Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Sec 3NA Quiz I
Încărcat de
Sharizah Bte Md AminDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Sec 3NA Quiz I
Încărcat de
Sharizah Bte Md AminDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Term 4, Week 2
Class
Index Number
Name Mark Scheme
Total
/20
ST. HILDAS SECONDARY SCHOOL Secondary Three Normal Academic Science (Chemistry) Quiz
Chapter 10 & 11 Acids, Bases & Salts
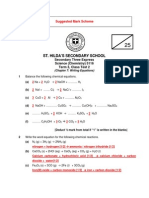
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (5 marks) 1 Which two substances react to form a salt and water only? A B C D Dilute sulfuric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide (acid + alkali -> salt + water) Dilute nitric acid and zinc (reaction of acid + metal -> salt + hydrogen) Dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium carbonate (acid + metal carbonate -> salt + carbon dioxide + water) Dilute sulfuric acid and aqueous barium nitrate (This is actually a precipitation reaction, where an insoluble salt is formed) Note: Even though, you have learnt in order to prepare insoluble salt, there is no need for use of acid. However, acid may be used to produce one of the intended anions, if you do not have any other salt solution to use.)
Students need to have a good understanding of reactions of acids in order to answer this question.( A ) 2 The table below gives a classification of the different types of oxides. Which classification of oxides is correct? Acidic A B C D magnesium oxide sulfur dioxide sulfur dioxide carbon monoxide Basic carbon monoxide magnesium oxide aluminium oxide magnesium oxide Amphoteric aluminium oxide aluminium oxide magnesium oxide aluminium oxide Neutral sulfur dioxide carbon monoxide carbon monoxide sulfur dioxide
Students who get this question wrong most likely did not memorise the definition of the different oxides well enough.( B )
Both magnesium oxide and magnesium carbonate react with dilute sulfuric acid. In what way are both the reactions the same? In order to answer the above question, you need to be able to identify the type of reaction and also the products. Magnesium oxide (base) + sulfuric acid -> magnesium sulfate + water Magnesium carbonate + sulfuric acid -> magnesium sulfate + carbon dioxide + water A A gas is produced during the reaction. B An acid is neutralized by a soluble base C Water is obtained as one of the products. D An insoluble salt is obtained as a product. ( C ) Aqueous potassium sulfate can be prepared by reacting dilute sulfuric acid with aqueous potassium carbonate. Which conclusion can be drawn from this information? This question is assessing your understanding on preparation of Na+/K+/NH4+ salts using Titration. A B C D Potassium carbonate is insoluble in water. Potassium sulfate is soluble in water. Potassium sulfate is an alkali. Potassium sulfate neutralizes sulfuric acid. ( B )
The table below shows the solubility of some salts of metal Y in cold water. Salt carbonate chloride sulfate Solubility in cold water insoluble soluble insoluble
What could metal Y be? This question is assessing if you have memorized the solubility table of salts well enough. A B C D barium lead magnesium sodium ( A )
Section B: Structured Questions (15 marks) 1 Complete the following word equations. (a) Dilute sulfuric acid + zinc zinc sulfate + hydrogen (b) Dilute nitric acid + lithium carbonate water Lithium nitrate + carbon dioxide +
(c) (d)
copper(II) oxide + dilute hydrochloric acid sodium chloride + silver nitrate
copper(II) chloride + water
sodium nitrate + silver chloride [4]
This question is about making salts. For each salt, suggest the name of the missing reagent and briefly describe how to obtain the solid product from the reaction mixture. (a) Salt to be prepared: magnesium nitrate reagent 1: dilute nitric acid. reagent 2: magnesium oxide / magnesium / magnesium carbonate [1] I could obtain solid magnesium nitrate by: Dissolve excess [1/2] magnesium carbonate in dilute nitric acid. Filter [1/2] the unreacted magnesium carbonate and collect the filtrate [1/2]. Heat [1/2] the filtrate to obtain a saturated [1/2] solution.
Cool the saturated solution to form crystals [1/2]. Collect the crystals and rinse them (optional) Dry in between sheets of filter paper (optional)
(b)
Salt to be prepared: barium sulfate reagent 1: aqueous potassium sulfate reagent 2: aqueous barium nitrate / aqueous barium chloride [1] I could obtain solid barium sulfate by: Mix the two aqueous salt solutions. [1/2] Filter the mixture and collect the residue [1/2]. [6]
When metal is added to dilute acid, salt is formed and hydrogen gas will be given off.
Mg (s) Salt A + Gas B
Dilute hydrochloric acid
CuCO3 (s) Gas C
Substance D (aq) Potassium chloride + water
(a)
Fill in the missing information in the table below. Chemical name Magnesium chloride [1/2] Hydrogen gas Chemical formula MgCl2 H2 [1/2] [1]
A B
(b)
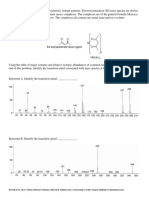
Describe a test to confirm the identity of Gas C. Students tend to be careless and did not focus on the reactants stated. You must realize that the reactant is a metal carbonate. Hence, the gas produced is carbon dioxide. Test: Bubble the gas through limewater [1/2] Observation: White precipitate is formed in limewater [1/2] Note: Carbon dioxide is formed.
(c)
Potassium chloride forms a colourless, neutral solution when mixed with water. Write down the chemical name of Substance D. (i) Potassium hydroxide [1] (ii) What colour change is observed when a few drops of Universal Indicator is added to the solution of potassium chloride? (In order to answer this
question, you need to understand that to prepare potassium chloride, we are reacting acid + alkali, which is a neutralization reaction. Hence, the overall pH value is 7.
Remains green [1] (iii) What is the name of the method used to prepare potassium chloride? Titration [1]
*** End of Paper ***
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Fairfield em 2 Prelim 2009Document15 paginiFairfield em 2 Prelim 2009JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4E 2009 ZhongHua Prelim 2 Maths Paper 1Document18 pagini4E 2009 ZhongHua Prelim 2 Maths Paper 1ZeneonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4E5N Math P1 Prelim 2009 With AnsDocument17 pagini4E5N Math P1 Prelim 2009 With AnsJASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tkss Prelim 2009 em p1Document13 paginiTkss Prelim 2009 em p1JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fairfield em 1 Prelim 2009Document17 paginiFairfield em 1 Prelim 2009JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4E5N Math P2 Prelim 2009 With AnsDocument12 pagini4E5N Math P2 Prelim 2009 With AnsJASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chij Prelim em 2 2009Document10 paginiChij Prelim em 2 2009JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tkss Prelim 2009 em p2Document10 paginiTkss Prelim 2009 em p2JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- ST Gabriels Prelim 2009 em p1Document17 paginiST Gabriels Prelim 2009 em p1JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics 4016/01: River Valley High School 2009 Preliminary Examination Secondary FourDocument16 paginiMathematics 4016/01: River Valley High School 2009 Preliminary Examination Secondary FourJASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020 Revision For Chapter 3 PDFDocument3 pagini2020 Revision For Chapter 3 PDFTimothy Handoko0% (1)
- 2021 Kinetics MCQ Quiz - Worked SolnsDocument3 pagini2021 Kinetics MCQ Quiz - Worked SolnsPROgamer GTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chij Prelim em 1 2009Document35 paginiChij Prelim em 1 2009JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4016 Mathematics Topic 1: Numbers and AlgebraDocument7 pagini4016 Mathematics Topic 1: Numbers and AlgebraMohammad AshfaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2235 2012Document33 pagini2235 2012poh_elsenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Siglap Secondary School: Go Forth With Wisdom and CourageDocument9 paginiSiglap Secondary School: Go Forth With Wisdom and CourageLim Kew ChongÎncă nu există evaluări
- O LVL Chemistry Hwa Chong Prelim 2010 PDFDocument39 paginiO LVL Chemistry Hwa Chong Prelim 2010 PDFSOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bowen 2009 Prelim em p1 + AnswersDocument16 paginiBowen 2009 Prelim em p1 + AnswersJASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catholic High School Preliminary Examinations (3) Secondary Four Additional Mathematics PaperDocument8 paginiCatholic High School Preliminary Examinations (3) Secondary Four Additional Mathematics PaperJASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dunman High School 2009 Maths D Paper 1Document20 paginiDunman High School 2009 Maths D Paper 1ZeneonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prelim 2 p3 2011 (For Sharing)Document14 paginiPrelim 2 p3 2011 (For Sharing)Yee Kai TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 S.3 1st Term TestDocument11 pagini2021 S.3 1st Term Testirene fungÎncă nu există evaluări
- NYJC 2023 H2 Maths PromoDocument6 paginiNYJC 2023 H2 Maths PromoMarcus Lin0% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Manipulation of Simple PolynomialsDocument19 paginiChapter 3 - Manipulation of Simple PolynomialseddiechowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tampines Prelim 2009 em 1Document15 paginiTampines Prelim 2009 em 1JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2023 Tut 2b Probability (Solution)Document9 pagini2023 Tut 2b Probability (Solution)HANNAH GOH (TJC)Încă nu există evaluări
- Answers - H2 Topical Chemistry 2014Document99 paginiAnswers - H2 Topical Chemistry 2014Ruel Arila Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- 4047 SP 01Document6 pagini4047 SP 01MaverickÎncă nu există evaluări
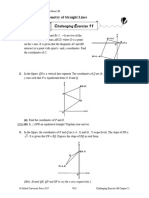
- F3 Challenging Exercise 11Document3 paginiF3 Challenging Exercise 11pgkbgjrh5pÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACSIAM1Document3 paginiACSIAM1JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 H2 Chemistry Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsDocument18 pagini2011 H2 Chemistry Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsLee Jun HuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 PJC Prelim Paper 1 SolutionsDocument15 pagini2015 PJC Prelim Paper 1 SolutionsnasyrahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Read These Instructions First: NAME: - CLASSDocument6 paginiRead These Instructions First: NAME: - CLASSJASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2008 A Levels P1 (No Worked Soln) and P2Document6 pagini2008 A Levels P1 (No Worked Soln) and P2toh tim lamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 JC1 H2 Math Term 2 Revision Test (Questions)Document1 pagină2019 JC1 H2 Math Term 2 Revision Test (Questions)Timothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bowen 2009 Prelim Am p1Document5 paginiBowen 2009 Prelim Am p1JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordinate Geometry Past PapersDocument7 paginiCoordinate Geometry Past PapersMrs R MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCI H3 PHY 9811 EoMP QP PDFDocument12 paginiHCI H3 PHY 9811 EoMP QP PDFLeng RyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020 Chemical Energetics Part 1 TutorialDocument13 pagini2020 Chemical Energetics Part 1 TutorialSalman ShethÎncă nu există evaluări
- RVHS 2017 Promo Q & A (Original)Document21 paginiRVHS 2017 Promo Q & A (Original)toh tim lamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ah Sem 2Document10 paginiAh Sem 2JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tampines Prelim 2009 Am 1Document6 paginiTampines Prelim 2009 Am 1JASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- NYJC 2009 Prelim H2 P2 QuestionDocument14 paginiNYJC 2009 Prelim H2 P2 QuestioncjcsucksÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACFrOgAKyT2lWc0c338OjLiBxz RO x8p YICpFWTezvDX 7ugC2AUM8xvSSl D TzW5Sd 80U4uIi 66 V8iWabtu KI3DqaxgzefGuxzqeRoyHXrqlXfve Y8fSz QN3IgQa7wL968V6jZ4PCDocument3 paginiACFrOgAKyT2lWc0c338OjLiBxz RO x8p YICpFWTezvDX 7ugC2AUM8xvSSl D TzW5Sd 80U4uIi 66 V8iWabtu KI3DqaxgzefGuxzqeRoyHXrqlXfve Y8fSz QN3IgQa7wL968V6jZ4PCTimothy HandokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nyjc - 2007 Jc1 h2 Promo p3 - AnswerDocument4 paginiNyjc - 2007 Jc1 h2 Promo p3 - AnswerSudibyo GunawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- VJC 2007Document14 paginiVJC 2007sswee_1Încă nu există evaluări
- 8.1 (B) Soluble SaltsDocument23 pagini8.1 (B) Soluble SaltsFidree AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dunman High School 2009 Maths D Paper 1 Answer KeyDocument28 paginiDunman High School 2009 Maths D Paper 1 Answer KeyZeneonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 04 QuestionDocument31 paginiChapter 04 Questionapi-19650882Încă nu există evaluări
- Answers: 1.1 Length and TimeDocument34 paginiAnswers: 1.1 Length and TimeL LHÎncă nu există evaluări
- H2 Chem Promo 2011Document18 paginiH2 Chem Promo 2011Andrew Seow100% (1)
- Tampines Prelim 2009 Am 2 SolutionsDocument3 paginiTampines Prelim 2009 Am 2 SolutionsJASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths F4 Final Year Examination 17Document5 paginiMaths F4 Final Year Examination 17CIKGU Rahmat NazriÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4E5N AMath P1 Prelim 2009 With AnsDocument6 pagini4E5N AMath P1 Prelim 2009 With AnsJASON_INGHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2006 JC 1 H2 JCT & Promo - Differential EquationsDocument3 pagini2006 JC 1 H2 JCT & Promo - Differential EquationsOccamsRazorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 3E&NA - Acids WS AnswersDocument19 paginiSec 3E&NA - Acids WS AnswersSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
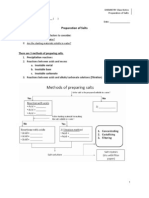
- Salt PreparationDocument4 paginiSalt PreparationAmna Yousaf100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Assignment Session 2017 - 18Document3 paginiChemical Reactions and Equations Assignment Session 2017 - 18Aaryan PanchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Previous Year Questions Acids, Bases & SaltsDocument21 paginiPrevious Year Questions Acids, Bases & Saltskingbakugou0Încă nu există evaluări
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Acids Bases Salts ADocument7 paginiImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Acids Bases Salts AYash KapoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Practical Manual 2012Document20 paginiChemistry Practical Manual 2012Sharizah Bte Md Amin100% (1)
- Sec 3exp Quiz I - Chapter 10Document2 paginiSec 3exp Quiz I - Chapter 10Sharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 3exp Quiz II - Chapter 10Document2 paginiSec 3exp Quiz II - Chapter 10Sharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative Analysis TipsDocument4 paginiQualitative Analysis TipsSharizah Bte Md Amin50% (2)
- SHSS SC Chemistry 3N (A) NTT EOY 2010 MSDocument12 paginiSHSS SC Chemistry 3N (A) NTT EOY 2010 MSSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 3exp Quiz III - Chapter 10 & 11Document4 paginiSec 3exp Quiz III - Chapter 10 & 11Sharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 3exp Class Test 2 - Chapter 7Document4 paginiSec 3exp Class Test 2 - Chapter 7Sharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- SHSS EOY2010 3NATT SC (Chem)Document14 paginiSHSS EOY2010 3NATT SC (Chem)Sharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Periodic Table Summary Worksheet: AnswersDocument29 paginiPeriodic Table Summary Worksheet: AnswersSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 3E&NA - Acids WS AnswersDocument19 paginiSec 3E&NA - Acids WS AnswersSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 3E&NA - Acids WS AnswersDocument19 paginiSec 3E&NA - Acids WS AnswersSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section A:: 2011 Marking Scheme For End-Of-Year Examination (Secondary Three Normal Academic)Document5 paginiSection A:: 2011 Marking Scheme For End-Of-Year Examination (Secondary Three Normal Academic)Sharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 3E & NA - Bases WSDocument17 paginiSec 3E & NA - Bases WSSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 3NA Quiz IDocument4 paginiSec 3NA Quiz ISharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Environment - PollDocument3 paginiLearning Environment - PollSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 1E Revision WS Answer SchemeDocument5 paginiSec 1E Revision WS Answer SchemeSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Sec 2E - C14 Chemical ChangesDocument7 pagini2011 Sec 2E - C14 Chemical ChangesSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 3E Science Exam InfosheetDocument1 paginăSec 3E Science Exam InfosheetSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Sec 2E - C14 Chemical ChangesDocument7 pagini2011 Sec 2E - C14 Chemical ChangesSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology - Structure & Function of CellsDocument24 paginiBiology - Structure & Function of CellsSharizah Bte Md Amin100% (1)
- Changes in StateDocument6 paginiChanges in StateSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec 3E Exam InfosheetDocument2 paginiSec 3E Exam InfosheetSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells, Tissues, Organs, SystemsDocument23 paginiCells, Tissues, Organs, SystemsSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- NAS S3E Class Test - SOR & PTDocument6 paginiNAS S3E Class Test - SOR & PTSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metals Worksheet 1Document2 paginiMetals Worksheet 1Sharizah Bte Md Amin100% (1)
- DNA Extraction PracticalDocument8 paginiDNA Extraction PracticalSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5E Approach To RespirationDocument4 pagini5E Approach To RespirationSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- NAS Sec 3E Revision WS AnswersDocument8 paginiNAS Sec 3E Revision WS AnswersSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- From Light To FoodDocument1 paginăFrom Light To FoodSharizah Bte Md AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Explosive Properties of Metal AmminesDocument2 paginiExplosive Properties of Metal AmminesJelena ZdravkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sequestrante OxigenioDocument10 paginiSequestrante OxigenioMárcia Elisabete Dos SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Knowledge MaterialDocument75 paginiDesign Knowledge MaterialAkin ErsozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout For Qualitative Analysis (Group9-10)Document9 paginiHandout For Qualitative Analysis (Group9-10)twelvefeetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 2 Notes (Sem 2)Document7 paginiGroup 2 Notes (Sem 2)Geethanjali SivakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Format Lplpo 2019Document42 paginiFormat Lplpo 2019Permana JuliansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Effect of Heat On SaltDocument3 pagini2 Effect of Heat On SaltJacelynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Depletion Gilding PDFDocument8 paginiDepletion Gilding PDFBernardDelorÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011f MT I.3Document3 pagini2011f MT I.3Nia Lisna100% (1)
- Color Code ChartDocument15 paginiColor Code ChartYel DG0% (1)
- Manual de Partes Wirtgen W200Document741 paginiManual de Partes Wirtgen W200Taller SamangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sulphuric AcidDocument12 paginiSulphuric AcidHarveyKhooÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1-Radiation and RadioactivityDocument20 pagini1-Radiation and Radioactivityعلاء محمدÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Material For OxygenDocument3 paginiPipe Material For Oxygenc_pythonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Red/Brown PPT of Purple Solution ofDocument1 paginăRed/Brown PPT of Purple Solution ofSusana Natsumy Apaza HuallpaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm B224Document4 paginiAstm B224DouglasÎncă nu există evaluări
- E 246 - 95 AstmDocument12 paginiE 246 - 95 AstmJOSE ABADÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Reactions and Uses of AmmoniaDocument4 paginiChemical Reactions and Uses of AmmoniaReckless RiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prelim 2 p3 2011 (For Sharing)Document14 paginiPrelim 2 p3 2011 (For Sharing)Yee Kai TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material With Electrode SelectionDocument3 paginiMaterial With Electrode SelectionpmkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peróxido de Hidrogênio USP 43Document1 paginăPeróxido de Hidrogênio USP 43Nice LimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 11 - Practice - Test - CHEMICAL REACTIONDocument6 paginiChapter - 11 - Practice - Test - CHEMICAL REACTIONLourdesCorpusMendoza100% (1)
- Solid Phase ExtractionDocument16 paginiSolid Phase ExtractionDAVID VELEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orrego Uranium Resources ChileDocument43 paginiOrrego Uranium Resources ChileJuanPerezRooneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- S3 Chemistry Chlorine and Its Compounda Revision QuestionsDocument3 paginiS3 Chemistry Chlorine and Its Compounda Revision Questionscharlotte0% (1)
- Tian Amalda Sabrina - Potassium BifluorideDocument1 paginăTian Amalda Sabrina - Potassium BifluorideTian Amalda SabrinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soldering and WeldingDocument36 paginiSoldering and Weldingneemu67% (3)
- Zam P BLOCK NW 4Document212 paginiZam P BLOCK NW 4mrrsiddiquiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aisi 1016 Carbon Steel (Uns g10160)Document2 paginiAisi 1016 Carbon Steel (Uns g10160)Naman TanejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common IonsDocument2 paginiCommon IonsthegodofgodÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsDe la EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (146)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDe la EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDe la EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (137)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDe la EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDe la EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookDe la EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDe la EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (90)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilDe la EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableDe la EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (22)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDe la EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDe la EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (3)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideDe la EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeDe la EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookDe la EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodDe la EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (20)
- Introduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisDe la EverandIntroduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsDe la EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireDe la EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (129)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalDe la EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- Phase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringDe la EverandPhase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (11)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsDe la EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)