Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
For Printing Grand Case Group1
Încărcat de
Joco Bordeos AripDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
For Printing Grand Case Group1
Încărcat de
Joco Bordeos AripDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
A Case Study in Congestive Heart Failure
Presented To The Faculty of the College of Nursing University of Perpetual Help System DALTA Alabang- Zapote Road, Las Pinas City
In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements In NCM 104 RLE
Submitted By: Abad, Maria Angelica S. Abangan, Daryl Rey A. Abarca, Weena Czarina Mae P Agnir, Marc Kharis G. Alindogan, Angelica P. Arcilla, Rinald Franz R. Argosino, Caszandra G. Arip, Sharmina B. Babasa, Carmen G. Bareno, Abigail R. Barrazona, Tricia S. Mrs. Gracila Ucag-Decena, RN, MAN Clinical Instructor February 2012
TABLE OF CONTENTS I. II. III. IV.
V. VI.
Introduction Patients profile Genogram Nursing History Physical Examination Diagnostic/Laboratory Examination 14
3 4 5 6 9
VII. Clinical Findings
16 17 20 20 21 29 34 36
VIII. IX. X. XI.
Anatomy and Physiology/Pathophysiology Problem Prioritization Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Care Plan
XII. Drug Study XIII.
Discharge Planning Reference/Bibliography
XIV.
I.
INTRODUCTION
Patient R.C.S is admitted at the University of Perpetual Help Medical Center with a chief complaint of Easy Fatigability. His admitting diagnosis is T/C CHF FC II, UTI HASCVD Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a condition in which the heart's function as a pump is inadequate to meet the body's needs. Signs and symptoms include fatigue, excess fluid in the lungs and shortness of breath, constipation, dizziness, sore throat, neck pain and lower back pain, along with headaches. Interventions on CHF would be such of lifestyle modifications, medicines and heart transplant. On the other hand UTI or urinary tract infection is an infection caused by pathogenic organisms such as bacteria, fungi, or parasites. In any of the structures that comprise the urinary tract. Signs and symptoms include painful and burning urination, cloudy and strongsmelling urine, pelvic pain for women and rectal pain on men. Treatment for thus include antibiotic therapy. We handled patient R.C.S during his second day at the hospital. We rendered nursing interventions such as established rapport, assessed patients overall and current status, regulatated and monitored intravenous fluid, due oral meds given, monitored intake and output, we also rendered health teaching for the enhancement of his health condition, vital signs taken and recorded, administered and monitored oxygen inhalation, performed physical assessment, interviewed patient using Gordons Functional Health Pattern to provide baseline data. Our purpose for accomplishing this case study is to provide further information to other students as well as nurses that may also need this case study in the future. It will also improve the quality of care rendered by nurses to patient. We also aim to prolong the lives of the patients. Lastly, it sets us to learn, enhance and gain knowledge, as well as helps patients to understand their current condition.
II. PATIENTS PROFILE Patients Name: Address: Sex: Civil Status: Age: Birthday: Occupation: Nationality: Religion: Admission Date: Institution: Physician: Admitting Diagnosis: Final Diagnosis: Chief Complain: Male Widowed 79 April 7, 1932 Retired Filipino Roman Catholic January 30, 2012 Admission Time: 8:30 pm R.C.S 31 Manggahan Burgos Street Laspinas City
University of Perpetual Help Dalta Medical Center Dr. Rodriguez, Andrei Rhonel T/C CHF FC II, UTI HASCVD CHF FC II, UTI Easy Fatigability
III.
GENOGRAM
GM
GF
GM
GF
? ?
G Legend: GM: Grandmother GF: Grandfather B: Boy G: Girl : Hypertension : Diabetic : Deceased ?? : Unknown number
Pt ..
IV.
NURSING HISTORY Three days prior to admission, patient R.C.S. was noted to have occasional episodes of
easy fatigability with dyspnea. No other associated symptoms such as chest pain or fever noted. No consultation were done and no medications were taken. Few hours prior to admission, patient still with episodes of easy fatigability sought consult at Jonelta OPD, then was later transferred to ER of University of Perpetual Help Dalta Medical Center and was advised for admissions. (+) Angiogram (Feb 2011), (+) Inguinal Hernia (year unknown), (-) DM, (-) HPN, (-) Asthma. Previous chronic smoker, occasional alcoholic beverage drinker. Pt. has undergone Coronary angiography and left ventriculography at St. Lukes Medical Center last February 3, 2011 with an operative diagnosis of Atherosclerotic CAD mild dse involving proximal and mid LAP, proximal to mid RCA. Patient RS tolerated the procedure well and was hemodynamically stable all- throughout.
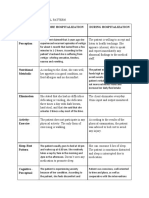
V. GORDONS FUNCTIONAL HEALTH ASSESSMENT 1. Health Perception Patient R.C.S describes health as having enough energy. The reason of his health care visit is easy fatigability. He manages his condition through having adequate rest. He takes medications for his illness. Patient R.C.S. seeks health advice from a resident doctor and follows the doctors advice for the betterment of his health condition. Patient R.S. used to smoke and drink alcohol when he was teenager. 2. Nutritional Metabolic Patterns Patient R.C.S. usually follows a soft diet meal such as soup and vegetables, and also observes a LFLS diet. He sometimes eats rice and meat. He also takes supplements like Centrum, a multivitamins that helps him to boost his immune system. He usually drinks water about 1 to 2 liters before, but currently limited to 500 ml per day. He sometimes experiences difficulty in swallowing when eating rice and meat while in the hospital. He has no allergy to any foods. He also has dental problems and wears dentures. 3. Elimination Pattern Patient R.C.S. voids 5 to 6 times a day. He stated that sometimes he feels pain when urinating. The color is amber yellow. He has a bowel movement every other day. His feces are hard and color brown. He also experienced having a urinary catheter because of pain in the prostate and difficulty in urinating. He also used laxatives or suppositories before. 4. Activity Exercise Pattern
Patient R.C.S. has easy fatigability and minimal participation on the house hold chores. He used to do some light exercises. He verbalized that he often sits in front of the TV. He has a problem in ambulating due to pedal edema and pain. When he has no illness, he can do things on his own but with assistance most of the time.
5. Sleep Pattern Patient R.C.S. usually sleeps at night around 8 to 9 oclock and wake up at 8 oclock in the morning. He usually takes 30 minutes to fall asleep and states that he feels like nalulunod. He also stated that most of the time, he is naaalimpungatan. 6. Cognitive Perceptual Pattern
Patient R.C.S is able to write and read. He has hearing difficulties. He also has eye problem and uses glasses when reading. His last eyexam was a year ago. He feels chest pain sometimes.
7. Role Relationship Pattern Patient R.C.S. lives with his daughter and grandchildren. His wife passed away due to liver cancer. The one that supports him financially and provides his needs are his children. His family is important to him. He said that they havent had any conflict in their family. 8. Coping/ Stress Tolerance Patient R.C.S. has major changes in his life the past two years, especially when he had undergone through a Coronary Angiography Left Ventriculography. When he has problems the one that he talked to is his children. He is always relaxed at home. He used to take alcohol or smoke tobacco whenever he has problem before. 9. Value Belief Pattern Patient R.C.S. had accomplished many things in life and thanks God for this life. He wants his grandchildren to finish their studies. And he always prays to God to give him good health in order for him to live longer and so he can spend more time with his family. He stated that his religion is important.] 10. Self-Esteem, Self-Concept, Self-Perception Pattern Patient R.C.S describes himself as family-oriented person. He loves his family the most. He also states that he has many friends. At present, he is concerned about how will he be able to cope up with his current health condition. He also states that he is already contented with the way his life is right now in terms of his childrens conditions.
VI. Date done: January 31, 2012
Parts General Survey Body Built Posture and Gait Hygiene and Grooming Body Odor Signs of distress Affect or Mood Speech Emotional state Vital Signs Temperature Pulse Rate Respiratory Rate Blood Pressure Inspection Palpation Inspection Inspection Inspection Inspection Inspection Inspection Techniques Used
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Normal Findings
Actual Findings
Analysis
Proportionate Relaxed and Erect Clean and neat No odor No distress Cooperative Understandable Happy
Thin Relaxed and Erect Clean and neat No odor No distress Cooperative Understandable Happy
Due to Lack of appetite Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal
Interview; Inspection Interview; Inspection Interview Observation
Axillary 60-100bpm: Radial 12-20cpm 120/80mmHg
35.5 degrees Celsius 79 beats/min: Regular 29 cpm: regular 90/70 mmHg: Sitting
Normal Normal Due to CHF Due to the inability of the heart to pump sufficient blood around the bod,y a complication of CHF
Skin and Nails
Color Symmetry of Color Edema Skin Lesion Moisture Skin Turgor Nail Curvature Texture Nail bed color Surrounding Tissue Capillary Refill Head Distribution Thickness Texture and Oiliness Infestations Body Hair Size and Shape Contour Facial Features
Inspection Inspection Inspection; Palpation Inspection Inspection Palpation upon pinching Inspection Inspection Inspection Inspection Blanch Test
Based on Race Uniform No edema Smooth Moist Good Convex 160 degrees Smooth Pink and Clear Intact Less than 4 seconds
Brown Uniform Grade 2 pitting edema Smooth; Flat Nevi Dry Poor Convex 160 degrees Smooth Pink and Clear Intact 6 seconds
Normal Normal Due to CHF Normal Decrease skin elasticity Excess Fluid Volume Normal Normal Normal Normal Decreased tissue perfusion
Inspection Inspection Inspection Inspection Inspection Inspection Inspection; Palpation Inspection
Even Thick Silky No Infestations Sparse Leg hair Normocephalic Smooth Symmetrical
Uneven Thin Silky No infestation Sparse leg hair Normocephalic Smooth Symmetrical
Due to aging Due to aging Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal
Eyes Eyebrows Eye Lashes Inspection Inspection Even distribution Even distribution Even distribution Even distribution Normal Normal 10
Pupils Conjunctiva Visual Acquity Ears Ear Canal Pinna Hearing Acquity Nose Symmetry Nasal Cavity Sinus Tenderness Pharynx Uvula Tonsils Gag Reflex
Inspection Inspection Inspection
PERRLA Pinkish Able to read
PERRLA Pale Able to read with glasses
Normal Decreased tissue perfusion Due to impaired visual acuity
Inspection Inspection Inspection Uniform color with skin Intact
Dry cerumen Uniform color; Symmetrical Poor hearing
Normal Normal Due to aging
Inspection Inspection Inspection
Symmetrical Septum in midline Not tender
Symmetrical Septum in midline Not tender
Normal Normal Normal
Inspection Inspection Inspection
In midline Pink and smooth Intact
In midline Pink and smooth Intact
Normal Normal Normal
Mouth Lips Teeth Tongue Palate Inspection; Palpation Inspection Inspection Inspection Soft and Symmetrical Complete and shiny white Midline Light pink and smooth Dry and symmetrical Dentures Midline Light Pink and smooth Normal Due to aging Normal Normal
11
Neck Muscle Movement Range of Motion Lymph Nodes Carotid Pulse Jugular Veins Chest and Lungs Breathing Pattern Inspection; Auscultation Inspection Inspection; Palpation Inspection Auscultation Quiet; Regular; Effortless Symmetrical Aligned Smooth Clear Use of accessory muscle Symmetrical Aligned Smooth Crackles Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space Normal Normal Normal Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space Normal Normal Normal Inspection Inspection Inspection Palpation Palpation Inspection Equal in size Coordinated Full Not palpable Symmetric Pulse Not visible Equal in size Coordinated Full Not palpable Symmetric Pulse Not visible Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal Normal
Shape and Symmetry Spinal Alignment Skin Breath Sounds
Breast size and shape Areola Nipples
Inspection Inspection Inspection
Rounded Rounded Round; Symmetric
Rounded Rounded Round; Symmetric
Heart Precordium Heart Sounds Abdomen Skin Integrity Contour Inspection Inspection Unblemished Rounded Unblemished Rounded Normal Normal 12 Auscultation Auscultation Pulsation S1 louder at S2 at Base Pulsation S3 Normal Due to CHF
Bowel Sounds Back Extremities Muscle Size Muscle tone Muscle Strength
Auscultation
Normoactive
Normoactive
Normal
Inspection Inspection Inspection
Equal Firm Equal
Equal Firm Unequal
Normal Normal Due to aging
Bones Range of Motion
Inspection Inspection
Tenderness Full
Tenderness Limited
Normal Due to weakness
VII.
DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY EXAMINATION University of Perpetual Help DALTA Medical Alabang-Zapote Road Pamplona III, Las Pinas Laboratory/Diagnostic Department
13
Name: R.S Age:79 y/o Sex: Male DATE and TIME 1/30/12 2:12 PM EXAMINATION CBC RBC Hematocrit Hemoglobin WBC Stabs/Bands Segmenters Lymphocytes Basophils Monocytes Eosinophils Platelet count 2:49 PM BUN Creatinine Mg K Na 4:01 PM Color Transparency pH Protein Glucose Spec. Gravity RBC Pus cell Epithelial Bacteria 8:40 PM SGPT 1/31/12 FBS 5.58 29 Yellow Turbid 6 +1 1.025 0-3HPF 15-20HPF Few M. Thread Few 10.2 88 .94 3.6 132 RESULTS
Patient No. 9B A.P: Tabang, Antonio NORMAL VALUE 4.5-6 0.40-0.54 120-160 4.5-10 0.00-0.05 0.50-0.70 0.20-0.40 0.00-0.01 0.00-0.07 0.00-0.05 150-400 3.2-7.1 58-110 0.7-1.0 3.5-5 137-145 Yellow Clear 5-7 none none 1.010-1.025 None None Absence or Few Absence or few 21-72 4.10-5.9 UNIT INTERPRETATION
3.24 0.34 114 7.1 0.66 0.10 .10 0.03 162
X10^12/L L g/L X10^9/L % % % % x10^9/L mmol/L mmol/L mmol/L mmol/|L mmol/L U/L mmol/L
Anemia Risk for fluid volume excess Anemia Normal Normal Normal Active infection or immunodeficiency Normal Bacterial infection Normal Normal Renal problem Normal Normal Normal r/t Fluid Volume excess Normal Risk for infection Normal Proteinuria Normal Normal Risk for infection Risk for in fection Normal Normal Normal Normal
14
11:27 AM
Cholesterol HD Lipoprotein LD Lipoprotein Triglyceride Albumin K
3.39 0.85 2.3 .59 34 4.2
0-5.2 0-1.55 0-3.9 0-1.69 35-50 3.5-5
mmol/L mmol/L mmol/L mmol/L g/L mmol/L
Normal Normal Normal Normal Inflammation Normal
2/4/12 1:43 PM
Examination: Chest X-ray Portable Date: 1/30/2012 Interpretation: - Cardiomegaly, biventricular pattern - Atheromatus Aorta - Minimal Pleural effusion, Thickening, Left
Examination: QRS Morphology Date: 1/30/2012 Interpretation: Inferior Myocardial Infarction and Anterior Myocardial Infarction, AGE undetermined
Examination: Chest Decubitus Portable Date: 1/31/2012 Interpretation: (-) for pleural effusion
VIII. CLINICAL FINDINGS Clinical Findings: Congestive Heart Failure Signs and Symptoms:
15
Dyspnea Tachycardia Pedal edema Fatigue Pleural effusion Nasal Flaring
Jugular venous distention Crackles Chest pain Use of accessory muscle Hypotension
Patient experienced some the above signs and symptoms of Congestive Heart Failure which are listed above. Use of accessory muscle, Crackles, Nasal flaring, Pedal edema, and Hypotension is evident. Chest pain and fatigue are the subjective cues verbalized by the patient.
IX.
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
16
The heart is a muscular structure with four chambers and four valves. The upper chambers, which are filling chambers, are called the left and right atria. The lower chambers, which are pumping chambers, are called the left and right ventricle.
Heart valves lie at the exit of each of the four heart chambers and maintain one-way blood flow through the heart. The four heart valves make sure that blood always flows freely in a forward direction and that there is no backward leakage.
The tricuspid valve regulates blood flow between the right atrium and right ventricle.
17
The pulmonic valve controls blood flow from the right ventricle into the pulmonary arteries, which carry blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The mitral valve lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle. It prevents blood from leaking back into the left atrium during left ventricular contraction. The aortic valve lies between the left ventricle and the aorta (the largest artery in the body). It opens the way for oxygen-rich blood to pass from the left ventricle into the aorta, where it is delivered to the rest of the body. Blood flow through the heart The "left" side of the heart controls the flow of oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the entire body. The "right" side of the heart controls the flow of oxygen-poor blood from the veins in the body to the lungs.
Blood flows from the right and left atria into the ventricles through the open tricuspid and mitral valves, respectively; when the ventricles are full, the mitral and tricuspid valves close. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atria while the ventricles contract.
As the ventricles begin to contract, the pulmonic and aortic valves are forced open and blood is pumped out of the ventricles through the open valves into the pulmonary artery toward the lungs, and into the aorta, to the body.
When the ventricles finish contracting and begin to relax, the aortic and pulmonic valves close. These valves prevent blood from flowing back into the ventricles. This cycle is repeated over and over, causing blood to flow continuously to the heart, lungs and body.
18
Pathophysiology Modifiable factors:
Sedentary lifestyle, smoker, alcohol drinker, high carbohydrate high fat diet
Non- Modifiable factors:
Age: 79 years old, Family history of Hypertension
Accumulation of fatty streak in the intima of arterial wall
Decreased oxygenation of myocardium
19
Ischemia in the myocardium
Reduced myocardial contractility
Increased preload and afterload
Increased Cardiac Workload
Decreased Renal Perfusion
Decreased Cardiac output
Impaired peripheral circulation
Hypotension
Sodium Retention
Increased Osmotic Pressure
Increased Anti-diuretic hormone
Fluid Retention
Chronic tissue congestion
Urinary Retention
Fluid Overload
Enlargement of the heart
Urinary Tract Infection
Proliferation of bacteria in the Urinary tract
Destruction of capillaries
X.
PROBLEM PRIORITIZATION
Edema
Congestive Heart Failure
1. Impaired Gas Exchange 2. Decreased Cardiac Output 3. Excess Fluid Volume 4. Risk for Injury 5. Risk for Non-compliance 20
XI.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS A. Actual Problem
1. Impaired gas exchange related to ventilation perfusion imbalance as manifested by with oxygen of 3-4L/min via nasal cannula,(+) Crackles @ Left lungs, (+) Nasal Flaring, Tachypneic with the RR of 29cpm, (+) Retraction, Cold clammy skin, BP of 90/70, and capillary refill (6 sec.) 2. Decreased Cardiac Output r/t as manifested by, Pitting Edema on the right foot. (10 sec) Grade is 2+, Weakness,Cold clammy skin,Capillary refill (6 sec.), Dizziness, Lethargy, BP of
90/70mmhg
3. Excess fluid volume related to water retention secondary to CHF as manifested by pitting edema on the right foot. (10 sec) Grade is 2+, (+)Crackles @ Left lung, RR of 29cpm, BP of 90/70mmHg
B. Potential Problem
1. Risk for injury r/t altered mobility as manifested by (+) weakness, Ambulatory w/ assistance, Blurred Vision, BP: 90/70, w/ O2 administration via cannula 2. Risk for non-compliance secondary to knowledge deficit as manifested by (+) confusion on present condition. And frequent asking of question
21
XII.
NURSING CARE PLAN A. Actual
Assessment Subjective: Nahirapan akong huminga pag wala nitong oxygen. -Fatigue Objective: With oxygen of 34L/min via nasal cannula (+) Crackles @ Left lung (+) Nasal Flaring Tachypneic with the RR of 29cpm (+) Retraction Cold clammy skin BP of 90/70 Capillary refill (6 sec.)
Diagnosis Impaired gas exchange related to ventilation perfusion imbalance as manifested by with oxygen of 3-4L/min via nasal cannula,(+) Crackles @ Left lungs, (+) Nasal Flaring, Tachypneic with the RR of 29cpm, (+) Retraction, Cold clammy skin, BP of 90/70, and capillary refill (6 sec.)
Planning After 6 hours of Nursing interventions the patient will be able to: Participate in the treatment regimen such as breathing exercises. Demonstrate improved ventilation without the presence of nasal flaring and retraction. Respiratory rate will decrease to normal range (12-20 cpm)
Selected Intervention Establish rapport
Implemented Intervention Established rapport
Rationale To gain trusting relationship with the patient. Predicator of fluid balance that should be clients usual range in healthy status To ensure accurate fluid status and to avoid further complications that may result to fluid overload To ensure accurate fluid status To identify of there is a presence of vasoconstriction To determine ascertain status and to note progress To provide airway and venous return To promote lung expansion
Assess vital signs
Monitored and recorded vital signs
Monitor and regulate IV fluid
Monitored and regulated IV fluids
Monitor I/O
Monitored I/O
Observe skin color & nailbeds. Auscultate breath sounds Elevate head and the feet Encourage frequent position changes and deep breathing exercises Provided oxygen at lowest concentration as indicated Encourage
Observed skin color & nailbeds. Auscultated breath sounds Elevated head and the feet Encouraged frequent position changes and deep breathing exercises Monitored the oxygen level of the patient Encouraged the patient to maintain adequate I/O
To provide sufficient ventilation
To avoid further complications that may result to fluid overload
Assessment Subjective: medyo nanghihina ako as verbalized by the client Objective:
Pitting Edema on the right foot. (10 sec) Grade is 2+
Diagnosis Decreased Cardiac Output r/t altered preload and afterload as manifested by,
Pitting Edema on the right foot. (10 sec) Grade is 2+,
Planning At the end of 6 hours nursing intervention the client will manifest a BP within normal range (120/80 mmhg)
Selected Intervention establish rapport assessment of clients overall condition provide comfort measures provide safety measures VS taking
Implemented Intervention established rapport rendered morning care assessed clients health status VS taken and recorded provided comfort measures such as: > positioning client in a trendelenburg reinforced safety and security measures e.g. raised side rails up.
Rationale for clients cooperation for clients comfort and hygiene to determine changes on clients condition for baseline data
Weakness,Cold clammy skin,Capillary refill (6 sec.), Weakness Dizziness, Cold Lethargy, BP of clammy skin 90/70mmhg
Capillary refill (6 sec.)
Dizziness Lethargy BP of 90/70mmhg
provide health teaching about the ff.: > medications > adequate rest > diet
for clients comfort and to increase blood flow for clients assistance to prevent injury
Assessment Objective: Pitting Edema on the right foot. (10 sec) Grade is 2+ (+)Crackle s @ Left lung RR of 29cpm BP of 90/70mmHg
Diagnosis Excess fluid volume related to water retention secondary to CHF as manifested by pitting edema on the right foot. (10 sec) Grade is 2+, (+)Crackles @ Left lung, RR of 29cpm, BP of 90/70mmHg
Planning After 6 hours of Nursing interventions the patient will be able to: Demonstrate adequate fluid balance AEB absence of crackles and decreasing edema Verbalize understanding of fluid restrictions
Selected Intervention Establish rapport
Implemented Intervention Established rapport Monitored and recorded vital signs
Rationale To gain trusting relationship with the patient. Predicator of fluid balance that should be clients usual range in healthy status To ensure accurate fluid status and to avoid further complications that may result to fluid overload To ensure accurate fluid status To determine ascertain status and to note progress To provide airway and to help the fluids move out to the extremities Body weight is a sensitive indicator of fluid balance. To know if fluid retention is present
Assess vital signs
Monitor and regulate IV fluid
Monitored and regulated IV fluids
Monitor I/O Auscultate breath sounds Elevate head (patient is dyspneic) elevate affected foot with one pillow. Weigh the patient regularly Measure abdominal girth
Monitored I/O Auscultated breath sounds Elevated head and foot
(Not implemented) (Not implemented)
Assessment Subjective: mabilis lang ako mapagod saka hirap na gumalaw parang matutumba as verbalized by the client. Objective: (+) weakness Ambulatory w/ assistance Blurred Vision BP: 90/70
Diagnosis Risk for injury r/t altered mobility as manifested by (+) weakness, Ambulatory w/ assistance, Blurred Vision, BP: 90/70, w/ O2 administration via cannula
Planning After 6 hours of nursing intervention the client will be able to be free from any injury such as fall.
Selected Intervention Establish rapport Monitor and regulate IVF Monitor and record vital signs. Identify contributing factors Provide comfort measures. Maintain quiet and calm environment Monitor environment for unsafe conditions. Reinforce LSLF diet Encourage to have adequate periods of rest.
Implemented Intervention Established rapport
Rationale to gain trust and confidence of the patient. for good hydration status Provides a baseline data. to know different factors that may affect the clients situation. to self enhancement to provide rest
Monitored and regulated IVF Monitored and recorded vital signs. Identified contributing factors Provide comfort measures Maintained quiet and calm environment. Monitored environment for unsafe conditions.
w/ O2 administration via cannula
to prevent factors that may harm the client.
Reinforced LSLF diet Encouraged to have adequate periods of rest.
to avoid any complications To prevent fatigue.
Discuss w/ family the importance of early detection and reporting of changes in condition or any unusual sign and symptoms Discuss importance of self-monitoring of condition or emotions (fatigue, anger, irritability) Instruct patient to call for assistance as needed. Instruct to always have companion
(Not Implemented)
Promotes early detection of developing complications.
(Not Implemented)
for the client to be aware that it can contribute to occurrence of injury
Instructed patient to call for assistance as needed.
to ensure safety
Instructed to always have companion.
to ensure safety
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Selected Intervention
Implemented Intervention
Rationale
Subjective: Hindi ko alam kung ano itong sakit ko sa puso, at kung bakit. as verbalized by the patient. Objective: (+) confusion on present condition. frequent asking of question.
Risk for noncompliance secondary to knowledge deficit as manifested by (+) confusion on present condition. And frequent asking of question.
At the end of 45 minutes of health teaching the patient will be able to: understand disease process, treatment and medication schedule. remember the health teaching conducted with the guidance of his SO.
Establish rapport Render morning care and comfort measures S/A changing of linens and gown. VS taking and monitoring. Assess knowledge of the patient regarding his present status. Conduct health teaching regarding safety precautions. Conduct health teaching regarding definition of disease, signs and symptoms. Discuss to the client together with his SO the drugs and its drug action. Emphasize strict compliance with prescribed diet. Emphasize to decrease fluid intake.
Established rapport. Rendered morning care and comfort measures S/A changing of linens and gown. VS taken and monitored. Assessed knowledge of the patient regarding his present status. Conducted health teaching regarding safety precautions. Conducted health teaching regarding definition of disease, signs and symptom. Discussed to the client together with his SO the drugs and its drug action. Emphasized strict compliance with prescribed diet. Emphasized to decrease fluid intake.
To gain patients trust. To provide comfort.
To establish baseline data. To know what to teach and explain to the client. To prevent injury.
Used laymans term in health teaching to prevent confusion. To know what are the expected side effects of the drugs and to take extra precaution. This will help to improve clients condition. Since the client has CHF.
XIII. Generic Name Furosemide
DRUG STUDY Brand Name Diumide, Diuspec, Frusema, Furide, Pharmix, and Pisamor
Mechanism of Action Furosemide is a potent diuretic (water pill) that is used to eliminate water and salt from the body.
Contraindications patients with anuria or who are hypersensitive to the drug.
Dosage The recommended adult daily dose of furosemide ranges from 20 mg to 200 mg. Once the effective single dose has been determined, it may be taken 1 to 3 times a day.
Effects and Adverse Effect Common side effects of furosemide include low blood pressure, dehydration and electrolyte depletion (for example, sodium, potassium) Increased blood sugar and uric acid levels also may occur. The most common side effects of aspirin involve the gastrointestinal system and ringing in the ears.
Nursing Responsibilities Observe patients receiving parenteral drug carefully; closely monitor blood pressure and vital signs. Sudden death from cardiac event has been reported
ASA(Acetylsalicylic acid)
Aspirin, Arthritis Foundation Safety Coated Aspirin, Bayer Aspirin, Bayer Children's Aspirin, Ecotrin
Captopril
Capoten
Aspirin is a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID) effective in treating fever, pain, and inflammation in the body. It also prevents blood clots (i.e., is antithrombotic). Captopril is an oral drug and a member of a class of drugs called angiotensin
People with kidney disease, hyperuricemia, or gout should not take aspirin because it inhibits the kidneys' ability to excrete uric acid, and thus may exacerbate these conditions ACE inhibitors, including captopril, can be harmful to the fetus and should
Adults: 325 to 500 mg P.O.q3 hrs, or 325 to 650 mg P.O. q4 hrs, or 650 to 1000 mg P.O q 6 hrs, to maximum dosage of 4,000 mg/day.
Tell patient to report ototoxicity symptoms, unusual bleeding and bruising Tell patient not to take other overthe-counter preparations containing aspirin Do not use salt substitutes containing potassium.
Acute Hypertension A dry, persistent cough has been reported commonly 12.5-25 mg PO; with the use of
converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. ACE inhibitors are used for treating high blood pressure, heart failure, and for preventing kidney failure due to high blood pressure and diabetes.
not be taken by pregnant women.
may repeat PRN Hypertension 25-150 mg PO BID/TID CHF 6.25-12.5 mg PO TID in conjunction with cardiac glycoside and diuretic therapy Diabetic Nephropath y
captopril and other ACE inhibitors. Other side effects include abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, rash, dizziness, fatigue, headache, loss of taste, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, fainting and numbness or tingling in the hands or feet.
Use two forms of birth control including hormonal and barrier methods. Avoid NSAIDs; may be present in OTC preparations.
Ciprofloxacin
Cipro, Cipro XR, Proquin XR
Ciprofloxacin Ciprofloxacin stops the multiplication of bacteria by inhibiting the reproduction and repair of their genetic material (DNA).
25 mg PO TID Ciprofloxacin is 500-750mg PO contraindicated in every 12 hr persons with a history of hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin, any member of the quinolone class of antimicrobial agents, or any of the product components.
The most frequent side effects of ciprofloxacin include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, rash, headache, and restlessness. Rare allergic reactions have been described, such as
If an antacid is needed, take it at least 2 hours before or after dose Drink plenty of fluids while your taking this drug
Omeprazole
omeprazole/sodiu m bicarbonate, Prilosec, Zegerid
Omeprazole is in a class of drugs called proton pump inhibitors (PPI) that block the production of acid by the stomach.
Are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any component of the formulation.
Trimetazidine
Carvedilol
Vastarel MR, Vastarel 20 mg, Vastarel LM, Vastarel LP, Preductal MR, Flavedon MR, Flavedon 20 mg, Cardaptan, Idaptan, Carvidon MR and Trizedon MR, vestar Coreg, Carvil Dilatrend Coronis Eucardic Carloc
Affects myocardial substrate utilization by inhibitrng fatty acid oxidation and shifting ATP production with less 02 consumption from FFA to glucose oxidation carvedilol, may greatly accentuate the effects of carvedilol and cause a steep decline in blood pressure
Hypersensitivity, pregnancy, breastfeeding (nursing mothers should stop breast-feeding).
hives and anaphylaxis (shock). 20 mg to 40 mg The most common once daily. Tablets side effects are should be taken at diarrhea, nausea, least 1 hour before vomiting, a meal. headaches, rash and dizziness. Nervousness, abnormal heartbeat, muscle pain, weakness, leg cramps, and water retention occur infrequently. Adults: 20mg thrice Feeling Dazed And daily after meals. Extreme Fatigue Children: Not recommended. abscess, disseminated intravascular coagulation, dysphonia.
assess patient routinely for epigastric or abdominal pain. give medication on time and at right dose. inform about possible side effect of the drug. use cautiously in patients with heart failure or hypertension and in e l d e r l y patients.
Ischaemic heart disease (angina pectoris, sequelae of infarction) Hypersensitivity. Patients with severe Hypertension: hepatic impairment 6.25 mg PO bid; maintain for 714 days, then increase to 12.5 mg PO bid if needed to control
The most common side effects of carvedilol are dizziness, edema (fluid accumulation),
Consult with physician about withdrawing drug if patient is to undergo surgery (withdrawal is
and/or heart rate.
BP. Do not exceed 50 mg/day. CHF: Monitor patient very closely, individualize dose based on patient response. Initial dose, 3.125 mg PO bid for 2 wk, may then be increased to 6.25 mg PO bid. Maximum dose, 25 mg PO bid in patients < 85 kg or 50 mg PO bid in patients > 85 kg. use cautiously with patient with cardiac disease and renal impairment The usual dietary intake of potassium by the average adult is 50 to 100 mEq per day
decreased heart rate, diarrhea and postural hypotension (a rapid decrease in blood pressure when going from the seated to the standing position that causes lightheadedness and/or fainting).
controversial). Monitor for orthostatic hypotension and provide safety precautions.
Kalium durule
Potassium chloride
replace potassium and maintain potassium level
Other common side effects of carvedilol are irregular heart rhythm, and abnormalities of vision. Nausea and Make sure the vomiting, powder are abdominal pain completely dissolve before Arrhythmias, heart giving block, hypotension cardiac arrest hyperkalemia respiratory paralysis The most common side effects of simvastatin are Instruct patient to report severe GI upset, changes in
Simvastatin
Zocor
Like lovastatin, simvastatin is a anticholesterol
Hypersensitivity to HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors.
The usual dose ranges from 5 to 80 milligrams (mg)
Liver diseases. Pregnancy and nursing period.
taken once daily. The recommended starting dose is 20 to 40 mg once a day
headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, muscle pain, and abnormal liver tests. The most serious potential side effects are liver damage and muscle inflammation or breakdown. Possible Motilium side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, irritability or agitation, nervousness and twitching.
vision, unusual bleeding or bruising, dark urine or lightcolored stools, fever, muscle pain, or soreness. Always check for presence of rashes. Before using this medication Conditions affecting use, especially: Sensitivity to domperidone Obtaining medical attention if fainting, dizziness, irregular heartbeat or pulse
Motilium
Domperidone
Domperidone elevates serum prolactin concentrations
Known history of breast cancer, Prolactinoma (a pituitary tumor which releases prolactin)
Adults and adolescents (over 12 years and weighing 35 kg or more) 1 to 2 of the 10mg tablets three to four times per day with a maximum daily dose of 80 mg.
XIV. DISCHARGE PLANNING Upon discharge, R.C.S with the support of significant others will adhere the following instruction: Medications: Exercise: The best way to control congestive heart failure and to help prolong your life is diet and exercise. You can perform inside the comfort of your home like: Treatment:
Mofloxacin 400mg/ tab OD Captopril 25mg/tab tab 2x a day Aldactone 50mg/tab 1tab OD Furosemide 40mg/tab 2x a day ASA 80mg/tab 1tab OD after lunch Clopidogrel 75mg/tab 1tab OD Simvastatin 40mg 1tab OD before time Digoxin 0.25mg 1tab OD Trimetazidine 35mg/tab 1tab 2x a day
Stretching yoga dangling of feet moving of arm and shoulder at full range, Deep breathing exercise coughing exercise Brisk walking Take medication as ordered Physical therapy Oxygen therapy Proper Diet
Health Teaching: Limit your daily salt (sodium) intake to 2000 mg or less.
Fluids may need to be limited to 2000 ml (2L) per day. doctor.
Check your weight daily. If you gain 5 or more pounds (2kg) in 1to 3 days contact your Eat heart healthy, less processed foods that are low fat and high fiber. If youre overweight, try to lose 5 to 10% of your present weight. Be active each day. Walking is great aim for 30 minutes each day! Limit alcohol consumption. Avoid smoking. Outpatient Appointment: Diet:
After 5 days on feb 10, 2012 (1-3pm) at Jonelta OPD with Serum K results. Follow a low fat and low salt diet Eat nutritious food like fish, vegetables and fruits Continue reading the Holy Bible as he desires Join Bible groups and fellowship Attend Sunday Mass as he desires
Spiritual:
XV. REFERENCE/BIBLIOGRAPHY Books: Doenges, Marilyn E., et. al. Nurses Pocket Guide. F. A. Davis Company. Philadelphia, 2010 Kozier, Barbara, et. al. Kozier & Erbs Fundamentals in Nursing Volume Two. Pearson Education South Asia PTE. LTD. Philippines, 2008. Moyet, Lynda Juall C., et. al. Handbook of Nursing Diagnosis. C&E Publishing, Inc. Philippines, 2009. Smeltzer, Suzanne C., et. al. Brunner and Suddarths Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing. Wolters Kluwer / Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Philippines, 2010.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- I.I Biographic DataDocument10 paginiI.I Biographic DataRobby James RabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study - OTITIS MEDIADocument9 paginiCase Study - OTITIS MEDIAHasing Amado100% (1)
- Exposure To Toxic SubstancesDocument21 paginiExposure To Toxic SubstancesDavid VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Heart FailureDocument11 paginiNCP Heart FailureaZhermAine100% (1)
- Final SDL 1Document21 paginiFinal SDL 1Cy PilapilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study Uro FinalDocument44 paginiCase Study Uro FinalDan Ataniel EnsaladaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final G CaseDocument34 paginiFinal G CaseMarielle SorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exposure To Toxic SubstancesDocument21 paginiExposure To Toxic SubstancesDavid VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- I. Patient Assessment Data Base A. Developmental HistoryDocument10 paginiI. Patient Assessment Data Base A. Developmental HistoryMar OrdanzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Upper Gi BleedingDocument23 paginiNursing Upper Gi BleedingLord Pozak Miller100% (3)
- Case StudyDocument29 paginiCase StudyGerome ValderamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute PyelonephritisDocument53 paginiAcute Pyelonephritiseeymee100% (1)
- Aplastic AnemiaDocument26 paginiAplastic AnemiaMark Anthony S. Castillo100% (1)
- Case StudyDocument23 paginiCase StudyFarah Jelimae BagniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Client'S Profile: A. Demographic DataDocument11 paginiClient'S Profile: A. Demographic DataLincoln Cullen Tumulak SumayloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vehicular AccidentDocument9 paginiVehicular AccidentCharm TanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 103 (RLE) : Bangued, AbraDocument26 paginiNCM 103 (RLE) : Bangued, AbraJess L PayagÎncă nu există evaluări
- BPHDocument15 paginiBPH'mYk FavilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care in Patients With A Medical Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus 1. Identity Patien IdentityDocument10 paginiNursing Care in Patients With A Medical Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus 1. Identity Patien IdentityRai SriyantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument12 paginiIntestinal ObstructionKamMappatao100% (1)
- Escarez, Zarah Jane F. BSN-3D D19 I. Client's ProfileDocument9 paginiEscarez, Zarah Jane F. BSN-3D D19 I. Client's ProfileZarah EscarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irene's Care StudyDocument68 paginiIrene's Care StudyLawrence AckahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerebrovascular Disease (Bleed)Document25 paginiCerebrovascular Disease (Bleed)Margaret Jenaw JenawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibn-Sina Nursing and Midwifery Collage Case Study "Nursing Management"Document14 paginiIbn-Sina Nursing and Midwifery Collage Case Study "Nursing Management"مالك مناصرةÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case StudyDocument7 paginiCase StudyMicah Jonah ElicañoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemorrhoids (Final Draft)Document40 paginiHemorrhoids (Final Draft)Orville Villacete50% (2)
- History of Past and Present IllnessDocument10 paginiHistory of Past and Present IllnessRenea Joy ArruejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peds Nursing Care PlanDocument9 paginiPeds Nursing Care Planapi-327793284100% (1)
- Adult Patient History & Physical Assessement: Central Philippine UniversityDocument11 paginiAdult Patient History & Physical Assessement: Central Philippine UniversityJoshua Elli BajadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Posting ElectiveDocument7 paginiPosting ElectiveThulasi tootsieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monek Case StudyDocument24 paginiMonek Case StudyashnairafatimamaulanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Case Study of A Patient W PowerpointDocument37 paginiA Case Study of A Patient W PowerpointMarivic Labartinos BacunganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Management of A Patient With: HyperthyroidismDocument31 paginiNursing Management of A Patient With: Hyperthyroidismember parkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Pres Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument34 paginiCase Pres Cerebrovascular DiseaseADRIATICO JAROSLUVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive Nursing Health History (Adult)Document5 paginiComprehensive Nursing Health History (Adult)Ciedelle Honey Lou DimaligÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study AnemiaaaaDocument40 paginiCase Study Anemiaaaageniziz rafaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0 CwuDocument7 pagini0 CwuSharvienraaj VelukumaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Takayasu'S Arteritis: A Case StudyDocument42 paginiTakayasu'S Arteritis: A Case StudyErnesto Trinidad Jr RNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chang CAse StudyDocument20 paginiChang CAse Studycharlene_00996Încă nu există evaluări
- Patient's ProfileDocument5 paginiPatient's ProfileSasha FongÎncă nu există evaluări
- NP For CholangitisDocument32 paginiNP For CholangitisEzron Kendrick DuranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument21 paginiDiabetic KetoacidosisDrishti ShresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case StudyDocument17 paginiCase StudyHomework PingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver CirrhosisDocument14 paginiLiver CirrhosisCharissa Magistrado De LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- AcuteAppendicitis-BSN 4ADocument28 paginiAcuteAppendicitis-BSN 4ALynetteCantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Analysis ON Cholelithiasis S/P CholecystectomyDocument18 paginiCase Analysis ON Cholelithiasis S/P CholecystectomyAllyssa AnastacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete Cholelithiasis Case AnalysisDocument18 paginiComplete Cholelithiasis Case AnalysisAllyssa AnastacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Analysis ON Cholelithiasis S/P CholecystectomyDocument18 paginiCase Analysis ON Cholelithiasis S/P CholecystectomyAllyssa AnastacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case+Study+Dengue FinalDocument21 paginiCase+Study+Dengue FinalNinz NunezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Body FinalDocument61 paginiThe Body FinalMhargie RomanillosÎncă nu există evaluări
- MS CaseDocument28 paginiMS CaseJuwaka OsakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sagun Pls Dont Dilit Huhuhhuhhu 123Document85 paginiSagun Pls Dont Dilit Huhuhhuhhu 123Star SagunÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHF, HPN and CAPDocument17 paginiCHF, HPN and CAPJhune VillegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exposure To Toxic SubstancesDocument21 paginiExposure To Toxic SubstancesDavid VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PELVIOLITHIASISDocument45 paginiPELVIOLITHIASISAriane VidalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thyroid Power: 10 Steps to Total HealthDe la EverandThyroid Power: 10 Steps to Total HealthEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (8)
- Best Clinical Guide for Your Family and Your Doctor: The Helper in Critical Health SituationsDe la EverandBest Clinical Guide for Your Family and Your Doctor: The Helper in Critical Health SituationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- How to Stop Heartburn: Simple Ways to Heal Heartburn and Acid RefluxDe la EverandHow to Stop Heartburn: Simple Ways to Heal Heartburn and Acid RefluxÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPPDocument11 paginiNCPPAngelo Miguel MuñozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anxiety Disorder by SlidesgoDocument55 paginiAnxiety Disorder by SlidesgoShey DraftsÎncă nu există evaluări
- FA CPR Workbook 0001Document56 paginiFA CPR Workbook 0001Shawn KimballÎncă nu există evaluări
- Janssen Pharmaceutica NVDocument63 paginiJanssen Pharmaceutica NVRj jÎncă nu există evaluări
- Food SafetyDocument2 paginiFood SafetymacmanueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Innovations in NursingDocument14 paginiInnovations in NursingDelphy Varghese100% (1)
- Fasting and Low Carb InfoDocument4 paginiFasting and Low Carb InfoKatrin NovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Health Issues - ADHD Among ChildrenDocument9 paginiMental Health Issues - ADHD Among ChildrenFelixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Typology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeDocument4 paginiTypology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeLeah Abdul KabibÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Architecture and Town Planning-Course-BrochureDocument42 paginiHistory of Architecture and Town Planning-Course-BrochureSabita AmaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pattern Before Hospitalization During HospitalizationDocument2 paginiPattern Before Hospitalization During HospitalizationJean WinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doctoral Experience Capstone PortfolioDocument29 paginiDoctoral Experience Capstone Portfolioapi-595108452Încă nu există evaluări
- Hauber 2019Document10 paginiHauber 2019Laura HdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calories Needed For A 17 Year Old, 70 KG MaleDocument7 paginiCalories Needed For A 17 Year Old, 70 KG Maleboom boomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Public Health Internship Cover LetterDocument8 paginiPublic Health Internship Cover Letterf5dct2q8100% (2)
- JUMPSTART TO SKINNY by Bob Harper: Rule #1Document8 paginiJUMPSTART TO SKINNY by Bob Harper: Rule #1Random House Publishing GroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ug Epidemiological Bulletin 2023Wk19Document8 paginiUg Epidemiological Bulletin 2023Wk19JACKLINE ONZIAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Occupational Therapy in Mental Health A Vision For Participation 2nd Edition Catana Brown Virginia C Stoffel Jaime MunozDocument3 paginiTest Bank For Occupational Therapy in Mental Health A Vision For Participation 2nd Edition Catana Brown Virginia C Stoffel Jaime MunozDavid Ortiz97% (36)
- Analytical and Hortatory ExpositionDocument3 paginiAnalytical and Hortatory ExpositionChie TjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensus Harian TGL 05 Maret 2022........Document104 paginiSensus Harian TGL 05 Maret 2022........Ruhut Putra SinuratÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acl Reconstruction Without Meniscus RepairDocument1 paginăAcl Reconstruction Without Meniscus Repairsathvik gowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HUMSS - Disciplines and Ideas in The Social Sciences CGDocument1 paginăHUMSS - Disciplines and Ideas in The Social Sciences CGDan LiwanagÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020 HivDocument1 pagină2020 HivhenkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prescribing For Transgender Patients ELHEDocument4 paginiPrescribing For Transgender Patients ELHEGe YgayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflexology For Migraine HeadachesDocument12 paginiReflexology For Migraine Headachescharles100% (1)
- Part 4abcDocument11 paginiPart 4abcMatthew Guevarra100% (1)
- Written Assignment Principles of Applied RehabilitationDocument17 paginiWritten Assignment Principles of Applied RehabilitationRuqaiyah RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Vitae Professor Ngai Ngan-pun (魏雁滨教授)Document22 paginiCurriculum Vitae Professor Ngai Ngan-pun (魏雁滨教授)api-26075761Încă nu există evaluări
- J Villanueva Group 2Document22 paginiJ Villanueva Group 2Caryl Jole PaligsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alexanders Care of The Patient in Surgery 14th Edition Rothrock Test BankDocument8 paginiAlexanders Care of The Patient in Surgery 14th Edition Rothrock Test BankMarkNorrisajmfkÎncă nu există evaluări