas exchange r/t ventilation perfusion imbalance secondary to heart failure. CUES OBJECTIVE INTERVENTIONS Subjective STO: Mag lisud ko ug Within 8 hours of nursing care, Monitor vital signs. ginhawa...nganong usahay kay mo patient will be able to participate in linkod nalang ko, as verbalized by treatment regimen such as Evaluate pulse oximetry to the pt. breathing exercise, effective determine oxygenation. coughing within level of Evaluate vital capacity. Objective: ability/situation. Elevate head of bed/position LTO: Irritability client appropriately, provide Within 3 days of nursing care, Tachycardia (109 bpm) airway adjuncts. patient will be able to demonstrate Diaphoresis Encourage frequent position improved ventilation and adequate Restlessness changes and deep breathing/ oxygenation as evidenced by report coughing exercise. Unstable vital signs: of absence of dyspnea. T: 37. 0C Encourage adequate rest and P: 109 bpm limit activities within client R: 30 cpm tolerance. Promote calm/ BP: 110/90 mmHg restful environment. Encourage client to stop smoking, attend cessation program as necessary.
RATIONALE Provides comparative baseline data. To assess respiratory insufficiency. To maintain airway.
EVALUATION Outcome met. Within 3 days of nursing care, patient was able to demonstrate improved ventilation and adequate oxygenation as evidenced by report of absence of dyspnea. T: 36. 9C P: 104 bpm R: 24 cpm BP: 110/80 mmHg
To promote good lung expansion. Helps limit oxygen needs/consumption. To improve lung function .
Nursing Care Plan Identified problem: Anxiety Nursing Diagnosis: Anxiety r/t shortness of breath and restlessness from inadequate oxygenation. CUES OBJECTIVE INTERVENTIONS Subjective STO: Ambot lang ngano pero dugay Within 8 hours of nursing care, Observe behavior indicative of dyud ko maka tulog sa gabie. As patient will be able to identity level of anxiety. verbalized by the patient. healthy ways to deal with and Note use of drugs (including Objective: express anxiety. alcohol, insomnia, limited LTO: Poor eye contact. avoidance of interactions with Within 3 days of nursing care, Extraneous others.) patient will appear relaxed and movements (hand arm Review coping skills used in report anxiety is reduced to a movements) the past in handling the manageable level as evidenced by Impaired situation. answering questions presented by attention/difficulty the nurse. concentrating Be aware of defense Restlessness Vital signs T: 36.9C P: 104 bpm R: 24 cpm BP: 110/80 mmHg
RATIONALE
EVALUATION Outcome not met. Within 3 days of care, patient did not appear relaxed as evidenced by uninteractive behavior. T: 36. 9C P: 104 bpm R: 24 cpm BP: 110/80 mmHg
It can be a clue to the clients level of anxiety. May be behavioral indicators of use of withdrawal to deal with problems. To determine these that might might be helpful in current circumstances. It may interfere with the ability to deal with the problem. Moderate anxiety heightens awareness and permits the client to focus with dealing with problems. To lessen effect of transmission of feelings.
mechanisms being used (client may be in denial). Assist patient to use anxiety for coping with situation. Provide for non threatening, consistent environment/atmosphere. Minimize stimuli and monitor visitors. Encourage the client to develop and exercise/ activity program. Refer to physician for drug management program/alteration of prescription regimen.
May be helpful in reducing level of anxiety by relieving tension. Drugs often cause symptoms of anxiety (include anticholinergics and dopamine).
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- NCP Heart FailureDocument11 paginiNCP Heart FailureaZhermAine100% (1)
- TLC Leadership Charter School ApplicationDocument132 paginiTLC Leadership Charter School ApplicationAlex Geli100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Altered Level of ConsciousnessDocument8 paginiNursing Care Plan for Altered Level of ConsciousnessJeffrey Dela Cruz50% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Congestive Heart FailureRalph Dumawaa60% (5)
- Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective Therapeutic Regimen Management RelatedDocument3 paginiNursing Diagnosis Ineffective Therapeutic Regimen Management RelatedbizzykenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health and Safety Induction Training SheetDocument2 paginiHealth and Safety Induction Training Sheetnil thaeuÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP: Chronic Renal FailureDocument14 paginiNCP: Chronic Renal FailureJavie77% (13)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument4 paginiNCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionKristine Maghari83% (6)
- Hypertension NCPDocument1 paginăHypertension NCPj4royce100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 paginiDecreased Cardiac Output NCPmicah1318100% (2)
- Excess Fluid Volume - Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - NurseslabsDocument8 paginiExcess Fluid Volume - Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - NurseslabsEricsonMitraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decreased Cardiac Output Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiDecreased Cardiac Output Nursing Care Planjudssalangsang86% (7)
- NCP For Mi PainDocument2 paginiNCP For Mi PainKahMallariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Market Research On Male Grooming IndustryDocument30 paginiMarket Research On Male Grooming IndustryMonalisa SethiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 paginiDecreased Cardiac Output NCPbaba69baba100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument9 paginiDecreased Cardiac OutputRae AnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument9 paginiNCPTracy Camille EscobarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge Deficit Related To HypertensionDocument2 paginiKnowledge Deficit Related To HypertensionChenee Mabulay100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Renal FailureDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan for Acute Renal FailureKian Herrera100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plans For Decreased Cardiac OutputCarmela Balderas Romantco80% (5)
- CAD NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 paginiCAD NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputLeizel Apolonio100% (3)
- NCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 paginiNCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionLeigh Kristel Andrion0% (1)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 paginiNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP For CHFDocument11 paginiNCP For CHFqingwen100% (5)
- A Karl Abraham - A Short Study of The Development of The Libido (1924)Document86 paginiA Karl Abraham - A Short Study of The Development of The Libido (1924)vanpec100% (1)
- NCP For HypertensionDocument4 paginiNCP For HypertensionCiariz Charisse83% (6)
- NoncomplianceDocument3 paginiNoncomplianceChristy BerryÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Altered Heart RateDocument2 paginiNCP - Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Altered Heart RateKian Herrera100% (1)
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 paginiRisk For Decreased Cardiac OutputSid Artemis FriasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument4 paginiIneffective Tissue PerfusionClariz Basco100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputRy Pablo83% (41)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 paginiIneffective Tissue PerfusionClaidelyn De Leyola100% (1)
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 paginiRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output NCPRobby James Rabe100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Management Nursing InterventionsDocument5 paginiFluid Volume Management Nursing InterventionsMerrill HansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poultry and Game Cookery TechniquesDocument38 paginiPoultry and Game Cookery TechniquesCyroz Austria Montibon100% (1)
- Myocarditis NCP 2Document8 paginiMyocarditis NCP 2astro_aaron117375% (4)
- NCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Document3 paginiNCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce100% (3)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaDocument2 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaAce Dioso Tubasco100% (1)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 paginiNCP Excess Fluid VolumeIngrid Nicolas100% (1)
- Gilbert Quizora v. Denholm Crew Management (Phils), Inc.Document2 paginiGilbert Quizora v. Denholm Crew Management (Phils), Inc.poppy2890Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care DeficitDocument5 paginiNCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care DeficitFrances Anne Pasiliao100% (3)
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Nursing Care PlansDocument21 pagini"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Nursing Care PlansCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument21 paginiLiver Cirrhosis NCPJeco Valdez100% (4)
- Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathyDocument2 paginiDecreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To Cardiomyopathywen_pil75% (8)
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocument4 paginiFluid Volume ExcessChristine Quirona100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument5 paginiIneffective Breathing PatternruguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 paginiDecreased Cardiac OutputTiffany Mathis100% (1)
- Knowledge, Attitude and Practices of School Children On Prevention and Control of Superficial Fungal in Western KenyaDocument7 paginiKnowledge, Attitude and Practices of School Children On Prevention and Control of Superficial Fungal in Western KenyaPremier PublishersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For HypertensionFranco Razon100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For CHFDocument7 paginiNursing Care Plan For CHFRosemarie Carpio100% (5)
- NCP Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument3 paginiNCP Rheumatic Heart DiseaseAdrian Mallar71% (28)
- NCP Heart BlockDocument3 paginiNCP Heart BlockEköw Santiago Javier33% (3)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 paginiDecreased Cardiac OutputDheza Rodis Santos0% (1)
- Risk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument5 paginiRisk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionElle Oranza100% (1)
- Care Plan Unstable AnginaDocument4 paginiCare Plan Unstable Anginaالغزال الذهبي50% (6)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 paginiDecreased Cardiac OutputEdrianne J.100% (2)
- NCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceDocument2 paginiNCP For CHF 3 Activity IntoleranceAngelyn ArdinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncp-Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Aortic Stenosis)Document2 paginiNcp-Ineffective Tissue Perfusion (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce67% (3)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 paginiDecreased Cardiac OutputChristine MatasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 paginiIneffective Tissue PerfusionDiane ReyÎncă nu există evaluări
- HyperkalemiaDocument5 paginiHyperkalemiaNolan Cabral50% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 paginiNursing Care PlanAnju Luchmun100% (2)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument2 paginiNCP Activity IntoleranceJill Catherine CabanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 paginiNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYDocument12 paginiCHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYMary Cris CanonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument6 paginiAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivebanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Mrs. MM Nursing Care PlanDocument34 paginiMrs. MM Nursing Care PlanIsobel Mae JacelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home Economics-Household Services "Prepare Hot and Cold Meals/Food" Meal/ Food Preparation Week 2 (1 Quarter)Document2 paginiHome Economics-Household Services "Prepare Hot and Cold Meals/Food" Meal/ Food Preparation Week 2 (1 Quarter)KISHAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biotechnology & Genetic EngineeringDocument16 paginiBiotechnology & Genetic EngineeringMohammed RidzuwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Does Age Matter in A RelationshipDocument3 paginiDoes Age Matter in A RelationshipEdraline LumawigÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 - St. Mary's - December 2020 AdmissionDocument100 pagini4 - St. Mary's - December 2020 AdmissionprashantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Program of Exam - Criminologists Feb 2024Document4 paginiProgram of Exam - Criminologists Feb 2024PRC BaguioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nexium hp7Document30 paginiNexium hp7jcsaraviapazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manguiat, Ciara Loreal M. BSN 1-Y2-5 NCMA 111: Nursing Care PlanDocument3 paginiManguiat, Ciara Loreal M. BSN 1-Y2-5 NCMA 111: Nursing Care PlanCiara ManguiatÎncă nu există evaluări
- How to Cite Patient Safety Incident Reporting SystemDocument7 paginiHow to Cite Patient Safety Incident Reporting System'Amel'AyuRizkyAmeliyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Epidemiology of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 in Asia: Systematic Review, Meta-Analyses, and Meta-RegressionsDocument16 paginiThe Epidemiology of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 in Asia: Systematic Review, Meta-Analyses, and Meta-Regressionsyenny handayani sihiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soal 3 Diagnosis PK 1 LatenDocument12 paginiSoal 3 Diagnosis PK 1 LatenMade SuryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Protocol - Diskwento Caravan - As of Oct 22, 2020Document2 paginiHealth Protocol - Diskwento Caravan - As of Oct 22, 2020Randell ManjarresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consumer preference towards tea consumption in Ahmedabad CityDocument6 paginiConsumer preference towards tea consumption in Ahmedabad CityVrushang MaturkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atp 45 (B)Document287 paginiAtp 45 (B)Samo PecanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interventions For Preventing Falls in People After Stroke (Review)Document68 paginiInterventions For Preventing Falls in People After Stroke (Review)Abdelrhman AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature Review and AbstractDocument6 paginiLiterature Review and Abstractm1dyhuh1jud2100% (1)
- ELIII - Vocabulary List Second TermDocument5 paginiELIII - Vocabulary List Second Termyacantomariana2Încă nu există evaluări
- Standard Operating ProcedureDocument15 paginiStandard Operating Procedureastroval100% (1)
- Emergency Response Plan TemplateDocument4 paginiEmergency Response Plan TemplateDilkhaz HSEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hc3.1. Homeless Population: Definitions and MethodologyDocument12 paginiHc3.1. Homeless Population: Definitions and Methodologypaulscribd1Încă nu există evaluări
- Case 1Document3 paginiCase 1Jeanny Lou Lago-FormosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3B User-Manual BPAP-25A RESmart BMC V1.2 ENG PDFDocument38 pagini3B User-Manual BPAP-25A RESmart BMC V1.2 ENG PDFBasheer AlmetwakelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Health Studyguide Part 1Document39 paginiMental Health Studyguide Part 1Ngoc TB VoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fenugreek Benefits PDFDocument10 paginiFenugreek Benefits PDFrecianzubyÎncă nu există evaluări