Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
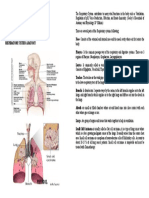
Breathing and Exchange of Gases
Încărcat de
jubinmb4181Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Breathing and Exchange of Gases
Încărcat de
jubinmb4181Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 17
Breathing and Exchange of Gases
1 Alveoli are made up of a. Endothelium b. Squamous epithelium e. Basement membrane c. Cuboidal epithelium
d. Columnar epithelium 2
The volume of air that remains in the lungs after a forceful expiration is: a. Tidal volume b. ERV c. RV d. VC e. IRV
Formation of carbonic acid in RBC is catalysed by a. Succinate dehydrogenase d. Hydrolase b. Carbonic anhyctoase e. Catalase produced by the tissues is transported as b. H Co3 Carboxy haemoglobin c. KHVO3 d. Carbaminohaemoglobin c. Oxygenase
70% of Co2 a. HHb e.
Tidal volume is a. 150 ml b. 500 ml c. 350 ml d. 1000 ml e. 3000 ml
TV + IRV + ERV is a. Vital capacity d. Functional residual volume b. Residual Volume e. Tidal volume c. Total lung capacity
Double layered membrane enclosing lungs is called: a. Pericardium e. Mesorarium b. Pleura c. Mediastinum d. Mesorchium
Name the respiratory organ of earthworm a. Parapodia b. skin c. Gills d. Book gills e. Both a & b
Which is the sound box? a. Larynx b. Pharynx c. Trachea d. Buccal e. Epiglottis
10
Oxyhaemoglobin is formed when a. b. c. d. e. Oxygen combines with water Oxygen combines with Hb Hb reacts with H+ CO2 reacts with HCO3 Dissociation of carbaminohaemoglobin
11
Where does the diffusion occur in the lungs? a. Primary bronchi d. Alveoli b. Secondary bronchi c. Bronchioles
e. Both a & b
12
Oxygen is transported to every cells by a. WBC b. RBC c. Plasma d. Both RBC and plasma
e. WBC, RBC and plasma 13 Which of the following is not a conducting part of the respiratory system? a. Alveoli 14 b. Bronchioles c. trachea d. External nares e. Bronchi
Epiglottis protects the opening of a. Larynx b. Pharynx c. Trachea d. Bronchi e. Bronchiole
15
Asthma is due to a. Inflammation of alveoli b. Inflammation of bronchi c. Inflammation of bronchiole d. Both a & b e. Both b & c
16
Which is an occupational lung disease? a. Silicosis b. Asthma c. Emphysema d. Pneumonia e. bronchitis
17
A decrease in respiratory surface due to permanent damage of alveolar walls is: a. Pneumonia b. Silicosis c. Cirrhosis d. Emphysema e. Hypoxia
18
At high altitude, the RBCs in the human blood will
a. Increase in
number
b. Decrease in number e. None of the above
c. Increase in size
d. decrease in size 19 Average breathing rate is a. 16 per minute d. 72 per minute 20
b. 14-16 per minute e. 78 per minute
c. 12-16 per minute
About 97% of oxygen is transported by RBC. The remaining 3% is a. Dissolved in plasma and transported c. Remain in trachea b. Remains in lungs e. None of the above
d. Associate with RBC
21
Volume of air that will remain in the lungs after a normal expiration. a. RV b. VC c. FRC d. IRV e. ERV
22
Every 100 ml of deoxygenated blood delivers approximately a. b. c. d. e. 3 ml of Co2 6 ml of Co2 2 ml of Co2 4 ml of Co2 8 ml of Co2 to the alveoli to the alveoli to the alveoli to the alveoli to the alveoli
23
Every 100 ml of oxygenated blood can deliver d around _________ water normal physiological conditions a. b. c. d. e. 8 ml of O2 to the tissues 6 ml of O2 to the tissues 9 ml of O2 to the tissues 4 ml of O2 to the tissues 5 ml of O2 to the tissues
24
The fastest known enzyme in biological system is a. Hexokinase d. Cytochrome b. AT Pase e. None c. Carbonic anhydrase
25
Oxygen debt in exercising muscles results in the accumulation of a. Pyruvic acid e. Co2 b. Lactic acid c. Acetyl CoA d. Isocitric acid
26
Sleeping in closed room with burning lamp may cause death due to a. Co2 poisoning e. SO2 b. O2 deficiency c. CO poisoning d. Smoking
27
During inspiration, the diaphragm a. expands b. shows no change c. contracts and flattens e. become are shaped
d. relaxes to become dome-shaped 28
What happens to the windpipe, or trachea, before in reaches the lungs? a. b. c. d. e. It branches in two directions It branches in three directions It vibrates and creates sound It closes up so that no oxygen can escape Both of them turns to one direction
29
Haemoglobin oxygen dissociation curve is a. Sigmoid b. Constant c. Straight line d. Parabolic e. Zig-zag
30
What body structure protects the lungs from outside harm? a. Cartilage b. Tiny sacs c. The rib cage d. The diaphragm e. Bone
ANSWERS:
1.b
2.c 14.a 26.c
3.b 15.e 27.c
4.b 16.a 28.a
5.b 17.d 29.a
6.a 18.a 30.c
7.b 19.c
8.b 20.a
9.a 21.c
10.b 22.d
11.d 23.e
12.d 24.c
13.a 25.b
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- BreathingDocument46 paginiBreathingRamnaresh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCA Cycle MCQDocument2 paginiTCA Cycle MCQTinsae WorkuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adult 1 Study Guide Exam 2Document7 paginiAdult 1 Study Guide Exam 2Christopher JamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 HypoxiaDocument37 pagini4 HypoxiaandrenicholastobingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breathing Organs Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiBreathing Organs Lesson PlanLONDONÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Difficulties in BreathingDocument4 paginiNCP Difficulties in BreathingKingJayson Pacman06Încă nu există evaluări
- The Six Minute Walk TestDocument4 paginiThe Six Minute Walk Testhm3398Încă nu există evaluări
- Management of Hypoxia During AnaesthesiaDocument5 paginiManagement of Hypoxia During AnaesthesiaNurhafizahImfista100% (1)
- A Case Study of Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation (Baiae)Document10 paginiA Case Study of Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation (Baiae)Janina RojoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alteration in VentilatoryDocument3 paginiAlteration in Ventilatoryjay camille buhanginÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument18 paginiAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeFasiha SamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap. RespiratorDocument42 paginiAp. RespiratorElena-Raluca CiolanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monal DM Respirator SpecificationsDocument3 paginiMonal DM Respirator SpecificationsMadhavesh KulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ans Key Class 7 Worksheet CH 10 ScienceDocument2 paginiAns Key Class 7 Worksheet CH 10 ScienceAishwarya DattaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Incidentsduring Perioperative Period Sept 2011Document106 paginiCritical Incidentsduring Perioperative Period Sept 2011wellawalalasithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Respiratory System Aniket DasDocument11 paginiHuman Respiratory System Aniket DasChep KepÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumothoraxDocument3 paginiPneumothoraxYara YousefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventilator Graphics.Document69 paginiVentilator Graphics.LauraAlvarezMulett100% (2)
- Mang Kanor ANAPHYDocument1 paginăMang Kanor ANAPHYChamelli RobinÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReportDocument7 paginiReportThomas Yeung100% (1)
- ADP ATP and Cellular RespirationDocument128 paginiADP ATP and Cellular RespirationLeona Trinity AranasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final PhysioDocument1.111 paginiFinal PhysioSana Savana Aman R100% (1)
- Lung Deposition Predictions of Airborne ParticlesDocument10 paginiLung Deposition Predictions of Airborne ParticlesJimmy Wea ChittiwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kerry GomesDocument23 paginiKerry GomesAbegail IbañezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Lungs and ThoraxDocument58 paginiAssessment of Lungs and ThoraxShahmeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examination of The Respiratory SystemDocument12 paginiExamination of The Respiratory SystemChris Jardine LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Compressed Cellular RespDocument11 pagini5 Compressed Cellular RespLIM ZHI SHUENÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem ListDocument2 paginiProblem List22 - Fernandez, Lyza Mae D.Încă nu există evaluări
- The Respiratory System: Read The Text Below. Then, Answer The Questions On Pages 2 and 3Document3 paginiThe Respiratory System: Read The Text Below. Then, Answer The Questions On Pages 2 and 3nasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxygen Administration and Monitoring ProcedureDocument6 paginiOxygen Administration and Monitoring ProcedureamitÎncă nu există evaluări