Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Textile Dyeing Document For Lab Matching With Various Dyes. (Exhaust Process)
Încărcat de
Khandaker Sakib FarhadTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Textile Dyeing Document For Lab Matching With Various Dyes. (Exhaust Process)
Încărcat de
Khandaker Sakib FarhadDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SOUTHEAST UNIVERSITY
Lab Works on Dyeing Technology By Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment No.
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Name of the Experiment
Page No.
2 10 17 24 30 35 40 46 52 56 61 66 73 78 81 85
Combined scouring and bleaching of cotton fabric Dyeing of cotton knit fabric with reactive dyes in combined shade (Cold brand) Tie die of cotton fabric with reactive dye (Cold brand) Batik printing of cotton fabric with reactive dye (Cold brand) Degumming of silk fabric Bleaching of degummed silk fabric Dyeing of Polyester and cotton blend fabric with disperse dye Dyeing of cotton/polyester blend fabric with direct dye (Cold brand) Discharge printing on the cotton dyed fabric Dyeing of cotton fabric with pigment Dyeing of silk fabric with acid dye Estimation of scouring and bleaching effect Color fastness to wash Dimensional stability to shrinkage% of washing Azo color test of dyed sample Color fastness to hot pressing.
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 01 Experiment name: Combined scouring and bleaching of cotton fabric. Introduction:
Scouring and bleaching are the most important processes of wet processing, because only good scouring and bleaching can assure an exact shade of dye on a particular textile material. Scouring is the treatment of textile materials made from cotton and other cellulosic fibers in an alkaline solution at boiling temperature by which all natural and adventitious impurities are removed. Such as, Oil &wax Fat Pectin Hemi-cellulose Proteins Dead & unripe cotton Husks Seeds.etc. The scouring process is done after enzymatic de sizing and before bleaching. Due to scouring 2% - 8% weight of the fabric is lost. If the weight loss is less than 2% then the scouring is uneven scouring and if the weight loss is more than 8% then the scouring is over scouring. Scouring process is also responsible converting a hydrophobic grey fabric into a hydrophilic water and dye absorbent fabric. On the other hand, Bleaching is the chemical treatment of textile fibers by which not only the impurities such as, dirt, oil, grease, fat, husks and seeds are removed from textile material but also it causes the removal of natural color of the fabric and brighten the fabric hence making it suitable for proper dyeing. Bleaching of cotton fabric is normally done by, Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl). Reduction bleach (used only for second stage). Bleaching powder {Ca(OCl)Cl}.
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Objects:
The objects of combined scouring and bleaching of cotton fabric is given below: To know about the scouring and bleaching process of cotton fabric. To know about the procedure of scouring and bleaching of cotton fabric. To know about the mechanism of scouring and bleaching process. To know the functions of various materials and reagents used in scouring and bleaching process. To remove cotton fabrics natural color and make it suitable for next process . To remove impurities from the cotton fabric. To make the cotton fabric highly hydrophobic and improving its absorbency. To achieve permanent whiteness of cotton fabric.
Dyeing recipe:
The recipe of combined scouring and bleaching of cotton fabric is given below: Caustic Soda (NaOH): 3-5gm/l. Soda ash (Na2CO3): 1-3gm/l. Detergent (Synthetic): 1-2 gm/l. Wetting agent: 1-2 ml/l. Sequestering agent: 1-2 ml/l. H2O2: 3-6gm/l. Stabilizer (Sodium silicate): 1-2 ml/l. Temperature: 900 -1000C Material: liquor: 1: 20. pH: 10.50.5. Sample weight: 100gms.
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Scouring & Bleaching mechanism:
The scouring and bleaching mechanism of cotton fabric is shown below:
Scouring mechanism:
Due to natural impurities such as, oil, wax, fats and other natural impurities present on the surface of the fabric it is impossible for the water soluble dye particles to penetrate into the grey fabric. By scouring process the following phenomenon occurs on the fabric, such are: Saponification of fats, wax and oil. Decomposition of proteins and pectin. Dissolution of husks, seeds and hemi-cellulose. The catalytic substances which interfere negatively are removed. Scouring also helps the fibers to increase more empty spaces in the amorphous region which helps the absorption of dyes.
Cross-sectional view of a typical cotton fiber before scouring
Cross-sectional view of a typical cotton fiber after scouring
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Bleaching mechanism:
For bleaching, the substance responsible for bleaching is OH- ions in H2O2. Naturally H2O2 is the main oxidizing agent which occurs bleaching. Bleaching takes place due to the decomposition of H2O2 which influences the important variables related to the fabric, such are; Time. Temperature. pH. Pressure of stabilizers. Catalysts. The rate of decomposition of H2O2 increases with temperature, pH and concentration of NaOH. So, H2O2 = H+ + H O2-. The main function of stabilizers in bleaching is to slow the decomposition of H2O2. If the decomposition is more than more H+ is produced than H O2- ion which causes breakage of cellulose. For the purpose of coloring that is turning the grey fabric color into bright white is done as the chromophoric group of natural cotton is oxidized and becomes colorless.
C= C
-O2H
C= C
HO HO Colored fabric Figure: Bleaching Mechanism. Colorless fabric
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used in combined scouring and bleaching of cotton fabric are given below: Cotton fabric sample. Electric balance. Thermometer. Bicker. Dyeing bath. Scissor. Gas burner. Measuring cylinder. Glass rod. Spoon.
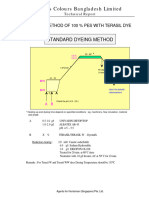
Dyeing curve:
The dyeing curve of combined scouring and bleaching of cotton fabric is shown below:
100 c & 2 hrs
0
600C
Temperature
Room Temperature
50 c
0
Wetting Sequestering Fabric Caustic Soda Detergent Stabilizer H2O2 Agent Agent Soda Ash Batch drop
Time
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Functions of chemicals:
The function of the chemicals used in combined scouring and bleaching of cotton fabric is given below: Wetting agent: The function of wetting agent is to reduce the surface tension between of the liquor in the dye bath and wetting the fabric. Sequestering agent: The function of sequestering agent is to reduce water hardness. Detergent (Synthetic): Detergent is used to ensure that the removed impurities are unable to regenerate into the cotton fabric. Caustic Soda (NaOH): Caustic Soda is used to ensure the alkaline medium into the dyeing bath of the fabric. Soda ash(Na2CO3): Soda ash is used to remove the impurities such as, fat, oil, wax, and husk etc. from the grey cotton fabric. H2O2: H2O2 is the main oxidizing agent used for bleaching. Stabilizer (Sodium silicate): Stabilizer is used for slowing the decomposition of H2O2. If the decomposition of H2O2 is more than the production of HO2 then causes cellulose breakage.
_
Calculation:
The calculation of combined scouring and bleaching process is given below: Total liquor: As, Material: Liquor=1:20 So, Total liquor=100 20 =2000cc
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
For Caustic soda : 1000cc of water requires =5gms So, 2000cc of water requires =10gms. For Soda ash: 1000cc of water requires = 3gms So, 2000cc of water requires =6gms. For Detergent: 1000cc of water requires = 2gms So, 2000cc of water requires =4gms For wetting agent: 1000cc of water requires = 2gms So, 2000cc of water requires =4gms For sequestering agent: 1000cc of water requires = 2gms So, 2000cc of water requires = 4gms. For H2O2: 1000cc of water requires = 6gms So, 2000cc of water requires = 12gms. For stabilizer: 1000cc of water requires = 2gms So, 2000cc of water requires = 4gms.
Working Procedure:
The working procedure of combined scouring and bleaching method is given below: At first the cotton sample was measured in the electric balance and 100gms of sample was taken. Then 2000cc of water was taken in the dyeing bath using a test tube. Then again 4gms of wetting agent was put into the dyeing bath. After that 4gms of sequestering agent was put into the dyeing bath. After that the cotton fabric sample was immersed into the bath. Next 10gms of caustic soda was added into the solution.
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Then 6gms of soda ash was added to the dye bath. After that 4gms of detergent was added to the dye bath. Then again4gms of Sodium silicate stabilizer was added to the solution and it was heated until the temperature had reached 600 C. When the temperature had reached 600 C, then 12gms of H2O2 was added to the solution. Then the dyeing bath temperature was raised to 1000 C and was heated for 1hours and 30minutes. Finally when 1hours and 30minutes had passed the dyeing bath was dropped. Then the fabric was taken for after treatment.
After treatment:
The after treatment for combined scouring and bleaching of cotton fabric is given below: Rinsing Neutralization by CH3COOH- 1gm/l, (10min, 600C) Washing Finally the fabric was put into the oven dryer for drying
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during combined scouring and bleaching method of cotton fabric are given below: We should use apron while dyeing the fabric for safety. All the apparatus should be used carefully. The temperature should be maintained carefully during heating the dyeing bath. The gas burner should be handled carefully for avoiding accidents. The chemicals should be measured carefully according to recipe.
Conclusion:
By scouring and bleaching process it is possible to achieve the desired dye absorbent brightened white fabric which is free from natural and adventitious impurities.
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 02 Experiment name: Dyeing of cotton knit fabric with reactive dyes in combined shade (Cold brand). Introduction:
Reactive dyes are the most commonly used dyes in modern times. In reactive dyeing, the color is formed by reacting with the fiber. In this process, the fixation of the color is achieved by direct chemical linkage with the fiber forming a covalent bond. This dyeing application is limited to mainly, Cellulose fibers. Protein fibers. Nylon fibers. Reactive dyes were first invented by the ICI Company in 1954 and were marketed in1956 as Procion dyes. At that time, the procion dyes were three types. Such are: Procion Yellow R Procion Brilliant Red 2B Procion Blue 3G When reactive dyes react with cellulose fiber a covalent bond is formed between dye and cellulose. So, the reaction takes place as shown below: C N Cellulose OH+Cl N N NH Dye SO3Na
C N Cellulose O N N NH Dye SO3Na
10
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Objects:
The objects of dyeing of cotton knit fabric with reactive dye are given below: To know about reactive dye. To know about the dyeing procedure of reactive dye. To know about the method of tie dyeing. To know about the dyeing mechanism of reactive dye. To produce various designs on the surface of the fabric.
Dyeing recipe:
The recipe of tie dyeing method of cotton fabric with reactive dye is shown below: Reactive dye (red): 0.5% (owf). Reactive dye (blue):1 %(owf). Reactive dye (yellow):0.5 %(owf). Salt (NaCl): 50-60 gm/l. Soda ash (Na2Co3): 12-15 gm/l. Wetting agent: 0.5-1 gm/l. Sequestering agent: 0.5-1 gm/l. Anti foaming agent: 0.5-1 gm/l. Anti creasing agent: 0.5-1 gm/l. Time: 45-60 minutes. Temperature: 400C- 600C. Material: liquor: 1: 20. pH : 10.5+/-0.5.
11
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Dyeing mechanism:
The dyeing mechanism of reactive dye is done in three stages, such are: Exhaustion of dye in presence of electrolytes. Fixation of dye under alkali condition. Wash off the unfixed dye from material surface.
Fixation
Phase-1 Exhaustion
Phase-2 Fixation
Phase-3 Wash off
Time
Figure: Dyeing Mechanism. Dye-X + HO- Cellulose
pH (10-12)
Dye O- Cellulose + HX.
Exhaustion of dye: When the fabric is immersed in the dye liquor an electrolyte is added to assist the exhaustion of dye. Here NaCl is added as an electrolyte which neutralizes the negative charges formed on the fabric surface and puts extra pressure for the penetration of dye molecules into the fabric. Fixation of dye: Fixation of dye means forming a strong covalent bond between the terminal groups OH or NH2 of fiber and the reactive groups of the dye. pH is controlled by adding alkali. Wash off: As the dyeing is completed a good wash must be applied to remove extra dye from the surface of the fabric and level dyeing is important.
12
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used in dyeing method of knit cotton fabric with reactive dye are given below: Cotton fabric sample. Electric balance. Thermometer. Bicker. Dyeing bath. Scissor. Gas burner. Measuring cylinder. Glass rod. Spoon.
Dyeing curve:
The dyeing curve of dyeing method of cotton knit fabric with reactive dye is shown below:
60 C & 45mins
0
45 C&10min 2 C/min
0 0
Room Temperature Temperature
50 C
0
Water Sequestering Agent
Wetting Agent
Salt
Dye
Material
Na2Co3 Batch drop
Time
13
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Functions of chemicals:
The function of the chemicals used in combined scouring and bleaching of cotton fabric is given below: Wetting agent: The function of wetting agent is to reduce the surface tension between of the liquor in the dye bath and wetting the fabric. Sequestering agent: The function of sequestering agent is to reduce water hardness. Soda ash(Na2CO3): Soda ash is used to fix the dye into the fabric. Salt: The function of salt is to penetrate dye liquor into the fabric surface. Anti foaming agent: The function of Anti foaming agent is to remove foam from the fabric surface. Anti creasing agent: The function of Anti creasing agent is to remove crease formation from the fabric surface.
Working Procedure:
The working procedure of this dyeing method is given below: At first a 66gm sample of cotton knit fabric was taken by measuring it in an electric balance. Then 132cc of water was taken in the dyeing bath. After that 0.132cc of sequestering agent was added to the dye bath. Next 0.132cc of wetting agent was added to the dye bath. Then 7.92gms of NaCl salt was added to the solution of the dye bath. After that 1.32gms of reactive dye was added to the solution in the dye bath. Next the 66gms sample of cotton knit fabric was dropped into dye solution. After that the dye solution was heated for 10mins at 450C temperature. As soon as 10mins had passed with 450C temperature, then 1.98gms of soda ash (Na2Co3) was added to the dye solution. Then the solution was heated at 600C temperature for 45 minutes. During that the temperature was checked by using thermometer. Finally when 45 minutes have passed the dyeing bath was dropped. Then the fabric was taken for after treatment.
14
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Calculation:
The calculation of reactive dyeing is given below: Total liquor: As, Material: Liquor=1:20 Total liquor= 66 20=132cc For dye: 100gms of fabric requires= 2gms So, 66gms of fabric requires= 1.32gms. For wetting agent: 1000cc of water requires=1cc So, 132cc of water requires= 0.132cc. For sequestering agent: 1000cc of water requires=1cc So, 132cc of water requires= 0.132cc. For salt(NaCl): 1000cc of water requires = 60gms So, 132cc of water requires = 7.92gms. For soda ash(Na2Co3): 1000cc of water requires = 15gms So, 132cc of water requires =1.98gms. For anti foaming agent: 1000cc of water requires=1cc So, 132cc of water requires= 0.132cc. For anti creasing agent: 1000cc of water requires=1cc So, 132cc of water requires= 0.132cc.
15
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
After treatment:
The after treatment for combined scouring and bleaching of cotton fabric is given below: Soap/Detergent- 1gm/l, 700C, 10-15mins Hot wash-2-3 times Neutralization by CH3COOH- 1gm/l Rinsing Finally the fabric was put into the oven dryer.
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during dyeing cotton knit fabric are given below: We should use apron while dyeing the fabric for safety. All the apparatus should be used carefully. The temperature should be maintained carefully during heating the dyeing bath. The gas burner should be handled carefully for avoiding accidents. The chemicals should be measured carefully according to recipe.
Conclusion:
Reactive dyeing is very important as by this dyeing method it is possible for producing bright color with good fastness properties.
16
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 03 Experiment name: Tie die of cotton fabric with reactive dye (Cold brand). Introduction:
Dyeing is the process by which physical or chemical changes occur to a textile material as it is immersed in an aqueous solution of dye. By tie die dyeing method cotton fabric is tied with a nylon thread to the places where dye is not supposed to penetrate which is used to create decorative designs on the fabric surface.
Objects:
The objects of tie dyeing method of cotton fabric with reactive dye are given below: To know about reactive dye. To know about the dyeing procedure of reactive dye. To know about the method of tie dyeing. To know about the dyeing mechanism of reactive dye. To produce various designs on the surface of the fabric.
Dyeing recipe:
The recipe of tie dyeing method of cotton fabric with reactive dye is shown below: Reactive dye (red): 3% (owf). Salt (NaCl): 60-70 gm/l. Soda ash (Na2Co3): 15-16 gm/l. Wetting agent: 0.5-1 gm/l. Sequestering agent: 0.5-1 gm/l. Anti foaming agent: 0.5-1 gm/l. Anti creasing agent: 0.5-1 gm/l. Time: 60 minutes. Temperature: 60 degrees. Material: liquor: 1: 40. pH : 10-11.
17
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Dyeing mechanism:
The dyeing mechanism of reactive dye is done in three stages, such are: a) Exhaustion of dye in presence of electrolytes. b) Fixation of dye under alkali condition. c) Wash off the unfixed dye from material surface.
Figure: Dyeing Mechanism.
pH(10-12)
Dye-X + HO- Cellulose
Dye O- Cellulose + HX.
Exhaustion of dye: When the fabric is immersed in the dye liquor an electrolyte is added to assist the exhaustion of dye. Here NaCl is added as an electrolyte which neutralizes the negative charges formed on the fabric surface and puts extra pressure for the penetration of dye molecules into the fabric. Fixation of dye: Fixation of dye means forming a strong covalent bond between the terminal groups OH or NH2 of fiber and the reactive groups of the dye. pH is controlled by adding alkali. Wash off: As the dyeing is completed a good wash must be applied to remove extra dye from the surface of the fabric and level dyeing is important.
18
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used in dyeing method of cotton fabric with reactive dye are given below: Nylon thread. Cotton fabric sample. Electric balance. Thermometer. Bicker. Dyeing bath. Scissor. Gas burner. Measuring cylinder. Glass rod. Spoon.
Dyeing curve:
The dyeing curve of dyeing method of cotton fabric with reactive dye is shown below:
Figure: Cold brand reactive dyeing method (Exhaust).
19
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Working Procedure:
The working procedure of this dyeing method is given below: At first a 5gm sample of cotton fabric was taken by measuring it in an electric balance. Then a nylon thread was used to tie the fabric according to the required design. After that a 1% solution of 20cc of wetting agent was made and taken in the dyeing bath. Next a 1% solution of 20cc of sequestering agent was made and taken in the dyeing bath. A solution of 3% reactive dye of 15cc was added in the dyeing bath which was made by adding 1gm of reactive dye in a 100cc solution. Then additional water of 145cc was added to the dyeing bath. After that 14gm of NaCl salt was added to the dyeing bath. Next the 5gm fabric sample was immersed into the dyeing bath and put on the gas burner for heating the dye solution. After 5 minutes of heating the dye solution 3.2gm of Na2Co3 soda ash was added to the solution. After that heat the dye solution at 60 degree temperature for 60 minutes. During that the temperature was checked by using thermometer. Finally when 60 minutes have passed the dyeing bath was dropped. Then the fabric was taken for after treatment.
Calculation:
The calculation of reactive dyeing is given below: For dye: Total Dyes =
For wetting agent: Total Wetting Agent =
20
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
For sequestering agent: Total Sequestering Agent =
For salt: 1000cc of water requires = 70gms So, 200cc of water requires = For soda ash: 1000cc of water requires = 16gms So, 200cc of water requires = For additional water: Total Additional Water= {200-(20+20+15)}= 145cc. . .
After treatment:
After completing dyeing the fabric, the fabric should be washed according to the following procedure: Soap wash- 2gm/l CH3COOH wash-1gm/l Cold wash Time Temperature: 10mins 60deg. Finally fabric was put into the dryer.
21
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Functions of chemicals:
The function of the chemicals used in reactive dyeing of cotton fabric is given below: Wetting agent: The function of wetting agent is to reduce the surface tension between the fiber and the dye liquor of the dye bath and increase the wet ability of the fabric. Salt: The function of salt is to penetrate the dye molecules into the fiber surface of the fabric and ensure proper exhaustion of dyes. Soda Ash: The function of soda or alkali is to create the alkaline medium for dyeing and fixing the dye molecules into the fabric surface. Anti-foaming Agent: The function of Anti-foaming agent is reducing the creation of foaming substance in the dye bath. Anti-Creasing Agent: The function of Anti-Creasing agent is to reduce crease formation on the fabric surface. Sequestering agent: The function of sequestering agent is to reduce water hardness and impurities. CH3COOH: The function of CH3COOH is to neutralize the dye.
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during dyeing are given below: We should use apron while dyeing the fabric for safety. All the apparatus should be used carefully. The temperature should be maintained carefully during heating the dyeing bath. The gas burner should be handled carefully for avoiding accidents. The chemicals should be measured carefully according to recipe.
22
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Conclusion:.
By tie die dyeing methods we can make various designs on the fabric surface without the help of any external apparatus and various print designs can be produced without extending the process. Ultimately this can be defined as one of the best cost saving process.
23
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 04 Experiment name: Batik printing of cotton fabric with reactive dye (Cold brand).
Introduction:
Dyeing is the process by which physical or chemical changes occur to a textile material as it is immersed in an aqueous solution of dye. By batik printing method of cotton fabric with reactive dye a mineral wax solution is used to create decorative designs on the fabric surface.
Objects:
The objects of batik printing method of cotton fabric with reactive dye are given below: To know about reactive dye. To know about the dyeing procedure of reactive dye. To know about the method of batik printing. To know about the dyeing mechanism of reactive dye. To produce various designs on the surface of the fabric.
Dyeing recipe:
The recipe of batik printing method of cotton fabric with reactive dye is shown below: Wax solution: Wax-70% Resin-30% Reactive dye (red): 3% (owf). Salt (NaCl): 60-70 gm/l. Soda ash (Na2Co3): 15-16 gm/l. Wetting agent: 0.5-1 gm/l. Sequestering agent: 0.5-1 gm/l. Anti foaming agent: 0.5-1 gm/l. Anti creasing agent: 0.5-1 gm/l. Time: 60 minutes. Temperature: 60 degrees. Material: liquor: 1: 40. pH : 10-11.
24
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Dyeing mechanism:
The dyeing mechanism of reactive dye is done in three stages, such are: d) Exhaustion of dye in presence of electrolytes. e) Fixation of dye under alkali condition. f) Wash off the unfixed dye from material surface.
Figure: Dyeing Mechanism. pH(10-12) Dye-X + HO- Cellulose Dye O- Cellulose + HX.
Exhaustion of dye: When the fabric is immersed in the dye liquor an electrolyte is added to assist the exhaustion of dye. Here NaCl is added as an electrolyte which neutralizes the negative charges formed on the fabric surface and puts extra pressure for the penetration of dye molecules into the fabric.
Fixation of dye: Fixation of dye means forming a strong covalent bond between the terminal groups OH or NH2 of fiber and the reactive groups of the dye. pH is controlled by adding alkali.
Wash off: As the dyeing is completed a good wash must be applied to remove extra dye from the surface of the fabric and level dyeing is important.
25
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used in dyeing method of cotton fabric with reactive dye are given below: Wax. Resin. Cotton fabric sample. Electric balance. Thermometer. Bicker. Dyeing bath. Scissor. Gas burner. Measuring cylinder. Glass rod.
Dyeing curve:
The dyeing curve of dyeing method of cotton fabric with reactive dye is shown below:
Figure: Cold brand reactive dyeing method (Exhaust).
26
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Working Procedure:
The working procedure of this dyeing method is given below: At first a 5gm sample of cotton fabric was taken by measuring it in an electric balance. Then a solution was made by heating 35gms of mineral wax and 35gms of rason in a bath by heating it with gas burner. Then the wax solutions were taken on a batik containing design and place it on the surface of the fabric. After that a 1% solution of 20cc of wetting agent was made and taken in the dyeing bath. Next a 1% solution of 20cc of sequestering agent was made and taken in the dyeing bath. A solution of 3% reactive dye of 15cc was added in the dyeing bath which was made by adding 1gm of reactive dye in a 100cc solution. Then additional water of 145cc was added to the dyeing bath. After that 14gm of NaCl salt was added to the dyeing bath. Next the 5gm fabric sample was immersed into the dyeing bath and put on the gas burner for heating the dye solution. After 5 minutes of heating the dye solution 3.2gm of Na2Co3 soda ash was added to the solution. After that heat the dye solution at 60 degree temperature for 60 minutes. During that the temperature was checked by using thermometer. Finally when 60 minutes have passed the dyeing bath was dropped. Then the fabric was taken for after treatment.
Calculation:
The calculation of reactive dyeing is given below: For dye: Total Dyes =
For wetting agent: Total Wetting Agent =
27
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
For sequestering agent: Total Sequestering Agent =
For salt: 1000cc of water requires = 70gms So, 200cc of water requires = For soda ash: 1000cc of water requires = 16gms So, 200cc of water requires = For additional water: Total additional water = {200-(20+20+15)}= 145cc. . .
After treatment:
After completing dyeing the fabric, the fabric should be washed according to the following procedure: Soap wash- 2gm/l CH3COOH wash-1gm/l Cold wash Time Temperature: 10mins 60degs. Finally the fabric was put into the oven dryer .
28
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Functions of chemicals:
The function of the chemicals used for reactive dyeing of cotton fabric is given below: Wetting agent: The function of wetting agent is to reduce the surface tension between the fiber and the dye liquor of the dye bath and increase the wet ability of the fabric. Salt: The function of salt is to penetrate the dye molecules into the fiber surface of the fabric and ensure proper exhaustion of dyes. Soda Ash: The function of soda or alkali is to create the alkaline medium for dyeing and fixing the dye molecules into the fabric surface. Anti-foaming Agent: The function of Anti-foaming agent is reducing the creation of foaming substance in the dye bath. Anti-Creasing Agent: The function of Anti-Creasing agent is to reduce crease formation on the fabric surface. Sequestering agent: The function of sequestering agent is to reduce water hardness and impurities. CH3COOH: The function of CH3COOH is to neutralize the dye.
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during dyeing are given below: We should use apron while dyeing the fabric for safety. All the apparatus should be used carefully. The temperature should be maintained carefully during heating the dyeing bath. The gas burner should be handled carefully for avoiding accidents. The chemicals should be measured carefully according to recipe.
29
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 05
Experiment name: Degumming of silk fabric.
Introduction:
Degumming is the process by which chemical changes occur to a silk fabric as it is immersed in an aqueous solution of soap/ detergent and soda ash as in this process an albuminoid protein insoluble substance named sericin is removed from silk fabric. So this process is called degumming of silk as in this process the gumming substance or sericin is removed from the fabric surface.
Objects:
The objects of Degumming of silk fabric are given below: To know about the degumming process. To know about the procedure of Degumming of silk fabric. To know about the mechanism of degumming process. To know the functions of various materials and reagents used in degumming process. To know about the properties of silk fabric. To produce a gum/ sericine free silk fabric. To make the silk fabric soft and glossy .
Dyeing recipe:
The recipe of Degumming of silk fabric is shown below: Soap/ Detergent: 15gm/l. Soda ash (Na2Co3):2 gm/l. Time: 60 minutes. Temperature: 60 degrees. Material: liquor: 1: 80. pH: 10-11. Sample weight: 2.8gms.
30
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Degumming mechanism:
The Degumming mechanism of silk fabric is shown below: The silk fabric is composed of such substances which are; Fibroin: 76.6% Ash of fibroin: 0.09% Sericin: 22.3% Wax and fat: 3% Salts: 1.6%. In the removal process of sericin from silk fabric in alkaline condition, the active alkaline content of the solution at 90 degrees temperature is lowered by its reaction with sericin which forms an alkaline sericin compound of indefinite composition. As the temperature increase of per 10 degrees it reduces the active alkali by forming free oleic acid from reaction with soap and liberates carbonic acid by reaction with sodium carbonate. By this reaction of soap and soda with sericin of silk fabric sufficient amount of sericin is removed and this reaction also causes no degradation of the protein fibroin in the silk.
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used in Degumming of silk fabric are given below: Silk fabric sample. Electric balance. Thermometer. Bicker. Dyeing bath. Scissor. Gas burner. Measuring cylinder. Glass rod. Spoon.
31
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Calculation:
The calculation of Degumming of silk fabric is given below: Sample weight: 2.8gms For water: As, material: Liquor = 1:80 So, Total Liquor=2.8 80= 224cc. For soap: 1000cc of water requires = 15gms So, 224cc of water requires = For soda ash(Na2Co3): 1000cc of water requires = 2gms So, 224cc of water requires = Weight of fabric after Degumming: Fabric Weight= 2.01gms. . .
Working Procedure:
The working procedure of Degumming of silk fabric is given below: At first the silk fabric sample was taken in an electric balance for measuring the weight. After measuring the fabric, it was found that the fabric has weighted 2.8gms. After that 3.36gms of soap was put into the dye bath containing 224cc of water. Then the fabric was put in a dye bath containing 224cc of water. Next 0.45gms of soda ash (Na2Co3) was put into the dye bath. After that heat the solution at 90 degrees temperature for 60 minutes. During that the temperature was checked by using thermometer. Finally when 60 minutes have passed the dyeing bath was dropped. Then the fabric was taken for after treatment.
32
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
After treatment:
After completion of the degumming procedure the silk fabric should be washed according to the following procedure: Hot wash Soap wash CH3COOH wash Hot wash: 10mins 60degrees. Finally the fabric was put into the oven dryer.
Functions of chemicals:
The function of the chemicals used for degumming of silk fabric is given below: Soap/Detergent: The function soap or detergent is to clean the fabric and remove unwanted impurities from the fabric. Soda Ash: The function of soda or alkali is to create the alkaline medium for removing sericine and for penetrating the detergent liquor into the fabric. To create the alkaline medium no Caustic Soda is used as it decomposes the silk fiber.
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during Degumming of silk fabric are given below: We should use apron while dyeing the fabric for safety. All the apparatus should be used carefully. The temperature should be maintained carefully during heating the dyeing bath. Necessary steps should be taken to avoid drying of the solution in the dyeing bath. The gas burner should be handled carefully for avoiding accidents. The chemicals should be measured carefully according to recipe.
33
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Conclusion:
By the process of Degumming of silk fabric it is possible to create soft and glossy without any gumming substance named sericin and the fabric also contains light weight and is much smoother than before.
34
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 06
Experiment name: Bleaching of degummed silk fabric.
Introduction:
Bleaching is the process by which dirt, oil, grease, fat etc. impurities are removed from the surface of the fabric. In case of silk fabric the bleaching process reduces the weight of the fabric.
Objects:
The objects of bleaching of Degummed silk fabric are given below: To know about the bleaching process of Degummed silk fabric. To know about the procedure of bleaching process of Degummed silk fabric. To know about the mechanism of bleaching process. To know the functions of various materials and reagents used in bleaching process. To know about the properties of silk fabric. To create a glowing effect on the silk fabric. To remove the dirt and dust particles from silk fabric.
Dyeing recipe:
The recipe of bleaching of Degummed silk fabric is shown below: H2O2: 3gm/l. Stabilizer: 2 gm/l (Sodium silicate). T.S.P: 5 gm/l. Wetting agent: 1 gm/l. Sequestering agent: 1 gm/l. Material: liquor: 1: 80. pH: 10-11. Sample weight: 1.5gms.
35
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Bleaching mechanism:
The bleaching mechanism of silk fabric is shown below: For bleaching, the substance responsible for bleaching is OH- ions in H2O2. Naturally H2O2 is the main oxidizing agent which occurs bleaching. Bleaching takes place due to the decomposition of H2O2 which influences the important variables related to the fabric, such are; Time. Temperature. pH. Pressure of stabilizers. Catalysts. The rate of decomposition of H2O2 increases with temperature, pH and concentration of NaOH. So, H2O2 = H+ + H O2-. The main function of stabilizers in bleaching is to slow the decomposition of H 2O2. If the decomposition is more than more H+ is produced than HO2- ion which causes breakage of cellulose.
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used in bleaching of Degummed silk fabric are given below: Silk fabric sample. Electric balance. Thermometer. Bicker. Dyeing bath. Scissor. Gas burner. Measuring cylinder. Glass rod. Spoon.
36
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Working Procedure:
The working procedure of this bleaching method is given below: At first measure the degummed silk fabric sample in the electric balance. Then add 160cc of water in the dyeing bath using a test tube. Then again put the sequestering agent of 0.32gms into the bath. After that immerse the degummed silk fabric sample inside the bath. Next add 0.48gms of H2O2 powder inside the solution. Add 0.32gms of Sodium silicate stabilizer inside the solution. After that add 0.8gms of T.S.P into the dyeing bath. Then start heating the solution at room temperature for 60 minutes. Finally when 60 minutes have passed drop the dyeing bath. Then take the fabric for after treatment.
Calculation:
The calculation of bleaching process is given below: For T.S.P : 1000cc of water requires = 5gms So, 160cc of water requires = For sequestering agent: 1000cc of water requires = 1gms So, 160cc of water requires = For H2O2: 1000cc of water requires = 3gms So, 160cc of water requires = For stabilizer: 1000cc of water requires = 2gms So, 160cc of water requires = . . . .
37
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
After treatment:
After completing bleaching the following procedure should be used for washing the fabric: Hot wash Soap wash CH3COOH wash Hot wash: 10mins 60degrees. Finally the fabric was put into the oven dryer.
Functions of chemicals:
The function of the chemicals used for degumming of silk fabric is given below: H2O2: Hydrogen Peroxide is used for bleaching the fabric and oxidizing the fabric by providing an oxygen ion. Stabilizers: The function of stabilizers is to reduce the regular decomposition of H2O2 which might lead to breakage of cellulose molecules. Wetting agent: The function of wetting agent is to reduce the surface tension between the fiber and the dye liquor of the dye bath and increase the wet ability of the fabric. Sequestering agent: The function of sequestering agent is to reduce water hardness and impurities. T.S.P: The function of T.S.P is to swell the silk fiber for the penetration of the chemicals for bleaching.
38
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during bleaching of Degummed silk fabric are given below: We should use apron while dyeing the fabric for safety. All the apparatus should be used carefully. The temperature should be maintained carefully during heating the dyeing bath. The gas burner should be handled carefully for avoiding accidents. The chemicals should be measured carefully according to recipe.
Conclusion:
By bleaching process it was possible to achieve a new, neat and clean silk fabric.
39
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 07 Experiment name: Dyeing of Polyester and cotton blend fabric with disperse dye.
Introduction:
The non-ionic dyes like disperse dyes are used to reduce the negative change on the surface of the hydrophobic fibers which are not influenced by the surface change as these dyes are non soluble and molecularly dispersed. As these dyes are molecularly dispersed, they are known as disperse dyes.
Objects:
The objects of Polyester/cotton blend fabric dyeing with disperse dye are given below: To know about the dyeing process of disperse dye. To know about the procedure of disperse dyeing. To know about the mechanism of disperse dyeing. To know about the properties of disperse dye.
Dyeing recipe:
The recipes of Polyester/cotton blend fabric dyeing with disperse dye is shown below: Disperse dye (red): 2% (owf). Dispersing agent: 2gm/l. Carrier: 2gm/l. CH3COOH: 1gm/l. Sequestering agent: 1 gm/l. Time: 60 minutes. Temperature: 90 degrees. Material: liquor: 1: 40. pH: 4.5-5.5.
40
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Dyeing mechanism:
The Disperse dyeing mechanism of polyester/cotton blend fabric is shown below:
Dissolution of dye: The dispersion of the dye occurs by breaking down into molecules in the water. This dissolution of the dyestuff in the dye bath depends on the dispersability and solubility of the dyestuff. It is aided by the presence of dispersing agent and rise of temperature. Adsorption of dye: Adsorption of dissolved dye from the solution to the fiber surface is occurred in the dye bath. This dyestuff adsorption is influenced by the solubility of the dye in the dye bath and in the fiber. Diffusion of dye: Diffusion of the dye molecules from the fiber surface into the interior of the fiber, towards the centre. The adsorption rate is higher than the diffusion rate. But the diffusion of dye governs the overall rate of dyeing.
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used in the disperse dyeing of polyester/cotton blend fabric are given below: Polyester/cotton blend fabric sample. Electric balance. Thermometer. Bicker. Dyeing bath. Scissor. Gas burner. Measuring cylinder. Glass rod. Spoon. pH meter.
41
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Dyeing curve:
The dyeing curve of disperse dyeing of polyester/cotton blend fabric is shown below:
Figure: Polyester/Cotton blend dyeing method (Exhaust).
Calculation:
The calculation of disperse dyeing of polyester/cotton blend fabric is given below: Sample weight: 5gms. For water: As, material: Liquor = 1:40 So, Total Liquor= For dye: Total amount of dyes = . For sequestering agent: 200cc of water requires = . 42
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
For Dispersing agent: 1000cc of water requires = 2gms So, 200cc of water requires = =40cc. For carrier: 1000cc of water requires = 2gms So, 200cc of water requires = =40cc. For CH3COOH: 200cc of water requires = . .
For additional water: {200-(10+40+40+20+20)}= 70cc.
Functions of chemicals:
The functions of the chemicals used in disperse dyeing of polyester/cotton blend fabric is given below: Dispersing agent: Dispersing agent is used to ensure uniform and trouble free dyeing. It is also used to give stable dispersion of the dye. Carrier: Carriers are organic substances which act as molecular lubricant and swell the fiber reducing inter molecular forces by constructing a loose complex. Sequestering agent: The function of sequestering agent is to reduce water hardness and impurities. CH3COOH: The function of CH3COOH is to neutralize the dye.
43
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Working Procedure:
The working procedure of disperse dyeing of polyester/cotton blend fabric is given below: At first a 5gm sample of polyester/cotton blend fabric was taken by measuring it in an electric balance. After that a 1% stock solution of 20cc of sequestering agent was made and taken in the dyeing bath. Next a 1% stock solution of 20cc of CH3COOH was made and taken in the dyeing bath. A solution of 2% disperse dye of 10cc was added in the dyeing bath which was made by adding 1gm of disperse dye in a 100cc solution. Then additional water of 70cc was added to the dyeing bath. After that a 1% stock solution of 40cc of dispersing agent was added to the dyeing bath. Then a 1% stock solution of 40cc of carrier was added to the dyeing bath. Next the 5gm fabric sample was immersed into the dyeing bath and put on the gas burner for heating the dye solution. After that heat the dye solution at 90 degree temperature for 60 minutes. During that the temperature was checked by using thermometer. Finally when 60 minutes have passed the dyeing bath was dropped. Then the fabric was taken for after treatment.
After treatment:
The After wash for disperse dyeing of polyester/cotton blend fabric is given below: Hydroze wash: 2gm/l. NaOH wash: 2gm/l. Time Temperature: 10mins 60degrees. Finally the fabric was put into the oven dryer.
44
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during disperse dyeing of polyester/cotton blend fabric are given below: We should use apron while dyeing the fabric for safety. All the apparatus should be used carefully. Necessary steps should be taken to maintain a temperature of solution. The gas burner should be handled carefully for avoiding accidents. The chemicals should be measured carefully according to recipe.
Conclusion:
By disperse dyeing of polyester/cotton blend fabric it is possible to create the best dyeing effect on the fabric which is much better than other dyes.
45
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 08 Experiment name: Dyeing of cotton/polyester blend fabric with direct dye (Cold brand). Introduction:
Dyeing is the process by which physical or chemical changes occur to a textile material as it is immersed in an aqueous solution of dye. The direct dye is an anionic dye having substantively for cellulosic fibers normally applied from an aqueous dye bath containing electrolytes. The dyes which have strong affinity towards the fiber and can be applied directly on the fiber without any help of any assistance are called direct dye. These dyes are also known as commercial dye.
Objects:
The objects of dyeing method of cotton/polyester blend fabric with reactive dye are given below: To know about direct dye. To know about the dyeing procedure of direct dye. To know about the method of dyeing cotton/polyester blend with direct dye. To know about the dyeing mechanism of direct dye. To know the functions of various materials and reagents used in direct dyeing process. To produce various designs on the surface of the fabric.
Dyeing recipe:
The recipe of dyeing of cotton/polyester blend fabric with direct dye is shown below: Direct dye (blue): 2% (owf). Salt (NaCl): 12 gm/l. Soda ash (Na2Co3): 2 gm/l. Wetting agent: 1 gm/l. Sequestering agent: 1 gm/l. Time: 60 minutes. Temperature: 60 degrees. Material: liquor: 1: 40. pH : 8-9.
46
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Dyeing mechanism:
This dyeing is normally applied to cellulosic fibers. The fibers which are dyed with direct dye are given below: Cotton fibers, Linen fibers, Viscose Rayon fibers, Silk fibers, Wool fibers, Mixture of fibers, etc. In this process, the direct dye does not react with the fiber, but creates hydrogen bond with the fiber of the fabric. As the fabric is immersed into the dye liquor the functional groups of high electronegative charge pairs with the hydrogen group of dye and produces hydrogen bond. This is shown in the following reaction: Dye-X + H- Cellulose
Dye Cellulose + HX.
The dye is treated in alkaline or neuyral aqueous dye bath without any preliminary treatment.
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used in dyeing of cotton/polyester blend fabric with direct dye are given below: Cotton/polyester blend fabric sample. Electric balance. Thermometer. Bicker. Dyeing bath. Scissor. Gas burner. Measuring cylinder. Glass rod. Spoon.
47
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Dyeing curve:
The dyeing curve of dyeing of cotton/polyester blend fabric with direct dye is shown below:
Figure: Polyester/Cotton blend Direct dyeing method (Exhaust).
Functions of chemicals:
The function of the chemicals used in direct dyeing of polyester/cotton blend fabric is given below: Wetting agent: The function of wetting agent is to reduce the surface tension between of the liquor in the dye bath. Sequestering agent: The function of sequestering agent is to reduce water hardness and impurities. Salt: Salt is used to ensure the penetration of dye into the fiber of the dyeing fabric. Soda ash: Soda ash is used to make the penetrated dye into the fix and stable in the fabric.
48
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Working Procedure:
The working procedure of cotton/polyester blend fabric dyeing with direct dye is given below: At first a 1% solution of 20cc of wetting agent was made and taken in the dyeing bath. Next a 1% solution of 20cc of sequestering agent was made and taken in the dyeing bath. A solution of 2% reactive dye of 10cc was added in the dyeing bath which was made by adding 1gm of reactive dye in a 100cc solution. Then additional water of 150cc was added to the dyeing bath. Next the 5gm fabric sample was immersed into the dyeing bath and put on the gas burner for heating the dye solution. After that 0.4gm of Na2Co3 soda ash was added to the dyeing bath. After 5 minutes of heating the dye solution 2.4gm of NaCl salt was added to the solution. After that heat the dye solution at 60 degree temperature for 60 minutes. During that the temperature was checked by using thermometer. Finally when 60 minutes have passed the dyeing bath was dropped. Then the fabric was taken for after treatment.
Calculation:
The calculation of reactive dyeing is given below: For dye: Total Dyes =
For wetting agent: Total Wetting Agent =
49
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
For sequestering agent: Total Sequestering Agent =
For salt: 1000cc of water requires = 12gms So, 200cc of water requires = For soda ash: 1000cc of water requires = 2gms So, 200cc of water requires = For additional water: {200-(20+20+10)}= 150cc. . .
After treatment:
The After wash for direct dyeing of polyester/cotton blend fabric is given below: Cold wash CuSO4 wash-2gm/l CH3COOH wash-0.5gm/l Time Temperature: 10mins 60degrees. Cold wash Finally the fabric was put into the oven dryer.
50
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during dyeing of cotton/polyester blend fabric with direct dye are given below: We should use apron while dyeing the fabric for safety. All the apparatus should be used carefully. The temperature should be maintained carefully during heating the dyeing bath. The gas burner should be handled carefully for avoiding accidents. The chemicals should be measured carefully according to recipe. We should be careful during after treatment as it has poor washing fastness property.
Conclusion:
The direct dyeing is the most commonly used dyeing process of modern times. As the cost of direct dye is very cheap and by this dyeing process it is possible to achieve the expected dyeing shade, so it can also said one of the best dyes of modern times.
51
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 09 Experiment name: Discharge printing on the cotton dyed fabric. Introduction:
Printing is the process by which a design is formed on the fabric surface by applying colorants with stencils, rollers, wooden blocks or screens. Normally fabrics are printed on one side of the fabric or both side of the fabric. In this process, the fabric is printed on the surface of the fabric and here the does not penetrate into the fabric. In this experiment we have used screen printing method. There are two styles of discharge printing. Such as, white style and colored style. Here the white style is used.
Objects:
The objects of discharge printing of cotton dyed fabric are given below: To know about the printing process. To know about the printing procedure of cotton dyed fabric. To know about the recipe of producing the printing paste. To know about the method of producing the printing paste. To know about the mechanism of printing with print paste. To know the functions of various materials and reagents used in the printing process. To produce various designs on the surface of the fabric.
Printing recipe:
The recipe of discharge printing of cotton dyed fabric for print paste forming is shown below: Rongolite /Hydroze: 15%. Starch: 50%. Titanium dioxide (TiO2): 20%. Egg elbomin: 10%. Water: 5%.
52
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Preparation of Print Paste:
The usual process for the preparation of print paste for discharge printing of cotton dyed fabric is shown below: Hydroze +Required water for producing the paste. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) + Required water for forming the paste. 8gms of starch + 100cc of water to make the solution. Add the above prepared pastes and solution to make the print paste.
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used for discharge printing of cotton dyed fabric are given below: Cotton dyed fabric sample. Printing screen. Thermometer. Bicker. Dyeing bath. Scissor. Gas burner. Measuring cylinder. Glass rod. Spoon.
Functions of chemicals:
The functions of the chemicals used in discharge printing of cotton dyed fabric are given below: Rongolite/Hydroze: The function of Rongolite/Hydroze is to extract the color from the dyed fabric according to the design. Starch: The function of starch is to make the print paste thick. Titanium dioxide (TiO2): Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is used to letting the paste fix on the surface of the fabric. Egg elbomin: Egg elbomin is used to produce white effect on the design of the printed area of the fabric.
53
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Working Procedure:
The working procedure of discharge printing of cotton dyed fabric is given below: At first add 15gms of hydroze with some water in a bicker and stir it with glass rod to make a paste. Next add 20gms of titanium dioxide with some water in a bicker and stir it with glass rod to make a paste. Then take 8gms of starch and 100cc of water in a dyeing bath and heat the dyeing bath by gas burner. When the starch and water has mixed and produced a thick paste then turn off the burner. After that add all the pastes in a bicker and then stir it to form a mixture of print paste. Then place the dyed cotton fabric under the designed printing screen and put the print paste over the printing screen. After that the printing paste is dragged over the screen with a wooden brush for producing the screen design on the surface of the fabric. Next the fabric is put into the oven dryer for drying. Finally the fabric was taken for after treatment.
After treatment:
The after treatment of discharge printing of cotton dyed fabric is given below: Drying Steaming Soap wash Cold wash
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during discharge printing of cotton dyed fabric are given below: We should use apron while printing the fabric for safety. All the apparatus should be used carefully. The gas burner should be handled carefully for avoiding accidents. The printing paste should be stirred carefully to avoid spilling of the pastes. The chemicals should be measured carefully according to recipe. We should be careful during after treatment as the print can easily be faded.
54
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Conclusion:
The printing is a common process and a process which is widely used as it spends less dyeing ingredients and at the same time is capable of producing required designs.
55
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 10 Experiment name: Dyeing of cotton fabric with pigment.
Introduction:
Dyeing is the process by which physical or chemical changes occur to a textile material as it is immersed in an aqueous solution of dye. The pigments are colored, black, white or fluorescent particulate organic or inorganic solids which usually are insoluble in water essentially physically and chemically by the vehicle or substrate in which they are incorporated. They alter appearance by selective absorption or by scattering of light. Pigments are usually dispersed in vehicle or substrate for application, as for instance in inks, paint plastic or other polymeric materials. Pigments contain a crystal or particulate structure throughout the coloration process.
Objects:
The objects of dyeing method of cotton fabric with pigment are given below: To know about pigments. To know about the dyeing procedure of pigment. To know about the method of dyeing cotton fabric with pigment. To know about the dyeing mechanism of pigment. To know the functions of various materials and reagents used in this process. To produce colored effect on the surface of the fabric.
Dyeing recipe:
The recipe of dyeing of cotton fabric with pigment is shown below: Pigment (red): 4% (owf). Binder: 30 gm/l. Fixing agent: 20 gm/l. CH3COOH: 4gm/l. Time: 40 minutes. Temperature: 40-50degrees. Material: liquor: 1: 20.
56
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
pH : 5-5.5.
Dyeing mechanism:
This dyeing mechanism of cotton fabric with pigment is shown below:
In this process, the pigments provide negative surface charge when they are dispersed in water. These negative surface charges attract the pigment particles to fiber surface for coloring the textile material which contains groups. Here no chemical reactions take place between the fiber and pigment. As the fibers have no attraction to pigment, thus they are treated with a suitable cat ionizing agent. Such as, Cat ionic polymers of polyacrylates. Cat ionic polymers of polyimidazoles.. The cat ionizing agents are used for attracting the anionic pigments to the fiber. This process is called cat ionic pretreatment. The pigments are set on the surface of the fiber and it is fixed on the fiber surface with the aid of binders.
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used in dyeing of cotton fabric with pigment are given below: Cotton fabric sample. Electric balance. Thermometer. Bicker. Dyeing bath. Scissor. Gas burner. Measuring cylinder. Glass rod. Spoon.
57
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Dyeing curve:
The dyeing curve of dyeing of cotton fabric with pigment is shown below:
Figure: Cotton fabric Pigment dyeing method (Exhaust).
Functions of chemicals:
The functions of the chemicals used dyeing of cotton fabric with pigment are given below: Binder: The function of binder is to attach the pigments on both surfaces of the fabric. Fixing agent: The function of fixing agent is to make sure the pigments remain on the fabric surface. CH3COOH: The function of CH3COOH is to neutralize the dye.
58
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Working Procedure:
The working procedure of dyeing of cotton fabric with pigment is given below:
At first 100cc of water was taken in a bicker. Then 0.2gms of pigment was added into the water of the bicker. Next 2gms of fixing agent was added to the solution of the bicker. After that 0.4cc of CH3COOH was added to the solution of the bicker. Next the 5gm fabric sample was immersed into the dyeing bath and the gas burner was put on for heating the dye solution. The temperature of the dyeing bath was maintained at 40 degrees for 10 minutes and the temperature was checked by using thermometer. During that time3gms of binder was added to the solution of the bicker. After that the dye solution was heated at 50 degree temperature for 30 minutes. During that the temperature was checked by using thermometer. Finally when 40 minutes was passed the dyeing batch was dropped. Then the fabric was taken for after treatment.
Calculation:
The calculations of dyeing of cotton fabric with pigment are given below: For dye: 100gms of fabric requires = 4gms 5gms of fabric requires =
For CH3COOH:
1000cc of water requires = 4gms
100cc of water requires =
For binder: 1000cc of water requires = 30gms
100cc of water requires =
For fixing agent: 1000cc of water requires = 20gms
100cc of water requires =
59
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
After treatment:
The after treatment of dyeing of cotton fabric with pigment is given below: Cold wash Soap wash-2gm/l Na2CO3 wash-2gm/l Cold wash Drying
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during dyeing of cotton fabric with pigment are given below: We should use apron while dyeing the fabric for safety. All the apparatus should be used carefully. The temperature should be maintained carefully during heating the dyeing bath. The gas burner should be handled carefully for avoiding accidents. The chemicals should be measured carefully according to recipe. We should be careful during after treatment as it has poor washing fastness property.
Conclusion:
The pigments are suitable for both natural and manmade fibers and are 100% water soluble addition to that it can be dyed easily and within less time period than other dyes. For this reason it has good demand in textile sectors.
60
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 11 Experiment name: Dyeing of silk fabric with acid dye. Introduction:
Dyeing is the process by which physical or chemical changes occur to a textile material as it is immersed in an aqueous solution of dye. Acid dyes are such dyes that dissociate in aqueous solution and thus produce color on the fabric. These dyes are so called because it is applied to fabric in organic and inorganic acid dyeing solution. They are commercially utilized for nylon, wool, silk acrylic, polypropylene and blends of the aforementioned fibers. Secondly they all are sodium salts of organic acids and the anions are active color components. Such as, CI acid orange7:
Objects:
The objects of dyeing method of silk fabric with acid dyes are given below: To know about acid dyes. To know about the dyeing procedure of acid dyes. To know about the method of dyeing silk fabric with acid dyes. To know about the dyeing mechanism of acid dyes. To know the functions of various materials and reagents used in this dyeing process. To produce bright colored effect on the surface of the fabric.
Dyeing recipe:
The recipe of dyeing of silk fabric with acid dyes is given below: Acid dye (red): 3% (owf).
Salt (NaCl): 15 gm/l.
CH3COOH: 2gm/l.
Wetting agent: 1 gm/l. Sequestering agent: 1 gm/l. Time: 45 minutes. Temperature: 90 degrees. Material: liquor: 1: 80. pH : 5-5.5.
61
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Dyeing mechanism:
The dyeing mechanism involved in silk fabric dyeing with acid dye is shown below: The generalized formula for acid dye molecules are, DSO 3 Na . Where, D: Color component,
+
DSO3 : Dye amino group, Na : Sodium ion. The chemical mechanism takes place between acid dye molecules and silk polymers. In this process, the hydrogen ions of acid having a net amount of positive charges combine with silk polymer to form positively charged amino groups. Such as,
HCL/H2SO4
+
Silk polymer-NH2+ H - >
Silk polymer-NH3 + Cl
Then an ionic link is formed between positively charged amino groups and dye anions. Such as, Silk polymer-NH3 + DSO3 - > Silk polymer-NH3 SO3D. Thus the colored effect is formed on the fabric surface.
+
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used in dyeing of silk fabric with acid dyes are given below: Silk fabric sample. Electric balance. Thermometer. Bicker. Dyeing bath. Scissor. Gas burner. Measuring cylinder. Glass rod. Spoon.
62
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Dyeing curve:
The dyeing curve of silk fabric with acid dyes is given below:
Figure: Silk fabric Acid dyeing method (Exhaust).
Functions of chemicals:
The function of the chemicals used in acid dyeing of silk fabric is given below: Wetting agent: The function of wetting agent is to reduce the surface tension between of the liquor in the dye bath. Sequestering agent: The function of sequestering agent is to reduce water hardness and impurities. Salt: Salt is used to ensure the penetration of dye into the fiber of the dyeing fabric. CH3COOH: The function of CH3COOH is to neutralize the dye.
63
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Working Procedure:
The working procedure of silk fabric dyeing with acid dye is given below: At first the degummed and bleaches silk was measured by the electric balance and the silk sample weighed 2.62gms. Next 210cc of water was taken in a dyeing bath. Then 0.21gms of sequestering agent was taken in the dyeing bath. After that 0.21cc of wetting agent was added to the dyeing bath. Next 0.42cc of CH3COOH was put into the dyeing bath. Then 0.08gms of acid dye was taken in the dyeing solution. After that 3.15gm of NaCl salt was added to the solution. Then the silk fabric was put into the dyeing solution. After that the dye solution was heated at 90 degrees temperature for 45 minutes. During that the temperature was checked by using thermometer. Finally when 45 minutes have passed the batch was dropped. Then the fabric was taken for after treatment.
Calculation:
The calculation of acid dyeing is given below: For fabric: Material: Liquor =1:80. So, 2.62gms fabric of sample needs =2.62 For dye: 100gms of fabric uses 3gms of dye. So, 2.62gms of fabric sample needs = For wetting agent: 1000cc of water requires = 1gms So, 210cc of water requires = For sequestering agent: 1000cc of water requires = 1gms So, 210cc of water requires = . .
80 = 209.6cc water.
64
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
For salt: 1000cc of water requires = 15gms So, 210cc of water requires = For CH3COOH: 1000cc of water requires = 2gms So, 210cc of water requires = . .
After treatment:
The after treatment of dyeing of silk fabric with acid dye is given below: Cold wash Soap wash-2gm/l Na2CO3 wash-1gm/l Time Temperature: 10mins 60degrees. Cold wash
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during dyeing of silk fabric with acid dye are given below: We should use apron while dyeing the fabric for safety. All the apparatus should be used carefully. The temperature should be maintained carefully during heating the dyeing bath. The gas burner should be handled carefully for avoiding accidents. The chemicals should be measured carefully according to recipe.
Conclusion:
The acid dyeing is the most commonly used dyeing process for dyeing manmade fibers as it can produce good color and also bright colored effect on the fabric.
65
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 12 Experiment name: Estimation of scouring and bleaching effect.
Introduction:
Scouring and bleaching is the most important processes of dyeing, because only good scouring and bleaching can assure an exact shade of dye on a particular textile material. The estimation of scouring and bleaching is important for dyeing a textile material as it is said that only good scouring and bleaching assures 50% of the dyeing procedure. Scouring removes the impurities present in the textile goods and bleaching assures the destruction of the natural color present into the fabric, thus gives it a white effect.
Objects:
The objects of estimation of scouring and bleaching effect are given below: To know that the scoured and bleached fabric has good affinity to dyes. To know if the scouring and bleaching process was uniform. To know that no fiber damage has occurred during scouring and bleaching. To know if the fabric has good reflectance to light. To know if the scoured and bleached fabric has achieved permanent whiteness. To know if the scoured and bleached fabric still contains chlorine in the fabric. To know if the scoured and bleached fabric is hydrophilic.
Scouring & Bleaching Effect Tests:
The scouring and bleaching effect of the fabric can be estimated through the following three tests: Drop test. Colum test/Wicking test. Immersion test.
66
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Drop Test:
Drop test is the process by which the uniformity of the scouring process can be estimated by dropping one drop of 0.1% direct dye solution on the fabric. Its absorbency is tested visually.
Test principle:
In the drop test process, the colored solution of 0.1% direct dye (red) solution is dropped on the scoured and bleached fabric by pipette and its absorbency is tested visually. The drop may have various shapes when absorbed. The absorbency is measured in two ways. Such are: Time of absorption: The standard time to absorb one drop of colored solution is normally 0.5-0.8secs, but up to sec is allowed. In this process the absorption is estimated visually. Shape of absorption: If the drop is circularly absorbed then we can say that the fabric is uniformly scoured. If the drop is circularly absorbed but in small are then it is also uniformly scoured, not well scoured, but if the drop is not circular then it is not uniformly scoured.
Pipette containing 0.1% direct dye
Fabric attaching Clamp
Scoured & bleached fabric Shapes of Drops
Figure: Drop test method for determining uniform Scouring.
67
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Test Apparatus:
The apparatuses used for drop test of the fabric are given below: Scoured and bleached cotton fabric sample. Pipette (5mm). Congured-0.1%. Fabric attaching clamp. Electric balance. Bicker. Scissors.
Test Sample:
The test sample was cut in a rectangular shape.
Test Procedure:
The procedures for drop test of the fabric are given below: At first 0.1gms of direct dye was measured in the electric balance. Then the dye was added in a bicker containing 100cc of water. After that small amount of 0.1% dye solution was poured into the 5mm pipette. Then the scoured and bleached cotton fabric was attached to the clamp. Next one drop of 0.1% direct dye was dropped on the fabric surface. The drop was absorbed within 1sec and the drop was circular in shape. The drop took almost 1cm diameter of round spread.
Test Results:
As the time to absorb the direct dye drop by the fabric was within 1sec and the shape of the drop was circular in shape having almost 1cm diameter, then we can say that the cotton fabric was uniform and well scoured and bleached.
68
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Colum Test/Wicking Test:
Wicking test is the process by which the uniformity of the scouring process can be estimated by immersing the scoured and bleached fabric sample in to a 1% direct dye solution. Thus analyze the distance of travel by the direct dye in to the fabric.
Test principle:
A cotton fabric sample is taken having 5cm 18cm dimension and the cotton sample is marked at the 1cm from the bottom. Then 1cm portion of the sample is immersed into 1% direct dye solution for 5mins and then the distance travelled by the colored solution about 1cm mark is noted. The acceptable range for the colored solution to travel is 3cm-5cm.
5cm
17cm
Stand
Immersed fabric
1 cm Dye Solution
Figure: Column test method for determining uniform Scouring.
69
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Test Apparatus:
The apparatuses used for drop test of the fabric are given below: Scoured and bleached cotton fabric sample. 1% direct dye solution. Fabric attaching stand. Marker. Bicker. Scissors.
Test Sample:
The test sample was cut in a 5cm 18cm rectangular shape and at 1cm from bottom was marked. To estimate the wicking of the dye 3cm and 5cm from bottom was also marked.
Test Procedure:
The procedures for wicking test of the fabric are given below: At first 1gms of direct dye was measured in the electric balance. Then the dye was added in a bicker containing 100cc of water. After that small amount of 1% dye solution was poured into the bicker. Next the fabric was marked at 1cm, 3cm and 5cm from the bottom. Then the scoured and bleached cotton fabric was attached to the fabric stand. Finally the fabric was immersed into the bicker containing 1% of direct dye.
Test Results:
After 5-6mins have passed it was found that the 1% direct dye solution has travelled about 5cm of the fabric from the bottom which indicates that the fabric has been well scoured and bleached.
70
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Immersion Test:
Immersion test is the process by which the absorbency of the scoured and bleached fabric can be found out. As in this process the fabric is placed on the surface of water and the time taken by the fabric to immerse is noted.
Test principle:
A sample is more absorbent when it is immersed. 1cm 1cm sample is placed on the water surface and the time taken by it to immerse is noted. The standard time for it to immerse is 5secs. If the time is up to 10secs then the sample is well scoured. But if the time is more than 10secs then sample was not well scoured.
Scale
Water containing bicker
Immersed fabric sample
Test Apparatus:
The apparatuses used for immersion test of the fabric are given below: Scoured and bleached cotton fabric sample. Marker. Bicker. Scissors. Scale.
71
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Test Sample:
The test sample was cut in a 1cm 1cm square shape.
Test Procedure:
The procedures for immersion test of the fabric are given below: At first a bicker was fully poured with water. Then the 1cm 1cm square sample was placed on water containing bicker. After that the height of the water was measured in the bicker. Next the height of the water was found to be 18cms. Then the time taken by the sample to fully immerse into the bicker was noted.
Test Results:
The fabric sample took about 6secs to fully immerse into the bicker and reach the end of the bicker. So, we can say that the fabric was well scoured and bleached.
Conclusion:
By the estimation of scouring and bleaching effect test it is possible to find out if the sample is suitable for next procedures. This is why it is said that a perfect scouring and bleaching confirms 50% of the dyeing process
72
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 13 Experiment name: Color fastness to wash.
Introduction:
Fastness is the unique property of a dyed fabric. Color fastness of a dyed fabric is the capacity of a dye on a textile material to resist a load or a destructive factor is referred to as fastness. The outstanding property of a dyed textile material is the fastness of shade. The color fastness of a dyed textile material normally depends on following factors: Color fastness to wash. Color fastness to light. Color fastness to rubbing. Color fastness to perspiration. Color fastness to bleaching agent. Color fastness to weathering. Color fastness to sea water. Etc. Color fastness to wash is very important for a sample. There are verities of testing procedures. Such are: Washing conditions may vary from one country to another. The methods depend on the use of dyed goods. To calculate repeated washing accelerated test methods are used.
Objects:
The objects of estimation of color fastness to wash are given below: To know that the dyed fabric can retain its color at high temperature. To know if the dyed fabric can retain its color at high pressure. To know if the dyed fabric can retain its color by using various chemicals. To know if the dyed fabric can retain its color at high mechanical action. To know if the dyed fabric can retain its color in the presence of hard water. To know if the dyed fabric can retain its color at acidic and alkaline conditions.
73
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Color fastness to wash tests:
Color fastness to wash can be measured by the change of color after washing which is referred to as fading of color and also by the staining of undyed textile material in contact of a dyed textile sample.
Test principle:
A specimen in contact with specified adjacent fabric or fabric is laundered, rinsed and dried. The specimen/composite sample is treated under appropriate condition in a chemical bath for a short time. The abrasive action is accomplished by the use of liquor ratio and an appropriate number of steel balls. The change in color of the specimen (dyed sample) and the staining of the fabric is assessed by recommended gray scales (1-5). The methods used for determining color fastness to wash are given below: ISO-105-C01 ISO-105-C02 ISO-105-C03 ISO-105-C04 ISO-105-C05 In this experiment, only ISO-105-C02 and ISO-105-C03 methods were practically done in the laboratory.
ISO-105-C02 test:
The ISO-105-C02 washing is one of the most common wash fastness tests of a dyed fabric. Normally it can be tested by using only soap and water.
Test recipe:
The standard recipe of washing the test sample according to ISO-105-C02 method is given below: Standard soap: 5gm/l. Material: Liquor: 1:50. Time & temperature: 45mins & 500C.
Test Sample:
The dyed sample was cut in a 10cm 4cm rectangular shape and then it was sewn with the same size multifiber fabric. Thus the composite test sample is achieved.
74
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Test apparatus:
The apparatuses used for color fastness to wash tests are given below: Dyed fabric sample. Adjacent multifiber fabric. Distilled water. Dyeing bath. Electric balance. Scissors. Scale. Gas burner. Grey scale.
Calculation:
The calculation of ISO-105-C02 method is given below: Sample weight: 2.32gms Total liquor: 2.32 50= 116cc. Standard soap: 5 116/1000= 0.58gms
Test Procedure:
The procedures for ISO-105-C02 method of testing of the fabric are given below: At first a 10cm 4cm dyed sample was cut and also a same size multifiber fabric was cut. Then the dyed sample was attached to the multifiber fabric sample. Then the bicker was poured with 116cc of water. After that the composite fabric sample was immersed into the dyeing bath. Next the 0.58gms of soap was added to the dyeing bath. Then the dyeing bath was heated at 500C temperature for 45 minutes. Finally when the 45 minutes have passed then the dyeing bath was dropped and the fabric was put into the oven dryer for drying.
Test Results:
In this case the dyed fabric sample has faded where as the adjacent multifiber has found to have reddish stain in them.
75
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
ISO-105-C03 test:
The ISO-105-C03 washing is one of the most common wash fastness tests of a dyed fabric. Normally it can be tested by using both soap and soda while washing in water.
Test recipe:
The standard recipe of washing the test sample according to ISO-105-C03 method is given below: Standard soap: 5gm/l. Soda ash: 2gm/l. Material: Liquor: 1:50. Time & temperature: 30mins & 600C.
Test Sample:
The dyed sample was cut in a 10cm 4cm rectangular shape and then it was sewn with the same size multifiber fabric. Thus the composite test sample is achieved.
Test apparatus:
The apparatuses used for color fastness to wash tests are given below: Dyed fabric sample. Adjacent multifiber fabric. Distilled water. Dyeing bath. Electric balance. Scissors. Scale. Gas burner. Grey scale.
Calculation:
The calculation of ISO-105-C03 method is given below: Sample weight: 2.32gms Total liquor: 2.32 50= 116cc. Standard soap: 5 116/1000= 0.58gms. Soda ash: 2 116/1000= 0.232gms.
76
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Test Procedure:
The procedures for ISO-105-C03method of testing of the fabric are given below: At first a 10cm 4cm dyed sample was cut and also a same size multifiber fabric was cut. Then the dyed sample was attached to the multifiber fabric sample. Then the bicker was poured with 116cc of water. After that the composite fabric sample was immersed into the dyeing bath. Next the 0.58gms of soap and 0.232gms of soda ash was added to the dyeing bath. Then the dyeing bath was heated at 600C temperature for 30 minutes. Finally when the 45 minutes have passed then the dyeing bath was dropped and the fabric was put into the oven dryer for drying.
Test Results:
In this case the dyed fabric sample has faded where as the adjacent multifiber has found to have more reddish stain in them then that of the ISO-105-CO2 method of color fastness to wash testing.
Table showing color fastness to wash:
Test Serial no. Changing 1. 2. 3. 3-4 4 4-5 Test results Staining 4-5 3-4 4
Conclusion:
Color fastness to wash is an important property of dyed fabric, because it is the only which really indicates the longevity of the dyed fabric and also determines the quality of both fabric and dye.
77
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 14 Experiment name: Dimensional stability to shrinkage% of washing.
Introduction:
Shrinkage test or dimensional stability test is a very important test for the purpose of manufacturing bulk production of fabric. Fabric shrinkage problem is the biggest problem in the case of manufacturing bulk amount of fabric. In fact it is rated one of the ten leading quality problems in the textile industry. The shrinkage problems mainly arise in the manufacturing operation as the fabric cannot retrain its original shape which leads to decrease or increase. Shrinkage is normally expressed as change of percentage.
Objects:
The objects of shrinkage test or dimensional stability test are given below: To know if the fabric has proper dimensional stability. To know the percentage of shrinkage after washing. To know the stability of the fabric towards washing. To find out the difference between original length and after wash length.
Principle:
This method of washing is used for textile fabrics, garments and other textile products which are normally washed in washing machine and dried after washing. In this process the fabric is washed and dried according to procedure and thus after that that the reduction in length is measured. This shrinkage is expressed in percentage by using the following formula: Final length (after wash)-Original length (before wash) Shrinkage%= Original length (before wash) 100%
78
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Recipe:
The recipe used for estimating shrinkage% or dimensional stability to wash is given below: Soap: 2gm/l. Time: 35mins. Temperature: 500C. Material: Liquor: 1:50.
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used for estimating shrinkage% or dimensional stability to wash are given below: Electronic balance. Stainless steel scale. Fabric sample. Bowl. Marker. Gas burner. Thermometer. Oven dryer. Distilled water. Reference soap. Scissors.
Sample measurement:
The fabric sample was cut in a 30cm 30cm or 50cm 50cm square shape having on hand of 5cms from all the edges of the fabric. In this fabric the 30cm square space is marked with the marker which helps to determine the shrinkage%.
79
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Working procedure:
The working procedure for determining the shrinkage% to wash is given below: At first the fabric was measured with a steel scale and it was marked according to specified measurements leaving the on hand out of the margin. Then the fabric was weighted in the electric balance which weighted about 17gms. According to material: liquor ratio 850cc of water was taken in a bowl. Then 1.7gms of soap was added to the liquor. After that the fabric was immersed into bowl containing liquor solution. Next the bowl containing fabric and liquor solution was heated for 35 minutes at 500C temperature. Finally when 35 minutes have passed, the fabric was put into oven dryer for drying.
Calculation:
The calculation of the shrinkage% towards warp and weft of the fabric is given below: Shrinkage% for weft = Shrinkage% for warp=
( ) ( ) ( )
100% 100%
Results:
After the experiment have finished the results that we have found are shown below: Shrinkage in weft direction = -2.9%. Shrinkage in warp direction = -8.1%.
Conclusion:
By this experiment, it can be possible to estimate fabric loss during bulk production.
80
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 15 Experiment name: Azo color test of dyed sample.
Introduction:
Azo dye is an integral part of every dyes as each and every dyes contain azo groups. If a dyed sample contains abouty 30% of azo groups then the dyed fabric sample is azo free and if the dyed sample contains more than 30% of azo groups then the dyed fabric sample is not azo free. Azo groups are very dangerous for health as it can lead to cancer to human body. So an acceptable range of azo contained dye is acceptable.
Objects:
The objects of azo color test of dyed fabric sample are given below: To know the amount of azo groups present in a dyed sample. To know the testing procedures of azo color test. To know if the fabric can be suitable to wear. To know if the fabric is harmful for health. To know if the color fastness of the dye is acceptable. In some cases it is possible to determine the dye used in the fabric.
Testing recipe:
The recipe used for testing azo color contamination in a dyed fabric sample is given below:
Caustic soda: 1gm/l. Hydrose: 2gm/l. Temperature: Boiling temperature. Time: 3-5mins.
81
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used for testing azo color contamination in a dyed fabric sample are given
below:
Burette. Test tube. Gas burner. Pipette. Thermometer. Dyeing bath/Bowl. Test tube
Test tube Test tube holder
Test tube Test tube holder
Dyed fabric sample
Dyed fabric sample
Gas burner
Gas burner
Testing procedure:
The procedures for azo color test of the dyed fabric sample are given below: At first 1litre of water was taken in the dyeing bath. Then 1gm of caustic soda and 2gms of hydrose was added to the dyeing bath. After that the 2/3 parts of the test tube was filled with the prepared solution. Next the dyed fabric sample was cut into a small piece and immersed into the solution. Then the test tube was brought towards the gas burner and it began heating. Finally the test tube was held over the gas burner until it had reached the boiling temperature.
82
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Test result:
There can be various results of the azo color test of a dyed fabric which are shown below: Observations Results
If the fabrics color remains unchanged The fabric is azo free and also it has and the liquor solution remains good wash fastness. colorless. If the fabric color changes as well as the The fabric is azo free but it has bad color of liquor solution. wash fastness. If the fabrics color changes and the The fabric is not azo free. liquor solution remains colorless. If the fabrics color changes and the The fabric is azo free. Mostly in case of liquor solution remains colorless. But if vat dyes. the color is removed after washing.
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during azo color testing of dyed fabric are given below: We should use apron while dyeing the fabric for safety. All the apparatus should be used carefully. The temperature and time should be maintained carefully during heating the test tube. The fabric should be observed throughout the process. The gas burner should be handled carefully for avoiding accidents. The chemicals should be measured carefully according to recipe.
83
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Conclusion:
By this process it can be easily determined if the quality of the dyed fabric is suitable for human health and the fastness of the dye can also be estimated.
84
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Experiment no.: 16 Experiment name: Color fastness to hot pressing.
Introduction:
Color fastness to hot pressing is very important for a textile dyed product. In this process, the capacity of the dyed fabric to retain its color at high temperature and pressure is determined. Normally the fabric has to undergo ironing process in domestic uses; by this process it will be easier to determine its resistivity of color fastness at ironing process
Objects:
The objects of color fastness to hot pressing are given below: To know if the fabric can resist its color properties at high temperature. To know if the fabric can resist its color properties at high pressure. To know the various changes of color of the dyed fabric at various conditions of the fabric. To know the fastness of color of the dyed fabric according to Grey scale (1-5).
Principle:
Determination of the resistance of the color of dyed textiles to ironing and pressing on the hot cylinders. The resistance of color of dyed textile material is determined by three processes which are given below: Dry pressing. Damp pressing. Wet pressing.
85
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Controlling points:
The controlling points of the hot pressing test of the fabric are given below: Sample size: 2-3 inch. Temperature: 1650C-1850C. Pressure: 2kg.
Apparatus:
The apparatuses used for hot pressing test of the fabric are given below: Dry fabric samples. Wet fabric samples. Calendaring iron with weight of 2kgs. Distilled water. Grey scale. A smooth asbestos sheet. Wool flannel. Scissors. Etc.
Sample specimen:
The fabric was cut in the warp direction of 2inch and in weft direction of 3incha in an almost square shape. The piece of fabric over which the test specimen is placed is double the length of the specimen and covering fabric has the same size.
Warp 2
Weft 3
Bottom fabric Cover fabric Sample specimen
86
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Dry pressing test:
Dry hot pressing test is done by placing a dry specimen on a dry bottom fabric and over the specimen a dry cover fabric is placed.
Test Procedure:
The procedures for dry hot pressing test of the fabric are given below: At first the dry specimen was placed on top of the cotton cloth covering the wool pad. Then another fabric was placed on the specimen. After that the calendaring iron was placed on the specimen for about 15secs with 2kg pressure. Finally when 15secs have passed the calendaring iron was removed from the specimen.
Damp pressing test:
Damp hot pressing test is done by placing a dry specimen on a dry bottom fabric and over the specimen a water soaked cover fabric is placed.
Test Procedure:
The procedures for damp hot pressing test of the fabric are given below: At first the dry specimen was placed on top of the cotton cloth covering the wool pad. Then another adjacent fabric which had 100% pick up in distilled water was placed on the dry specimen. After that the calendaring iron was placed on the specimen for about 15secs with 2kg pressure. Finally when 15secs have passed the calendaring iron was removed from the specimen.
87
Lab works of Dyeing Technology
Khandaker Sakib Farhad
Wet pressing test:
Wet hot pressing test is done by placing a soaked wet specimen on a dry bottom fabric and over the specimen a water soaked cover fabric is placed.
Test Procedure:
The procedures for wet hot pressing test of the fabric are given below: At first the dry specimen was soaked in water to make it wet. Then the specimen was placed on top of the dry cotton cloth covering the wool pad. Then the other adjacent fabric which had 100% pick up in distilled water was placed on the dry specimen. After that the calendaring iron was placed on the specimen for about 15secs with 2kg pressure. Finally when 15secs have passed the calendaring iron was removed from the specimen.
Test Results:
After the test has concluded we have found stain marks on the fabric for dry and damp test, but no stain mark was found for wet test.
Precaution:
The precautions that should be taken during color fastness to hot pressing test are given below: We should carefully handle the iron calendar. We should carefully place the iron calendar on the fabric. We should heat the iron calendar carefully.
Conclusion:
By this process fabric resistivity to heat and pressure could be improved.
88
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 90 Questions of Garments Washing & Dyeing.Document26 pagini90 Questions of Garments Washing & Dyeing.Ferdous Khan RubelÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Management and Technology: Textile Labs Wet Processing Lab Manual TX-232Document16 paginiUniversity of Management and Technology: Textile Labs Wet Processing Lab Manual TX-232Safdar ZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition:: ScouringDocument13 paginiDefinition:: Scouringপ্রমিত সরকারÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dictionary of Textile Finishing: Deutsch/Englisch, English/GermanDe la EverandDictionary of Textile Finishing: Deutsch/Englisch, English/GermanEvaluare: 1.5 din 5 stele1.5/5 (3)
- Mercerization ParametersDocument2 paginiMercerization Parametersahmer adnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyeing-Pad Batch AssignmentDocument22 paginiDyeing-Pad Batch AssignmentTooba Anum100% (1)
- Process Control in Wet ProcessingDocument23 paginiProcess Control in Wet ProcessingKirti Nagda75% (4)
- Introduction To Wet ProcessingDocument84 paginiIntroduction To Wet Processingzynab123Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic DyeDocument14 paginiBasic DyePrita SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corelation Between Lab and BulkDocument38 paginiCorelation Between Lab and BulkSuraj Raghv0% (1)
- Wet Processing of Polyester MicrofibresDocument12 paginiWet Processing of Polyester MicrofibresEdward Menezes100% (1)
- Dyeing - Cold Pad Batch Project PDFDocument93 paginiDyeing - Cold Pad Batch Project PDFJaywant Bari86% (22)
- Textile Pretreatment: Processes for Removing Impurities from Cotton FabricDocument23 paginiTextile Pretreatment: Processes for Removing Impurities from Cotton FabricAyman BrohiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study On Different Types of Dyeing Faults PDFDocument10 paginiStudy On Different Types of Dyeing Faults PDF呂仲書Încă nu există evaluări
- Exhaust Dyeing Polyester with Disperse DyesDocument16 paginiExhaust Dyeing Polyester with Disperse DyesBurak EmekliogluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyeing ProblemsDocument12 paginiDyeing ProblemsShivam Bajpai100% (1)
- Vat DyesDocument23 paginiVat DyesImran Anwar100% (3)
- Working Process of Jigger Dyeing MachineDocument10 paginiWorking Process of Jigger Dyeing MachineKhushaLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polyester ProcessingDocument16 paginiPolyester ProcessingSoumen Bag100% (3)
- Jigger Dyeing MachineDocument36 paginiJigger Dyeing MachineProfessorTextech100% (1)
- Barium Activity NumberDocument1 paginăBarium Activity NumberImran NazirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finishing Collection and Guide Line RecipeDocument29 paginiFinishing Collection and Guide Line Recipeapi-19663176Încă nu există evaluări
- Garment Wash by AsifaDocument34 paginiGarment Wash by AsifaRizwan JavaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automat Process For Reactive DyeingDocument3 paginiAutomat Process For Reactive DyeingRezaul Karim Tutul100% (1)
- Tinting or OverdyeingDocument4 paginiTinting or OverdyeingDelwar Hossain67% (3)
- Textile Yarn Dyed Tips & TechniqueDocument23 paginiTextile Yarn Dyed Tips & TechniqueMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Testing For FabricDocument24 paginiChemical Testing For FabricParth Dev Verma100% (3)
- Semi Continuous Dyeing ProcessDocument3 paginiSemi Continuous Dyeing ProcessMonjur MorshedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyeing Machines and MethodsDocument20 paginiDyeing Machines and MethodsAnonymous UoRu4s100% (3)
- CPB DyeingDocument2 paginiCPB DyeingSubba RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPB Seminar CHTDocument277 paginiCPB Seminar CHTSamuel Maldonado100% (3)
- Continous Dyeing ProjectDocument147 paginiContinous Dyeing ProjectAamir Shabbir83% (6)
- Disperse PrintingDocument20 paginiDisperse PrintingCamila Suarez100% (1)
- Cotton Fabric Dyeing with Reactive DyesDocument6 paginiCotton Fabric Dyeing with Reactive DyesShaheen Monir HossainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pad Steam MachineDocument27 paginiPad Steam Machineahmer adnan88% (8)
- Project of Denim DyeingDocument111 paginiProject of Denim Dyeingdani100% (1)
- Thermefix 338 Continuous Dyeing RangeDocument48 paginiThermefix 338 Continuous Dyeing RangeImran Malik100% (1)
- Quality & Process Control in Textile ProcessingDocument56 paginiQuality & Process Control in Textile ProcessingKeshav Dhawan100% (3)
- Pretreatment of Fabrics That Contain SpandexDocument8 paginiPretreatment of Fabrics That Contain SpandexaymanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyeing FaultsDocument100 paginiDyeing FaultsNaim UddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyeing Faults & RemediesDocument13 paginiDyeing Faults & RemediesSHEIKH SADI100% (1)
- Terasil Standard Dyeing MethodDocument1 paginăTerasil Standard Dyeing MethodKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Textile TestingDocument33 paginiTextile TestingMunazza Sohail100% (3)
- Migration Inhibitors Effect On Fabric PropertiesDocument61 paginiMigration Inhibitors Effect On Fabric PropertiesAsad Jamil Rana100% (6)
- Denim Washing Process GuideDocument22 paginiDenim Washing Process Guideİbrahim Güneş100% (2)
- CPB Method of Reactive DyeingDocument4 paginiCPB Method of Reactive DyeingMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pretreatment Handbook ITMA Munich1Document29 paginiPretreatment Handbook ITMA Munich1Cesar Enriol100% (2)
- Industrial Attachment Report On Micro Fibre GroupDocument125 paginiIndustrial Attachment Report On Micro Fibre GroupDigonto Das50% (2)
- Jet Dyeing MachineDocument16 paginiJet Dyeing Machinesyed asim najamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disperse Dyes Used Polyester DyeingDocument23 paginiDisperse Dyes Used Polyester DyeingPratik Minj100% (3)
- FM-1 SizingDocument18 paginiFM-1 SizingTextile Department Help Desk.Diu100% (1)
- Exhaust DyeingDocument60 paginiExhaust DyeingLieven Verraest50% (4)
- Dyeing of Acrylic FibresDocument19 paginiDyeing of Acrylic FibresHugo Eduardo Ipiales Mesa100% (1)
- Main File Denim Rope DyeingDocument50 paginiMain File Denim Rope DyeingMuhammad Asad Nawaz75% (4)
- The Chemistry of Synthetic Dyes V6: Reactive DyesDe la EverandThe Chemistry of Synthetic Dyes V6: Reactive DyesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- ScouringDocument20 paginiScouringtamimhossen8262Încă nu există evaluări
- The Gameplay Called War_compressedDocument1 paginăThe Gameplay Called War_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- True Timeline of World History-_compressedDocument7 paginiTrue Timeline of World History-_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hidden One or the Antichrist_compressedDocument3 paginiThe Hidden One or the Antichrist_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- COVID Kitchens of Hell_compressedDocument2 paginiCOVID Kitchens of Hell_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gameplay Called Moon Voyage_compressedDocument2 paginiThe Gameplay Called Moon Voyage_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Image of AI Based Interrogation in the Name of Avoiding Self Abuse_compressedDocument2 paginiThe Image of AI Based Interrogation in the Name of Avoiding Self Abuse_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- What We Sell in the Name of Women Power_compressedDocument1 paginăWhat We Sell in the Name of Women Power_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Divide and Conquer Policy_compressedDocument1 paginăThe Divide and Conquer Policy_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Christians an Entire Religion Turned Into a Joke_compressedDocument2 paginiChristians an Entire Religion Turned Into a Joke_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Unfortunate Countries of the World and the Conspiracy Surrounding Those_compressedDocument8 paginiList of Unfortunate Countries of the World and the Conspiracy Surrounding Those_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gameplay of Targeted Human Beings_compressedDocument2 paginiThe Gameplay of Targeted Human Beings_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Is Albert Einstein a Genius or a Fake_compressedDocument2 paginiIs Albert Einstein a Genius or a Fake_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proof of Allah Being the Almighty_compressedDocument1 paginăProof of Allah Being the Almighty_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economical Take Over by the International Organizations_compressedDocument2 paginiEconomical Take Over by the International Organizations_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corruption Done by New Industrialists to Turn Their Carrier of Servitude to Entrepreneurship_compressedDocument2 paginiCorruption Done by New Industrialists to Turn Their Carrier of Servitude to Entrepreneurship_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach Towards Developing Education Program_compressedDocument2 paginiApproach Towards Developing Education Program_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation in Weft KnittingDocument13 paginiCalculation in Weft KnittingFazley BD80% (10)
- Tender Documents For Freight Forwarding, Clearing & Transportation Agent Dated 23.01.14.Document27 paginiTender Documents For Freight Forwarding, Clearing & Transportation Agent Dated 23.01.14.Khandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knitting CalculationsDocument10 paginiKnitting CalculationsWaqas Ashraf100% (3)
- PVC Coating Uses and PropertiesDocument18 paginiPVC Coating Uses and PropertiesAhmed SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- I M Com QT Final On16march2016Document166 paginiI M Com QT Final On16march2016Khandaker Sakib Farhad0% (1)
- Terasil STD MethodDocument1 paginăTerasil STD MethodKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terasil STD MethodDocument1 paginăTerasil STD MethodKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Battle Strategy of Israel and the Possible Outcome_compressedDocument2 paginiBattle Strategy of Israel and the Possible Outcome_compressedKhandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Tannic Acid and Metallic Mordants On The DyeingDocument5 paginiEffect of Tannic Acid and Metallic Mordants On The DyeingHëss EmmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consumption For FabricDocument5 paginiConsumption For Fabrickimtienthao_26289Încă nu există evaluări
- NH Desn 1Document96 paginiNH Desn 1Khandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Market Structures ExplainedDocument18 paginiMarket Structures ExplainedAmii RahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research & Development in TextileDocument40 paginiResearch & Development in Textileapi-19978170100% (2)
- Tender Documents For Freight Forwarding, Clearing & Transportation Agent Dated 23.01.14.Document27 paginiTender Documents For Freight Forwarding, Clearing & Transportation Agent Dated 23.01.14.Khandaker Sakib FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrosulfite Types: Technical InformationDocument8 paginiHydrosulfite Types: Technical InformationKushagradhi DebnathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised Products Effective April 2008Document65 paginiRevised Products Effective April 2008EslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assay Ob Borax PDFDocument14 paginiAssay Ob Borax PDFAbram Louies Hanna100% (1)
- MCQ Madness 1 PDFDocument15 paginiMCQ Madness 1 PDFnotabc gamerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compilation of Activity in General Chemistry 1Document12 paginiCompilation of Activity in General Chemistry 1Lalaine ConejosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caustic Soda Data SheetDocument5 paginiCaustic Soda Data SheetKudakwashe Walter MakoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sulfinol ProcessDocument50 paginiSulfinol Processsada sivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determine Amylase Activity Using Amylazyme TabletsDocument4 paginiDetermine Amylase Activity Using Amylazyme TabletsKasper DeflemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prospect and Challenges of Basic Chemicals Industries in BangladeshDocument7 paginiProspect and Challenges of Basic Chemicals Industries in BangladeshAsiful IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Offer #Qu000766: Com/mig/qu000766Document73 paginiOffer #Qu000766: Com/mig/qu000766mohammedshehu100% (2)
- The Pfitzinger Reaction. (Review)Document38 paginiThe Pfitzinger Reaction. (Review)jabberwocky123Încă nu există evaluări
- Nonionic Surfactant Specification for Texas AgenciesDocument3 paginiNonionic Surfactant Specification for Texas AgenciesNana AdomakoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basicity of an AcidThis reaction involves determining the basicity of an acid from a titration experiment. The basicity is found to be 2 from the mole ratioDocument12 paginiBasicity of an AcidThis reaction involves determining the basicity of an acid from a titration experiment. The basicity is found to be 2 from the mole ratioMaku MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Icp Tup Chem Tech Review Acids and BasesDocument7 paginiIcp Tup Chem Tech Review Acids and BasesAimee MangubatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes Salts (Chemistry)Document32 paginiNotes Salts (Chemistry)Darishana100% (1)
- Mcgraw-Hill Series in Chemical Engineering: The Chemical Process IndustriesDocument67 paginiMcgraw-Hill Series in Chemical Engineering: The Chemical Process IndustriesSHASHWA USOPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neutralization Titration IDocument7 paginiNeutralization Titration IJarren BautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sigma CoteDocument2 paginiSigma Coteadamos1945Încă nu există evaluări
- Specimen 2016 QP - Paper 6 CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument12 paginiSpecimen 2016 QP - Paper 6 CIE Chemistry IGCSEEszÎncă nu există evaluări
- Holik Book PagesDocument30 paginiHolik Book PagesKris BillmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Proponent: Plot No. D-2/CH/148, GI DC, Dahej II-392110, Tal-Vagra, Dist - BharuchDocument51 paginiProject Proponent: Plot No. D-2/CH/148, GI DC, Dahej II-392110, Tal-Vagra, Dist - BharuchSaritha NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hull Cell Plating TestsDocument23 paginiHull Cell Plating TestsDavidAlejandroGaona100% (3)
- CL-B0061 (LA) Smooth Strawberry MeringueDocument2 paginiCL-B0061 (LA) Smooth Strawberry MeringueIvica KrsticÎncă nu există evaluări
- 尼斯第八版商品1-34類Document215 pagini尼斯第八版商品1-34類hanlin7Încă nu există evaluări
- 06 Chapter 10Document34 pagini06 Chapter 10M Zia DogarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination of Dimer in Acrylic Acid: Standard Test Methods ForDocument5 paginiDetermination of Dimer in Acrylic Acid: Standard Test Methods ForDeepak D MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Volumetric AnalysisDocument10 paginiA Volumetric AnalysisTDUY059109Încă nu există evaluări
- Plomo 2Document14 paginiPlomo 2Octavio ContrerasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Reactions and EquaDocument10 paginiChemical Reactions and Equas sachinÎncă nu există evaluări
- GS Yuasa Battery Europe Ltd. Safety Data SheetDocument11 paginiGS Yuasa Battery Europe Ltd. Safety Data SheetVioleta MitićÎncă nu există evaluări