Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pneumonia With Dehydration
Încărcat de
Sam ParkTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pneumonia With Dehydration
Încărcat de
Sam ParkDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
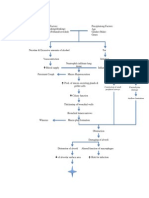
Chapter 6
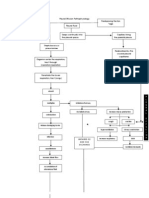
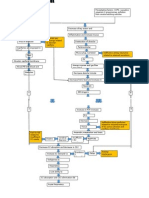
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Predisposing Factor
Age (7 y/o)
Precipitating Factor
Poor Diet Atmospheric Pollutants
Risk Factor
Asthmatic Patient IgE Stimulation Mast cell Degranulation Asthma attacks
Streptococcus Pneunoniae
Gain access to the center of the respiratory tract through Inspiration or aspiration
Activation of defense mechanism Lose effectiveness of defense mechanism Penetrate the LRT (lungs) Multiply Impaired mucocilary reaction
Colonization begins Release of damaging toxin
Exudates from Bacteria Erodes the lungs Inflammation
Irritation of airway
Increase goblet cell
airway
Occluded airway
Increase mucus production
Vasodilation
Occluded Airway
Mucus become increasingly viscous
Increase blood flow Dead space happened Cough Plasma and carbohydrates rich fluid leakage Increase respiratory Crackles Airway constriction DOB
Accumulation of edematous fluid
Impaired O2 and CO2 exchange
Inflamed & fluid filled alveolar sacs
Increase airway resistance
Decrease CO2
Respiratory muscle works harder
Lung consolidation
Muscle fatigue & exhaustion
Hypoxia Body malaise Decrease Fluid intake Excessive sweating
Fluid Volume deficit Dehydration Loss of fluid and electrolyte Impaired thirst sensation Hypomagnesemia
Malabsorption process disorder Impaired absorption of
Hypophosphatemia
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Common Health ProblemDocument36 paginiCommon Health ProblemAmanda ScarletÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atelectasis, (Lung Collapse) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related DiseasesDe la EverandAtelectasis, (Lung Collapse) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related DiseasesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiCap PathophysiologyNoriel Henricks Acuna100% (3)
- COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)Document8 paginiCOPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)Emily Anne86% (7)
- NP1 Nursing Board Exam December 2006 Answer Key OKDocument13 paginiNP1 Nursing Board Exam December 2006 Answer Key OKSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPD Case PresentationDocument15 paginiCOPD Case PresentationBola Kwentua29% (7)
- Copd 200412082048Document139 paginiCopd 200412082048Richard ArceÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPDDocument52 paginiCOPDSoySauceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandRespiratory Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breath Holding TimesDocument28 paginiBreath Holding TimesReina RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPDDocument73 paginiCOPDBroken OreosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document32 paginiChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)matrixtrinityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study PneumoniaDocument13 paginiCase Study Pneumonialavparedes93% (44)
- Pathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureDocument2 paginiPathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureKimberly Regacho88% (8)
- A Simple Guide to the Asthma and Lung DiseasesDe la EverandA Simple Guide to the Asthma and Lung DiseasesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Pathophysiology Copd-ChfDocument2 paginiPathophysiology Copd-ChfZaira Batalo100% (2)
- IX: Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorsDocument2 paginiIX: Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorsCandace AlcarazÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Mechanics of Inhaled Pharmaceutical Aerosols: An IntroductionDe la EverandThe Mechanics of Inhaled Pharmaceutical Aerosols: An IntroductionÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPD PTDocument49 paginiCOPD PTSathish RathnamÎncă nu există evaluări
- CopdDocument51 paginiCopdFretzie Anne Gonzales Gomez100% (2)
- Nursing Research (Word)Document26 paginiNursing Research (Word)Sam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument18 paginiCOPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseemilliansÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Simple Guide to Hypoxemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDe la EverandA Simple Guide to Hypoxemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 24 Management of Patients With Chronic Pulmonary DisordersDocument3 paginiChapter 24 Management of Patients With Chronic Pulmonary DisordersPeej Reyes100% (1)
- Nursing Practice IDocument17 paginiNursing Practice Istuffednurse100% (2)
- Laporan Pendahuluan Ppok (Penyakit Paru Obstruktif Kronik)Document20 paginiLaporan Pendahuluan Ppok (Penyakit Paru Obstruktif Kronik)angler jiggingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure: For EMT ProvidersDocument44 paginiContinuous Positive Airway Pressure: For EMT ProvidersYabetsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CopdDocument54 paginiCopdHerty FeliciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study 5 (Respiratory) - COPDDocument6 paginiCase Study 5 (Respiratory) - COPDSamantha AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument2 paginiPa Tho PhysiologyBobbie SisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- AsthmaDocument6 paginiAsthmaJay Hipulan QuiranteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Order 2763068Document9 paginiOrder 2763068skylineco4Încă nu există evaluări
- COPD Treatment and ManagementDocument3 paginiCOPD Treatment and ManagementHydie Mae AlcabedosÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPD Case StudyDocument10 paginiCOPD Case Studyskylineco4Încă nu există evaluări
- Obstructive LunDocument10 paginiObstructive Lunabenezer isayasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Donna Skurat Spring 212Document14 paginiDonna Skurat Spring 212siscasepangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respi. DistressDocument2 paginiRespi. DistressDorothy Joy CumigadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predisposing FactorDocument2 paginiPredisposing FactorEm Hernandez AranaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of COPD - The BasicsDocument11 paginiPathophysiology of COPD - The BasicstiaranindyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Onchi & CopdDocument8 paginiOnchi & CopdAngellene GraceÎncă nu există evaluări
- STUDY QUESTIONS in RespirationDocument3 paginiSTUDY QUESTIONS in Respirationshallonngabirano29Încă nu există evaluări
- COPD & RLDDocument17 paginiCOPD & RLDhis.thunder122Încă nu există evaluări
- Mostafa 33 2Document12 paginiMostafa 33 2Ahmed AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kuliah PPOK - JamurDocument79 paginiKuliah PPOK - Jamurmarshella brendaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmunary DiseaseDocument39 paginiChronic Obstructive Pulmunary DiseaseshaitabliganÎncă nu există evaluări
- PN21 Health and Healing - Pre-Class Activities - Test 2 PDFDocument33 paginiPN21 Health and Healing - Pre-Class Activities - Test 2 PDFRachel HomesÎncă nu există evaluări
- CopdDocument4 paginiCopdapi-3739910100% (2)
- Respiration CH 43.Dr SarahDocument59 paginiRespiration CH 43.Dr Sarahaiman siddiquiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower Respiratory Disorders Part 1Document70 paginiLower Respiratory Disorders Part 1Joseph Krafft100% (1)
- COPD and AsthmaDocument47 paginiCOPD and AsthmaLaiza DonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breathlessness EdittedDocument2 paginiBreathlessness EdittedSalwani MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Mntforpulmonarydiseases 120228022846 Phpapp02Document75 pagini1 Mntforpulmonarydiseases 120228022846 Phpapp02Faisal AliÎncă nu există evaluări
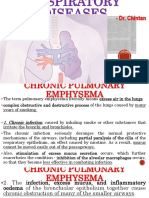
- Dr. ChintanDocument26 paginiDr. ChintanArshad KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aging Changes in The Body and Their Effects On Their Respiratory FunctionsDocument3 paginiAging Changes in The Body and Their Effects On Their Respiratory FunctionsDawnmurph Dharlene Wag-eÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuberculosis: Lifestyle (Smoking) Environment Age GenderDocument2 paginiTuberculosis: Lifestyle (Smoking) Environment Age GenderhannahleatanosornÎncă nu există evaluări
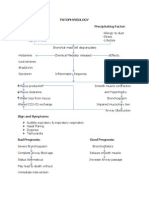
- Patophysiology Predisposing Factor: - Genetic - Race - Age (3-8 Y/o)Document1 paginăPatophysiology Predisposing Factor: - Genetic - Race - Age (3-8 Y/o)Ejie Boy IsagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease REVISEDDocument37 paginiCOPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease REVISEDSonny AgultoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analisis Kasus COPD KMBDocument36 paginiAnalisis Kasus COPD KMBTHERESA SETIAWANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease .: Swathi Swaroopa. BDocument29 paginiChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease .: Swathi Swaroopa. BKavya sriÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPD Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing COPD Symptoms, With Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanDe la EverandCOPD Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing COPD Symptoms, With Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardio Vascular DiseasesDocument34 paginiCardio Vascular DiseasesSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Published On May 13Document1 paginăPublished On May 13Sam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Health Care LawsDocument8 paginiPhilippine Health Care LawsSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Health Care LawsDocument8 paginiPhilippine Health Care LawsSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- IV Solution Cheat SheetDocument1 paginăIV Solution Cheat SheetSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRC Requirements in Filing For The NLEDocument2 paginiPRC Requirements in Filing For The NLESam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma Care PlanDocument3 paginiAsthma Care PlanSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardio Vascular DiseasesDocument34 paginiCardio Vascular DiseasesSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- NursingDocument1 paginăNursingSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burns ResportDocument5 paginiBurns ResportSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Name of The Biggest Part of The Human BrainDocument2 paginiWhat Is The Name of The Biggest Part of The Human BrainSam Park100% (1)
- Asthma Care PlanDocument3 paginiAsthma Care PlanSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defense Mechanism of PhobiaDocument9 paginiDefense Mechanism of PhobiaSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlveolusDocument1 paginăAlveolusSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disaster and Multicasualty NursingDocument9 paginiDisaster and Multicasualty NursingSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter1 5Document26 paginiChapter1 5Sam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Name of The Biggest Part of The Human BrainDocument2 paginiWhat Is The Name of The Biggest Part of The Human BrainSam Park100% (1)
- Nursing AuditDocument7 paginiNursing AuditSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Name of The Biggest Part of The Human BrainDocument2 paginiWhat Is The Name of The Biggest Part of The Human BrainSam Park100% (1)
- Clinical ManifestationDocument7 paginiClinical ManifestationSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poison 1Document1 paginăPoison 1Sam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- ExamDocument2 paginiExamSam ParkÎncă nu există evaluări