Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
MYDRIATIC
Încărcat de
Manik BashaDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MYDRIATIC
Încărcat de
Manik BashaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MYDRIATIC & MIOTIC EFFECT OF DRUGS ON RABBIT'S EYE.
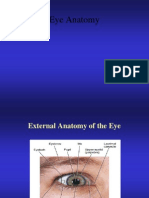
Object To study the mydriatic & miotic effect of topically applied drugs on rabbit's eye. Experimental Animal: Rabbit - (2.5 Kg in wt.) Experimental Requirement; - Torch, Scale (6 small), Cotton, Hair aesthesiometer, Scissors, Dropper, Rabbit holder (cage) Drugs : Normal saline 0.9% Pilocarpine 1-2% Ephedrine 4% Atropine 0.5-1% Phenylepherine 5% Xylocaine 0.5% Principle Local action of a large number of drugs in an eye can be achieved without systematic effect by the application of drugs as eye drops or eye ointment. Most of these drugs belong to antimicrobial, autonomic or local anaesthetic groups. The eye is supplied both by sympathetic & parasympathetic nerves. The iris has two types of muscles 1. Dilator pupillae (radial muscle) 2. Sphincter pupillae (circular muscle) Circular muscle has parasympathetic supply while radial muscle has sympathetic supply. The cilliary muscle is also supplied by parasympathetic nerves & when it contracts, the cilliary body move inwards & forwards. Because of this the lens bulges forwards & eye is accommodated for near vision. The opposite effect is produced by the relaxation of cilliary muscles resulting in paralysis of accommodation (cycloplegia). When the pupil dilates the iris folds back near the opening of the canal of schlemn & the drainage of aquous humour is decreased thereby increasing intraocular pressure and constriction of pupil by opposite action that will increase drainage & reduce intra ocular tension. Topically applied drugs can affect the eye by changing conjunctival congestion, pupillary size, corneal sensitivity & intra ocular pressure. However the effect of drugs on Pupillary size, Light Reflex (L.R.) & Corneal Reflex (C.R) can be studied easily. 1. Pupillary size- Can be measured by placing a transparent plastic scale in front of the eye, as close as possible. 2. LR- Elicited by directing the light of a torch towards the pupil from back. The positive response shows constriction of pupil. 3. Corneal Reflex- Sensitivity of cornea is tested by touching cornea gently with a fine cotton wick/hair aesthesiometer from the side & not from the front of the eye.Positive response show blinking of the eyelids. Physostigmine is a reversible cholenestrase inhibitor which increases the endogenous acetylcholine, this inturn stimulates the circular muscle of iris to produce pupillary constriction without producing loss of light reflex & corneal reflex.
Ephedrine & Phenylephrine- Stimulate the radial muscle of the iris, this produces dilatation of pupil without any effect on light reflex & corneal reflex. Atropine- An antimuscarinic agent, block the effect of endogenously released. ACh in the circular muscle of the iris. This also causes stimulation of ciliary muscle. This produces mydriasis & spasm of accommodation leading to cycloplegia but without producing loss of corneal reflex. Ciliary muscle is present in the eye mainly supplied by parasympathetic nerves & weak sympathetic supply. This is responsible for accommodation. Anticholinergic drugs eg. atropine causes paralysis of ciliary muscle, tightening of suspensory ligaments, the lens is flattened & focal length increases. Eye is fixed for far vision known as 'paralysis of accomodation' or cycloplegia EXPERIMENTAL SET UP (PROCEDURE) One rabbit is used to study the action of one drug. Different rabbits are required to study the action of various drugs. Their eye lashes are trimmed with scissors, as they interfere with elicitation of corneal reflex/conjunctival reflex. Place a rabbit in the rabbit holder box. Keeping its head outside. Observe size of the pupil, LR & CR in both the eyes [examine the LR by holding the torch in front of the eye moving light beam to & fro (from back to front), examine the corneal reflex by touching side of the cornea with horse hair aesthesiometer or cotton wick. One eye of the rabbit is used (RE) as 'control' for the experiment. Instill few drops of normal saline in right eye & atropine(Drug) in left eye (test eye). Record the pupillary size, LR & CR after 10 mins of drug instillation & tabulate the observation Repeat the test with other drugs (pilocarpine, ephedrine etc) OBSERVATION TABLE Drugs Size of Pupil(mm) Light Reflex Corneal Reflex Remarks (inference) Pilocarpine 2% RE LE RE LE RE LE Miotic response is seen causing constriction of pupil, no effect on LR/ CR. could be a Parasympatho-mimatic drug. BABABABABABA 5552PPPPPPPP Atropine 1% 5 5 5 10 P P P Ab P P P p Mydriatic effect is seen i.e. (dilatation of pupil) no change in CR LR is lost. So possibility of parasympa-tholytic drug Ephedrine 4% 5 5 10 P P P P P P P P P Mydriatic effect is seen. CR and LR both remain unaffected. Hence, possibility of a sympathomimetic drug. B- Before drug instillation - P- Present A- After the drug instillation - Ab- Absent Definitions Mydriatics: These are the drugs which causes dilation of the pupil. Miotics: These are the drugs, which produce constriction of the pupil.
Cycloplegic: These are the drugs, which cause loss of the accommodation by casing paralysis of the ciliary muscle. Discussion (Effect of Drugs) Pilocarpine : Is a parasympathomimetic drug. It acts directly. It causes contraction (++) of circular muscle of the iris & leads to decrease in size of pupil (constriction of pupil). Physostigine (Eserine): Is indirectly acting drug it is anticholineterase agent. It decreases the metabolism of ACh. Hence increase the concentration of ACh locally. Thus, causes miosis. (same as parasympathomimetics). Adrenaline /Ephedrine These are sympathomimetic drugs they cause contraction of radial muscle (++) (Ephedrine act indirectly by releasing Adr / NA & causes mydriasis. The light reflex & corneal reflex are not affected by these drugs. Atropine: It is a parasympatholytic drug. It causes paralysis of circular muscles by blocking muscarinic receptors which release ACh. Thus, causing predomination of sympthetic action. There is unopposed action on radial muscles this produces mydriasis and there is loss of accomodation (cycloplegia) & light reflex, due to action on cilliary ganglion. Advantages of the Experiment 1. To study the effects of drugs on ANS (eye) 2. Also to screen the drugs for surface anaesthesia. Clinical relevance 1. Miotic effect of physostigmine is useful in glaucoma as drainage of aquous humor is facilitated resulting into decrease in I.O.P. 2. Short acting mydriatic effect of phenylepherine is used in fundoscopy, where topical anticholinergic (mydiatrics) are avoided. 3. Topical effect of xylocaine is used to produce surface anaesthesia for minor local surgery eg. Foreign body removal, symptomatic relief of corneal/ conjunctival irritation. 4. Atropine is used for fundoscopy & to provide rest to the iris, e.g. in iritis 5. To counteract the mydriatic & cycloplegic effect miotics are used. Miotic effect of phystostigmine is used in glaucoma as the drainage of aquous humor is facilitated & decrease in I.O.P occurs Phenylepherine is short acting and not causing cycloplegia. Hence, often preferred over atropine and its substitutes specially in elderly. MYDRIATIC AND MIOTICS (VIVA-VOCE QUESTIONS) Q. 1 What are mydriatics? Name some mydriatic agents
Ans. Those drugs which cause dilatation of pupil, are called mydratics. The commonly used mydriatics are a. Atropine - Having slow and long lasting action. b. Homatropine - less potent than atropine short duration of action c. Cyclopentolate, tropicamide. d. Sympathomimetics ephedrine, adrenaline, phenylepherine. Q. 2 Discuss the mechanism of mydriasis, what do you understand by Active mydrasis and Passive mydriasis ? Ans. There are two types of muscles present in the iris a) Dilator pupillae or radial muscle, is supplied by both and and receptors innervated by sympathetic nerves. b) Sphinctor pupillae or circular muscle, it is having muscarinic cholinergic receptor innervated by parasympathetic nerves. Topical instillation of sympathemimetic in the eye causes stimulation of radial muscle of iris and causes mydriasis because there is constriction of muscle, it is called 'active mydriasis' this is not associated with cycloplegia. When anti cholinergic drugs, like atropine instilled locally in the eye it causes paralysis of circular muscle of the iris and there is unopposed action of dilator pupillae or radial muscles. This causes dilation of pupil this is called 'passive mydriasis' because it is caused by paralysis of muscle. This is associated with cycloplegia. Q. 3 What is cycloplegia? Ans : Mydriasis caused by atropine is associated with paralysis of circular muscle. This produces tightening of the suspensory ligament, resulting in flattening of lens with a consequent increase in the focal length of the lens. Thus, the individual is able to see things clearly only at a long distance due to fixing of lens for far vision. He is unable to constrict the pupil due to paralysis of circular muscle for viewing of near objects or in response to bright light (photophobia) this phenomenon is known as loss of accomodation or cycloplegia. Q.4 Name some drugs which produces mydriasis with cycloplegia? Ans. Sympathomimetics, viz. adrenaline, phenylepherine, cyclopentolete (less cycloplegia). Q. 5 Name mydriatic agent which preferred in children? Ans. Atropine and homatropine. Q.6 Name mydriate agent in elderly Ans Phenylepherine, tropicamide, sympathomimetics. Q. 7 Why atropine is not preferred in elderly? Ans. Because of aging process elderly have shallow anterior chamber of eye. So, when we use atropine it causes mydriasis with cycloplegia it may precipitate glaucoma. Also it may cause systemic adverse effects, e.g retention of urine. Q. 8 Why atropine substitue are preferred over atropine? Ans. Mydriasis caused by atropine is long lasting. Also it causes cycloplegia. Some times it may cause severe adverse effects if absorbs systemically specially, in children. So, atropine substitutes are
preferred over atropine. Q. 9 Can cocaine is used for opthalmic purpose? Ans. Cocaine is a local anaesthetic agent causes mydriasis due to a receptor action. It is not used for this action purpose because it causes corneal necrosis. Also it is a drug of abuse and leads to strong psychological dependence. It also stimulate CNS Other systemic effects are seen like rise in BP, tachycardia, etc. Q. 10 Enumerate the therapeutic uses of mydriatics ? Ans (a) For the refraction and others ophthalmic examinations like retinoscopy fundoscopy. (b) To break adhesion between iris and cornea or iris and lens, used alternatively with miotics. (c) In inflammatory conditions of eye to relieve pain. C/I of mydriatics Glaucoma Q. 11 What are miotics? Name some miotic agents. Ans. Those drugs which cause constriction of pupil are called miotics. Commonly used miotics are : Pilocarpine occusert Phystostigmine, neostingmine Carbachol a- adrenergic antagonist. Adrenergeric neuron blockers Demcarium is the longest acting miotic but not used clinically because it accelerate the development of cataract. Pilocarpene (occusert) is available now as (long DDS). Q. 12 What is the mechanism of action of miotics? Ans. Topical instillation of parasympathomimetic drug in the eye stimulates circular Muscle of the iris and causes miosis. Q. 13 What is glaucoma? Name drugs used in glaucoma Ans. Increase in I.O.T. is known as glaucoma (>19mm Hg). In Acute narrow angle. Glaucoma. 1. Timolol topical b - blocker 2. Miotics pilocarpine 3. Hypertonic mannitol 4. Acetazolamide In chronic angle glaucoma 1. b- Blocker Timolol 2. Miotics 3. a - adrenergic agonist Dipivefrine 4. Acetazolamide Mechanism of Action of drugs used in glaucoma Miotics Increase the tone of cilliary muscle and sphinctor pupilae thus facilitate the flow of aq. humour. But short acting so fluctuation in I.O.T is common. b blockers no fluctuation/ no change in size of pupil, no induced myopia, no headache but causes systemic adverse effects e.g. bronchospasm; bradycardia, CHF specially, in elderly. a - adr agonist increase aq outflow, increase aq formation e.g. Dipivefrine is a prodrug of adrenaline, longer and consistent action used as adjuvant to miotics or b blockers.
Betaxolol b1 selective antagonist, less effective and few adverse effects. Q. 14. What are the advantages and disadvantages of b blockers used in glaucoma? Ans. Discussed in mechanism of action. Q. 15 Name the drug which produces miosis by central action? Ans: Morphine Q. 16 Will morphine produce miosis when applied locally in the eye? Ans. No, because morphine causes miosis due to its action on E.P nucleus of 3rd cranial nerve which is its central action. Morphine does not have local miotic action. Q. 17 Enumerate therapeutic uses of miotics? Miotics are used in the treatment of glaucoma Alternatively with mydratics, they are used to prevent adhesions or to break adhesion in iritis. To counteract the mydriatic effect of atropine and others.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Dose Adjustment in Renal and Hepatic FailureDocument27 paginiDose Adjustment in Renal and Hepatic Failurevanita100% (1)
- Eye Pathology An Atlas and TextDocument697 paginiEye Pathology An Atlas and TextEric Wong100% (3)
- Pharmaceutical Care Plan and Documentaion of Pharmacotherapy Intervention (MTM)Document67 paginiPharmaceutical Care Plan and Documentaion of Pharmacotherapy Intervention (MTM)CAROL ANN PATITICOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of PK in Clinical SitutionDocument42 paginiApplication of PK in Clinical Situtionsafia mehmood100% (1)
- Antihyperlipidemic AgentsDocument79 paginiAntihyperlipidemic AgentsKishori Kedia100% (1)
- Toxicokinetic PDFDocument29 paginiToxicokinetic PDFKirush MitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring: RVS Chaitanya KoppalaDocument33 paginiTherapeutic Drug Monitoring: RVS Chaitanya KoppalaDr. Raghavendra Kumar GundaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical PharmacologDocument81 paginiClinical PharmacologSHILOTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The EyeDocument18 paginiIntroduction To The EyeJúnior Alves100% (1)
- The EyeDocument22 paginiThe Eyeapi-309893409Încă nu există evaluări
- Frcophth 400 Sbas and CrqsDocument262 paginiFrcophth 400 Sbas and CrqsZaheer Ullah Soleh100% (1)
- Pharmacokinetics AbsorptionDocument27 paginiPharmacokinetics AbsorptionchondroboraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics 1Document92 paginiChapter 1 Introduction To Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics 1Marc Alamo100% (2)
- Clinical PharmacokineticsDocument31 paginiClinical PharmacokineticsArdiyanti Puspitasari100% (1)
- Principles of Pharmacology Chapter 1Document37 paginiPrinciples of Pharmacology Chapter 1Muhammad ZakriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sulfonamides: By: Dr. Shruthi Rammohan Final Year PG Pharmacology RRMCHDocument45 paginiSulfonamides: By: Dr. Shruthi Rammohan Final Year PG Pharmacology RRMCHAli Veer Ali VeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal HandlingDocument28 paginiAnimal Handlinglovehope100% (1)
- AntiemeticsDocument10 paginiAntiemeticsnk999999100% (1)
- Fundamentals of PharmacyDocument66 paginiFundamentals of PharmacyLHYRA KATHLEEN LOPEZ100% (1)
- 4-Pharmacokinetics IDocument88 pagini4-Pharmacokinetics IMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Încă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacotherapeutics 140828123349 Phpapp02Document14 paginiPharmacotherapeutics 140828123349 Phpapp02Anonymous s9i0WyKF200% (1)
- Text Book Vision SceinciesDocument316 paginiText Book Vision SceinciesCarpetali GatitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacotherapeutics UNIT1Document44 paginiPharmacotherapeutics UNIT1Bharti ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4-Drug Delivery Systems (Autosaved)Document41 pagini4-Drug Delivery Systems (Autosaved)Chelle PaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyDocument55 paginiIntroduction To Autonomic PharmacologyMuammar Alfarouq100% (1)
- Experimental PharmacologyDocument72 paginiExperimental Pharmacologythamizh555100% (4)
- Glaucoma PPT For Final YearDocument57 paginiGlaucoma PPT For Final YearDarshan SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transes PharmacodynamicsDocument36 paginiTranses PharmacodynamicsGwyneth Koleen Lopez100% (1)
- 9autacoids 14010v9023022 Phpapp02Document109 pagini9autacoids 14010v9023022 Phpapp02h3cn1r3100% (1)
- Past Exam PaperDocument5 paginiPast Exam PaperDavid Le50% (2)
- Dr. Ruth NamyaloDocument62 paginiDr. Ruth NamyaloHarun MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- PharmacologyDocument57 paginiPharmacologyarun231187Încă nu există evaluări
- 5E Lesson PlanDocument14 pagini5E Lesson PlanAdrianJake ManayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acetylcholine Stimulates Muscle Contraction in Guinea Pig Ileum and Atropine Diminishes The Extent of ContractionDocument2 paginiAcetylcholine Stimulates Muscle Contraction in Guinea Pig Ileum and Atropine Diminishes The Extent of Contractionleh.mo931580% (5)
- AtropineDocument14 paginiAtropineKrazygopa BalorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experimental PharmacologyDocument20 paginiExperimental PharmacologyMarcha Debby SaraswatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology Practical Manual - Student Copy2Document11 paginiPharmacology Practical Manual - Student Copy2NareshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To PharmacologyDocument28 paginiIntroduction To Pharmacologynadar shahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bp503t Pcol Unit-IIIDocument38 paginiBp503t Pcol Unit-IIIAakkkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical 1-Far 161-FinishDocument10 paginiPractical 1-Far 161-FinishZulkifli Khairuddin100% (1)
- Cholinergic and AnticholinergicDocument77 paginiCholinergic and Anticholinergicsweta sumanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autocoids and Their AntagonistsDocument19 paginiAutocoids and Their AntagonistsHossein Sehati100% (1)
- Antiplatelet and Thrombolytic DrugsDocument48 paginiAntiplatelet and Thrombolytic DrugsNofa PuspitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit I General PharmacologyDocument16 paginiUnit I General PharmacologycuolyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organ Bath ReportDocument13 paginiOrgan Bath ReportYusri Yusoff100% (1)
- Experimental Pharmacology (PDFDrive)Document168 paginiExperimental Pharmacology (PDFDrive)Priya MohiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spectro ParacetamolDocument5 paginiSpectro ParacetamolAdang FirmansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Clinical PharmacyDocument32 paginiIntroduction To Clinical PharmacySuhail Ahmed SahitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1 PharmacoDocument3 paginiExperiment 1 PharmacoNur NabilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction PharmaceuticsDocument9 paginiIntroduction PharmaceuticsVIJAY KUMAR TIRUKKACHIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biopharmaceutics and PharmacokineticDocument4 paginiBiopharmaceutics and PharmacokineticRiyaz AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bronchodilator & Other Drugs Used in AsthmaDocument15 paginiBronchodilator & Other Drugs Used in AsthmaGenta JagadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Answer of PharmacologyDocument45 paginiFinal Answer of Pharmacologynidhhu100% (1)
- Drugs Affecting Myometrium1 PDFDocument9 paginiDrugs Affecting Myometrium1 PDFЛариса ТкачеваÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacotherapy of HTNDocument57 paginiPharmacotherapy of HTNAbera JamboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument75 paginiLecture 1 PDFBasil Elbushra Ahmed DomiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mouse Handling Techniques PacketDocument24 paginiMouse Handling Techniques PacketLovely Ann AyapanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nuclear Receptors 2006Document31 paginiNuclear Receptors 2006lsintaningtyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharma 1.2 - Pharmacokinetics (Wini Ong) PDFDocument11 paginiPharma 1.2 - Pharmacokinetics (Wini Ong) PDFVon Javier GamateroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology of Insulin and It'S AnaloguesDocument31 paginiPharmacology of Insulin and It'S AnaloguesVikas VikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protein Synthesis InhibitorsDocument25 paginiProtein Synthesis InhibitorsSawsan Z. JwaiedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Utilisation Evaluation: Keerthana.N 1 Year M.Pharm Dept. of Pharmacy Practice Grace College of PharmacyDocument28 paginiDrug Utilisation Evaluation: Keerthana.N 1 Year M.Pharm Dept. of Pharmacy Practice Grace College of PharmacykeerthanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Serotonin (5-HT)Document35 paginiSerotonin (5-HT)adeesasaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology of The GITDocument31 paginiPharmacology of The GITmarviecute22Încă nu există evaluări
- 1-Introduction To Pharmacology of Cardiovascular Drugs 0ct10Document12 pagini1-Introduction To Pharmacology of Cardiovascular Drugs 0ct10Idrissou FmsbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Pharmacy Benchmarking Guideline 2011Document33 paginiCommunity Pharmacy Benchmarking Guideline 2011omer tariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument32 paginiCholinergic DrugsApt FianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingDe la EverandMechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingH. RaškováÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zhu2012 - Eye AnatomyDocument9 paginiZhu2012 - Eye Anatomytobing704Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of EyeDocument19 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of Eyeashwini priyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Drugs Acting On The Eye - OkeDocument42 pagini1 Drugs Acting On The Eye - OkeSintia AyuningsihÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 AccommodationDocument18 pagini3 AccommodationJiyaa PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cyclorefraction 171008103447Document38 paginiCyclorefraction 171008103447Sayoki GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eye PharmacologyDocument23 paginiEye Pharmacologyغادة وائلÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Pharmacology of Drugs Acting On The Eye (Updated)Document22 pagini2 - Pharmacology of Drugs Acting On The Eye (Updated)loubnarymÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ocular Embryology With Special Reference To Chamber Angle DevelopmentDocument2 paginiOcular Embryology With Special Reference To Chamber Angle DevelopmentnabilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uveal TractDocument56 paginiUveal Tractmaf manÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pemeriksaan Refraksi Sikloplegik Pada AnakDocument38 paginiPemeriksaan Refraksi Sikloplegik Pada AnakTia AfelitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of The EyeDocument4 paginiAssessment of The EyeAira Nicole ROMASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eye AnatomyDocument21 paginiEye AnatomyHammad afzal100% (2)
- #05 Autonomic Pharmacology v2Document122 pagini#05 Autonomic Pharmacology v2tasnemaldaherÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOBRAMYCINDocument2 paginiTOBRAMYCINKhristle DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ocular Pharmacology PDFDocument54 paginiOcular Pharmacology PDFbenny christantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cholinomimetic DrugsDocument44 paginiCholinomimetic DrugsMohamed Abdi Baffo100% (1)
- Anatomy Slides Answer 28Document18 paginiAnatomy Slides Answer 28SriKavya DevineniÎncă nu există evaluări
- BNS 200 Drugs and The EyeDocument36 paginiBNS 200 Drugs and The EyeAnthony MoepengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Devices-Physio Eye PresentationDocument37 paginiMedical Devices-Physio Eye PresentationPharmacy Admission ExpertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visual Pathway: With Dr. Craig CanbyDocument28 paginiVisual Pathway: With Dr. Craig CanbyNicole YatawaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- MYDRIATICDocument6 paginiMYDRIATICManik BashaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ocular AnatomyDocument56 paginiOcular AnatomyJulianto KeceÎncă nu există evaluări