Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Present Continuous
Încărcat de
Andreea BalabanDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Present Continuous
Încărcat de
Andreea BalabanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
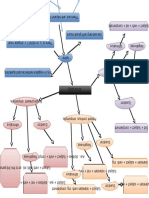
Present Continuous The present continuous tense (also called the present progressive tense) is commonly used in English
for actions happening right now, or in the future. This page will explain the rules for forming the tense with regular verbs. Forming the present continuous tense Verbul a fi (to be) + verbul conjugat + terminatia ing Subject I You He She It We They BE am are is is is are are -ING form singing singing singing singing singing singing singing
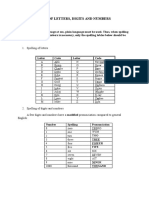
How to make the -ING form With many verbs, you can simply add -ING to the end of the verb. However, with some verbs, you need to change the ending a little. Here are the rules: Verb ending in... one vowel + one consonant How to make the -ING form Examples Double the consonant, then add -ING swim - swimming hit - hitting get - getting Remove E, then add -ING come - coming lose - losing live - living Add -ING say - saying go - going walk - walking Forming a negative Negatives in the present continuous are formed by adding not or n't after the verb BE: Positive sentence Negative sentence Contracted negative I am eating. I am not eating. I'm not eating. You are working. You are not working. You aren't working. He is driving. He is not driving. He isn't driving. She is teaching. She is not teaching. She isn't teaching. It is raining. It is not raining. It isn't raining. We are reading. We are not reading. We aren't reading. They are writing. They are not writing. They aren't writing. Forming a question Yes/no questions are created by moving the verb BE to the beginning of the sentence. WH-questions are formed by moving the verb BE, and then adding the WH- word. Here are the rules: Statement Yes/no question WH- question I am eating. Am I eating? What am I eating?
one vowel + one consonant + E
[anything else]
You are crying. He is going. She is arriving. It is sleeping. We are leaving. They are fighting.
Are you crying? Is he going? Is she arriving? Is it sleeping? Are we leaving? Are they fighting?
Why are you crying? Where is he going? When is she arriving? Why is it sleeping? When are we leaving? Why are they fighting?
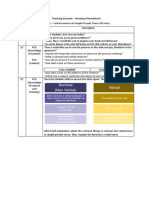
USE 1 Now Use the Present Continuous with Normal Verbs to express the idea that something is happening now, at this very moment. It can also be used to show that something is not happening now. Examples: You are learning English now. You are not swimming now. Are you sleeping? I am sitting. I am not standing. Is he sitting or standing? They are reading their books. They are not watching television. What are you doing? Why aren't you doing your homework? USE 2 Longer Actions in Progress Now In English, "now" can mean: this second, today, this month, this year, this century, and so on. Sometimes, we use the Present Continuous to say that we are in the process of doing a longer action which is in progress; however, we might not be doing it at this exact second. Examples: (All of these sentences can be said while eating dinner in a restaurant.) I am studying to become a doctor. I am not studying to become a dentist. I am reading the book Tom Sawyer. I am not reading any books right now. Are you working on any special projects at work? Aren't you teaching at the university now? USE 3 Near Future Sometimes, speakers use the Present Continuous to indicate that something will or will not happen in the near future. Examples: I am meeting some friends after work. I am not going to the party tonight. Is he visiting his parents next weekend? Isn't he coming with us tonight? USE 4 Repetition and Irritation with "Always" The Present Continuous with words such as "always" or "constantly" expresses the idea that something irritating or shocking often happens. Notice that the meaning is like Simple Present, but with negative emotion. Remember to put the words "always" or "constantly" between "be" and "verb+ing."
Examples: She is always coming to class late. He is constantly talking. I wish he would shut up. I don't like them because they are always complaining. Task 1: Make the following sentences negative. 1. I am thinking. 2. You are singing. 3. He is eating jelly. 4. She is studying hard. 5. It is raining now. 6. We are having tea. 7. They are driving to Toronto Task 2 1. They ........................ (study) at the moment. 2. She ........................ TV. 3. What ........................ (you/read) at the moment? 4. I ........................ (cook) dinner tonight. Would you like to come? 5. It ........................ (work). I think it's broken. 6. He ........................ (learn) German for his job.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Sesion 6 Present ContinuousDocument24 paginiSesion 6 Present ContinuousWalter Atao SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Likes, Dislikes, Preferences1Document4 paginiLikes, Dislikes, Preferences1Hanz ElmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses: She Works Five Days A Week. Father Takes A Train To Go To Office. A Mouse Eats My Food Every MorningDocument62 paginiTenses: She Works Five Days A Week. Father Takes A Train To Go To Office. A Mouse Eats My Food Every MorningdiniiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Past Simple Continuous PDFDocument2 pagini02 Past Simple Continuous PDFManuel PérezÎncă nu există evaluări
- EsctructursDocument1 paginăEsctructursJoan SebastianÎncă nu există evaluări
- SILABUS Semester II BandungDocument13 paginiSILABUS Semester II Bandungsari hafizhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Simple-Interrogative Form and Short AnswersDocument1 paginăPast Simple-Interrogative Form and Short AnswersSebi BerbinschiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ed Ing AdjectivesDocument2 paginiEd Ing AdjectivesAndrew TurveyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus Progredito - INGLESE: CompetencesDocument6 paginiSyllabus Progredito - INGLESE: CompetencesChiara BortolussiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planificacion Ingles 1 UstDocument19 paginiPlanificacion Ingles 1 UstJuan Pablo Ojeda AndersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- English+Sentence PatternsDocument19 paginiEnglish+Sentence PatternsAndini100% (1)
- Unit 1Document2 paginiUnit 1Ana KosÎncă nu există evaluări
- I, Em, 1, IfrDocument72 paginiI, Em, 1, IfrIulia CerneschiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 - Grammar PDFDocument4 paginiUnit 1 - Grammar PDFRicardo CezarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SILABUSDocument16 paginiSILABUSMUKSINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 Meteorological Conditions and Navigational WarningsDocument4 paginiUnit 3 Meteorological Conditions and Navigational WarningsWeslyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self Study HandoutDocument45 paginiSelf Study HandoutMacarena Arévalo AlarcónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bab 5678 FaniDocument107 paginiBab 5678 FaniFianico Sukmana RozyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2-Maritime Communication - Part 2-Week 14 - Session 2Document27 paginiUnit 2-Maritime Communication - Part 2-Week 14 - Session 2BettoPerverttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 11Document20 paginiUnit 11Petrish JohnnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Progressive TenseDocument21 paginiPresent Progressive TenseWillan Bustamante SánchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Present Simple: Emma Pedley, M.A. (Cantab) CELTADocument12 paginiThe Present Simple: Emma Pedley, M.A. (Cantab) CELTAMoisés IsraelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Present Simple Tense: Zion LanguagesDocument23 paginiThe Present Simple Tense: Zion LanguagesZion Languages100% (1)
- Modal VerbsDocument5 paginiModal VerbsAdrián SarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 11 Report EventsDocument15 paginiUnit 11 Report EventsSariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teaching Scenario - Simple Present Tense (Nominal and Verbal)Document3 paginiTeaching Scenario - Simple Present Tense (Nominal and Verbal)PearlÎncă nu există evaluări
- My New Normal" Recursos PDFDocument7 paginiMy New Normal" Recursos PDFWander Miguel Mendoza ChinchayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Silabus DP - IV Pembentukan 9 - 24Document20 paginiSilabus DP - IV Pembentukan 9 - 24sari hafizhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Port ProcedureDocument21 paginiUnit 1 Port ProcedureSariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modul Bahasa Inggris Semester IiDocument75 paginiModul Bahasa Inggris Semester IiIkhwal MaulanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jadwal Training Me StipDocument1 paginăJadwal Training Me StipSariÎncă nu există evaluări
- He Went To Buy Some Bread. Smoking Is Dangerous. He Would Like To See His Frinds TonightDocument2 paginiHe Went To Buy Some Bread. Smoking Is Dangerous. He Would Like To See His Frinds TonightGeorgiana LuminiţaÎncă nu există evaluări
- B - All, Most, Some, Any, NoneDocument2 paginiB - All, Most, Some, Any, NoneCamila PaulucciÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjectives and Adverbs The ComparisonDocument2 paginiAdjectives and Adverbs The Comparisonthaziz100% (1)
- Materi Marlin Bab 13-14Document18 paginiMateri Marlin Bab 13-14Fianico Sukmana RozyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect & ProgressiveDocument16 paginiPresent Perfect & ProgressiveRizqi AmaliyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardinal Directions Lesson Plan: Abbie RossmanDocument6 paginiCardinal Directions Lesson Plan: Abbie RossmanKathleen MoradaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engleza Sem.iDocument28 paginiEngleza Sem.iMaron NamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading QuestionnaireDocument3 paginiReading QuestionnaireSariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Talking About TimeDocument5 paginiTalking About TimeNajibur Rasul100% (1)
- Curs IMO EnglezaDocument11 paginiCurs IMO EnglezaSalam AlecuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal Pronouns and Possessive Adjectives Drawing Game PDFDocument2 paginiPersonal Pronouns and Possessive Adjectives Drawing Game PDFBegoña Santamaria100% (1)
- Ifr em I, 1 U4Document8 paginiIfr em I, 1 U4Marian MunteanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMLP Click Here!Document9 paginiIMLP Click Here!thomnav100% (2)
- GR PhoneticsDocument2 paginiGR PhoneticsFeritFazliuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conjugación Del Presente SimpleDocument3 paginiConjugación Del Presente Simpleivos27100% (1)
- 7 Passive VoiceDocument10 pagini7 Passive VoiceMuhammadMahmoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATERI & SOAL BAHASA INGGRIS MARITIM KELAS X 24 MaretDocument2 paginiMATERI & SOAL BAHASA INGGRIS MARITIM KELAS X 24 MaretIsma SariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1) Mayday Mayday MaydayDocument4 pagini1) Mayday Mayday MaydayciortescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 - Ship OrganizationDocument20 pagini12 - Ship OrganizationmarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LESSONPLANDocument3 paginiLESSONPLANRan FlixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teaching Scenario - Verbal Simple Present Tense (Habit)Document5 paginiTeaching Scenario - Verbal Simple Present Tense (Habit)PearlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Simple vs. ContinuousDocument2 paginiPast Simple vs. ContinuousGeorgiana LuminiţaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Say The DateDocument2 paginiSay The DateManuela Elena Monceanu Neagoie100% (1)
- Act2 Exp8 Ingles A2 5toDocument4 paginiAct2 Exp8 Ingles A2 5toDarckiiTo Prince IglesiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Continuous FormsDocument3 paginiPresent Continuous FormsAdina100% (1)
- Present Simple or Continuous Review Clasa A 6Document6 paginiPresent Simple or Continuous Review Clasa A 6Liliana GheorgheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Continuous TenseDocument3 paginiPresent Continuous TenseRaihani Tania Ghinawati Tania GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present ContinuousDocument4 paginiPresent ContinuousCamelia PleșaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present and ContinousDocument6 paginiSimple Present and ContinousVanja GrujicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hebrew Basic Lessons - Learn To Read Biblical HebrewDocument78 paginiHebrew Basic Lessons - Learn To Read Biblical Hebrewpronounsir89% (9)
- Hebrew Basic Lessons - Learn To Read Biblical HebrewDocument78 paginiHebrew Basic Lessons - Learn To Read Biblical Hebrewpronounsir89% (9)
- Handbook To The Exegesis of The New Testament PDFDocument654 paginiHandbook To The Exegesis of The New Testament PDFAndreea Balaban92% (12)
- Handbook To The Exegesis of The New Testament PDFDocument654 paginiHandbook To The Exegesis of The New Testament PDFAndreea Balaban92% (12)
- Possessive SDocument2 paginiPossessive SAndreea BalabanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal PronounsDocument2 paginiPersonal PronounsAndreea BalabanÎncă nu există evaluări
- K. Joseph Lourie (1992) Soviet Refuseniks' Turn To Orthodox Judaism, East European Jewish AffairsDocument13 paginiK. Joseph Lourie (1992) Soviet Refuseniks' Turn To Orthodox Judaism, East European Jewish AffairsAndreea BalabanÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 3 Class Activity Part C 28 To 39Document34 paginiEnglish 3 Class Activity Part C 28 To 39PUpi Ggz0% (3)
- German Signalling PDFDocument35 paginiGerman Signalling PDFcarlikisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Future Perfect TenseDocument3 paginiFuture Perfect TenseMirjana PaunovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogue - Cambridge Exams Resources MaterialDocument162 paginiCatalogue - Cambridge Exams Resources MaterialBrinzea Laura100% (1)
- Islcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Preintermediate A2 Intermediate b1 Upperintermediate b2 Adults Students With Spec 20243063855760b0239d23d7 03043871Document2 paginiIslcollective Worksheets Elementary A1 Preintermediate A2 Intermediate b1 Upperintermediate b2 Adults Students With Spec 20243063855760b0239d23d7 03043871Francoes MitterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be Able ToDocument5 paginiBe Able ToMarcosTupiaAronesÎncă nu există evaluări
- USE 2 Facts or Generalizations: Simple PresentDocument3 paginiUSE 2 Facts or Generalizations: Simple PresentSusanManchegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 4 I. Decide Which Parts of Speech Are The Underlined WordsDocument3 paginiTest 4 I. Decide Which Parts of Speech Are The Underlined WordsAngelina KostovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The PassiveDocument3 paginiThe PassivemariepalmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kabaddi Rules and Measurement of Kabaddi FieldDocument5 paginiKabaddi Rules and Measurement of Kabaddi FieldSatyam kumar Upadhyay80% (5)
- Reported Speech 21Document25 paginiReported Speech 21mscanlanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Point RPP 3.2 RafflesiaDocument15 paginiPower Point RPP 3.2 RafflesiaArip WicaksonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 11Document189 paginiExp 11toporiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bs en Iso 17637 PreviewDocument8 paginiBs en Iso 17637 PreviewUlviyye ElesgerovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dodgeball Tournament RulesDocument2 paginiDodgeball Tournament Rulesapi-275848882Încă nu există evaluări
- Squib 1Document11 paginiSquib 1Jonathan Andrew CrumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Articles, Nouns and Pronouns OverviewDocument12 paginiArticles, Nouns and Pronouns OverviewbijendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- New 4th MT Grade 1Document13 paginiNew 4th MT Grade 1Miriam VillegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Degrees of ComparisonDocument7 paginiDegrees of ComparisonrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Checklist For IGCSE FLE 0500 FINAL2Document13 paginiRevision Checklist For IGCSE FLE 0500 FINAL2Nalina Balasingam100% (5)
- List of Past ParticipleDocument3 paginiList of Past Participlepuya_57497100% (2)
- Anul Scolar 2010-2011 Profesor: Disciplina: Limba Engleza Cls. A VIII-a, 2h/sapt., L1 Manual: High Flyer (Upper Intermediate), Editura LongmanDocument3 paginiAnul Scolar 2010-2011 Profesor: Disciplina: Limba Engleza Cls. A VIII-a, 2h/sapt., L1 Manual: High Flyer (Upper Intermediate), Editura LongmanDaniela MincaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canada Soccer Pathway Coachs Tool Kit 3Document72 paginiCanada Soccer Pathway Coachs Tool Kit 3Felipe Almada OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan of Junior High School EnglishDocument7 paginiLesson Plan of Junior High School Englishoceansaway2100% (6)
- Direct and Indirect Speech - (With Examples and Exercises)Document21 paginiDirect and Indirect Speech - (With Examples and Exercises)Abbas MaliknaseemÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRACTICE (Conditionals, Modal Verbs, Relative Clauses, Reported Speech)Document2 paginiPRACTICE (Conditionals, Modal Verbs, Relative Clauses, Reported Speech)Andreia SimõesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hocak DictionaryDocument127 paginiHocak Dictionaryalexandreq100% (2)
- Connectors in English GrammarDocument6 paginiConnectors in English GrammarBily ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Starter Teacher's Guide: Notes On The Third EditionDocument17 paginiGrammar Starter Teacher's Guide: Notes On The Third EditionmariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar and Vocabulary-SyllabusDocument84 paginiEnglish Grammar and Vocabulary-SyllabusHiteshRawal100% (1)
- Body Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.De la EverandBody Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (81)
- Summary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (4)
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonDe la EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (21)
- Writing Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsDe la EverandWriting Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageDe la EverandWordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (428)
- Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSurrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- Learn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachDe la EverandLearn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (15)
- How Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideDe la EverandHow Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageDe la EverandThe Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (916)
- On Speaking Well: How to Give a Speech with Style, Substance, and ClarityDe la EverandOn Speaking Well: How to Give a Speech with Style, Substance, and ClarityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (15)
- The Practice of Poetry: Writing Exercises From Poets Who TeachDe la EverandThe Practice of Poetry: Writing Exercises From Poets Who TeachÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundDe la Everand1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (13)
- Learn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachDe la EverandLearn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (81)
- Everything You'll Ever Need: You Can Find Within YourselfDe la EverandEverything You'll Ever Need: You Can Find Within YourselfEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (41)
- How to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingDe la EverandHow to Read a Book: The Classic Guide to Intelligent ReadingEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (26)
- Idioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsDe la EverandIdioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (7)
- Dictionary of Fine Distinctions: Nuances, Niceties, and Subtle Shades of MeaningDe la EverandDictionary of Fine Distinctions: Nuances, Niceties, and Subtle Shades of MeaningÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do You Talk Funny?: 7 Comedy Habits to Become a Better (and Funnier) Public SpeakerDe la EverandDo You Talk Funny?: 7 Comedy Habits to Become a Better (and Funnier) Public SpeakerEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (20)
- Learn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachDe la EverandLearn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (136)
- Learn Italian with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Italian Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachDe la EverandLearn Italian with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Italian Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (47)
- The History of English: The Biography of a LanguageDe la EverandThe History of English: The Biography of a LanguageEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (8)
- Writing to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllDe la EverandWriting to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (83)
- Learn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachDe la EverandLearn German with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: German Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (151)
- The Art of Writing: Four Principles for Great Writing that Everyone Needs to KnowDe la EverandThe Art of Writing: Four Principles for Great Writing that Everyone Needs to KnowEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (21)
- Spanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesDe la EverandSpanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)