Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Iec 61660-3
Încărcat de
BALLOUK SoufianeTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Iec 61660-3
Încărcat de
BALLOUK SoufianeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
This is a preview - click here to buy the full publication
RAPPORT TECHNIQUE TECHNICAL REPORT
CEI IEC TR 61660-3
Premire dition First edition 2000-02
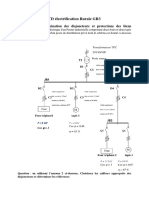
Courants de court-circuit dans les installations auxiliaires alimentes en courant continu dans les centrales et les postes Partie 3: Exemples de calculs Short-circuit currents in d.c. auxiliary installations in power plants and substations Part 3: Examples of calculations
IEC 2000 Droits de reproduction rservs Copyright - all rights reserved
Aucune partie de cette publication ne peut tre reproduite ni utilise sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun procd, lectronique ou mcanique, y compris la photo-copie et les microfilms, sans l'accord crit de l'diteur. No part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without permission in writing from the publisher.
International Electrotechnical Commission 3, rue de Varemb Geneva, Switzerland Telefax: +41 22 919 0300 e-mail: inmail@iec.ch IEC web site http://www.iec.ch
Commission Electrotechnique Internationale International Electrotechnical Commission
CODE PRIX PRICE CODE
Pour prix, voir catalogue en vigueur For price, see current catalogue
This is a preview - click here to buy the full publication
TR 61660-3 CEI:2000
SOMMAIRE
Pages
AVANT-PROPOS........................................................................................................................4
Articles
Gnralits ............................................................................................................................8 1.1 Domaine dapplication et objet ....................................................................................8 1.2 Documents de rfrence ...............................................................................................8 1.3 Dfinitions, symboles et indices, et quations ..............................................................8 Installation alimente en courant continu et donnes sur le matriel.................................... 10 Calcul du courant de court-circuit ....................................................................................... 12 3.1 Emplacement du court-circuit F1 ............................................................................... 12 3.2 Emplacement du court-circuit F2 ............................................................................... 26 3.3 Emplacement du court-circuit F3 ............................................................................... 40 3.4 Emplacement du court-circuit F4 ............................................................................... 54 Calcul des effets mcaniques et thermiques......................................................................... 72 4.1 4.2 Effets mcaniques ...................................................................................................... 72 Effets thermiques ....................................................................................................... 88
2 3
Annexe A Facteur de correction j pour les courants de court-circuit partiels en F3 de la figure 1 ........................................................................................................................ 92 Figure 1 Installation alimente en 220 V continu et emplacements des court-circuits F1 ... F4 Donnes lectriques concernant le matriel ......................................................... 10 Figure 2 Courants de court-circuit partiels et courant de court-circuit i k (t) lemplacement du court-circuit F1 (voir figure 1) .............................................................. 24 Figure 3 Courants de court-circuit partiels corrigs, et courant de court-circuit i k (t) lemplacement du court-circuit F2 (voir figure 1) .............................................................. 38 Figure 4 Courants de court-circuit partiels, corrigs, et courant de court-circuit i k (t) lemplacement du court-circuit F3 (voir figure 1) .............................................................. 52 Figure 5 Courants de court-circuit partiels corrigs, et courants de court-circuit i k (t) en L1 et lemplacement du court-circuit F4 (voir figure 1)................................................. 70 Figure 6 Disposition des conducteurs et des lments de renfort ........................................ 72 Figure A.1 Schma pour le calcul de j dans le cas de F3 selon la figure 1......................... 92 Tableau 1 Courants de court-circuit en F1 ......................................................................... 22 Tableau 2 Rsistances R ij et R resj ........................................................................................ 34 Tableau 3 Courants de court-circuit partiels et courant de court-circuit total en F2 ............ 36 Tableau 4 Courants de court-circuit partiels et courant de court-circuit en F3 .................... 48 Tableau 5 Rsistances R ij et R resj ........................................................................................ 62 Tableau 6 Courants de court-circuit partiels et courants de court-circuit total en L1 et F4..... 64
This is a preview - click here to buy the full publication
TR 61660-3 IEC:2000
CONTENTS
Page
FOREWORD ...............................................................................................................................5
Clause
General..................................................................................................................................9 1.1 Scope and object ..........................................................................................................9 1.2 Reference documents ...................................................................................................9 1.3 Definitions, symbols, subscripts and equations ............................................................9 DC installation and data of the equipment ........................................................................... 11 Short-circuit current calculation .......................................................................................... 13 3.1 Short-circuit location F1 ............................................................................................ 13 3.2 Short-circuit location F2 ............................................................................................ 27 3.3 Short-circuit location F3 ............................................................................................ 41 3.4 Short-circuit location F4 ............................................................................................ 55 Calculation of the mechanical and thermal effects............................................................... 73 4.1 4.2 Mechanical effects ..................................................................................................... 73 Thermal effect ........................................................................................................... 89
2 3
Annex A Correction factor j for the partial short-circuit currents in F3 of figure 1 ........... 93 Figure 1 220 V d.c. installation and short-circuit locations F1 ... F4 Electrical equipment data ..................................................................................................................... 11 Figure 2 Partial short-circuit currents and short-circuit current i k (t) at the short-circuit location F1 (see figure 1) ..................................................................................................... 25 Figure 3 Partial short-circuit currents, corrected, and short-circuit current i k (t) at the short-circuit location F2 (see figure 1)............................................................................ 39 Figure 4 Partial short-circuit currents, corrected, and short-circuit current i k (t) at the short-circuit location F3 (see figure 1)............................................................................ 53 Figure 5 Partial short-circuit currents, corrected, and short-circuit currents i k (t) in L1 and at the short-circuit location F4 (see figure 1) ................................................................. 71 Figure 6 Arrangement of conductors and stiffening elements ............................................. 73 Figure A.1 Scheme for the calculation of j in the case of F3 in figure 1 ........................... 93 Table Table Table Table Table Table 1 2 3 4 5 6 Short-circuit currents in F1 ................................................................................... 23 R ij and R resj resistances .......................................................................................... 35 Partial short-circuit currents and total short-circuit current in F2 .......................... 37 Partial short-circuit currents and short-circuit current in F3 .................................. 49 R ij and R resj resistances .......................................................................................... 63 Partial short-circuit currents and total short-circuit currents in L1 and F4 ............. 65
This is a preview - click here to buy the full publication
TR 61660-3 CEI:2000
COMMISSION LECTROTECHNIQUE INTERNATIONALE
____________
COURANTS DE COURT-CIRCUIT DANS LES INSTALLATIONS AUXILIAIRES ALIMENTES EN COURANT CONTINU DANS LES CENTRALES ET LES POSTES Partie 3: Exemples de calculs
AVANT-PROPOS
1) La CEI (Commission lectrotechnique Internationale) est une organisation mondiale de normalisation compose de l'ensemble des comits lectrotechniques nationaux (Comits nationaux de la CEI). La CEI a pour objet de favoriser la coopration internationale pour toutes les questions de normalisation dans les domaines de l'lectricit et de l'lectronique. A cet effet, la CEI, entre autres activits, publie des Normes internationales. Leur laboration est confie des comits d'tudes, aux travaux desquels tout Comit national intress par le sujet trait peut participer. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernementales, en liaison avec la CEI, participent galement aux travaux. La CEI collabore troitement avec l'Organisation Internationale de Normalisation (ISO), selon des conditions fixes par accord entre les deux organisations. 2) Les dcisions ou accords officiels de la CEI concernant les questions techniques reprsentent, dans la mesure du possible, un accord international sur les sujets tudis, tant donn que les Comits nationaux intresss sont reprsents dans chaque comit dtudes. 3) Les documents produits se prsentent sous la forme de recommandations internationales. Ils sont publis comme normes, spcifications techniques, rapports techniques ou guides et agrs comme tels par les Comits nationaux. 4) Dans le but d'encourager l'unification internationale, les Comits nationaux de la CEI s'engagent appliquer de faon transparente, dans toute la mesure possible, les Normes internationales de la CEI dans leurs normes nationales et rgionales. Toute divergence entre la norme de la CEI et la norme nationale ou rgionale correspondante doit tre indique en termes clairs dans cette dernire. 5) La CEI na fix aucune procdure concernant le marquage comme indication dapprobation et sa responsabilit nest pas engage quand un matriel est dclar conforme lune de ses normes.
6) Lattention est attire sur le fait que certains des lments du prsent rapport technique peuvent faire lobjet de
droits de proprit intellectuelle ou de droits analogues. La CEI ne saurait tre tenue pour responsable de ne pas avoir identifi de tels droits de proprit et de ne pas avoir signal leur existence.
La tche principale des comits dtudes de la CEI est llaboration des Normes internationales. Toutefois, un comit dtudes peut proposer la publication dun rapport technique lorsquil a runi des donnes de nature diffrente de celles qui sont normalement publies comme Normes internationales, cela pouvant comprendre, par exemple, des informations sur ltat de la technique. Un rapport technique ne doit pas ncessairement tre rvis avant que les donnes quil contient ne soient plus juges valables ou utiles par le groupe de maintenance.
This is a preview - click here to buy the full publication
TR 61660-3 IEC:2000
INTERNATIONAL ELECTROTECHNICAL COMMISSION
____________
SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENTS IN DC AUXILIARY INSTALLATIONS IN POWER PLANTS AND SUBSTATIONS Part 3: Examples of calculations
FOREWORD
1) The IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) is a worldwide organization for standardization comprising all national electrotechnical committees (IEC National Committees). The object of the IEC is to promote international co-operation on all questions concerning standardization in the electrical and electronic fields. To this end and in addition to other activities, the IEC publishes International Standards. Their preparation is entrusted to technical committees; any IEC National Committee interested in the subject dealt with may participate in this preparatory work. International, governmental and non-governmental organizations liaising with the IEC also participate in this preparation. The IEC collaborates closely with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in accordance with conditions determined by agreement between the two organizations. 2) The formal decisions or agreements of the IEC on technical matters express, as nearly as possible, an international consensus of opinion on the relevant subjects since each technical committee has representation from all interested National Committees. 3) The documents produced have the form of recommendations for international use and are published in the form of standards, technical specifications, technical reports or guides and they are accepted by the National Committees in that sense. 4) In order to promote international unification, IEC National Committees undertake to apply IEC International Standards transparently to the maximum extent possible in their national and regional standards. Any divergence between the IEC Standard and the corresponding national or regional standard shall be clearly indicated in the latter. 5) The IEC provides no marking procedure to indicate its approval and cannot be rendered responsible for any equipment declared to be in conformity with one of its standards.
6) Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements of this technical report may be the subject of patent
rights. The IEC shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights.
The main task of IEC technical committees is to prepare International Standards. However, a technical committee may propose the publication of a technical report when it has collected data of a different kind from that which is normally published as an International Standard, for example "state of the art". Technical reports do not necessarily have to be reviewed until the data they provide are considered to be no longer valid or useful by the maintenance team.
This is a preview - click here to buy the full publication
TR 61660-3 CEI:2000
La CEI 61660-3 qui est un rapport technique, a t tablie par le comit dtudes 73 de la CEI: Courants de court-circuit. Ce rapport technique doit tre utilis conjointement avec la CEI 61660-1 et la CEI 61660-2. Le texte de ce rapport technique est issu des documents suivants:
Projet d'enqute 73/106/CDV Rapport de vote 73/109/RVC
Le rapport de vote indiqu dans le tableau ci-dessus donne toute information sur le vote ayant abouti lapprobation de ce rapport technique. Cette publication a t rdige selon les Directives ISO/CEI, Partie 3. Ce document, purement informatif, ne doit pas tre considr comme une Norme internationale. La CEI 61660 comprend les parties suivantes, prsentes sous le titre gnral: Courants de courtcircuit dans les installations auxiliaires alimentes en courant continu dans les centrales et les postes: Partie 1: Calcul des courants de court-circuit Partie 2: Calcul des effets Partie 3: Exemples de calculs
This is a preview - click here to buy the full publication
TR 61660-3 IEC:2000
IEC 61660-3, which is a technical report, has been prepared by IEC technical committee 73: Short-circuit currents. This technical report should be read in conjunction with IEC 61660-1 and IEC 61660-2. The text of this technical report is based on the following documents:
Enquiry draft 73/106/CDV Report on voting 73/109/RVC
Full information on the voting for the approval of this technical report can be found in the report on voting indicated in the above table. This publication has been drafted in accordance with ISO/IEC Directives, Part 3. This document which is purely informative is not to be regarded as an International Standard. IEC 61660 consists of the following parts, under the general title: Short-circuit currents in d.c. auxiliary installations in power plants and substations: Part 1: Calculation of short-circuit currents Part 2: Calculation of effects Part 3: Examples of calculations
This is a preview - click here to buy the full publication
TR 61660-3 CEI:2000
COURANTS DE COURT-CIRCUIT DANS LES INSTALLATIONS AUXILIAIRES ALIMENTES EN COURANT CONTINU DANS LES CENTRALES ET LES POSTES Partie 3: Exemples de calculs
1
1.1
Gnralits
Domaine dapplication et objet
La CEI 61660-3 qui est un rapport technique fournit une aide pour appliquer la CEI 61660-1 et la CEI 61660-2. Par consquent, le calcul destin aux installations alimentes en courant continu indiques la figure 1 sont strictement ralises en conformit avec la CEI 61660-1 et la CEI 61660-2. Le schma dinstallation correspondant lemplacement du court-circuit F3 de la figure 1 ne correspond pas la figure 3 de la CEI 61660-1. Par consquent, des considrations supplmentaires portant sur le facteur de correction j sont ncessaires et il convient de consulter lannexe A. La ligne de connexion L1 de la figure 1 est constitue de barres en cuivre (voir article 4). Les lignes de connexion L2 et L3 sont des connexions par cble. Par consquent, les effets mcaniques et thermiques sont uniquement calculs pour L1 en cas de court-circuit lemplacement F4. 1.2 Documents de rfrence
CEI 61660-1:1997, Courants de court-circuit dans les installations auxiliaires alimentes en courant continu dans les centrales et les postes Partie 1: Calcul des courants de court-circuit CEI 61660-2:1997, Courants de court-circuit dans les installations auxiliaires alimentes en courant continu dans les centrales et les postes Partie 2: Calcul des effets CEI 60909-0:, Courants de court-circuit dans les rseaux triphass courant alternatif Partie 0: Calcul des courants 1) 1.3 Dfinitions, symboles et indices, et quations
Les dfinitions, les symboles et indices, ainsi que les quations, sont les mmes que dans la CEI 61660-1 et dans la CEI 61660-2. Les rfrences donnes larticle 3 correspondent la CEI 61660-1 et les rfrences donnes larticle 4 correspondent la CEI 61660-2. Ces rfrences sont indiques entre crochets.
________
1)
A publier.
This is a preview - click here to buy the full publication
TR 61660-3 IEC:2000
SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENTS IN DC AUXILIARY INSTALLATIONS IN POWER PLANTS AND SUBSTATIONS Part 3: Examples of calculations
1
1.1
General
Scope and object
IEC 61660-3 which is a technical report gives help for the application of IEC 61660-1 and IEC 61660-2. Therefore, the calculations for the d.c. installation in figure 1 are strictly carried out in accordance with IEC 61660-1 and 61660-2. The installation scheme with respect to the short-circuit location F3 in figure 1 does not correspond to figure 3 of IEC 61660-1. Therefore, additional considerations related to the correction factor j are necessary and annex A should be consulted. The connecting line L1 in figure 1 consists of copper bars (see clause 4). The lines L2 and L3 are cable connections. Therefore, the mechanical and thermal effects are calculated only for L1 in case of a short circuit at the location F4. 1.2 Reference documents
IEC 61660-1:1997, Short-circuit currents in d.c. auxiliary installations in power plants and substations Part 1: Calculation of short-circuit currents IEC 61660-2:1997, Short-circuit currents in d.c. auxiliary installations in power plants and substations Part 2: Calculation of effects IEC 60909-0:, Short-circuit currents in three-phase a.c. systems Part 0: Calculation of currents 1) 1.3 Definitions, symbols, subscripts and equations
Definitions, symbols, subscripts and equations are the same as those used in IEC 61660-1 and IEC 61660-2. References in square brackets in clause 3 relate to IEC 61660-1 and references in square brackets in clause 4 relate to IEC 61660-2.
________
1)
To be published.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Théorie et conception des filtres analogiques, 2e édition: Avec MatlabDe la EverandThéorie et conception des filtres analogiques, 2e édition: Avec MatlabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stockage D'Énergie Du Volant: Augmenter ou diminuer la vitesse, pour ajouter ou extraire de la puissanceDe la EverandStockage D'Énergie Du Volant: Augmenter ou diminuer la vitesse, pour ajouter ou extraire de la puissanceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normes Collection (Version 2)Document24 paginiNormes Collection (Version 2)AdrienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iec 61660-1Document9 paginiIec 61660-1BALLOUK Soufiane50% (2)
- D 4423Document10 paginiD 4423mohamed bounaouaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iec 61660-2Document9 paginiIec 61660-2BALLOUK SoufianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation Et Raccordement D'une Centrale Photovoltaïque Au Réseau ONEE 22 kV-1Document64 paginiSimulation Et Raccordement D'une Centrale Photovoltaïque Au Réseau ONEE 22 kV-1coulibalyabdoulk15Încă nu există evaluări
- CT 212Document32 paginiCT 212ahmedenisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corrige Sujet ET2006Document37 paginiCorrige Sujet ET2006maher alouiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protection 1Document13 paginiProtection 1Lalouli AbderrezzakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iec 61660 1 1997Document80 paginiIec 61660 1 1997David Moreno100% (1)
- Lignes Aériennes: Matériels: IsolateursDocument10 paginiLignes Aériennes: Matériels: IsolateursOuzeren AbdelhakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- chap1-SLT (Mode de Compatibilité)Document63 paginichap1-SLT (Mode de Compatibilité)boudardara mohamed amineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architecture Des Postes Source HTB - HTA - SifoeeDocument1 paginăArchitecture Des Postes Source HTB - HTA - SifoeeKaparoNedMarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Des Machines Tournantes: Etienne Dion 15 Septembre 2022Document39 paginiDiagnostic Des Machines Tournantes: Etienne Dion 15 Septembre 2022Souhaib BoukabesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fusibles SOLEFUS FUSARC Merlin GerinDocument20 paginiFusibles SOLEFUS FUSARC Merlin Gerinermanos3Încă nu există evaluări
- CT 8 Protection Des Transformateurs de PuissanceADocument62 paginiCT 8 Protection Des Transformateurs de PuissanceAharoldÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1MRK506275-UFR B FR Manuel de Reference Technique REL670Document1.010 pagini1MRK506275-UFR B FR Manuel de Reference Technique REL670AlifBaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiche CanecoHTDocument2 paginiFiche CanecoHTrjedias100% (1)
- Eco DialDocument42 paginiEco DialRaphael ReignierÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPostes À Haute Et Très Haute Tensions - Postes Sous EnveloDocument2 paginiDPostes À Haute Et Très Haute Tensions - Postes Sous EnveloYounis MolayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cours 2 Reseau EEEEEEEDocument38 paginiCours 2 Reseau EEEEEEEakliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrotechnique DistributionDocument74 paginiElectrotechnique DistributionBationo Antoine De padoueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact Des Perturbations Électriques Sur La Stabilité D'un Réseau ÉlectriqueDocument52 paginiImpact Des Perturbations Électriques Sur La Stabilité D'un Réseau ÉlectriqueChristopherÎncă nu există evaluări
- LES PARAFOUDRES en HT Et MTDocument38 paginiLES PARAFOUDRES en HT Et MTIssam100% (1)
- Les Reducteurs de Mesure TC TT PDFDocument19 paginiLes Reducteurs de Mesure TC TT PDFSoumya SalmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pratique Des Regimes de NeutreDocument6 paginiPratique Des Regimes de NeutreAYAD AHMEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProtectionDocument70 paginiProtectionHassanHajjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEC 60269-4-1 Low-Voltage Fuses - Supplementary Requirements For Fuse-Links For The Protection ofDocument42 paginiIEC 60269-4-1 Low-Voltage Fuses - Supplementary Requirements For Fuse-Links For The Protection ofĐặng Xuân ViệtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etude Des Harmoniques Et Techniques de CDocument3 paginiEtude Des Harmoniques Et Techniques de Crida beniboujÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapitre13 PDFDocument30 paginiChapitre13 PDFABELWALIDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enedis PRO RES - 50E PDFDocument35 paginiEnedis PRO RES - 50E PDFCakpo Eric AgbangbatinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verouillage CléDocument50 paginiVerouillage Cléruterboy100% (1)
- Chapitre 33Document40 paginiChapitre 33Khadija rhiliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Info Iec60383-2 (Ed1.0) B.img PDFDocument9 paginiInfo Iec60383-2 (Ed1.0) B.img PDFSyeda Turan NaqviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fils en Alliage de Cuivre Pour Conducteurs de Lignes AériennesDocument17 paginiFils en Alliage de Cuivre Pour Conducteurs de Lignes AériennesAli Ben Belgacem Mahrouk100% (1)
- TD Electrification RuraleDocument4 paginiTD Electrification RuraleGEORGES NICODÈME AKEME ETOUKE EWANEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcul ICCDocument10 paginiCalcul ICCMED77Încă nu există evaluări
- Iec 61000-4-7 (2000)Document57 paginiIec 61000-4-7 (2000)Carlos Vidales100% (1)
- Plaque Signalétique PDFDocument2 paginiPlaque Signalétique PDFWaheb ArdÎncă nu există evaluări
- S 10 Frua 11Document52 paginiS 10 Frua 11lemsouguerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapitre 2 Modes de Transport, Répartition Et Distribution de L'énergie ÉlectriqueDocument7 paginiChapitre 2 Modes de Transport, Répartition Et Distribution de L'énergie ÉlectriqueAbdelghani ChenikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogue SOCABEL FinalDocument74 paginiCatalogue SOCABEL FinalalantemesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ait Mohammed WalidDocument46 paginiAit Mohammed WalidNour SwamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schneider Electric - Cahier Technique 198 - La Coupure Du Courant Électrique Dans Le VideDocument36 paginiSchneider Electric - Cahier Technique 198 - La Coupure Du Courant Électrique Dans Le VideZorbanfrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memoire ELT IND VSC HVDCDocument111 paginiMemoire ELT IND VSC HVDCHadil SellamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esprit Certification Onduleurs PV de Cembre 2011Document58 paginiEsprit Certification Onduleurs PV de Cembre 2011babisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Web SF1 User Manu FRDocument52 pagini05 Web SF1 User Manu FRCharaf BelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide dApplicationsC PDFDocument44 paginiGuide dApplicationsC PDFSahliMohamed100% (1)
- Modules Papier HarmoniquesDocument13 paginiModules Papier Harmoniquesnabil nabilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micom P441/P442/P444: Protection de Distance NumériqueDocument722 paginiMicom P441/P442/P444: Protection de Distance NumériqueBOUCHTAOUI IlyassÎncă nu există evaluări
- DisjoncteurDocument14 paginiDisjoncteurFatima100% (1)
- Protection MoteursDocument5 paginiProtection MoteursferibrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcul ICCDocument10 paginiCalcul ICCAnouar Bh100% (1)
- Cours410 Document Synthã SeDocument148 paginiCours410 Document Synthã Seferiel aissiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tapcon 240Document76 paginiTapcon 240YAOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planification Des Réseaux Électriques: Université Ibn-Khaldoun de TiaretDocument112 paginiPlanification Des Réseaux Électriques: Université Ibn-Khaldoun de TiaretLotfi AbidiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AFNOR C15-500 (Juillet 2015)Document90 paginiAFNOR C15-500 (Juillet 2015)Karim KammounÎncă nu există evaluări
- Livre ELE2302 PDFDocument259 paginiLivre ELE2302 PDFkoopa00Încă nu există evaluări
- RadioNavCom1 L3 Ima DM V6Document52 paginiRadioNavCom1 L3 Ima DM V6Baudri LembiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flexo Solutions FRDocument4 paginiFlexo Solutions FRBALLOUK Soufiane0% (1)
- Ingénieur Canandien PDFDocument778 paginiIngénieur Canandien PDFBALLOUK SoufianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NF C 18-510Document253 paginiNF C 18-510BALLOUK Soufiane100% (2)
- Pratique Du LeanDocument208 paginiPratique Du LeanAnovar_ebooks100% (3)
- CH 18 Mise en OeuvreDocument5 paginiCH 18 Mise en OeuvreBALLOUK SoufianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indis Technique GraphikDocument98 paginiIndis Technique GraphikBALLOUK SoufianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide Pratique Professionel 2017Document20 paginiGuide Pratique Professionel 2017BALLOUK SoufianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6Document46 pagini6JeanDD03100% (3)
- Clim8 ClimatisationDcent PDFDocument8 paginiClim8 ClimatisationDcent PDFHassan OuikhalfenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ute C 15 900Document71 paginiUte C 15 900Patran ValentinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcul Section Cable Eclairage - PublicDocument4 paginiCalcul Section Cable Eclairage - Publiccherif yahyaoui100% (2)
- UTE C17-205U Guide Pratique Dim Conducteur Eckairage PublicDocument24 paginiUTE C17-205U Guide Pratique Dim Conducteur Eckairage PublicBALLOUK Soufiane83% (6)
- Analyse de La Réglementation Marocaine Régissant Les Installations ÉlectriquesDocument3 paginiAnalyse de La Réglementation Marocaine Régissant Les Installations ÉlectriquesBALLOUK SoufianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norme UTE C 15 712Document32 paginiNorme UTE C 15 712ABELWALID100% (2)
- Chap 3Document9 paginiChap 3Melody NixonÎncă nu există evaluări
- UTE C15 712 1 Photovoltaique ReseauDocument65 paginiUTE C15 712 1 Photovoltaique ReseauBALLOUK Soufiane100% (5)
- Protection Des Installations ÉlectriquesDocument65 paginiProtection Des Installations ÉlectriquesBESSEMYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norme de Passage Des Reseaux SouterrainsDocument12 paginiNorme de Passage Des Reseaux SouterrainsBALLOUK SoufianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toute La Fonction QSSE (Qualité Sécurité Environnement)Document526 paginiToute La Fonction QSSE (Qualité Sécurité Environnement)BALLOUK Soufiane91% (11)
- Securite Groupe ElectrogeneDocument6 paginiSecurite Groupe ElectrogeneABELWALIDÎncă nu există evaluări
- NF C11 201 Reseaux de Distribution Publique D EnergieDocument134 paginiNF C11 201 Reseaux de Distribution Publique D Energiebadrezzamane93% (15)
- Management Des Risques D'entreprise - Le Modèle Triple Impact™Document8 paginiManagement Des Risques D'entreprise - Le Modèle Triple Impact™Mohamed ZoubairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogue Normes Marociane Electricité Édition Mai 2015Document54 paginiCatalogue Normes Marociane Electricité Édition Mai 2015BALLOUK Soufiane100% (1)
- CV BALLOUK SoufianeDocument1 paginăCV BALLOUK SoufianeBALLOUK SoufianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cours Des Moteurs AsynchronesDocument40 paginiCours Des Moteurs AsynchronesBALLOUK Soufiane100% (5)
- Echos N19 PDFDocument20 paginiEchos N19 PDFdonsallusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dimensionnement SolaireDocument73 paginiDimensionnement SolaireN.NASRI Matlablog100% (25)
- Psim OnduleurDocument149 paginiPsim OnduleurHuong Thao Le LuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Variateurs de Vitesse - de La Régulation Cascade À La Commande Vectorielle PSIMDocument55 paginiVariateurs de Vitesse - de La Régulation Cascade À La Commande Vectorielle PSIMBALLOUK Soufiane100% (4)
- Echos N18Document16 paginiEchos N18BALLOUK SoufianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Info Iec60383-1 (Ed4.0) FR D.imgDocument11 paginiInfo Iec60383-1 (Ed4.0) FR D.imgJosé Adony TSAFACKÎncă nu există evaluări
- MasterPacT MTZ - LV865307Document4 paginiMasterPacT MTZ - LV865307Soumana Hassane Abdoul RafiouÎncă nu există evaluări
- PFE Nouhaila BELMAJDOUBDocument67 paginiPFE Nouhaila BELMAJDOUBNabil El haririÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cables Et ConduitsDocument26 paginiCables Et ConduitsHadja SavanéÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso TR 24971 2020Document15 paginiIso TR 24971 2020Abir RegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ie3 Norme Cei 60034 30 PDFDocument2 paginiIe3 Norme Cei 60034 30 PDFKDAÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO-6780-2003 Palettes Plates Pour La ManutentionDocument11 paginiISO-6780-2003 Palettes Plates Pour La ManutentionSam DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abb Uno DMDocument6 paginiAbb Uno DMJoseph Léopold Birane FayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso Iec TS 17021-2-2012Document18 paginiIso Iec TS 17021-2-2012Yh AmrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preventa XCS - XCSLE2525312Document3 paginiPreventa XCS - XCSLE2525312HITIMAN-AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tabela Rebobinamento WegDocument2 paginiTabela Rebobinamento WegEverton Alves80% (15)
- LIS 02 LISTE DES NORMES GUIDES APPLICABLES ET RESOLUTIONS Du 31.07.2019Document14 paginiLIS 02 LISTE DES NORMES GUIDES APPLICABLES ET RESOLUTIONS Du 31.07.2019tirlireÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO-ISO 50003 (F) Systèmes de Management de L'énergieDocument28 paginiISO-ISO 50003 (F) Systèmes de Management de L'énergiezakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Veille Normative Et Reglementaire LABELIANS DocExternes122020Document5 paginiVeille Normative Et Reglementaire LABELIANS DocExternes122020Anonh AdikoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cahier Des Charges Lampe Tercking PDFDocument26 paginiCahier Des Charges Lampe Tercking PDFdxsszszÎncă nu există evaluări
- ILAC - G28 - 07 - 2018 Version FRDocument20 paginiILAC - G28 - 07 - 2018 Version FRTarek HaddarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iec 61083-2-2013Document70 paginiIec 61083-2-2013saulÎncă nu există evaluări
- NF en Iso 5167-2-2003Document60 paginiNF en Iso 5167-2-2003Rem FgtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competences - 73 - 0817 COFRACDocument7 paginiCompetences - 73 - 0817 COFRACS.HALIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso 21049 PDFDocument118 paginiIso 21049 PDFAzize Razam100% (1)
- NF en Iso 6947 - 2011Document25 paginiNF en Iso 6947 - 2011Daniel LoriniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction À La Compatibilité Électromagnétique (CEM) : Compatibilite ElectromagnetiqueDocument15 paginiIntroduction À La Compatibilité Électromagnétique (CEM) : Compatibilite ElectromagnetiqueSimi NeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iec 60479-3-1998Document38 paginiIec 60479-3-1998Ronald Arpi100% (2)
- Dispositif RéglemmentaireDocument17 paginiDispositif Réglemmentaireinstru MentationÎncă nu există evaluări
- TD2: Synthèse VHDL: Exercice 1Document4 paginiTD2: Synthèse VHDL: Exercice 1Dhouha BenzinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normes ISO 27000Document21 paginiNormes ISO 27000Lamia El Fachtali86% (7)
- ISO IEC Guide 99 2007 (Bilingual) - International Vocabulary of Metrology - Basic and General Concepts and Associated Terms (VIM)Document108 paginiISO IEC Guide 99 2007 (Bilingual) - International Vocabulary of Metrology - Basic and General Concepts and Associated Terms (VIM)Alia MaroufÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rapport Final PFE 2013Document142 paginiRapport Final PFE 2013bsaid77Încă nu există evaluări
- 5 Cable DataDocument268 pagini5 Cable DataFrederic QuerriauxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nibt Greme CH1Document23 paginiNibt Greme CH1havoc2012Încă nu există evaluări