Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
ANATOMICAL STUDY OF ANOMALY STRUCTURE IN Cucurbita
Încărcat de
Galuh Novita AyuDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ANATOMICAL STUDY OF ANOMALY STRUCTURE IN Cucurbita
Încărcat de
Galuh Novita AyuDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ANATOMICAL STUDY OF ANOMALY STRUCTURE IN Cucurbita
Galuh Novita Ayu, Etik Kusumawati , Putri Rizkiyah, Dianita Puspitasari & Nina Fadlila risqi Prasiwi,
International Biology Class, Mathematics and Sains Faculty, Surabaya State University, 2012, Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia.
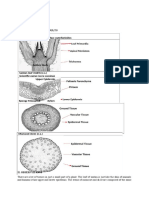
ABSTRACT Cucurbitaceae are important family consisting of approximately 125 genera and 960 species, mainly in tropical and subtropical. All the species are sensitive to frost. Most of the plants in this family are annual vines but there are also woody lianas, thorny shrubs, and trees (Dendrosicyos). The purpose of this experiment to know what kind of anomaly and why the anomaly can be we conduct this anatomical study especially for cucurbitaceae. This research conduct in the Biologys laboratory of Mathematics and Sains Faculty, Surabaya State University in March, 30th 2012 by using the Cucurbita permanent microscope slide stem. This research is done to know Cucurbita anatomical structure and the anomalous growth of dicothyl plant. To compared the anatomical structure of the vascular bundle and find the anomalous structure of cucurbitaceae. A special feature of the Cucurbitaceae is on its structure of vascular bundle of the stem. It has 2 rings of vascular bundle. The first one is located in the cortical area and the second one is located in the medullary area. (Ray F. Evert 2006)
INTRODUCTION Cucurbitaceae are a medium size plant family (T.C. Andres 1995). They live mainly in tropical and subtropical. Most of the plants in this family are annual vines but there are also woody lianas, thorny shrubs, and trees (Dendrosicyos). Plant almost always either herbaceous annual or perennial by means of a storage root, often succulent (sometimes softly woody), vines (rarely shrub or tree, e.g. Acanthosicyos and Dendrosicyos), prostrate or climbing by means of tendrils, coarse and often scabrous with trichomes containing phytoliths, stems typically 5-angled, characterized anatomically by bicollateral vascular bundles often arranged in 2 concentric rings (T.C. Andres 1995). Genus Cucurbita contains some of the earliest domesticated plant species (Smith 1997; Piperno and Stothert 2003). Cucurbita can be called as pumkin. Pumkin seed oil and extraction are increasingly esteemed for their excellent nutritional quality and medicinal value, especially in the prevention and treatment of benign prostate hyperplasia (Blumenthal et al. 1998; Kreuter 2000; Schmidlin and Kreuter 2003). The recent increase in the popularity of pumpkin has stimulated the breeding of new cultivars An anomaly is defined as an unusual but harmless variation from the expected normal. There are anomaly structures in some plants. To know what kind of anomaly and why the anomaly can be there we should know about the plants anatomy. A special feature of the Cucurbitaceae is on its structure of vascular bundle of the stem. It has 2 rings of vascular bundle. The first one is located in the cortical area and the second one is located in the medullary area. (Ray F. Evert 2006)
METODOLOGY This research conduct in the Biologys laboratory of Mathematics and Sains Faculty, Surabaya State University in March, 30th 2012 by using the Cucurbita permanent microscope slide stem. This research is done to know Cucurbita anatomical structure and the anomalous growth of dicothyl plant. Despite the anatomical structure of stem Cucurbita permanent microscope slide would provide a highly efficient descriptive tool for the identification of taxa (families, genera or species). Setting it under the microscope with a low to high magnification to observe anatomy excellently. Further, compared the anatomical structure of the vascular bundle and find the anomalous structure of . After all, using digital camera to take the picture of result microscope observation by using Sonny Digital camera. RESULT Based on the horizontally slice of stem shows different anatomy structure of some species. The anatomical structural of Cucurbita in transverse section from outside toward inside of stem is epidermis, cortex area, vascular bundle, center cell cavity, pith. Cucurbita is dicotyl also. There is occur to secondary growth. In the primary growth havent shows procambium clearly. In Cucurbita Vascular bundles contain both xylem and phloem, but these tissues are arranged differently with the stem bundles of normally structure. Epidermis does not specialized. The cortex is composed of parenchyma and collenchyma (Beck). Vascular bundles of Cucurbita are arranged in two rings. The outer vascular bundle named cortical vascular bundle and the inner named medullary vascular bundle. Meanwhile the vascular bundles of normally structure is arranged in one ring. each having phloem on opposite sides of the xylem (bicollateral bundles).
The vascular region is delimited on the outside by sclerenchyma (perivascular fibers) (Beck)
Schlerenchyma Cucurbita anatomical structure The stems of Cucurbita contain large sieve tube members (Roberts,2011), in phloem bundles that occur both on the outside and on the inside of the xylem (this arrangement is called a bicollateral bundle) (Roberts,2011). Examine cross sections of Cucurbita stem and identify sieve plates and red-staining p-protein, which blocks the sieve plates following injury (Roberts,2011). Examine longitudinal sections of Cucurbita phloem.The cell wall of phloem is very thin so it safe by sclerenchyma as stronger vascular. Xilem area in Cucurbita is modified to form tracheary. In normally structure have functional specialization of xylem cell types there are tracheary and fibers.
tracheary Cucurbita have big cavity in center side but in younger condition, Cucurbita have no cavity yet. In normally structure have no cavity in young stems, but able in old also. DISCUSSION Phloem Cucurbitaceae has tendrils and belong to dycot herbaceous plant. The cortex is composed of parenchyma and
collenchyma. There is an epidermis. It has big cavity in the center of the stem. A cavity has replaced the pith The function of this cavity is used to stored water. The vascular bundle is located between the cell cavity and epidermical tissue. In each vascular bundle consist of sclerencyhma, parenchyma, trachea and phloem. A special feature of the Cucurbitaceae is on its structure of vascular bundle of the stem. It has 2 rings of vascular bundle. The first one is located in the cortical area and the second one is located in the medullary area. (Ray F. Evert 2006) Cortical bundles are leaf traces that extend over great longitudinal distances in the stem prior to entering the leaves. Two primary vascular bundles, often referred to as medullary bundles, occupy the very center of the stem. These are enclosed by an irregular inner cylinder of similar bundles. Enclosing this cylinder is an outer cylinder of vascular bundles in which cambium develops. Cambial activity results in large, radially extended regions of secondary vascular tissues that are separated from each other by wide ray-like regions of primary parenchyma (often called medullary rays). Upon cessation of activity of an initial vascular cambium, additional cambia differentiate successively to the exterior in cortical tissue. Their activity results in a series of cylinders of secondary vascular tissues, separated by narrow cylinders of parenchyma. Cambial activity results in the production of some secondary xylem and phloem and the consequent increase in their size. Upon cessation of cambial activity in these bundles a new vascular cambium, forming a continuous cylinder, differentiates to the exterior in cortical tissue. The cortical bundle is a vascular system which allows the transportation of water and nutrients through the cortex area. Medullary bundle is a vascular bundle located within the pith or central
ground tissue of a stem. (David F. Cutler, Ted Botha, and Dennis Wm. Stevenson 2007). This cortical and medullary bundles are belong to anomalous of stem because the vascular bundle usually present only in one ring. But, in Cucurbitaceae present two rings of vascular bundle. Many variations of stem primary structure are usually called anomalies. CONCLUSION The different structure of stem anatomy from the usual structure is called by Anomaly. Cucurbitaceae has anomaly structure especially in its vascular bundles arrangement in its stem anatomy. Cucurbitaceae has two rings of vascular bundles. The first one is located in the cortical area and the second one is located in the medullary area BIBLIOGRAPHY http://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajb/articl e/viewFile/15014/58918 acessed in April 5th 2012-04-05 at 11.22 a.m.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/art icles/PMC2413107/ April 12nd 2012
http://books.google.co.id/books?id=0iou 9iOxAMwC&pg=PA149&lpg=PA 149&dq=anomalous+in+stem+anat omical+structure+of+cucurbitaceae &source=bl&ots=bkAqNhvUBK&s ig=k8m9iFqI4x_P8li9TgKnP5_VFE& hl=id&sa=X&ei=RoB9T4DjPNCzr AfWrnrDA&ved=0CBoQ6AEwADgK# v=onepage&q=anomalous%20in% 20stem%20anatomical%20structure %20of%20cucurbitaceae&f=false acessed in April 5th 2012-04-05 at 09.30 p.m.
http://www.cucurbit.org/family.html ?=cucurbitsp.html accessed in April 11st 2012
Peterson,R.Larry , Carol Anne Peterson, Lewis H. Melville. 2008. Teaching Plant Anatomy Through
Creative Laboratory Exercises. NRC Research Press : Canada Evert,Ray F . 2006. Esaus Plant Anatomy. A John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Publication : New Jersey
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Free Printable at Home Brain Breaks and Active CalmingDocument12 paginiFree Printable at Home Brain Breaks and Active Calmingapi-505036826Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology SS1 2ND Term E-NotesDocument51 paginiBiology SS1 2ND Term E-NotesINIOLUWA AKEJU100% (3)
- Care of The Normal Newborn: M. Rogers-Walker, MSN/Ed, RNDocument28 paginiCare of The Normal Newborn: M. Rogers-Walker, MSN/Ed, RNyanetp01Încă nu există evaluări
- Disorders of The Digestive SystemDocument108 paginiDisorders of The Digestive SystemNina Lao CamamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Botany Laboratory Exercises 1-3 (First Set)Document19 paginiGeneral Botany Laboratory Exercises 1-3 (First Set)Kristel Padilla100% (3)
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument16 paginiAnatomy of Flowering Plantsmothi26_pcmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiology MCQDocument12 paginiCardiology MCQAhmed MahanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report Plant PhysiologyDocument5 paginiLab Report Plant Physiologysarahyahaya100% (1)
- Anatomy of Chest PDFDocument61 paginiAnatomy of Chest PDFRizwan QureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Luria. Higher Cortical Function in ManDocument653 paginiLuria. Higher Cortical Function in ManAlex Lir100% (2)
- Lab Report Plant TissuesDocument8 paginiLab Report Plant TissuesMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRI100% (6)
- Report SheetDocument11 paginiReport SheetMikhail LandichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Young Stems and RootsDocument11 paginiYoung Stems and RootsHailey CoutuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture II - MidtermDocument23 paginiLecture II - MidtermENGETS IT7Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1Document8 paginiLab 1JeemCarloFagelaPulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Structure of Dicot and Monocot StemsDocument6 paginiInternal Structure of Dicot and Monocot StemsMatthew Reyes RemegiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Citrullus Colocynthis Citrullus Lanatus (Annual) and Cucumis Myriocarpus (Annual)Document9 paginiCitrullus Colocynthis Citrullus Lanatus (Annual) and Cucumis Myriocarpus (Annual)Alissa QothrunnadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Root Growth and StructureDocument3 paginiRoot Growth and StructureJohn Matthew Jobo100% (1)
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument10 paginiAnatomy of Flowering PlantssuryababaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Stem and Root Anatomy of Sanmiguelia lewisiiDocument41 paginiThe Stem and Root Anatomy of Sanmiguelia lewisiiShafa NnisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Botn 21n - Exercise 12 - Stems and Secondary GrowthDocument17 paginiBotn 21n - Exercise 12 - Stems and Secondary GrowthABIEGAIL LAMBERTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument8 paginiChapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plantsswayamdey71Încă nu există evaluări
- PAWERPOYNTDocument20 paginiPAWERPOYNTBella ReadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cycas: Genus-Cycas Distribution of CycasDocument22 paginiCycas: Genus-Cycas Distribution of CycasAnto RashwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Physiology LAB REPORT XDocument5 paginiPlant Physiology LAB REPORT XBoyd benson kayomboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primary Dicot Stem and Root in SunflowerDocument10 paginiPrimary Dicot Stem and Root in SunflowerPushkar kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 16Document5 paginiLab 16bridgettÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histo-Anatomical Aspects of The Ajuga Genevensis L. and AjugaDocument8 paginiHisto-Anatomical Aspects of The Ajuga Genevensis L. and AjugaAlina LambaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WMSU Lab Exercise on Plant TissuesDocument9 paginiWMSU Lab Exercise on Plant TissuesJames Carbonell Dela PeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 9 MolluscaDocument51 paginiAssignment 9 MolluscaGale AustriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Botany NotesDocument101 paginiPractical Botany NotesAnilÎncă nu există evaluări
- FBS 221 Lab - Edited With QuestionsDocument10 paginiFBS 221 Lab - Edited With QuestionsashleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 2-Excercise 2Document10 paginiGroup 2-Excercise 2James Carbonell Dela PeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Botany MidtermDocument4 paginiBotany MidtermMatthew PerryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant TissueDocument19 paginiPlant TissueKAMESH .G100% (1)
- Tissue 11Document5 paginiTissue 11Adnan Al-asbahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomical Studies On The Genus Euphorbia L Saudi Arabia Subgenera Triucalli Ermophyton Esula and ChamaesyceDocument24 paginiAnatomical Studies On The Genus Euphorbia L Saudi Arabia Subgenera Triucalli Ermophyton Esula and ChamaesyceCrisMaya100% (1)
- LABORATORY MANUAL 3: APICAL MERISTEMS, STEM AND ROOTSDocument9 paginiLABORATORY MANUAL 3: APICAL MERISTEMS, STEM AND ROOTSEizuwanEizuddin0% (1)
- 307 48 ET V1 S1 - File1 PDFDocument22 pagini307 48 ET V1 S1 - File1 PDFaaaatniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 9Document1 paginăLab 9Tishonna DouglasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tissues Comprehensive NotesDocument16 paginiTissues Comprehensive NotesMuhammad SaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Morphological Features of CycasDocument41 paginiMorphological Features of CycasHamid JoiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edu246 Botany 2Document8 paginiEdu246 Botany 2ANNE MARGUERITE BARETEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Support and MovementsDocument44 paginiSupport and MovementsSohaib MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- FC101 Act.5 Root Morphology and AnatomyDocument8 paginiFC101 Act.5 Root Morphology and AnatomyCristine egagamaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 EquisetumDocument13 pagini3 EquisetumCDB 1st Semester 2077Încă nu există evaluări
- Entamoeba 4Document3 paginiEntamoeba 4Shyenette SarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Activity 5: Plant Morphology: StemDocument5 paginiLab Activity 5: Plant Morphology: StemPaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 2307@23502205 PDFDocument33 pagini10 2307@23502205 PDFRoseli QueirozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tissue - Class 9Document9 paginiTissue - Class 9Rohit Jain100% (1)
- 6.anatomy of Flowering Plants-FDocument28 pagini6.anatomy of Flowering Plants-Fshrutianand8915Încă nu există evaluări
- PHAR301 Lecture 2bDocument30 paginiPHAR301 Lecture 2bNuhu SibaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Green Algae Chlorophyta OverviewDocument4 paginiGreen Algae Chlorophyta OverviewRyan TamherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure and Tissue Systems of StemsDocument4 paginiStructure and Tissue Systems of StemsSandra Jonas SaviromoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parenchyma: Vulgaris and Other MesophytesDocument3 paginiParenchyma: Vulgaris and Other Mesophytesdamsel in distressÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1 Plant MorphologyDocument5 paginiLab 1 Plant MorphologyNabilah SyahirahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flora of China Vol 23 Cyperaceae PDFDocument298 paginiFlora of China Vol 23 Cyperaceae PDFHabibÎncă nu există evaluări
- TISSUESDocument4 paginiTISSUESaditinandpal338Încă nu există evaluări
- Diversity of Seed Plants and Their Systematics by DR Nupur BhowmickDocument26 paginiDiversity of Seed Plants and Their Systematics by DR Nupur Bhowmickdapolra55100% (2)
- Report SheetDocument6 paginiReport SheetMikhail LandichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Plants Survive: The Structure and Functions of Plant Organs, Tissues, and CellsDocument27 paginiHow Plants Survive: The Structure and Functions of Plant Organs, Tissues, and CellsAlejandro SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparative Study On The Petiolar Histology of Selected Plants in Capparidaceae and SterculiaceaeDocument48 paginiA Comparative Study On The Petiolar Histology of Selected Plants in Capparidaceae and SterculiaceaeAnumod IllathÎncă nu există evaluări
- TissueDocument14 paginiTissueBarkha Agrawal100% (1)
- A Fossil Megasporophyll With A Two Ovules From The Deccan Intertrappean Beds of Marai Patan in The Region of Chandrapur, Maharashtra, IndiaDocument5 paginiA Fossil Megasporophyll With A Two Ovules From The Deccan Intertrappean Beds of Marai Patan in The Region of Chandrapur, Maharashtra, IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dokumen - Tips Lab 3 Report Plant AnatomyDocument11 paginiDokumen - Tips Lab 3 Report Plant AnatomyAin SufizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duke University Nurse Anesthesia Program (Acct #7042) Montgomery, Kelly Barton (Semester 7) Is Logged inDocument3 paginiDuke University Nurse Anesthesia Program (Acct #7042) Montgomery, Kelly Barton (Semester 7) Is Logged inkellyb11Încă nu există evaluări
- Upper Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideDocument15 paginiUpper Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideLeen abusarhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Symptoms of Pregnancy - What Happens Right Away - Mayo ClinicDocument3 paginiSymptoms of Pregnancy - What Happens Right Away - Mayo ClinicAmjad_2020Încă nu există evaluări
- ImciDocument3 paginiImciJohn Benzon0% (1)
- Strain SprainDocument17 paginiStrain SprainPuterinugraha Wanca ApatyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9966 Cons enDocument225 pagini9966 Cons enOmz DonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artigo RolfingDocument8 paginiArtigo RolfingIsis CalioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemorrhage and HemostasisDocument36 paginiHemorrhage and HemostasisRinor MujajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacto PeptoneDocument1 paginăBacto PeptonedobtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions and Answers in Maternal and Health NyrsingDocument10 paginiQuestions and Answers in Maternal and Health Nyrsingreden14Încă nu există evaluări
- Elec Eng 3Bb3:: Cellular BioelectricityDocument15 paginiElec Eng 3Bb3:: Cellular BioelectricityJens RydÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunology of Pediatric HIV InfectionDocument51 paginiImmunology of Pediatric HIV InfectionPotafingersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yoga Journal - Bird of ParadiseDocument3 paginiYoga Journal - Bird of Paradisesrobertson70Încă nu există evaluări
- The Fundamental Unit of Life: CBSE Class 9th NCERT Solution: ScienceDocument7 paginiThe Fundamental Unit of Life: CBSE Class 9th NCERT Solution: ScienceShyamlal BairwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sleep Disorders in Children and Adolescents: Understanding Causes and Treatment OptionsDocument50 paginiSleep Disorders in Children and Adolescents: Understanding Causes and Treatment OptionsCitra Sukri Sugesti100% (1)
- Global Burden of Bronchial Asthma and Community-Based Management /TITLEDocument43 paginiGlobal Burden of Bronchial Asthma and Community-Based Management /TITLEMarius-Sorin CionteaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glucocorticoid Signaling From Molecules to Mice to ManDocument387 paginiGlucocorticoid Signaling From Molecules to Mice to ManKuldeepSinghBanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMA ProtocolsDocument14 paginiEMA ProtocolsMattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disorders of Blood and Blood Forming Organs in EquineDocument89 paginiDisorders of Blood and Blood Forming Organs in EquineasheneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dry Cow ManagementDocument16 paginiDry Cow ManagementMuhammad Farrukh HafeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macmillan Science Level 4 Pupil S Book Unit 1 PP 11 16Document6 paginiMacmillan Science Level 4 Pupil S Book Unit 1 PP 11 16reema2050reemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Esr BT CTDocument9 pagini6 Esr BT CTdlerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology MCQ With Answers PDFDocument4 paginiPathophysiology MCQ With Answers PDF02 Babar Saurabh NavnathÎncă nu există evaluări
- THYMUS PPT Final 7marDocument15 paginiTHYMUS PPT Final 7marRajesh UgalmugleÎncă nu există evaluări