Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Refrigeration Cycle EES
Încărcat de
Alper OrakDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Refrigeration Cycle EES
Încărcat de
Alper OrakDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
File:C:\EES32\USERLIB\EXAMPLES\Refrig.ees 15.12.2011 02:37:03 Page 1 EES Ver. 6.
883: #434: For use only by Kwangil Kim of Samsung Electronics Co. 1163 [kPa] 48 [C] 55,12 [C]
Condenser
3 Valve 4
20 [C]
1 Evaporator
566,8 [kPa] 20 [C]
Compressor
Calculate
"!Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle" "This problem demonstrates the use of the built-in refrigerant property tables for calculating the performance of a simple refrigeration cycle." {Select Solve Table from the Parametrics menu (or F3) to produce a table of Coefficient of Performance (COP) vs Evaporator temperature (T[1]). A plot of the COP vs T[1] can be viewed in the Plot window.} {Plot Window 2 shows a P-h plot for R12 with the refrigeration cycle state points for T[1]=10 C superimposed. This plot was constructed by setting T[1]=10 in the equations window. The Solve command calculates the state point information and places it in the Arrays Window. A P-h plot for R12 was generated using the Property Plot command in the Plot menu. Then the Overlay Plot command was used to plot the P vs h state point information in the Arrays window.} R$='R12' "! Compressor" x[1]=1 P[1]=pressure(R$;T=T[1];x=x[1]) h[1]=enthalpy(R$;T=T[1];x=x[1]) s[1]=entropy(R$;T=T[1];x=x[1]) P[2]=pressure(R$;T=T[3];x=0) h_2_ID=ENTHALPY(R$;P=P[2];s=s[1]) W_c_ID=(h_2_ID-h[1]) Eff=0,8 W_c=W_c_ID/Eff h[2]=h[1]+W_c s[2]=entropy(R$;h=h[2];P=P[2]) T[2]=temperature(R$;h=h[2];P=P[2]) "string variable used to hold name of refrigerant" "assume inlet to be saturated vapor" "properties for state 1"
"this is the pressure in the condenser" "ID for ideal identifies state as isentropic" "energy balance on isentropic compressor" "Isentropic efficiency" "definition of compressor isentropic efficiency" "energy balance on real compressor-assumed adiabatic" "properties for state 2"
"!Condenser" T[3]=48 [C] "known temperature of sat'd liquid at condenser outlet" P[3]=P[2] "neglect pressure drops across condenser" h[3]=enthalpy(R$;T=T[3];x=0) "properties for state 3" s[3]=entropy(R$;T=T[3];x=0) Q_Con=h[2]-h[3] "energy balance on condenser" "!Valve" h[4]=h[3] x[4]=quality(R$;h=h[4];P=P[4]) s[4]=entropy(R$;h=h[4];P=P[4]) T[4]=temperature(R$;h=h[4];P=P[4]) "!Evaporator" P[4]=P[1] Q_Evap=h[1]-h[4]
"energy balance on throttle - isenthalpic" "properties for state 4"
"[kPa] neglect pressure drop across evaporator" "[kJ/kg] energy balance on evaporator"
File:C:\EES32\USERLIB\EXAMPLES\Refrig.ees 15.12.2011 02:37:03 Page 2 EES Ver. 6.883: #434: For use only by Kwangil Kim of Samsung Electronics Co.
COP=abs(Q_Evap/W_c) $TabWidth 2 cm Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle
"definition of COP"
This problem demonstrates the use of the built-in refrigerant property tables for calculating the performance of a simple refrigeration cycle. R$ = 'R12' Compressor x1 P1 h1 s1 P2 h 2;ID W c;ID = 1 assume inlet to be saturated vapor properties for state 1 string variable used to hold name of refrigerant
= P R$ ; T = T 1 ; x = x 1 = h R$ ; T = T 1 ; x = x 1 = s R$ ; T = T 1 ; x = x 1 = P R$ ; T = T 3 ; x = 0 = h R$ ; P = P 2 ; s = s 1 = h 2;ID h 1
this is the pressure in the condenser ID for ideal identifies state as isentropic
energy balance on isentropic compressor
Eff = 0,8
Isentropic efficiency
Wc = h2 s2 T2
W c;ID Eff
definition of compressor isentropic efficiency energy balance on real compressor-assumed adiabatic properties for state 2
= h1 + W c
= s R$ ; h = h 2 ; P = P 2 = T R$ ; h = h 2 ; P = P 2
Condenser T3 P3 h3 s3 = 48 = P2 [C] known temperature of sat'd liquid at condenser outlet neglect pressure drops across condenser properties for state 3
= h R$ ; T = T 3 ; x = 0 = s R$ ; T = T 3 ; x = 0 = h2 h3
Q Con Valve h4 x4 s4 T4
energy balance on condenser
= h3
energy balance on throttle - isenthalpic properties for state 4
= x R$ ; h = h 4 ; P = P 4 = s R$ ; h = h 4 ; P = P 4 = T R$ ; h = h 4 ; P = P 4
Evaporator
File:C:\EES32\USERLIB\EXAMPLES\Refrig.ees 15.12.2011 02:37:03 Page 3 EES Ver. 6.883: #434: For use only by Kwangil Kim of Samsung Electronics Co.
P4
= P1
[kPa] neglect pressure drop across evaporator [kJ/kg] energy balance on evaporator
Q Evap COP =
= h1 h4 Q Evap Wc
definition of COP
Unit Settings: [kJ]/[C]/[kPa]/[kg]/[degrees] COP = 7,123 QCon = 128,8 [kJ/kg] W c = 15,86 [kJ/kg]
Parametric Table: Table 1 T1 COP QEvap
Eff = 0,8 QEvap = 113 [kJ/kg] W c,ID = 12,69 [kJ/kg]
h2,ID = 208,5 [kJ/kg] R$ = 'R12'
[C] Run 1 Run 2 Run 3 Run 4 Run 5 10 12 14 16 20 4,864 5,214 5,606 6,048 7,123
[kJ/kg] 108,9 109,7 110,6 111,4 113
104
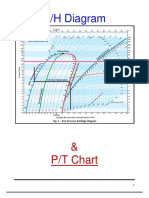
Location of state points on P-h plot for T1=10 C
103
48 C 10 C
P [kPa]
102 101 0
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
225
h [kJ/kg]
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Mec 2405 - Thermodynamics (Refrigeration Report)Document15 paginiMec 2405 - Thermodynamics (Refrigeration Report)Sean ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 4 Combined Convection and RadiationDocument3 paginiExp 4 Combined Convection and RadiationHaitham S Khouri50% (2)
- Assignment 12Document7 paginiAssignment 12Anonymous mqIqN5zÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examples of Psychrometric Calculations For Summer and WinterDocument50 paginiExamples of Psychrometric Calculations For Summer and WinterlakshminarayananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edoc - Pub 318849347 Solution Manual To Principles of HeatingDocument233 paginiEdoc - Pub 318849347 Solution Manual To Principles of HeatingЕрнесто Юниор Барриентос Баусел100% (1)
- Full Report Heat PumpDocument8 paginiFull Report Heat PumpFhaliesha ZakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example1. Air at 12°C DBT and 85% RH Is To Be Brought To 36°C DBT and 23.2°C WBTDocument33 paginiExample1. Air at 12°C DBT and 85% RH Is To Be Brought To 36°C DBT and 23.2°C WBTAhmed QasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Code For Cooling Load CalculationDocument8 paginiMatlab Code For Cooling Load CalculationKidus yared100% (1)
- Vapour Compression Refrigeration Test RigDocument1 paginăVapour Compression Refrigeration Test RigPawan NkÎncă nu există evaluări
- EES ReportDocument12 paginiEES ReportJoseph Samir FaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1 RefrigerationDocument4 paginiExperiment 1 RefrigerationErlangga Sulaiman Razak100% (1)
- Energy Balance - HumidificationDocument13 paginiEnergy Balance - Humidificationnhalieza1067Încă nu există evaluări
- Methods of Improving COP of Refrigeration CycleDocument18 paginiMethods of Improving COP of Refrigeration CycleGanesh Shewale100% (2)
- Heat TransferDocument121 paginiHeat TransferGirinda BayuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 7 PowerCyclesDocument12 paginiCH 7 PowerCyclescarleston thurgoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Exchanger Sample Report 2018Document55 paginiHeat Exchanger Sample Report 2018RahulSrivastava100% (1)
- Cooling Systems in IC Engines: Prepared By: Hardeep Singh MannDocument14 paginiCooling Systems in IC Engines: Prepared By: Hardeep Singh MannLokesh RajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brayton CycleDocument5 paginiBrayton CycleAnonymous yorzHjDBd100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Refrigeration CyclesDocument20 paginiChapter 11 Refrigeration Cycleskalite123Încă nu există evaluări
- Refrigeration CycleDocument85 paginiRefrigeration CycleNeha MiracleÎncă nu există evaluări
- M8 - Vapor Absorption RefrDocument29 paginiM8 - Vapor Absorption RefrAbraham KhaleedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 7. Heating and Cooling Load CalculationsDocument44 paginiLecture 7. Heating and Cooling Load Calculationsaddisudagne63% (8)
- Cooling With Dehumidification PDFDocument9 paginiCooling With Dehumidification PDFKevin TsuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Double Pipe Heat Exchanger ExperimentDocument7 paginiDouble Pipe Heat Exchanger ExperimentBenedicta Monis100% (1)
- Heat Exchangers ReportDocument16 paginiHeat Exchangers Report刘羿村Încă nu există evaluări
- Pressure EnthalpyDocument9 paginiPressure Enthalpypunk cmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 7: Solved ProblemsDocument15 paginiModule 7: Solved Problemscaptainhass67% (6)
- Heat Exchanger - Effectiveness - NTU MethodDocument15 paginiHeat Exchanger - Effectiveness - NTU MethodhendiyrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 Refrigerating Machine Reversed Carnot Cycle Simple Vapor Compression CycleDocument14 paginiLecture 1 Refrigerating Machine Reversed Carnot Cycle Simple Vapor Compression CycleDeniell Joyce MarquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vapour Compression Refrigeration PDFDocument5 paginiVapour Compression Refrigeration PDFjose100% (1)
- Lecture 3. Refrigeration Cycles 2Document37 paginiLecture 3. Refrigeration Cycles 2addisudagneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To EES PDFDocument18 paginiIntroduction To EES PDFMohammad Mustafa AkbariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Capillary Tube Length On The Vcrs Performance: Experiment No. (1) Mechanical LabDocument15 paginiEffect of Capillary Tube Length On The Vcrs Performance: Experiment No. (1) Mechanical LabDilshad S FaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 2Document19 paginiExperiment 2Dilshad S FaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat and Mass Transfer NotesDocument48 paginiHeat and Mass Transfer Notessanthanam102Încă nu există evaluări
- SBS5311 1718 07-Refrigeration PDFDocument66 paginiSBS5311 1718 07-Refrigeration PDFRatnin PanityingÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of SymbolsDocument4 paginiList of Symbolstotoq51Încă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam Review ProblemsDocument9 paginiFinal Exam Review ProblemsalvinchuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 1 - Refrigeration UnitDocument33 paginiExp 1 - Refrigeration UnitastigeÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Zakho College of Engineering Mechanical DepartmentDocument22 paginiUniversity of Zakho College of Engineering Mechanical DepartmentDilshad S FaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture-17: Multi-Stage Vapour Compression Refrigeration SystemsDocument13 paginiLecture-17: Multi-Stage Vapour Compression Refrigeration SystemsMuhaamad TiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Cycle BraytonDocument15 paginiBasic Cycle BraytonMarin Andreea100% (1)
- Design of Cooling TowerDocument4 paginiDesign of Cooling TowerHadis ShojaeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigeration Test RigDocument7 paginiRefrigeration Test Rigshibin874141100% (1)
- University of Zakho College of Engineering Mechanical DepartmentDocument14 paginiUniversity of Zakho College of Engineering Mechanical DepartmentDilshad S FaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Convection Heat Transfer CoefficientDocument3 paginiConvection Heat Transfer CoefficientGerry LouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Window - Air - Conditioning - Test - Rig Lab ManualDocument6 paginiWindow - Air - Conditioning - Test - Rig Lab ManualSandeep SainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEET310 - Refrigeration System - Research PaperDocument41 paginiMEET310 - Refrigeration System - Research Paperpipeds100% (1)
- Vapour Compression RefrigerationDocument38 paginiVapour Compression RefrigerationArvind75% (4)
- Heat Transfer and Mass Sheets FinalDocument22 paginiHeat Transfer and Mass Sheets FinalMahmuod Abdalrahman100% (1)
- Fanno FlowDocument30 paginiFanno FlowAitizaz KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 External ConvectionDocument68 paginiChapter 4 External Convectionpvr2k1Încă nu există evaluări
- AC 6edDocument375 paginiAC 6ed김호Încă nu există evaluări
- Static Regain Method NEWDocument6 paginiStatic Regain Method NEWMarzookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eesy Solutions: Engineering Equation Solver NewsletterDocument8 paginiEesy Solutions: Engineering Equation Solver NewsletterFarman AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me313 Notes Chapter10Document28 paginiMe313 Notes Chapter10PajhmanAwghanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omestic Refrigerator: StatementDocument4 paginiOmestic Refrigerator: StatementHoracio RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brayton Cycle (Cold Air Standard) : Instructions Sample ProblemDocument4 paginiBrayton Cycle (Cold Air Standard) : Instructions Sample Problembincoleto5536Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual EBMV3103Document13 paginiLab Manual EBMV3103VOON KIN ONNÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03-Gas Compression FundamentalsDocument28 pagini03-Gas Compression Fundamentalssyahrieza100% (1)
- ERGA04-08DVA Capheat 3D112789D ENDocument1 paginăERGA04-08DVA Capheat 3D112789D ENPeter TitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- R19 - Mech - VI - HVACR - Sample Question BankDocument6 paginiR19 - Mech - VI - HVACR - Sample Question BankSailee AcharekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arshad Siddiqui: HighlightsDocument3 paginiArshad Siddiqui: HighlightsMuhammad FaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panasonic R134a SF SeriesDocument4 paginiPanasonic R134a SF SeriesChan Gel YasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.DB Flats (1-7) & SMDB TypicalDocument9 pagini4.DB Flats (1-7) & SMDB TypicalhpzenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fan Sizing VENTILATIONDocument1 paginăFan Sizing VENTILATIONArun KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 Mazda 6 Grand Touring 2.5LDocument88 pagini2015 Mazda 6 Grand Touring 2.5LData JuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 Vapour Compression Refrigeration System 1Document18 paginiLecture 2 Vapour Compression Refrigeration System 1Meftah ElfituriÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIDEA UGRADJENO Air Cooled Chillers 50Hz 20131216 PDFDocument39 paginiMIDEA UGRADJENO Air Cooled Chillers 50Hz 20131216 PDFDragisa DjukicÎncă nu există evaluări
- صياتة اجهزة التكييف الموحدDocument64 paginiصياتة اجهزة التكييف الموحدoth369Încă nu există evaluări
- Free Match Light Commercial IndoorsDocument30 paginiFree Match Light Commercial Indoorscmorley5057Încă nu există evaluări
- Danx Pool enDocument68 paginiDanx Pool enenzo scifoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC07 - 4x2 Merged MergedDocument4 paginiAC07 - 4x2 Merged MergedHaris YusoffÎncă nu există evaluări
- HVAC Control SystemDocument111 paginiHVAC Control Systemjvfcv100% (1)
- 102 Ac Amc EstimateDocument23 pagini102 Ac Amc Estimatevenkatesh bitraÎncă nu există evaluări
- ResistanceDocument13 paginiResistanceMaheshk GowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dokumen - Tips - Incalzire Cu Pompe de CalduraDocument34 paginiDokumen - Tips - Incalzire Cu Pompe de CalduraPitique De TarencriqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- KDK Exhaust FanDocument6 paginiKDK Exhaust FanATMANEGARA TV100% (1)
- PricelistDocument57 paginiPricelistalex guzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Fire and Smoke Damper Installations - NFPADocument9 paginiBasics of Fire and Smoke Damper Installations - NFPAumerÎncă nu există evaluări
- VVT System VentilationDocument9 paginiVVT System Ventilationenlightened1718Încă nu există evaluări
- HVAC Systems 13: VentilatingDocument2 paginiHVAC Systems 13: VentilatingrohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chiller SelectionDocument2 paginiChiller Selectionrize1159Încă nu există evaluări
- Catalogo Tecnico Split Ducto Baja SiluetaDocument120 paginiCatalogo Tecnico Split Ducto Baja SiluetaPavlo Rodriguex100% (2)
- Evaporative CoolingDocument68 paginiEvaporative Coolingshivas34regal100% (1)
- AIRCON - Powerpoint PresentationDocument64 paginiAIRCON - Powerpoint PresentationAnonymous zMXgZVEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Munir Ahmad Muhammad Shafi Shad Driver License Light Vehicle (Manual)Document3 paginiMunir Ahmad Muhammad Shafi Shad Driver License Light Vehicle (Manual)AtiqSayalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 200VLD-H SS No EconomizerDocument2 pagini200VLD-H SS No EconomizerAnas ElwakilÎncă nu există evaluări