Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
IQ Correction
Încărcat de
srinivasnaik1989Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
IQ Correction
Încărcat de
srinivasnaik1989Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
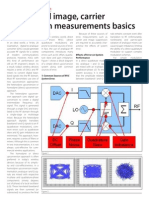
Effects of IQ Imbalance A low cost implementation of OFDM physical layers is challenging for taking acco unt of impairments associated
with the analog components .There are mainly two d ifferent receiver architectures utilized when the received radio frequency (RF) signal is downconverted to baseband. One is the direct conversion RF receiver wi th its potential for low cost and low power implementation on silicon, and the o ther one is the super-hetrodyne receiver .The direct conversion structure is int roduced by popular zero intermediate frequency. Although the structure rejectio n filter ,disadvantages are accompanied such as DC offset ,IQ imbalance,etc The direct down conversion to baseband is implemented by what is known as co mplex down conversion,as shown in fig1 ,It is an attractive scheme ,since it avo ids costly IF filters and allows for easier integration than the super heterodyn e structure. A complex down-converter basically multiplies the RF signal by the complex waveform, where is the local oscillator frequency at the receiver .To p erform the complex down-conversion ,both of the sine and cosine waveforms are r equired .As seen in Fig.1,in-phase ,quadrature-phase ,and two multipliers are re quired to perform the complex down conversion ,where is the amplitude param eter of amplitude imbalance .Furthermore , the receiver is divided into I a nd Q branches .The key is that the effective sine and cosine waveform at the r eceiver preforming the down-conversion need to be orthogonal , i.e., exactly w ith phase difference and with the same amplitude .Any mismatch between the proc essing performed on the overall IQ imbalance in the system and can significantl y affect the system performance .Effects of IQ Imbalance A low cost implementation of OFDM physical layers is challenging for taking acco unt of impairments associated with the analog components .There are mainly two d ifferent receiver architectures utilized when the received radio frequency (RF) signal is downconverted to baseband. One is the direct conversion RF receiver wi th its potential for low cost and low power implementation on silicon, and the o ther one is the super-hetrodyne receiver .The direct conversion structure is int roduced by popular zero intermediate frequency. Although the structure rejectio n filter ,disadvantages are accompanied such as DC offset ,IQ imbalance,etc The direct down conversion to baseband is implemented by what is known as co mplex down conversion,as shown in fig1 ,It is an attractive scheme ,since it avo ids costly IF filters and allows for easier integration than the super heterodyn e structure. A complex down-converter basically multiplies the RF signal by the complex waveform, where is the local oscillator frequency at the receiver .To p erform the complex down-conversion ,both of the sine and cosine waveforms are r equired .As seen in Fig.1,in-phase ,quadrature-phase ,and two multipliers are re quired to perform the complex down conversion ,where is the amplitude param eter of amplitude imbalance .Furthermore , the receiver is divided into I a nd Q branches .The key is that the effective sine and cosine waveform at the r eceiver preforming the down-conversion need to be orthogonal , i.e., exactly w ith phase difference and with the same amplitude .Any mismatch between the proc essing performed on the overall IQ imbalance in the system and can significantl y affect the system performance .
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Key Issues in RF and RFIC Circuit Design PDFDocument405 paginiKey Issues in RF and RFIC Circuit Design PDFDorothy KirbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Half-Bridge LLC Resonant Converter Design Using FSFR-Series Fairchild Power Switch (FPS™)Document17 paginiHalf-Bridge LLC Resonant Converter Design Using FSFR-Series Fairchild Power Switch (FPS™)ihsanjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of A 1 Volt, 1.86 MW Folded-Cascode Even Harmonic Mixer With DC Offset AnalysisDocument11 paginiDesign of A 1 Volt, 1.86 MW Folded-Cascode Even Harmonic Mixer With DC Offset AnalysisRajen Kumar PatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Fiber Link Radio Expansion System For Weak Reception AreaDocument5 paginiOptical Fiber Link Radio Expansion System For Weak Reception AreaFreddyJaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Space Optics ResearchDocument6 paginiFree Space Optics ResearchRF_RAJAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Efficient Supply Modulator For Wide-Band Envelope Elimination and Restoration Power AmplifiersDocument5 paginiEfficient Supply Modulator For Wide-Band Envelope Elimination and Restoration Power Amplifiersgaurav bhargavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fairchild AnDocument17 paginiFairchild AnhvhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buck or Boost Tracking Power ConverterDocument4 paginiBuck or Boost Tracking Power ConverterBishoo ShenoudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Considerations For An LLC Resonant ConverterDocument9 paginiDesign Considerations For An LLC Resonant ConverterBOLFRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct RF Sampling Mixer With Recursive Filtering in Charge DomainDocument4 paginiDirect RF Sampling Mixer With Recursive Filtering in Charge DomainBinod AdhikariÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC8491 CT Notes Full - by WWW - EasyEngineering.net 4 PDFDocument152 paginiEC8491 CT Notes Full - by WWW - EasyEngineering.net 4 PDFvijay kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FairchildDocument17 paginiFairchildshounakroyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lem In2000 Paper v4b SroDocument9 paginiLem In2000 Paper v4b SromarinkokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active Capacitor Multiplier PDFDocument7 paginiActive Capacitor Multiplier PDFTridentBhattÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Isolated Series Resonant Converter For PV Application: Manalan108@gmailcomDocument4 paginiAn Isolated Series Resonant Converter For PV Application: Manalan108@gmailcomRaja SajinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conference-201410-Shahzad-LLC Series Resonant Converter With PID Controller For Battery Charging ApplicationDocument6 paginiConference-201410-Shahzad-LLC Series Resonant Converter With PID Controller For Battery Charging ApplicationTocean DuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis PLLDocument44 paginiThesis PLLrah0987Încă nu există evaluări
- HFE1103 RaabPart4 PDFDocument7 paginiHFE1103 RaabPart4 PDFtrc_wmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decentralized Control Strategy For Input-Series-Output-Parallel Modular LLC Resonant DC/DC ConvertersDocument5 paginiDecentralized Control Strategy For Input-Series-Output-Parallel Modular LLC Resonant DC/DC ConvertersRaja ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reduction of Electromagnetic Interference in DC-DC Converter Using ChaosDocument4 paginiReduction of Electromagnetic Interference in DC-DC Converter Using ChaosPrasenjit WakodeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synopsis VCO BDCoEDocument9 paginiSynopsis VCO BDCoEraymar2kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Considerations For Direct-Conversion Receivers: Behzad RazaviDocument8 paginiDesign Considerations For Direct-Conversion Receivers: Behzad RazaviLupusVorgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Harvester Design For Semi-Passive UHF RFID Tag Using A Tunable Impedance TransformationDocument5 paginiPower Harvester Design For Semi-Passive UHF RFID Tag Using A Tunable Impedance TransformationM AÎncă nu există evaluări
- State-Space Modelling of LLC Resonant Half-BridgeDocument10 paginiState-Space Modelling of LLC Resonant Half-BridgeSung Ryoung LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- An IC For Linearizing RF Power Amplifiers Using Envelope Elimination and RestorationDocument7 paginiAn IC For Linearizing RF Power Amplifiers Using Envelope Elimination and Restorationgaurav bhargavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ieee Transactions On Industrial Electron PDFDocument12 paginiIeee Transactions On Industrial Electron PDF李漢祥Încă nu există evaluări
- Emi PapaerDocument12 paginiEmi PapaerMohit SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Modular Single-Phase Power-Factor-Correction Scheme With A Harmonic Filtering FunctionDocument8 paginiA Modular Single-Phase Power-Factor-Correction Scheme With A Harmonic Filtering FunctionhkaruvathilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baluns For Microwave Applications PDFDocument19 paginiBaluns For Microwave Applications PDFAgus SantosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WCEL05 Cutillon Mateo Ocampo Short Paper PDFDocument6 paginiWCEL05 Cutillon Mateo Ocampo Short Paper PDFarmel mateoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atta I Anese 2009Document8 paginiAtta I Anese 2009Adolfo Valdez BahenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Differences Between Receiver Types Part 2Document4 paginiThe Differences Between Receiver Types Part 2abdessalem_tÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transient Control and Soft Start-Up For 1-MHz LLC Converter With Wide Input Voltage Range Using Simplified Optimal Trajectory ControlDocument14 paginiTransient Control and Soft Start-Up For 1-MHz LLC Converter With Wide Input Voltage Range Using Simplified Optimal Trajectory Controltj.lin1024Încă nu există evaluări
- Direct Conversion Radio Transceivers For Digital CommunicationsDocument12 paginiDirect Conversion Radio Transceivers For Digital CommunicationsA. VillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eeiol 2008sep15 RFD Test Ta 01Document3 paginiEeiol 2008sep15 RFD Test Ta 01Jojo ManaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of A 2.4 GHZ High-Performance Up-Conversion Mixer With Current Mirror TopologyDocument6 paginiDesign of A 2.4 GHZ High-Performance Up-Conversion Mixer With Current Mirror TopologyAkhendra KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Fixed Frequency Zero-Voltage-Switching On-Board EV ChargerDocument9 paginiA Fixed Frequency Zero-Voltage-Switching On-Board EV Chargeraravind chukliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal Jpe 7-1 1597982850Document8 paginiJournal Jpe 7-1 1597982850Lê Trần Bích HằngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Very FastDocument6 paginiAnalysis of Very FastFelipe BittarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eliminating Ground Current in A Transformerless Photovoltaic ApplicationDocument8 paginiEliminating Ground Current in A Transformerless Photovoltaic ApplicationKarim EfthuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3Ghz 7Ghz Fast-Hopping Frequency Synthesizer For Uwb: SandnerDocument5 pagini3Ghz 7Ghz Fast-Hopping Frequency Synthesizer For Uwb: Sandnerengr_mohsinÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Integrated I-Q Mixer For Software-Defined Radio ApplicationsDocument5 paginiAn Integrated I-Q Mixer For Software-Defined Radio Applicationsarunkr1Încă nu există evaluări
- Vetec 1992 245460Document4 paginiVetec 1992 245460tedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequency Tracking Burst-Mode PDM-controlled Class-D Zero Voltage Soft-Switching Resonant Converter For Inductive Power Transfer ApplicationsDocument8 paginiFrequency Tracking Burst-Mode PDM-controlled Class-D Zero Voltage Soft-Switching Resonant Converter For Inductive Power Transfer ApplicationsLuis Alfonso Martinez FdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 A Low-Power Low-Noise Amplifier For EEG ECG Signal Recording ApplicationsDocument4 pagini12 A Low-Power Low-Noise Amplifier For EEG ECG Signal Recording ApplicationsViplaw KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation and Analysis of LLC Resonant Converter Using Closed Loop PI ControllerDocument3 paginiSimulation and Analysis of LLC Resonant Converter Using Closed Loop PI ControllerijaertÎncă nu există evaluări
- RF MEMS Devices and Applications: Jung-Mu Kim Ignacio Llamas-GarroDocument4 paginiRF MEMS Devices and Applications: Jung-Mu Kim Ignacio Llamas-GarroSalvador SierraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.5 A Quadrature Relaxation Oscillator With A Process-Induced Frequency-Error Compensation LoopDocument3 pagini5.5 A Quadrature Relaxation Oscillator With A Process-Induced Frequency-Error Compensation Loopeng_abdelghany1979Încă nu există evaluări
- An-721 Impedance Matching Networks Applied To RF Power TransistorsDocument16 paginiAn-721 Impedance Matching Networks Applied To RF Power TransistorsEdward YanezÎncă nu există evaluări
- (International Journal of Electronics and Telecommunications) A 5 DBM 400MHz OOK Transmitter For Wireless Medical ApplicationDocument6 pagini(International Journal of Electronics and Telecommunications) A 5 DBM 400MHz OOK Transmitter For Wireless Medical Applicationjohn8880Încă nu există evaluări
- A Single-Chip 2.4Ghz Low-Power Cmos Receiver and Transmitter For Wpan ApplicationsDocument4 paginiA Single-Chip 2.4Ghz Low-Power Cmos Receiver and Transmitter For Wpan ApplicationsBhumika SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Robust RF-MEMS Phase Shifters in Ka-BandDocument13 paginiDesign of Robust RF-MEMS Phase Shifters in Ka-Bandloga rajesh waranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Six-Port Modulator Based RF Transmission System Application in An OFDM EnviromentDocument6 paginiSix-Port Modulator Based RF Transmission System Application in An OFDM EnviromentWalter Santiago Campos ArandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PV MPPT With Inductor PDFDocument7 paginiPV MPPT With Inductor PDFrajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- High-Frequency-Fed Unity Power-Factor AC-DC Power Converter With One Switching Per CycleDocument9 paginiHigh-Frequency-Fed Unity Power-Factor AC-DC Power Converter With One Switching Per CycleDeep ShikhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resumo 75133Document10 paginiResumo 75133biswajitntpcÎncă nu există evaluări
- RF ImpairmentsDocument6 paginiRF ImpairmentsinduÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Hybrid Modulation Method For Single-Stage Soft-Switching Inverter Based On Series Resonant Converter PDFDocument12 paginiA Hybrid Modulation Method For Single-Stage Soft-Switching Inverter Based On Series Resonant Converter PDFwangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Încă nu există evaluări
- 2.mil-Std-461e and FDocument100 pagini2.mil-Std-461e and Fmuvin236Încă nu există evaluări
- Microwave Antenna 2016Document353 paginiMicrowave Antenna 2016Андрей КузьминÎncă nu există evaluări
- B02760 PCC CellreselDocument4 paginiB02760 PCC CellreselRuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM Generation SlidesDocument7 paginiFM Generation SlidesJunaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec7105-Microwave EngineeringDocument9 paginiEc7105-Microwave EngineeringKushal GellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antenna Splitter For Broadcast and 144 MHZDocument4 paginiAntenna Splitter For Broadcast and 144 MHZJosé Devidé FilhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Umwd 06516 XD PDFDocument3 paginiUmwd 06516 XD PDFceca89Încă nu există evaluări
- A Practical Approach To Spectrum Analyzing Unit Using RTL-SDRDocument10 paginiA Practical Approach To Spectrum Analyzing Unit Using RTL-SDRstanpjames2309Încă nu există evaluări
- Report - Planar Transmission LinesDocument9 paginiReport - Planar Transmission LinesAmeer AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- E 412 F 04 Lec 13Document19 paginiE 412 F 04 Lec 13Vedran IbrahimovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tsel Lte Omc GuidelineDocument35 paginiTsel Lte Omc GuidelineKuda BetinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microstrip Antenna Design For Ultra-Wide Band ApplicationsDocument4 paginiMicrostrip Antenna Design For Ultra-Wide Band ApplicationsinventionjournalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toko DielectricDocument5 paginiToko DielectricRati GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- R Rec F.636 3Document4 paginiR Rec F.636 3neerajgvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Communication Engineering: Lavish Bagga 18105128Document17 paginiAssignment Communication Engineering: Lavish Bagga 18105128Anonymous Xw1jpCpV5gÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap2011 Assignment 10Document2 paginiAp2011 Assignment 10MertKarahan0% (1)
- Gmrs Cheatsheet PDFDocument1 paginăGmrs Cheatsheet PDFJC AdamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Counters in Template - MSC PoolDocument9 paginiCounters in Template - MSC PoolkiennaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar On OFDMDocument21 paginiSeminar On OFDMDeepesh JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM-to-UMTS Training Series 19 - Introduction To UMTS RAN KPI - V1.0Document35 paginiGSM-to-UMTS Training Series 19 - Introduction To UMTS RAN KPI - V1.0myososÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radio Communication Jto Lice Study Material SampleDocument17 paginiRadio Communication Jto Lice Study Material SampleArghya PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Axell Cellular Off-Air CoverageDocument18 paginiAxell Cellular Off-Air CoverageAkterRokyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guia RisoDocument184 paginiGuia RisoToni PonsÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Survey On Reconfigurable Microstrip FiltennaDocument21 paginiA Survey On Reconfigurable Microstrip FiltennaKani MozhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdms India. (Partial Discharge Monitoring Services India)Document17 paginiPdms India. (Partial Discharge Monitoring Services India)VISHAL TELANGÎncă nu există evaluări
- World's Most Trusted Family of Handheld RF and Microwave AnalyzersDocument6 paginiWorld's Most Trusted Family of Handheld RF and Microwave AnalyzersTareq NadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MR303Document4 paginiMR303Joao CarameloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zigzag Antenna 06027445Document4 paginiZigzag Antenna 06027445sudokubk38Încă nu există evaluări
- Electronics Forum - Oscillator Coil For Aa5 Radio.Document10 paginiElectronics Forum - Oscillator Coil For Aa5 Radio.radiolandiaÎncă nu există evaluări