Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
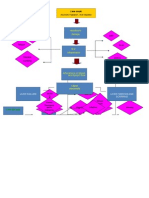
Pathophysiology of Stroke
Încărcat de
ACe JAyDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pathophysiology of Stroke
Încărcat de
ACe JAyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
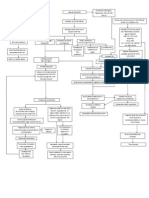
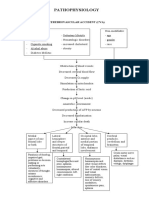
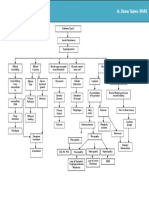
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF LEFT CEREBRAL INFARCTION
Legend: Etiology Disease process
Signs and symptoms
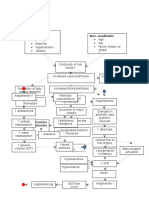
Modifiable risk factor: Diabetes mellitus HPN
Non-modifiable risk factors: Genetics: Family Hx of HPN Age: 70 Race : Asian
Laboratory Studies
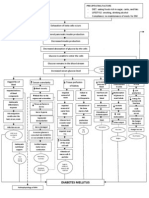
peripheral insulin resistance
Insulin does not bind into cell membrane Glucose cannot enter the cell glucose in the bloodstream
-cells in the pancreas increases insulin secretion to maintain balance between glucose and insulin in the bloodstream
-cells become exhausted and decreases insulin secretion
Balance between insulin and glucose is disrupted glucose in the bloodstream
FBS:
7.45 mmol/L
Body utilizes stored fats as food for the cells
Stored fats are converted into glucose
Waste products (lipids) in the conversion process are secreted in the bloodstream
serum lipid in the bloodstream Lipid accumulate in the blood vessel wall Diameter of the blood vessel wall narrows Heart pumps harder to meet bodys O2demand pressure exerted by the blood on the blood vessel wall blood flow through the blood vessel blood supply to the kidney blood supply to the myocardium SA node is damaged Prolonged low blood supply Electrical impulse is affected Cardiac rhythm is altered Atrial fibrillation X-ray Impression: Atheromatous aorta Plaque buildup in the blood vessel wall
Baroreceptors detects the decreased blood volume Renin is secreted Renin converts angiotensin to angiotensin I ACE in the lungs converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II permeability of glomeruli membranes RBC passes through the glomeruli membrane RBCescape into the urine blood pressure Urinalysis: RBC : 6-10/hpf glomerular filtration
+
Damage to glomeruli
kidney tubular reabsorption sodium reabsorption Na retains fluid
Irregular heart ryhtm develops
Atheroma is dislodged Embolus travels through the blood vessel
Angiotensin II causes vasoconstriction
urine output Fluid accumulates in the interstitial space Passes through the internal carotid artery Embolus reaches the Left middle cerebral artery
Edema +2
Embolus occludes the vessel Blood supply is disrupted O2 supply to brain cells is diminished Cells cannot proceed with aerobic respiration Mitochondria switches to anaerobic respiration Less ATP is produced Lactic acid is produced
CT Scan Impression: Left middle cerebral artery districution
Less ATP to power cellular activities Membrane pump fails
Sodium and calcium ions will rush into the cell
Glutamate will exit the cell
Cerebral cells begin to die Damage to brain stem Damage to Left Frontal Lobe Brocas area is affected Level of Consciousness is altered Gag reflex is diminished
Gastric acid aspiration
Aspiration pneumonia Motor control is diminished Control of speech is diminished Sensory perception diminished Coma
Productive Cough Right sided paralysis Aphasia Decreased sensation
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- NBME 16 Complete PDFDocument112 paginiNBME 16 Complete PDFSilar Khan67% (18)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 paginiChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept maps100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAy100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiStroke PathophysiologyJaessa Feliciano100% (2)
- Pathophysiology CVADocument1 paginăPathophysiology CVANenette Aquino100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of NephrosclerosisDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of NephrosclerosisJessica Damasen Caballero0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of StrokeJoy Rachelle Fermin100% (2)
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiStroke PathophysiologyMaureen EricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisDocument4 paginiPathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisCyrus Ortalla RobinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology CVADocument2 paginiPathophysiology CVASewyel Garburi100% (6)
- Cancer Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăCancer Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (4)
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăHypertension PathophysiologyZaida Eunice EstabayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionKen100% (1)
- Banquet ManagerDocument10 paginiBanquet ManagerACe JAy100% (1)
- Benedetta Monzani - Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD)Document15 paginiBenedetta Monzani - Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD)EmmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy & Physiology Bootcamp NotesDocument51 paginiAnatomy & Physiology Bootcamp Notesgeorgia robinsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 paginăPathophysiology of CVAChristine Joy Ilao PasnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology HPN CvaDocument1 paginăPathophysiology HPN Cvatresdos09Încă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument2 paginiPathophysiology CHFPerry Oliver AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVA PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiCVA Pathophysiologyshmily_0810Încă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology CVD InfarctDocument1 paginăPathophysiology CVD InfarctElisa KerrÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCVD KoDocument10 paginiHCVD KoMarianne BaquilalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho Physiology of Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument2 paginiPa Tho Physiology of Hemorrhagic StrokeMerlash MerlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiAngina Pectoris PathophysiologyALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Pathophysiology CVADocument10 paginiSchematic Pathophysiology CVAheiyu100% (5)
- PATHOPHYDocument3 paginiPATHOPHYArlly Faena AbadÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDocument3 pagini"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăPathophysiologynitlihpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument1 paginăPathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeJeffrey Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intracranial HemorrhageDocument41 paginiIntracranial Hemorrhagedoctormussieaberra100% (1)
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDocument2 paginiPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18Încă nu există evaluări
- Stoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Document7 paginiStoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Mark Anthony Taña GabiosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patof DMDocument1 paginăPatof DMxerwaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument7 paginiPathophysiology of StrokeCHANDAN RAIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocument5 paginiStroke Pathophysiologycinnabon_heart9100% (3)
- Pathophysiolgoy Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument3 paginiPathophysiolgoy Coronary Artery DiseaseNursesLabs.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrosclerosis PathophysiologyDocument14 paginiNephrosclerosis PathophysiologyAllene Paderanga0% (1)
- V. Pathophysiology Modifiable Non-ModifiableDocument3 paginiV. Pathophysiology Modifiable Non-ModifiableSteffi MurielÎncă nu există evaluări
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Document7 paginiPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Tiger Knee100% (3)
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 paginiPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 paginiGeneral Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsIrish Nicole DCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 paginiHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CVA (Final2)Document10 paginiPathophysiology CVA (Final2)Jayselle Costes FelipeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 paginiAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esrd Diagram PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiEsrd Diagram PathophysiologySTEPHANIE JOSUE100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Document1 paginăPathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- CKD PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăCKD Pathophysiologylloyd_santino67% (3)
- CvaDocument47 paginiCvasagnay100% (2)
- CeVD, MI, HCVD & Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiCeVD, MI, HCVD & Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyJjessmar Bolivar FamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of HCVDDocument5 paginiPathophysiology of HCVDNicolne Lorraine100% (1)
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesDocument3 paginiSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument11 paginiPa Tho PhysiologyJonathan CuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument3 paginiPa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusPong's Teodoro SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stages of ShockDocument13 paginiStages of ShockA. P.Încă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDocument3 paginiPathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsErrol B. TiozonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shock NotesDocument7 paginiShock NotesAnitha NoronhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument123 paginiFluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceBrealaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOL 2292 NotesDocument12 paginiBIOL 2292 Notesfglo188Încă nu există evaluări
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument10 paginiCongestive Heart FailurekarenbelnasÎncă nu există evaluări
- ShockDocument7 paginiShockAli S. Al-SinanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HMRG &shock 2022-2023Document54 paginiHMRG &shock 2022-2023Asraa ThjeelÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Pathophysiology, Types & MGT) : ShockDocument37 pagini(Pathophysiology, Types & MGT) : ShockApriliani Nur Puspita SariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tac DTR (Adjustment Payroll)Document2 paginiTac DTR (Adjustment Payroll)ACe JAyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questionnaire NewDocument5 paginiQuestionnaire NewACe JAyÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument1 paginăUntitledACe JAyÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are The Causes of A Cyst?: Chronic Genetic EmbryoDocument3 paginiWhat Are The Causes of A Cyst?: Chronic Genetic EmbryoACe JAyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adaptive StrategiesDocument22 paginiAdaptive StrategiesACe JAyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glycogen Storage DiseasesDocument1 paginăGlycogen Storage DiseasespiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Morphological Transitions and The Genetic Basis of The Evolution of Extraembryonic Tissues in FliesDocument123 paginiMorphological Transitions and The Genetic Basis of The Evolution of Extraembryonic Tissues in FliesMatteen RafiqiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current BioinformaticsDocument12 paginiCurrent BioinformaticsSunil KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annex 3 - MedcertDocument3 paginiAnnex 3 - MedcertFCÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Role of The Microbiota in Periodontal DiseaseDocument12 paginiThe Role of The Microbiota in Periodontal DiseaseNishtha KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kayatsha - Gastroschisis and Omphalocele A Case ReportDocument4 paginiKayatsha - Gastroschisis and Omphalocele A Case ReportAffannul HakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hybridoma TechnologyDocument16 paginiHybridoma TechnologyDhanush BharadwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar Pustaka SpaDocument10 paginiDaftar Pustaka SpaRina PratiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular ResponsesDocument19 paginiCellular ResponsesFu Xiao ShanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal TestingDocument10 paginiAnimal Testingsefic dzanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viruses 14 02468Document18 paginiViruses 14 02468Michael Cebral LópezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal Issaas v15n1 POSTER ABSTRACTSDocument28 paginiJournal Issaas v15n1 POSTER ABSTRACTSChai YawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- UG BS Curriculum UpdatedDocument2 paginiUG BS Curriculum UpdatedyayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sinh Lý MáuDocument4 paginiSinh Lý MáuJonh MikeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical E Book TitlesApril 2017Document35 paginiMedical E Book TitlesApril 2017kevin CTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infectious Mononucleosis Learning ContentDocument3 paginiInfectious Mononucleosis Learning ContentJAN ELMER L. LABESORESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transfer Rnas As Dynamic and Critical Regulators of Cancer ProgressionDocument16 paginiTransfer Rnas As Dynamic and Critical Regulators of Cancer Progressionliliana-contrerasÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRP-C5 Sensor Odontoblastos FrioDocument13 paginiTRP-C5 Sensor Odontoblastos FrioIgna Sarquis AbumohorÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSB QA What Is DigestionDocument37 paginiHSB QA What Is DigestionVivienne WrightÎncă nu există evaluări
- CM1 - Bacteria and Archaea WorksheetDocument12 paginiCM1 - Bacteria and Archaea WorksheetRebecca DaouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complex Patterns of Inheritance NotebookDocument4 paginiComplex Patterns of Inheritance NotebookFarah abu hashimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panayiotopoulos SyndromeDocument37 paginiPanayiotopoulos SyndromeZakaria MukallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- choi2018ENZYMEEE PDFDocument37 paginichoi2018ENZYMEEE PDFSJ JungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anemia NotesDocument6 paginiAnemia NotesElstella Eguavoen Ehicheoya100% (2)
- Medical MCQ Center - Liver Mcqs For Mccee, Aipgmee, Pgiee, Jipmer, Fmge, State PG EntranceDocument3 paginiMedical MCQ Center - Liver Mcqs For Mccee, Aipgmee, Pgiee, Jipmer, Fmge, State PG Entrancenarendrakumar94100% (1)
- Etiologic Agents: Laporga, Stephani Grace A. S2ADocument4 paginiEtiologic Agents: Laporga, Stephani Grace A. S2AMonique Nofuente ZamudioÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Prevention of SchizophreniaDocument6 paginiThe Prevention of SchizophreniaMale BajoÎncă nu există evaluări