Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Bronchiectasis Pathophysiology
Încărcat de
Rayne Dunstan Pascual Vergara0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
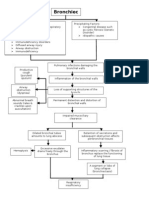
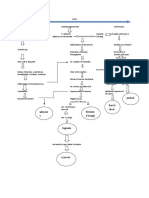
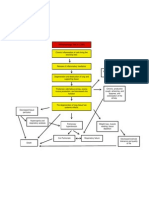
750 vizualizări1 paginăPulmonary infection walls become distended and distorted Inflammatory Process Damage in bronchial walls Productive cough Hemoptysis Loss of supporting structure Impaired mucociliary clearance. Saccular bronchiectasis: Dilated peribronchial tube virtually amounts to a lung abscess Exudates freely flow through the bronchus Localized in a segment or lobe of a lung.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
bronchiectasis pathophysiology
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentPulmonary infection walls become distended and distorted Inflammatory Process Damage in bronchial walls Productive cough Hemoptysis Loss of supporting structure Impaired mucociliary clearance. Saccular bronchiectasis: Dilated peribronchial tube virtually amounts to a lung abscess Exudates freely flow through the bronchus Localized in a segment or lobe of a lung.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
750 vizualizări1 paginăBronchiectasis Pathophysiology
Încărcat de
Rayne Dunstan Pascual VergaraPulmonary infection walls become distended and distorted Inflammatory Process Damage in bronchial walls Productive cough Hemoptysis Loss of supporting structure Impaired mucociliary clearance. Saccular bronchiectasis: Dilated peribronchial tube virtually amounts to a lung abscess Exudates freely flow through the bronchus Localized in a segment or lobe of a lung.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
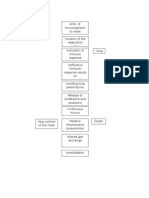
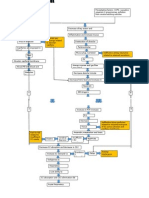
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Etiologic Factors Pulmonary Infection Walls become distended and distorted Inflammatory Process Damage in bronchial walls
Productive cough Hemoptysis Loss of supporting structure
Impaired mucociliary clearance
In saccular bronchiectasis: Dilated peribronchial tube virtually amounts to a lung abscess Exudates freely flow through the bronchus Localized in a segment or lobe of a lung (usually in lower lobes) Retention of secretion
Obstructs bronchi
Decreased lung compliance
Difficulty in breathing
Respiratory Insufficiency
Clubbing of fingers
Increased ratio of residual vol. to total lung capacity Decreased vital capacity Decreased ventilation
Ventilation perfusion imbalance Fibrosis
Hypoxemia
Atelectasis
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Pathophysiology Flow Chart of BronchiectasisDocument2 paginiPathophysiology Flow Chart of BronchiectasisEsmareldah Henry SirueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiBronchiectasis PathophysiologyKim Gonzales86% (7)
- COPD PathoDocument1 paginăCOPD PathoLeah May AnchetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Copd PDFDocument24 paginiCopd PDFyabaeve100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Bronchial AsthmaDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Bronchial AsthmaFirenze Fil100% (21)
- BRONCHIECTASISDocument36 paginiBRONCHIECTASISNishanth ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Patho) PTB COPDDocument1 pagină(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of COPD - The BasicsDocument11 paginiPathophysiology of COPD - The BasicstiaranindyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of VSDDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of VSDMarlon CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ards Concept MapDocument1 paginăArds Concept Mapchristine louise bernardo100% (1)
- Copd PathoDocument2 paginiCopd PathoAlvin RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study (Bronchiectasis Chest)Document1 paginăCase Study (Bronchiectasis Chest)Sarra Mood Iman100% (1)
- Pneumonia Pathophysiology 3Document2 paginiPneumonia Pathophysiology 3billiam123Încă nu există evaluări
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocument2 paginiPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- SinusitisDocument6 paginiSinusitisRae Marie AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARDS With PathophysiologyDocument79 paginiARDS With Pathophysiologymabec pagaduan95% (19)
- Concept MapDocument4 paginiConcept Mapdejosep_informaticsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument8 paginiPulmonary EmbolismspoilttbrattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Copd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Document3 paginiCopd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Israel Soria EsperoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discharge Planning PaperDocument5 paginiDischarge Planning Paperapi-283173905Încă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderBlessyl Mae EstenzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Copd Pathophysiology DiagramDocument2 paginiCopd Pathophysiology DiagramVHyneh Basher100% (1)
- COPD PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăCOPD PathophysiologyJustin Ahorro-Dionisio33% (3)
- Patho Tree COPDDocument1 paginăPatho Tree COPDLaura MitchellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nasal PolypsDocument20 paginiNasal PolypsPauleenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Posterior Mold: PurposeDocument3 paginiPosterior Mold: PurposeSheryl Ann Barit PedinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - PathophysiologyDocument5 paginiAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - PathophysiologyJoann67% (3)
- De Sagun, Leila Camille, A. NCMB312-RLE BSN3Y1-1B Course Task #1Document1 paginăDe Sagun, Leila Camille, A. NCMB312-RLE BSN3Y1-1B Course Task #1Carl SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia PathoDocument2 paginiPneumonia PathoDerick Nyl PascualÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ards Cmap FinalDocument4 paginiArds Cmap FinalPam Araune67% (3)
- FlashPath - Lung - Bronchopulmonary DysplasiaDocument15 paginiFlashPath - Lung - Bronchopulmonary DysplasiaHazem AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patho PneumoniaDocument2 paginiPatho Pneumoniaailyne_galicia100% (2)
- Hemothorax HandoutsDocument2 paginiHemothorax HandoutsJunathan L. DelgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCA2 PosttestsDocument20 paginiNCA2 PosttestsCzarena Ysabelle PayotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Brain Abscess Secondary To Chronic Otitis MediaDocument5 paginiPathophysiology of Brain Abscess Secondary To Chronic Otitis Mediafufulabrador100% (1)
- Nursing ManagementDocument16 paginiNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Pneumoniaoxidalaj97% (31)
- Bronchial Asthma Nursing Care PlansDocument2 paginiBronchial Asthma Nursing Care PlansdeincediannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Copd-ChfDocument2 paginiPathophysiology Copd-ChfZaira Batalo100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureDocument2 paginiPathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureKimberly Regacho88% (8)
- NCP #2Document4 paginiNCP #2Nutz TolentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 NCP Chronic Heart FailureDocument5 pagini2 NCP Chronic Heart FailureLovely CacapitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 paginiAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeAndrea Chua BuadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bronchitis PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăBronchitis PathophysiologyMichael Urrutia100% (1)
- Causative Agents Causative Agents: Headache, Myalgia, & Nausea Are Added S/SX For Streptococcal PharyngitisDocument21 paginiCausative Agents Causative Agents: Headache, Myalgia, & Nausea Are Added S/SX For Streptococcal PharyngitisDon Chiaw Manongdo100% (1)
- Pneumothorax (Collapsed Lung)Document34 paginiPneumothorax (Collapsed Lung)james garcia100% (3)
- Otitis Media: Dr. YasserDocument64 paginiOtitis Media: Dr. YasserYasser GaberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument36 paginiChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseHazel ManuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARDS Concept Map - BunayogDocument2 paginiARDS Concept Map - BunayogJacela Annsyle BunayogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of ShocksDocument33 paginiTypes of Shocksmark OrpillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of EmphysemaDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of EmphysemaApple Maiquez Garcia100% (1)
- PneumoniaDocument2 paginiPneumoniaPia MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumothoraxDocument6 paginiPneumothoraxminmin69100% (1)
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument4 paginiBronchiectasis PathophysiologyBrunhild BangayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- AtelectasisDocument43 paginiAtelectasismulan557100% (1)
- Clinical Physiology of Respiration: Dr. M Qathar RF TDocument76 paginiClinical Physiology of Respiration: Dr. M Qathar RF TTiwi Lestari TiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPD PTDocument49 paginiCOPD PTSathish RathnamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airway Obstruction: TraumaDocument16 paginiAirway Obstruction: TraumaSamuel Hotma Rotua SinagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Christine Loren T. Laya BSN 3-1Document41 paginiChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Christine Loren T. Laya BSN 3-1Kristine CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPDDocument52 paginiCOPDSoySauceÎncă nu există evaluări
- PAPP Clinical Practice Guidelines For Pediatric Asthma 2021 (Abridged Version)Document69 paginiPAPP Clinical Practice Guidelines For Pediatric Asthma 2021 (Abridged Version)Kai Chua100% (1)
- Pulmonology 3 COPD (Completed)Document6 paginiPulmonology 3 COPD (Completed)Benjamin NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- English For AnalystDocument51 paginiEnglish For AnalystChitraÎncă nu există evaluări
- National ExamDocument55 paginiNational Examabel100% (1)
- Emergency in Respiratory MedicineDocument73 paginiEmergency in Respiratory MedicineIndra MahaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nitheesh (Roll No. 28) (STHANA ROHITHA MARMA) PDFDocument22 paginiNitheesh (Roll No. 28) (STHANA ROHITHA MARMA) PDFThala ThalapatyÎncă nu există evaluări
- FAELDONEA, PJ - Nursing Care PlanDocument6 paginiFAELDONEA, PJ - Nursing Care PlanPatricia Jean Faeldonea100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Cystic FibrosisDocument9 paginiChapter 7 Cystic FibrosisMariana DariiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Suppurative Desease of Lungs and PleuraDocument26 paginiSuppurative Desease of Lungs and PleuraGarima SahuÎncă nu există evaluări
- USMLE Questions SummarizedDocument85 paginiUSMLE Questions SummarizedJamesIwu89% (19)
- Lewiss Medical-Surgical Nursing in Canada Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 5th Edition (Jane Tyerman, Shelley Cobbett Etc.) (Z-Library)Document1.957 paginiLewiss Medical-Surgical Nursing in Canada Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 5th Edition (Jane Tyerman, Shelley Cobbett Etc.) (Z-Library)mwhitefinkle67Încă nu există evaluări
- USMLE STEP 1 Review - StudentDocument81 paginiUSMLE STEP 1 Review - StudentKawther AbdallahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pages From Harrison's - Self - Assessment - and - Board-2Document66 paginiPages From Harrison's - Self - Assessment - and - Board-2abutalebheba95Încă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory DiseaseDocument206 paginiRespiratory Diseasemulugetaketema394Încă nu există evaluări
- Rapidly Growing Mycobacterial Infections - Mycobacteria Abscessus, Chelonae, and Fortuitum - UpToDateDocument31 paginiRapidly Growing Mycobacterial Infections - Mycobacteria Abscessus, Chelonae, and Fortuitum - UpToDateioana antonesiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Medicine 1Document23 paginiInternal Medicine 1Asif Newaz100% (1)
- Respirology 2023 FinalDocument127 paginiRespirology 2023 FinalBelinda ELISHAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory PathologyDocument42 paginiRespiratory PathologyMorgan PeggÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCRADM 2019 Exec SummaryDocument103 paginiPCRADM 2019 Exec SummaryDivye GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bronchiectasis 1Document22 paginiBronchiectasis 1Imam MardaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- SN Chugh - Bedside Medicine Without TearsDocument454 paginiSN Chugh - Bedside Medicine Without Tearsnb280100% (11)
- Block 4 Lung PathDocument31 paginiBlock 4 Lung PathShalini ShanmugalingamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest Wall, Lung, MediastinumDocument124 paginiChest Wall, Lung, MediastinumKenn BrillanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 Cavitary & Cystic LesionsDocument110 pagini07 Cavitary & Cystic Lesionsapi-25944730100% (4)
- Head N Neck-MCQsDocument57 paginiHead N Neck-MCQsbhargavi pasagadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 - Respiratory SystemDocument38 paginiChapter 10 - Respiratory SystemAsma MuhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Cough Differential DiagnosisDocument6 paginiChronic Cough Differential DiagnosisUbaidillah HafidzÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPD Case Study ResearchDocument5 paginiCOPD Case Study ResearchErica MotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet - Respiratory ExaminationDocument11 paginiSheet - Respiratory ExaminationbakesamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diseases of The Respiratory SystemDocument71 paginiDiseases of The Respiratory SystemZafir SharifÎncă nu există evaluări