Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
ATLS 2 - Donna P. Moniaga, MD
Încărcat de
serli_piranhaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ATLS 2 - Donna P. Moniaga, MD
Încărcat de
serli_piranhaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
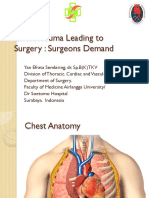
THORACIC TRAUMA Life threatening condition that need to be identified and treated immediately on Primary Survey Airway Laryngeal
Injury Sign of upper airway obstruction ( stridor) Hoarseness/emphysema subcutaneous emphysema/palpable fracture of the larynx Humidified Oxygen/IV access/Prepare for early intubation or surgical airway/ ENT consult If edema larynx : Dexamethasone, adult 4 mg IV, ped: 0.25 mg 0.5 mg/kg IV Fracture /Dislocation of Sternoclavicular joint Obvious sign of trauma on the base of the neck with palpable defect on the sternoclav. Joint Closed reduction of the sternoclavicular joint in supine position Breathing Tension Pneumothorax Clinical diagnosis : Chest pain / respiratory distress/tachycardia/ hypotension/ tracheal deviation/unilateral absence of breath/JVD/cyanosis Needle thoracocentesis ( large bore needle , 14-16 G, 2nd intercostal space, midclav) followed by insertion of chest tube Open Pneumothorax Large defects of chest wall which remain open or sucking chest wound Close the defect with sterile occlusive dressing, large enough to overlap the wound, tapes securely on 3 sides Flail chest Multiple ribs fractures ie, two or more ribs fractured in two or more places Paradoxical movement of the chest wall ( inspiration/expiration) Main problem is the underlying lung disease : Pulmonary contusion Humidified oxygen/fluid resuscitation/analgesic Asses adequate ventilation for the need for assisted ventilation /intubation Circulation Massive Hemothorax > 1500 ml blood in the chest cavity or blood loss > 200 ml/hour for 2 to 4 hours shock associated with the absence of breath sound and or dullness on percussion on one side of the chest
Management : Fluid resuscitation/blood transfusion simultaneously with decompression of chest cavity ( chest tube)
Cardiac Tamponade Commonly associated with penetrating injury Becks triad : JVD/hypotension/muffled heart sounds, not always present PEA in the absence of hypovolemia/tension pneumothorax Pericardiocentesis Secondary Survey Further physical examination CXR P ox /Blood Gas Analysis ECG Simple Pneumothorax Decreased breath sounds / hyperresonance /CXR If pneumothorax < 15 %, no cardiovascular or respiratory compromise : observe for 4 to 6 hours and repeat CXR , if no change : discharge otherwise chest tube insertion Hemothorax Shown in CXR , needed to be evacuated with chest tube Pulmonary contusion Cause respiratory failure Intubation Blunt Cardiac Injury Traumatic Aortic Disruption Persistent hypotension CXR: widened mediastinum Subcutaneous emphysema Not require treatment Underlying injury If needed to assist ventilation with positive pressure, anticipate possible pneumothorax Rib fractures Upper ribs : 1-3 : severe injury , associated with other serious injury ( major blood vessels) Lower ribs : 10 -12 : considered hepatosplenic injury Common associated injury : pneumohemato thorax Treatment : adequate pain management to improve ventilation. Risk of infection esp. in elderly
Traumatic Diaphragmatic injury More common in the left side Sternum/scapular fractures Generally results of direct pressure Sternum fracture can accompanied by lung contusion/blunt cardiac injury
ABDOMINAL TRAUMA Primary survey : ABCDE , Hypotension? Obvious sign of trauma on the abdomen : blunt/penetrating injury Internal organ injury : Liver/spleen/pancreas/hollow viscus/kidney Sign of peritonitis ( distension /tenderness/muscle guarding/ rebound) Serial Hb/urinalysis/pregnancy test Abdominal series /USG Pelvic Injury , associated with major blood vessel Genito-urinary trauma : blood OUE/scrotal-perineal hematoma/high riding prostate or blood on the rectal exam , precaution for urinary catheter. Penetrating injury : closed wound with gauze soaked with NS
MUSCULOSKELETAL TRAUMA AB C DE IV/O2 /Monitor Hipovolemic shock Femur fr. Pain management . Narcotic pain relief ( Pethidine/Morphine) Asses N V D ( Neurovascular distal) . Always check colour/pulsation/capillary refill / sensation, compare bilaterally, and documented prior and after every manipulation /splint Open wound Open fractures ? , cover with sterile dressing Splint , immobilized one joint above and one joint below the injury site Mal-aligned/ compromise NVD : attempt to realign by gentle traction. If after traction NVD compromise worsened back to position before and splint in that position Do not forced re-alignment if difficult splint in that position Tetanus prophylaxis : vaccine/Ig Antibiotic : Cefazolin ( gr I ) , + gentamycine ( gr II / III ) , dose check on 5MEC Orthopedic consult Compartment syndrome o Pain is the earliest symptoms esp. with passive stretching of the involved groups of muscle o Other ischemic sign: 5 P :pain /pressure/paresis/paresthesia/pulse o Unconscious patient is at increased risk
NEAR DROWNING Near Drowning : survival at least a day after submersion Secondary drowning : Complication of near drowning after initially successful resuscitation ( may be delayed by up to 12 hours in otherwise normal appearing patient) In near drowning, aspiration as little as 2 cc/kg may cause lung damage/hypoxia : Surfactant loss/alveolar dysfunction Direct tissue toxicity , pulmonary edema V/Q mismatch , vasoconstriction Even without aspiration, life threatening pulmonary edema may occur due to cerebral hypoxia or cardiac failure ( dry drowning) Management Prehospital ABCDE with neck/spinal injury and hypothermia ( especially in children) precaution Begin CPR immediately with max Oxygen IV/ Monitor No role for trying to evacuate water by Heimlich or other maneuvers Asymptomatic patient still need to be observe for possible secondary drowning Patient with Cardio pulmonary arrest /.P ox < 90 % with max Oxygen, should be transported to hospital with facility of Intubation Emergency Department Consider other associated injuries ( spine/head/other trauma) and medical condition ( AMI/Disrythmia/ stroke) Patient who arrived awake but with respiratory distress or hypoxia IV /O2 max with NRB/Monitor CXR PA/Lat and other X-ray if needed ECG / ABG / electrolyte/BUN /Creatinin/CBC/ Glucose If unable to maintain P ox > 90 % with max O2, need to intubate Antibiotic : Levofloxacine 500 mg QD Observation for 12-24 hours Repeat CXR/lab test every 6 to 12 hours Patient who arrived without any symptoms If physical exam/CXR and Pox normal , patient may be discharged after 6 hours of observation ( repeat CXR/lab test)
High risk patient Loss of consciousness Cardiopulmonary arrest Cyanotic /tachypnoe / respiratory distress Seizures Prolonged time under water /water ingestion Preexisting medical condition /elderly/young children
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 1 - PPT DR Taufik Nur Yahya SPBTKVDocument46 pagini1 - PPT DR Taufik Nur Yahya SPBTKVAmry YusufÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pemicu 2 KGD AditDocument80 paginiPemicu 2 KGD AditAditya SuksmawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Responsi Spontan PneumothoraxDocument49 paginiResponsi Spontan PneumothoraxNizarAbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Incidentsduring Perioperative Period Sept 2011Document106 paginiCritical Incidentsduring Perioperative Period Sept 2011wellawalalasithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest TraumaDocument39 paginiChest Traumayared getachewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest Trauma Leading To Surgery: Surgeons DemandDocument55 paginiChest Trauma Leading To Surgery: Surgeons Demandmark chrisatyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest TraumaDocument115 paginiChest TraumaЕвгений ХанькоÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest Trauma BCECDocument25 paginiChest Trauma BCECTandin SonamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest Trauma and Diseases: Mexigin Gayatri Akash JohannaDocument80 paginiChest Trauma and Diseases: Mexigin Gayatri Akash JohannadidiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BECK's Triad (3D) : PneumothoraxDocument20 paginiBECK's Triad (3D) : PneumothoraxMichael WonggokusumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal TraumaDocument66 paginiAbdominal Traumaofficial.drjainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax During Anesthesia: A 54-Year-Old Man Under GA, Was Found Abnormal Diaphragm Movement During OperationDocument27 paginiPneumothorax During Anesthesia: A 54-Year-Old Man Under GA, Was Found Abnormal Diaphragm Movement During OperationRupankar NathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tension Pnemothorax 2022Document18 paginiTension Pnemothorax 2022DrKrishna ChaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torso TraumaDocument58 paginiTorso TraumaAbidisHereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study PneumothoraxDocument9 paginiCase Study PneumothoraxLee_Cabral_693967% (3)
- Surgery TCVS SGD Guide KKDocument7 paginiSurgery TCVS SGD Guide KKFu Xiao ShanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penetrating Chest InjuryDocument33 paginiPenetrating Chest InjuryJARRIE BADJIEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest Physiotherapy With Sputum CollectionDocument41 paginiChest Physiotherapy With Sputum CollectionEduardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower Resp TraumaDocument62 paginiLower Resp TraumaA Rezki ChairamsyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traumatic Chest InjuryDocument26 paginiTraumatic Chest InjurySarahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anesthesia For Emergency SurgeryDocument85 paginiAnesthesia For Emergency Surgeryansuh22100% (11)
- Chest Trauma SeminarDocument45 paginiChest Trauma Seminarha9719199Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit V (E) Management of Patients With Obstructive Lung DiseasesDocument25 paginiUnit V (E) Management of Patients With Obstructive Lung DiseasesArooj FatimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach To Trauma PatientDocument49 paginiApproach To Trauma PatientHadinur Jufri100% (1)
- Chest Tension PneumothoraxDocument34 paginiChest Tension PneumothoraxNoppames SrijarusithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recent Advances in Early Assessment & Management of Severe TraumaDocument18 paginiRecent Advances in Early Assessment & Management of Severe TraumadoctortareqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach To TruamaDocument29 paginiApproach To TruamaIbsa ShumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Trauma Life SupportDocument8 paginiAdvanced Trauma Life SupportazlanajaibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Incidents KeyDocument38 paginiCritical Incidents KeyayeshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest Trauma: Annet Mary Mathew Anu Krishna Arathi.KDocument60 paginiChest Trauma: Annet Mary Mathew Anu Krishna Arathi.KAsif AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest Tubes, Pneumonectomy, Lobectomy, PleuralDocument40 paginiChest Tubes, Pneumonectomy, Lobectomy, PleuralMuhammad AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stab Wound PathophysiologyDocument5 paginiStab Wound PathophysiologyJaessa Feliciano86% (7)
- Pneumothorax: by Amera GumamaDocument20 paginiPneumothorax: by Amera GumamaGumama AmeiyrhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recognition & Treatment of Pneumothorax Hemothorax, Flail Chest, Stove in ChestDocument59 paginiRecognition & Treatment of Pneumothorax Hemothorax, Flail Chest, Stove in ChestAnusha VergheseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thoracic Trauma - Navy - PSPD 2021Document45 paginiThoracic Trauma - Navy - PSPD 2021Naavy LaksmonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax FinalDocument62 paginiPneumothorax FinalmithramuruganÎncă nu există evaluări
- AirwayDocument15 paginiAirwayYonathan asnakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest Trauma: by Dr. M. C. Odiakosa Hod of Anaesthesia NoheDocument91 paginiChest Trauma: by Dr. M. C. Odiakosa Hod of Anaesthesia NoheKeanis JayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach For Poly-Trauma PatientDocument63 paginiApproach For Poly-Trauma PatientPrince Jeyaraj100% (1)
- ATLS ProtocoloDocument21 paginiATLS Protocoloedgarjavier65100% (2)
- Chest Trauma ManagementDocument78 paginiChest Trauma ManagementHassan Shoukat100% (1)
- Thoracic Trauma: Noer Faisal Darmi Surgery Department of Syiah Kuala UniversityDocument101 paginiThoracic Trauma: Noer Faisal Darmi Surgery Department of Syiah Kuala UniversitySyafril LubisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Trauma Life Support (Atls) : DR Eko Setiawan, SpotDocument67 paginiAdvanced Trauma Life Support (Atls) : DR Eko Setiawan, Spotyuliana khairiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument19 paginiPulmonary EmbolismIbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest InjuriesDocument8 paginiChest InjuriesNavjot BrarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPCRDocument35 paginiCPCRIkhsan AmadeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABCDE of TraumaDocument35 paginiABCDE of TraumaIqe ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Operative ComplicationsDocument36 paginiPost Operative ComplicationsPrincewill SeiyefaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airway and Ventilatory ManagementDocument19 paginiAirway and Ventilatory ManagementChynthea ParamithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emergency Medicine كتاب ايمرجنسي مفيد للروتيترز الجدد وملخص مفيدDocument46 paginiEmergency Medicine كتاب ايمرجنسي مفيد للروتيترز الجدد وملخص مفيدSri PoopaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- NursingBulletin Notes On PneumothoraxDocument27 paginiNursingBulletin Notes On Pneumothoraxseigelystic100% (11)
- Approach For Poly-Trauma PatientDocument63 paginiApproach For Poly-Trauma PatientvadimmadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax, COPD, CVDsDocument156 paginiPneumothorax, COPD, CVDsakoeljames8543Încă nu există evaluări
- Mengapa Pasien Didapatkan Akral Dingin?: Learning Surgery: The Surgery Clerkship ManualDocument26 paginiMengapa Pasien Didapatkan Akral Dingin?: Learning Surgery: The Surgery Clerkship Manualiqbal ulumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Failure: by Amera GumamaDocument26 paginiRespiratory Failure: by Amera GumamaGumama AmeiyrhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Day 1 - APPEC 2021Document492 paginiDay 1 - APPEC 2021GaurieÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5-Thoracic Surgery PT &ot 2023-2024-1Document114 pagini5-Thoracic Surgery PT &ot 2023-2024-1MUGISHA GratienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandPleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guideline Perkeni 2019 - 4Document36 paginiGuideline Perkeni 2019 - 4jktrlsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Food HandlersDocument27 paginiFood HandlersNickz AgbayaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study Colorectal CancerDocument23 paginiCase Study Colorectal CancerLeogalvez BedanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Periodontal SurgeryDocument16 paginiPeriodontal SurgeryadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 3 PPTnewDocument9 paginiScience Form 3 PPTnewRedzuan SulaimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach To Delay PubertyDocument33 paginiApproach To Delay PubertyRaja Iqbal Mulya HarahapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Client Intake Form: Date Patient Last: First Initial Address City Zip Date of Birth Phone CellDocument6 paginiClient Intake Form: Date Patient Last: First Initial Address City Zip Date of Birth Phone Celljayson_tamayo2Încă nu există evaluări
- E Stimation of HemoglobinDocument13 paginiE Stimation of HemoglobinSANAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smoking Poor Dietary Habits Sedentary Lifestyle: Lung Cancer Diabetes Heart DiseaseDocument2 paginiSmoking Poor Dietary Habits Sedentary Lifestyle: Lung Cancer Diabetes Heart DiseaseKien Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- PWAT (Panographic Wound Assesment Tool) RevisedDocument4 paginiPWAT (Panographic Wound Assesment Tool) RevisedYunie ArmyatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preventing Hip Dysplasia BrochureDocument2 paginiPreventing Hip Dysplasia Brochurepcr_22Încă nu există evaluări
- American College of Women's Health PhysiciansDocument16 paginiAmerican College of Women's Health PhysiciansSex & Gender Women's Health CollaborativeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Medical Emergencies: Jude D. Positos, RNDocument27 paginiCommon Medical Emergencies: Jude D. Positos, RNNenen PositosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery: SciencedirectDocument3 paginiClinical Neurology and Neurosurgery: SciencedirectYubitza NaviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug InteractionDocument151 paginiDrug Interactionapi-3724213100% (1)
- Fact Sheet Central Retinal Vein OcclusionDocument2 paginiFact Sheet Central Retinal Vein OcclusionAini Nur Syafa'ahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Y10 Chapter+13 ExcretionDocument67 paginiY10 Chapter+13 ExcretionLOW YUEBEI RIJÎncă nu există evaluări
- DORO - Cranial Stabilization and Retractor SystemsDocument32 paginiDORO - Cranial Stabilization and Retractor SystemsBooBleGooMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study AzathioprineDocument3 paginiDrug Study AzathioprineBunnie AlphaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study For DMDocument5 paginiCase Study For DMJermeLou Bao100% (1)
- The History of PsychiatryDocument12 paginiThe History of PsychiatryMarkoff Chaney100% (1)
- First Aid For Snake BiteDocument11 paginiFirst Aid For Snake BiteHenryVanDerSchyffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osce, BaselDocument302 paginiOsce, Baselbpjavi78% (9)
- Efektivitas Pemberian Ikan Gabus Kukus Terhadap Penyembuhan Laserasi Perineum Pada Ibu PostpartumDocument9 paginiEfektivitas Pemberian Ikan Gabus Kukus Terhadap Penyembuhan Laserasi Perineum Pada Ibu Postpartumjulimarni13Încă nu există evaluări
- Historical and Contemporary Perspectives, Issues of Maternal and Child HealthDocument96 paginiHistorical and Contemporary Perspectives, Issues of Maternal and Child HealthBindu Philip100% (1)
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument27 paginiCardiogenic ShockMuhammad Ikbar100% (1)
- NCP BaiaeDocument7 paginiNCP BaiaeJonathan Delos ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotic Skin TestingDocument8 paginiAntibiotic Skin TestingFitz JaminitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yoga & Lifestyle: Topics of Unit: 3Document14 paginiYoga & Lifestyle: Topics of Unit: 3UNKNOWN KNOWLEDGEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Values: Interpreting Chemistry and Hematology For Adult PatientsDocument36 paginiLab Values: Interpreting Chemistry and Hematology For Adult PatientsBrian Johnson100% (1)