Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Review Transport System Taylor
Încărcat de
Paola MontenegroDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Review Transport System Taylor
Încărcat de
Paola MontenegroDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Essential Biology 06: 6.
2 The Transport System
Digested food molecules are carried in the blood around the body. 1. Other than digested food molecules, what other substances are transported in the blood? Respiratory gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide), hormones secreted by endocrine glands, waste material, and ions 2. What are the functions of the following components of blood: Plasma: Excrete waste products, carrying nutrients for cell metabolism, transport hormones, containing antibodies and clotting agents. Platelets: Maintenance of clot formation. Erythrocytes: Carry oxygen to all the body cells. Leukocytes: Prevent the spreading of disease. This includes protection from pathogens, bacteria, viruses as the killing of cancerous cells. 3. Draw and label a simple diagram of the heart showing: Right and left atria and ventricles, atrio-ventricular and semi-lunar valves, aorta, pulmonary artey, pulmonary vein, vena cava and cardiac muscle.
Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com
Bandung International School
Essential Biology 06: 6.2 The Transport System
Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com
Bandung International School
Essential Biology 06: 6.2 The Transport System
4. Where is the cardiac muscle thickest? Why? In the left ventricle. Because it because it needs to pump blood to most of the body systemic (while the right ventricle fills only the lungs pulmonary). Distinguish between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Oxygenated blood is with oxygen. Deoxygenated blood has no oxygen. Oxygenated is found in arteries like the Aorta. Deoxygenated blood is found in the veins.
5.
6. Outline the journey of a single red blood cell taking one full circuit of the transport system, starting and finishing at the liver. You could use a flow chart/cycle for this. The red blood cell goes from the liver out the portal vein to the inferior vena cava to the right side of the heart (right atrium, then right ventricle) to the pulmonary artery to the lung, back via the pulmonary vein to the left side of the heart (left atrium and then the left ventricle), out the aorta through to the right iliac artery, then the right femoral artery into the right legs. Between the arteries and the veins are smaller arteries and veins and capillaries. And then it goes back to the heart through the veins and the cycle repeats. Why is the flow of blood described as double circulation? Because it contains the pulmonary system and the systemic system. (Pulmonary going to the lungs only, and Systemic going through the rest of the body). What is a myocyte? A muscle cell. Explain the myogenic origin of the heartbeat. Myogenic heart has a pacemaker system. There is a pacemaker of specialized cardiac muscle located in the right auricle. It sends an impulse which goes to the AV node and then to the bundle of HIs and Purkinje fibres to complete a cardiac cycle.
7.
8.
9.
10. Name and label the parts of the heart
responsible for initiation and propagation of the heart beat. The SA and AV nodes.
Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com
Bandung International School
Essential Biology 06: 6.2 The Transport System
11. What is meant by the term indefatigable?
That it is persistently tireless.
12. Complete a flow chart to show how heart rate changes with exercise. Include the roles of the blood, medulla oblongata, nerves, SA node and the Vagus nerve.
13. What is the effect of the hormone adrenalin? It increases the heart rate as it dilates the blood vessels and air passages. Also as air passages are dilated, it allows for more oxygen to be breathed in at one time; thus providing the body with more energy, and similarly allowing more Carbon Dioxide 14. Compare the structure and functions of these blood vessels: Artery Capillary Vein
Diagram (labeled, cross section)
Function
Transport blood out of the heart.
Allow the diffusion of gases, nutrients, and wastes between plasma and other fluids.
Transport blood back to the heart.
Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com
Bandung International School
Essential Biology 06: 6.2 The Transport System
Travels How is structure related to function? From heart Thick, more pumping potential Through tissue More surface area, faster process To heart Thin, less pumping potential
Stephen Taylor http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com
Bandung International School
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 paginiCirculatory SystemYusuf AzeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCLEX LabValues CheatSheetDocument2 paginiNCLEX LabValues CheatSheetOlrac Agairdam100% (1)
- Biology - Circulatory System Notes 1Document13 paginiBiology - Circulatory System Notes 1archit.kulkarni7756Încă nu există evaluări
- Mammary Gland Development - Methods and Protocols PDFDocument357 paginiMammary Gland Development - Methods and Protocols PDFMihaela FloreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NeuroSensory ExamsDocument26 paginiNeuroSensory Examsquidditch07100% (1)
- Guidelines FCPS Part 1Document27 paginiGuidelines FCPS Part 1Dr Dileep Kumar Khatri100% (3)
- Biodanza and ParkinsonDocument4 paginiBiodanza and ParkinsonAndreaKószóÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System Q&A.Document77 paginiCirculatory System Q&A.Alyasin FrougaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document3 pagini1NathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 42 Reading GuideDocument5 paginiChapter 42 Reading GuideCaleb SchantzÎncă nu există evaluări
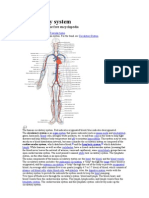
- Circulatory System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 paginiCirculatory System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBruce WayneÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO2 - 4.04 - ANIMAL GAS EXCHANGE AND CIRCULATION (v.2023 WITH VITAL SIGN MONITORING)Document80 paginiBIO2 - 4.04 - ANIMAL GAS EXCHANGE AND CIRCULATION (v.2023 WITH VITAL SIGN MONITORING)MARKIEL JUSTINE DOMOSMOGÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are The Circulatory System Parts?Document5 paginiWhat Are The Circulatory System Parts?Quốc Thái TrươngÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Long Fontanel Last For Babycirculatory SystemDocument8 paginiHow Long Fontanel Last For Babycirculatory SystemRoszana RafliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organ System Amino Acids Electrolytes Blood Cells PH HomeostasisDocument25 paginiOrgan System Amino Acids Electrolytes Blood Cells PH HomeostasismilkosmalcolmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System: Sir Jayr TaroyDocument30 paginiCirculatory System: Sir Jayr TaroyDelfin Jr UrbanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sistem Peredaran DarahDocument4 paginiSistem Peredaran DarahIndah SariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 paginiCardiovascular SystemAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Anp2001 Test 1 Questions 2014Document7 paginiAnp2001 Test 1 Questions 2014Jerilee SoCute WattsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete - SLASh - Science9 - Week 1 and 2Document5 paginiComplete - SLASh - Science9 - Week 1 and 2Creative ImpressionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument6 paginiCirculatory SystemRatiram LilhareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report Exp 4Document13 paginiLab Report Exp 4NURUL AIHAN AHMAD HILMIÎncă nu există evaluări
- KS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2Document15 paginiKS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2f72ktyd78nÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument12 paginiCirculatory SystemDipanshu JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport SystemDocument14 paginiTransport SystemAkiela JohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular System Lecture 1 2020 2021Document5 paginiCardiovascular System Lecture 1 2020 2021olawandeilo123Încă nu există evaluări
- B SC 4 Sem BiotechHuman Phy Heart by DR Santosh ThakurDocument10 paginiB SC 4 Sem BiotechHuman Phy Heart by DR Santosh ThakurMicaela Marcela Baldwin BarrigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnaPhy Rot. 5johnDocument2 paginiAnaPhy Rot. 5johnJohn Emmanuel RevilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kami Export - Circulatory System Study Questions WorksheetDocument2 paginiKami Export - Circulatory System Study Questions WorksheetEshrat TushyÎncă nu există evaluări
- I. ConclusionDocument1 paginăI. ConclusionJARISSA DIZON GALLAZAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Circulatory SystemDocument8 paginiBlood Circulatory SystemstephanietoppoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 paginiCirculatory SystemMahamad BakrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 paginiCardiovascular SystemDhea BugnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular System: Iii. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 paginiCardiovascular System: Iii. Anatomy and PhysiologyYam Bite-Size FabelloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory Word OfficeDocument6 paginiCirculatory Word OfficeMaria Christina CaceresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Transport 2015Document6 paginiAnimal Transport 2015Jacob ZumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Sum CH 3Document5 paginiBio Sum CH 3Thijmen van de VrieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anaphy Cardio XIIDocument15 paginiAnaphy Cardio XIIRue Cheng MaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Science Part 2Document21 paginiMedical Science Part 2Gauge FalkÎncă nu există evaluări
- M10 Myself - JawapanDocument4 paginiM10 Myself - JawapanSteven OwenÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 paginiAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLuis WashingtonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 Human Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFDocument27 pagini07 Human Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFJohn DeHans100% (2)
- Transport in HumansDocument8 paginiTransport in HumansRaima QaiserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Circulation and Transport: Prepared By: PN - Tan Seoah Chee SMK Desa Skudai 2010Document61 paginiBlood Circulation and Transport: Prepared By: PN - Tan Seoah Chee SMK Desa Skudai 2010lccjane8504100% (1)
- Transport Systems Objective 2-1Document4 paginiTransport Systems Objective 2-1darielleollivierreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 paginiCirculatory SystemSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System: VocabularyDocument4 paginiRespiratory System: VocabularyFely NatadÎncă nu există evaluări
- About The Circulatry System 001Document46 paginiAbout The Circulatry System 001gaboelgaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.2 Transport in HumansDocument11 pagini5.2 Transport in Humans박찬우Încă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System Vascular TissueDocument8 paginiCirculatory System Vascular TissueDrSachin SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation NotesDocument12 paginiTransportation NotesavanishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventricle and Atria), Have Different Blood VesselsDocument5 paginiVentricle and Atria), Have Different Blood VesselsAnastasia MartynenkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument17 paginiCardiopulmonary ResuscitationRisavina Dorothy CondorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument71 paginiCirculatory SystemAnas Mustafa HashmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHP 05 (Blood and Circulation) DrRiyadAhmed PC 3Document69 paginiCHP 05 (Blood and Circulation) DrRiyadAhmed PC 3Kamrun NaherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 paginiCirculatory SystemWisdom DzombeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory SystemDocument5 paginiCirculatory Systemkashaf bhuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart Structure and Blood Circulation Pathways in AnimalsDocument8 paginiHeart Structure and Blood Circulation Pathways in AnimalsKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vascular SystemDocument20 paginiVascular SystemHama HamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper English Cardiovascular System: Compiled By: Group IVDocument9 paginiPaper English Cardiovascular System: Compiled By: Group IVSuryantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CirculatoryDocument9 paginiCirculatoryJason Vinluan Carinan100% (1)
- Cardiovascular System: Halabja Technical College of Applied SciencesDocument6 paginiCardiovascular System: Halabja Technical College of Applied SciencesELYANÎncă nu există evaluări
- CirculatoryDocument8 paginiCirculatoryKristel Faye DioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Minggu 13 Peredaran DarahDocument11 paginiMinggu 13 Peredaran Darahcuksam27Încă nu există evaluări
- 0610 s14 QP 13Document16 pagini0610 s14 QP 13hosni_syr50% (2)
- A Study On The Correlation of ABO Blood Group System and HypertensionDocument4 paginiA Study On The Correlation of ABO Blood Group System and HypertensionHema SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Paper +1ANNUALDocument5 paginiPhysical Paper +1ANNUALprabhnoorprimeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Meena Pole RoundsDocument2 paginiDr. Meena Pole RoundsaashishÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Three-Dimensional Digital Insertion Guide For Palatal Miniscrew PlacementDocument11 paginiA Three-Dimensional Digital Insertion Guide For Palatal Miniscrew Placementjorge florÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrocardiogram - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument16 paginiElectrocardiogram - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRaJeev K SookunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caregiving 12 Module 1 4th QuarterDocument23 paginiCaregiving 12 Module 1 4th QuarterBethuel AlquirozÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELC550 ANS KEY - 22january2019-VettedDocument3 paginiELC550 ANS KEY - 22january2019-VettedCtÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArtikelDocument9 paginiArtikelArkan Nuriel ErizalyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education and Psychological Test Scores: Indian J. Psychiat. (1980) - 22, 179-181Document3 paginiEducation and Psychological Test Scores: Indian J. Psychiat. (1980) - 22, 179-181John PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aiml Assignment 1Document6 paginiAiml Assignment 1charaninamadarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questionnaire On The Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices Towards COVID-19Document4 paginiQuestionnaire On The Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices Towards COVID-19Mae GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- RoPE Score CalculatorDocument1 paginăRoPE Score CalculatorEliza PopaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EssayDocument5 paginiEssayBM1-0620 Sem Shu HuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Map Health 7Document11 paginiCurriculum Map Health 7Mary Kryss DG SangleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colorectal AdenocarcinomaDocument48 paginiColorectal Adenocarcinomamingchuan chuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of The Body: Teacher: Miss Nataly Oñate GDocument8 paginiParts of The Body: Teacher: Miss Nataly Oñate Gcarmen gloriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accu-Chek 360 View ToolDocument2 paginiAccu-Chek 360 View Toolsayang12155100% (1)
- Chapter 4: Modifiable Risk Factors of Lifestyle DiseasesDocument64 paginiChapter 4: Modifiable Risk Factors of Lifestyle DiseasesJemah AnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study On The Evaluation of Oral Rehabilitation Using Dental Implant by Qantifying Osteoprotegerin and InterleukinDocument7 paginiStudy On The Evaluation of Oral Rehabilitation Using Dental Implant by Qantifying Osteoprotegerin and InterleukinNordsci ConferenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 5 13B: End Stage Renal Failure Secondary To Diabetes NephropathyDocument68 paginiGroup 5 13B: End Stage Renal Failure Secondary To Diabetes NephropathyJinski007100% (1)
- Antibacterial, Phytochemical and Antioxidant Activities of The Leaf Extracts of Gliricidia Sepium and Spathodea CampanulataDocument8 paginiAntibacterial, Phytochemical and Antioxidant Activities of The Leaf Extracts of Gliricidia Sepium and Spathodea CampanulataEloísaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemostasis Specimen Collection and HandlingDocument5 paginiHemostasis Specimen Collection and HandlingDENILLE AIRA NOGOYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dokumen - Pub - Feldenkrais Australia Journal 3 VisionDocument36 paginiDokumen - Pub - Feldenkrais Australia Journal 3 VisionGeorge NicolaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Naskah Role Play Citra Dan ElaADocument3 paginiNaskah Role Play Citra Dan ElaA0072Putu ElaÎncă nu există evaluări