Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
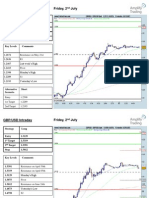
Steps For Fundamental Analysis
Încărcat de
Raghav SagarDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Steps For Fundamental Analysis
Încărcat de
Raghav SagarDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
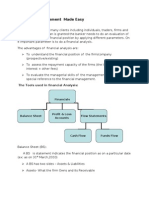
General Guidelines for Fundamental Analysis: Relative Valuation Approach
Relative Valuation Approach
An advantage of the relative valuation approach is that they provide information about how the market is currently valuing the stock at several levels i.e. aggregate markets, different industries and individual stocks within industries. While the good news is that the relative valuation approach provides information about how the market is currently valuing the security, the bad news is that any one-valuation metric cannot be relied upon to arrive at a correct value. A firm needs to be evaluated using a minimum of 2-3 relative valuation metrics like price to earnings, price to book value and price to cash flow. Evaluating it using more than one metric is likely to give a much better picture of the overall valuation levels of a firm. Relative valuation techniques are appropriate to consider under two circumstances. 1. There are good sets of comparable entities i.e. comparable companies that are similar in terms of industry, size and risk. 2. The aggregate market and the firms industry are not at valuation extremes i.e. they are not seriously undervalued or overvalued.
1. Economic Analysis On the basis of economic indicators(like GDP, Industry sales fig.) specifically leading indicators (like crude oil prices, industry capex, Rainfall, CRR & Interest rate cut/increase etc.) we would try to forecast the stages of economy. After the forecast we may find that the economy may be expected to be in any one of the following stages in near future: a. Growth b. Boom (Peak) c. Slow down d. Recession e. Trough (Bottom) f. Recovery g. Growth If it shows the upward cycle of economy then we should choose cyclical industry & if the forecast says it is downward cycle then we should select the defensive industry.
Cyclical Industry: cyclical industry is one which moves along the economic cycle. Examples: Automobile, Real Estate, cement etc. Defensive Industry: Industry which is less effected by economic cycles because the products are either necessity or addiction products. Examples: Food FMCG, Pharmaceutical, Tobacco. 2. Industry Analysis After selecting the desired type of industry i.e. cyclical or defensive we will go for industry analysis. For Eg. we may choose cyclical industry. In industrial analysis we will look at the market structure of industry. We will prefer oligopoly & monopoly as the profit margins are normally good in such market structure. With the help of porter analysis we will find out the industry which has competitive edge. Then we also have a look at industry life cycle & we will select the industry which is in growth stage. For Eg: Healthcare, Automobiles etc. Whatever industry is selected, complete analysis of that industry is to be done with the help of news available, information available in research reports of several brokerage houses and any other information source.
3. Company analysis i) For the selected industry go to the money control website (or any other website where financial, PE ratio and other data is available) we will look at the EPS of all industry players. If we find a company with high EPS & low PE, this may be a value stock. Another choice may be growth stock, for a growth stock, PE will be high and EPS may be low or fair, but the company is on rapid growth path. If we are selecting a value stock, investment horizon must be 1 to 3 years and for growth stock it can be a shorter horizon of less than a year. We will finalize 2-3 stocks & we will analyze for these companies only. The EPS should be either Trailing Twelve Months (TTM) EPS or forward EPS. Face value of the selected stock should be checked. If it is different from Rs. 10/- then their EPS has to be adjusted in order to make it comparable with other players in the industry. Also check if the consolidated EPS differs greatly from stand-alone EPS then consolidated EPS should be taken into account. In order to decide which PE has to be considered as high or low, it should be compared with industry PE or PE of the comparable firms. Comparable firms are the firms which are similar in terms of risk, growth and cash-flow characteristics. Normally firms in the same
ii)
iii)
industry with the similar asset sizes are considered as comparable firm. But again they should be similar on these three characteristics.
iv)
Next step is the financial analysis of selected company
The financial statements should be the latest available annual results. The latest information should be checked through Quarterly results. The consolidated statements as well as standalone results should be checked. Balance Sheet : a) Trend of Net Block and CWIP has to be checked. If they are increasing, it shows the expansion. A high CWIP in latest year shows that company is growing. In such case benefits of expansion will start coming after some time when expansion will be completed. If CWIP was high in last 1 or 2 year and now it has declined then it shows that company has already invested for growth and now it will reap the benefit of the expansion completed recently. If the trend shows normal growth or stable pattern then it may be a stable company. Trends of investments have to be checked. Investments could be either in subsidiaries or in other companys shares, debentures, mutual funds etc. If it is in subsidiary it is a favorable sign otherwise it should be considered as neutral. Look at the composition of debt and equity. Debt should not be very high in comparison to equity especially in the cyclical industries as their cash flows have a fluctuating pattern. The existence of high debt increases the risk as the interest and principal payments are mandatory irrespective of companys earnings and cash flows. However use of debt may also lead to higher return on equity because debt is cheaper source of funds. Therefore a trade-off between debt and equity is required. Income Statement: Operating profit should show an increasing trend over a period and should be good for the current period. Then net profit has to be checked. If it also shows an increasing trend then it is considered as favorable. If there is a decline in recent quarter then causes have to be found through news and research reports about the stock. . If operating profit is high then we can go ahead even if net profit is low but vice-versa is not true. i.e. if net profit is high but operating profit is low then it implies that companys profits are coming from
non-operating sources which will not be a regular source of income. Such stock should be discarded. Quarterly Results: Look at the quarterly results if it is having an increasing trend of profits and EPS, give it a +ve weightage as it gives the latest information about the company however a falling pattern should be considered as unfavorable Ratio Analysis: Implications of few ratios: Solvency Ratio helps to analyze ability to pay debts. High debt means more risk. Look at solvency ratios, debt to total assets ratio should be 60% or less in most of cases. The ideal debt-equity ratio is considered as 2:1. However for the companies with volatile cash-flow patterns, (cyclical or seasonal products) lesser debt-equity ratio should be preferred. Interest coverage ratio has to be checked in order to find whether company is able to service the debt properly or not. Specifically, If debt-equity ratio is high then companys debt servicing capacity has to be immediately checked with the help of interest coverage ratio. Then operating profit ratio, net profit ratio, Return on Assets and Return on Equity has to be checked. Return on equity means how much return is generated for equity shareholders. Their trend should show an increasing pattern. These ratios should be compared with peer group in order to assess that how the company is doing in comparison to its industry peers. If they are good they are acceptable. If there is a decline in recent quarter then causes have to be found through news and research reports about the stock. Normally a 15-16% operating profit ratio and 9-10% net profit ratio is considered good for volume based industries (for example telecom, food FMCG etc.) however in value based industries (for example hotel industry, luxury cars etc.) it should be quite high. Current Ratio It shows availability of net working capital to meet the day to day expenses. A high ratio indicates smooth operations. Look a current ratio, it should be 2:1 but normally it is acceptable near 1.33. Then look at dividend pay out ratio. If it is low then it implies company is retaining profits for growth/expansion, modernization, investment in subsidiary, mergers & acquisition and financial investment. Cause of retention should be checked, if it is financial investment then it should be ignored, all the other causes of retention are considered as positive signs. If the payout ratio is moderate then it may imply that company is retaining some portion for growth,
rest of the profits are distributed as dividends to shareholders. Some external funds through debt or equity might have been raised for expansion. This is again considered as favorable as company is distributing profits as well as expanding. High payout of profits may imply company is maturing. It should not be confused with rate of dividend declared. Dividend declared rate may be high for example a company may declare 150% dividend It is acceptable if dividend payment makes only a reasonable part of net profit, say 40% payout ratio. Dividend payout should not be very high in comparison to total net profit. Cash Flow Analysis: Cash flow from investment (CFI): if it is negative causes may be increase in plant & machinery (Net Block), CWIP, it is considered favorable. Go to balance sheet and check increase in Net Block & CWIP. If there is an increase then it implies real expansion (+ve factor). Another cause of negative cash flows from investments is increase in investments. Go to the balance sheet and check the increase in investment. The investment may be in subsidiary (favorable sign) or may be in financial investments (neutral sign). If investment amount is high then it should be checked through difference in value of investments in standalone results and consolidated results. If there is no difference it implies entire amount is invested into financial instruments. If there is a difference that indicates the difference amount is being invested into subsidiary. Cash flow from operations (CFO): if it is positive or high then it is a favorable sign. It shows companies operations are successfully generating cash flows. Only for high growth firms small amount of operating cash flows is acceptable Cash flow from financing (CFF): If it is positive it is favorable as it may show that expansion is being funded through with the help of funds raised through equity, debt, preference shares or loans. But caution has to be applied if high amount of debt funds being raised. It may be negative because of interest/dividend payment or loan repayment, redemption of debentures/preference shares or buy back of shares. It is good but not as enthusiastic as expansion. Competition Analysis: Look at the comparison with peer group. Compare the sales turnover & Net Profit among industry players, sales turnover will give a idea of market shares. Net Profit margin [(Net profit/sales)*100] will enable us to compare profitability in spite of different sizes. If the companys margin matches with the peer group or more then it is considered good. Return on Assets [(Net Profit/Total Assets)*100] which is a combined measure of profit margin and efficiency has to be compared for the peer group. If the ROA of the selected stock matches
with comparable firms or more then it is considered as acceptable sign. If all these financial analysis is positive this means the co. is strong. Next step is to check the qualitative info. About the company 4. Qualitative Info. a. Look for the latest news available about the stock. Check whether it can give some idea about near future performance expectations about the company. b. Shareholding pattern: find out total promoters shareholding. Promoter shareholding should be stable, check for last 3-4 quarters. Then look at the pledge of share. %age of pledged shares should be low. Pledging of share may imply indirect exit by the promoters when valuations were high. If promoter shareholding is exceptionally low & pledge is high then look at the pattern for last 3-4 quarters. If the trend shows falling pattern of shareholding then avoid the stock. c. Corporate Action: check for any stock split, dividend etc. d. Corporate announcement: look at any major announcement if there. Company website: Check the business in which the company is. Check growth prospects and any other information which is available. Look at the investor information. (past 10yrs trend analysis & presentation) Research Reports: Then go to myiris.com (or any other website like live mint, angel broking) for the research reports for the stock under consideration and sector report. These websites gives the research reports broker wise as well as stock wise. Till the time we have analyzed only the TTM PE EPS and past financial data. Read the research report of the company under consideration. This gives the latest information/news about the company their future plan and forecasted income statement. Read them and look at the forecasted PE on the basis of forecasted earnings. if it is on a lower side and our previous analysis is positive, this stock should be considered a buy/hold and vice-versa.
Conclusion:
It should be borne in mind that neither of the valuation technique is complete in itself. This is because of the fact that arriving at a valuation of a company requires estimates running well into the future and predicting the same with a high level of accuracy time and again is beyond humans.
Hence, it is important to have an appropriate margin of safety incorporated into ones estimates so that even if there is an error, the fall in the stock price is not so huge so as to erode a significant portion of ones capital. In other words, higher the margin of safety, lower the chance of losing ones capital.
***************
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- C OptionsPlaybook 2nded 1 3 PDFDocument33 paginiC OptionsPlaybook 2nded 1 3 PDFnadir82460% (5)
- Alpha & BetaDocument41 paginiAlpha & BetaMark SinsheimerÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMTProgram BrochureDocument12 paginiCMTProgram BrochureAbe-ScribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Analysis 101 V3Document25 paginiTechnical Analysis 101 V3hnif2009Încă nu există evaluări
- Trading SessionsDocument22 paginiTrading SessionsAdam SehramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamental Analysis & Technical AnalysisDocument44 paginiFundamental Analysis & Technical Analysisjyothi joÎncă nu există evaluări
- Professional Services Brochure PDFDocument24 paginiProfessional Services Brochure PDFDahagam SaumithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polymedicure TIADocument28 paginiPolymedicure TIAProton CongoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Options The Upside Without DownsideDocument69 paginiOptions The Upside Without Downsideasifanis100% (1)
- How To Catch BlockbusterstocksDocument12 paginiHow To Catch Blockbusterstocksdr.kabirdev100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Thickness Gaging: by Tom NelliganDocument4 paginiUltrasonic Thickness Gaging: by Tom NelliganCarlos BustamanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buy Level Buy LevelDocument9 paginiBuy Level Buy LevelJeniffer RayenÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Analyse An Annual ReportDocument3 paginiHow To Analyse An Annual ReportAhmad Fauzi MehatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trading Research, Analysis & Strategy: Prepared By: Junior TradersDocument26 paginiTrading Research, Analysis & Strategy: Prepared By: Junior TradersLuigiMangayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Credit Default SwapDocument10 paginiCredit Default SwapDalmia Finance 2018-20Încă nu există evaluări
- PivotPointPresentation P1MarketAuctionTheoryDocument28 paginiPivotPointPresentation P1MarketAuctionTheoryManik AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost and Managment Accounting PDFDocument142 paginiCost and Managment Accounting PDFNaveen NaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Target Level Profit TimeDocument6 paginiTarget Level Profit Timeherwick100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Financial AnalysisDocument39 paginiChapter 3 - Financial AnalysisHeatstroke0% (1)
- Air AsiaDocument14 paginiAir AsiaFaiz AlwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument3 paginiFinancial Statement AnalysisAmit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Candle Stick PatternsDocument5 paginiBasics of Candle Stick PatternsRahul KatariyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Eddy Current Inspection Method Pt4Document4 paginiThe Eddy Current Inspection Method Pt4vrapciudorianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical and Fundamental AnalysisDocument10 paginiTechnical and Fundamental AnalysisRakesh BhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Price Action Traders One Crore ProfitDocument13 paginiMy Price Action Traders One Crore ProfitIgnites MarketÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Thesis) 2007 - Using Boosting For Automated Planning and Trading Systems - Germán CreamerDocument186 pagini(Thesis) 2007 - Using Boosting For Automated Planning and Trading Systems - Germán CreamerFaridElAtracheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Costing Quick RevisionDocument21 paginiCosting Quick RevisionsuriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Support and Resistance BasicsDocument17 paginiSupport and Resistance BasicsMong is not hereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trading MethodDocument3 paginiTrading MethodkanannnÎncă nu există evaluări
- M022 Jsa For Magnetic Penetration TestDocument4 paginiM022 Jsa For Magnetic Penetration TestYahafis MaulanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auto Trend ForecasterDocument15 paginiAuto Trend ForecasterherbakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inspection Trends (January 2013 Vol. 16 No. 1)Document28 paginiInspection Trends (January 2013 Vol. 16 No. 1)Patrick DominguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stock MarketDocument9 paginiStock Marketsoumya chatterjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nifty Options (Positional) Delta HedgingDocument4 paginiNifty Options (Positional) Delta HedgingsachinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buy Low Sell HighDocument20 paginiBuy Low Sell HighDamon BankheadÎncă nu există evaluări
- XM Philippines Forex Webinar Series: With Jonathan Lou ReyesDocument14 paginiXM Philippines Forex Webinar Series: With Jonathan Lou ReyesNd ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- FII Trading Activity and Intraday Volatility 0Document9 paginiFII Trading Activity and Intraday Volatility 0Marudavanan SomasundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Futures Oi: Join TelegramDocument3 paginiFutures Oi: Join TelegramJeniffer RayenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integrated Tool User ManualDocument28 paginiIntegrated Tool User Manualsoumya ranjan pandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- U.T ProcedureDocument10 paginiU.T ProceduretreyX67Încă nu există evaluări
- NDT Procedure PCN Test1Document32 paginiNDT Procedure PCN Test1anon_249267450Încă nu există evaluări
- Business Model: ManagementDocument12 paginiBusiness Model: ManagementAmirul HafizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stock-Option-Trading-Tips-Provided-By-Theequicom-For Today-24-September-2014Document7 paginiStock-Option-Trading-Tips-Provided-By-Theequicom-For Today-24-September-2014Riya VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- XM Philippines Forex Webinar Series: With Jonathan Lou ReyesDocument18 paginiXM Philippines Forex Webinar Series: With Jonathan Lou ReyesNd Reyes100% (1)
- Internal Block Diagram of 8086Document33 paginiInternal Block Diagram of 8086Salitha100% (1)
- Hertz DT StrategryDocument13 paginiHertz DT Strategrysandra akinseteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implied Volatility Chart For Nifty, Bank Nifty and Other Stocks - SensibullDocument1 paginăImplied Volatility Chart For Nifty, Bank Nifty and Other Stocks - Sensibullabhishek0% (1)
- Introduction To Fundamental Analysis: Presented by Sukhada DesaiDocument12 paginiIntroduction To Fundamental Analysis: Presented by Sukhada DesaiSukhada DesaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chaikin Power Gauge Report JPM 08sep2011Document4 paginiChaikin Power Gauge Report JPM 08sep2011Chaikin Analytics, LLC100% (2)
- Bisnews Technical AnalysisDocument33 paginiBisnews Technical AnalysisWings SVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stock Gap Research Paper Dow AwardDocument21 paginiStock Gap Research Paper Dow AwardContra_hourÎncă nu există evaluări
- FX Strategy 02 Jul 10Document5 paginiFX Strategy 02 Jul 10mendinetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Regression Slope: Sensitivity Test: Oxford Capital Strategies LTD: Trading Strategy: Commission & Slippage: $0Document8 paginiLinear Regression Slope: Sensitivity Test: Oxford Capital Strategies LTD: Trading Strategy: Commission & Slippage: $0Oxford Capital Strategies LtdÎncă nu există evaluări
- R56 Technical AnalysisDocument20 paginiR56 Technical AnalysisxczcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology NotesDocument47 paginiBiology NotesMahesh sainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Candlestick Exam (30marks)Document35 paginiCandlestick Exam (30marks)Justine JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inspection Programs For Internal Corrosion in PipingDocument6 paginiInspection Programs For Internal Corrosion in PipingsajimaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- PROJECT REPORT ON Mutual Fund Industry PDFDocument46 paginiPROJECT REPORT ON Mutual Fund Industry PDFUjjwal ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trading Strategies of Institutional Investors in ADocument4 paginiTrading Strategies of Institutional Investors in AJames OkramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Analysis ProgramDocument4 paginiTechnical Analysis ProgramKeshav KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moving Averages Exponential Moving Averages: RSI IndicatorDocument14 paginiMoving Averages Exponential Moving Averages: RSI Indicatorokey obiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trade Score PDFDocument30 paginiTrade Score PDFvenkat.sqlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Afs RatioDocument25 paginiAfs Ratioansarimdfarhan100% (1)
- Q1. Explain The Basic Elements of Income Statement? Income StatementDocument5 paginiQ1. Explain The Basic Elements of Income Statement? Income StatementMina TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpretation of AccountDocument36 paginiInterpretation of AccountRomeo OOhlalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nestle New Product Development Feb 06Document16 paginiNestle New Product Development Feb 06Raghav SagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coca Cola Great Britain Edition 9 Lesson SuggestionsDocument4 paginiCoca Cola Great Britain Edition 9 Lesson SuggestionsAna MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RBS Case Write UpDocument6 paginiRBS Case Write UpRaghav SagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstfeld and Rogoff 1995 The Mirage of Fixed Exchange RatesDocument42 paginiObstfeld and Rogoff 1995 The Mirage of Fixed Exchange RatesJéssicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13 Financing The DealDocument27 paginiChapter 13 Financing The DealK60 Phạm Thị Phương AnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- StressTesting Guidelines by SBPDocument21 paginiStressTesting Guidelines by SBPkrishmasethiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pooled Funds 2019 EditionDocument97 paginiPooled Funds 2019 EditionPatrick CuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 009Document33 paginiChapter 009AfnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- On January 1 2015 James Company Purchases 70 of TheDocument1 paginăOn January 1 2015 James Company Purchases 70 of TheMuhammad ShahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Whitepaper UniswapxDocument6 paginiWhitepaper UniswapxdimitrissteriperiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACC501 01 FINAL Fall20082-1Document15 paginiACC501 01 FINAL Fall20082-1Fun NÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSE Assignment SummaryDocument14 paginiDSE Assignment SummaryDipongkorPaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beige Brown Minimal Organic Creative Project Presentation PDFDocument17 paginiBeige Brown Minimal Organic Creative Project Presentation PDFAbdul WahabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dokumen - Tips - Standard Settlement Instructions Ssi Ssi Last Version 150617xlsxpdfeuroclearDocument2 paginiDokumen - Tips - Standard Settlement Instructions Ssi Ssi Last Version 150617xlsxpdfeuroclearZou CongjunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation of Stock BetaDocument2 paginiCalculation of Stock Betamanoranjan838241Încă nu există evaluări
- Sub: FIMMDA CBRICS Corporate Bond Reporting Platform Participant Application AgreementDocument4 paginiSub: FIMMDA CBRICS Corporate Bond Reporting Platform Participant Application AgreementharikrishnanmscphysicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summer InternshipDocument17 paginiSummer InternshipAnkit Pal100% (1)
- Forexpedia: "Blue Gas" Could End TSLADocument6 paginiForexpedia: "Blue Gas" Could End TSLAAdebowale EmmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Particulars Yes NoDocument18 paginiParticulars Yes Nokashyappathak01Încă nu există evaluări
- Fin 2101 Module 4 - Analyses of Financial Ratios and Their Implications To ManagementDocument7 paginiFin 2101 Module 4 - Analyses of Financial Ratios and Their Implications To ManagementSamantha Nicoleigh TuasonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample IntroductionDocument1 paginăSample IntroductionJojie GenayasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security Analysis and Portfolio Management: Question BankDocument12 paginiSecurity Analysis and Portfolio Management: Question BankgiteshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of Sebi in Regulating Capital Market in IndiaDocument7 paginiRole of Sebi in Regulating Capital Market in IndiaSunil KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are NFT StocksDocument9 paginiWhat Are NFT StocksWeb3oclockÎncă nu există evaluări
- IF Sem IV Word Success and ThakurDocument28 paginiIF Sem IV Word Success and ThakurSanket MhetreÎncă nu există evaluări
- 66 - 4 - 1 - Business StudiesDocument23 pagini66 - 4 - 1 - Business StudiesbhaiyarakeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCX Annual Report FY2015Document236 paginiMCX Annual Report FY2015Da BaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM Questions RevisedDocument15 paginiFM Questions RevisedRajarshi DaharwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company 1 PDFDocument5 paginiCompany 1 PDFDhriti KarnaniÎncă nu există evaluări