Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 1 Waves SPM
Încărcat de
Azwin NuraznizaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 1 Waves SPM
Încărcat de
Azwin NuraznizaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CHAPTER 1 WAVES
Definitions 1. Transverse wave a wave in which the particles in the medium vibrate 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
azwinazniza
perpendicular to the propagation of the wave Longitudinal wave a wave in which the particles in the medium vibrate parallel to the propagation of the waves Amplitude the maximum displacement from the mean position Wavelength horizontal distance between two successive equivalent points on the wave Period time taken to complete one oscillation Frequency number of complete oscillations in one second Refraction a change of direction in the propagation of the waves from one medium to another due to a change of speed. (* shallow/deep) Diffraction spreading out of waves when they move through an obstacle
Frequency increase -> less obvious Wavelength increase -> obvious Small obstacle -> obvious Small/narrow gap -> obvious Wavelength, frequency x tukar (amplitude decreases after diffraction) Interference superposition of two waves originating from two coherent sources Constructive interference occurs when two wave crests or troughs meet (maximum amplitude) Destructive interference occurs when the crest of one wave meets the trough of another wave (resultant amplitude is zero) Coherent souce - waves which have the same frequency, amplitude and are in phase. Monochromatic light light that consists of one wavelength and frequency only Stroboscope- freeze the image of waves (function)
9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14.
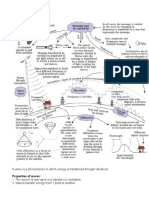
Characteristics question CHARACTERISTICS Built at the bay Retaining wall is built EXPLANATION *Water is calmer at the bay compared to cape *small wave amplitude *to reflect the waves from the shore *reduces direct impact of the waves on the share *reduces soil erosion *pressure increase with depth *less destruction to the wall *reduce energy absorption *to prevent overflow of water *diffraction can occur *energy of the water waves decreases *energy does not dissipate easily *to detect a wide range of wave
Sloping structure of retaining wall Uneven surface of the retaining wall High retaining wall Wall with narrow gaps is built Use signal with high energy (effectiveness of communication system) Use a receiver with a big diameter (effectiveness of communication system) Power of the loud speakers is high The distance between the two speakers must be further apart Speakers arranged side by side Soft boards (dinding dewan) Large diameter of the parabolic disc (satellites) Distance of the signal receinver from the centre of the parabolic disc is equal to to its focal length Microwave Height of the parabolic disc from the ground is high
*To produce a longer and louder sound *less interference
*prevent reflection *prevent reflection *to enable more signals to be transmitted at one time *better eception *parallel signals from the radar system can be reflected and focused on the signal receiver *shorter wavelength *can penetrate the atmosphere easily *prevent the signals from being blocked by obstacles
FORMULA:
V=f
=ax D
:wavelength a: distance between two slits/speakers x:distance between two consecutive fringes/soft and loud sound
ESSAY QUESTIONS
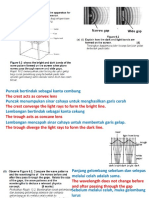
1.Explain how dark and light bands are formed on the screen/explain how patterns are formed on the screen -waves consist of crests and troughs -the crest of the wave acts like a conves lens -the light rays passing through the crest will be converged to form a light band -the trough of the wave acts like a concave lens -the light rays passing through the through will be diverged to form a dark band 2.Explain why the wavefronts in the sea follow the shape of the coastline as the water becomes shallower(refraction) -As the wave move towards the shore, the depth of the sea decreases -Therefore the speed decreases -This causes the waves to refract and bend towards the normal and take the shape of the coastline 3. How does the wall barrier (have narrow gap) would be able to protect the ship? -The waves will be diffracted when it passes through the opening of the wall barrier -After diffraction occurs, the amplitude of the wave decreases hence the energy of the wave decreases
4.Explain why the water at the bay is calmer than the water at the cape -At the bay, water waves undergoes refraction as it travels from steep to shallow region -The divergence of the waves energy at the bay produces waves of small amplitude -The convergence of the waves energy at the cape produces waves of big energy
5.The sound waves from the train can be heard loudly and clearly at night.Explain this situation. -At night, the layers of air close to the ground are cooler than the layers further from the ground. -Cool air is denser than warmer air -Sound travels at a slower speed in cold air -As a result, the sound waves are refracted towards the ground.
6.Explain how interference of sound occurs. -Interference is the superposition of two waves originating from two coherent sources -Loud sound is caused by constructive interference which occurs when both the wave crests or troughs meet. -Soft sound is caused by destructive interference which occurs when the crest of one wave meets the trough of another wave
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Jackson Electrodynamics 3rd Edition SolutionsDocument18 paginiJackson Electrodynamics 3rd Edition SolutionsKadir Simsek50% (2)
- Wave and SoundDocument19 paginiWave and Soundanwar9602020Încă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Coal Power Plant CycleDocument47 paginiUnderstanding Coal Power Plant CycledaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksDe la EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waves and Wave MotionDocument15 paginiWaves and Wave MotionDom Christian Last100% (1)
- SJPO Special Round 2011 Sample PDFDocument10 paginiSJPO Special Round 2011 Sample PDFziwei_from_chinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sound WaveDocument28 paginiSound Wavehhnflaws290% (1)
- Day 7 - 9 Echo Sounder and Speed MeasurementDocument32 paginiDay 7 - 9 Echo Sounder and Speed MeasurementSto Cu100% (8)
- 3.1 Newton's Universal Law of GravitationDocument20 pagini3.1 Newton's Universal Law of GravitationPauling ChiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ocean Wave RefractionDocument5 paginiOcean Wave RefractionSifiso NdabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Form 5 Chapter 1Document39 paginiPhysics Form 5 Chapter 1Leong Laichuo40% (5)
- Daily Events Check With Horary and Birth Chart: Branches of AstrologyDocument18 paginiDaily Events Check With Horary and Birth Chart: Branches of AstrologySudharshan Srinath50% (2)
- Chemistry Paper 1 Topical Unsolved MCQsDocument34 paginiChemistry Paper 1 Topical Unsolved MCQsNobodyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BU3 Acoustics PDFDocument257 paginiBU3 Acoustics PDFeyo rimasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 5 Physic Waves SlideDocument41 paginiForm 5 Physic Waves SlideemeilimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics NotesDocument6 paginiPhysics NotesLegend RR3Încă nu există evaluări
- Sound Propagatio N: Assignment 1Document5 paginiSound Propagatio N: Assignment 1jovelynÎncă nu există evaluări
- ch11 2Document90 paginich11 2tara.jojiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics NotesDocument4 paginiPhysics Notesscott reuvenyyÎncă nu există evaluări
- fIZIK 1Document14 paginifIZIK 1AaronAlwynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waves: Carriers of EnergyDocument5 paginiWaves: Carriers of EnergylittlepenguinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Superposition 2 Updated.Document110 paginiSuperposition 2 Updated.Zerne GrahamÎncă nu există evaluări
- اECHO SOUNDERDocument15 paginiاECHO SOUNDERArwa HusseinÎncă nu există evaluări
- WavesDocument52 paginiWavesapi-508592459100% (1)
- WavesDocument52 paginiWavesapi-245497801Încă nu există evaluări
- Longitudinal Waves Are Waves That Travel Parallel To The Direction of MotionDocument21 paginiLongitudinal Waves Are Waves That Travel Parallel To The Direction of MotionshreyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neets Module 10 SummaryDocument11 paginiNeets Module 10 SummarySigmund VesaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MRSM SBP Bab 6Document79 paginiMRSM SBP Bab 6Muhammad QawiemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essay Waves Esei Gelombang 2018Document35 paginiEssay Waves Esei Gelombang 2018S.NeroshineÎncă nu există evaluări
- WavesDocument6 paginiWavesTai ValiantÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHY 121 7 - Diffraction of WavesDocument11 paginiPHY 121 7 - Diffraction of WavesChristopher NdamboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architectural Acoustics.Document14 paginiArchitectural Acoustics.maniÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Physics 2 Module 3 My AnswersDocument3 paginiGeneral Physics 2 Module 3 My AnswersMatth N. ErejerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Limba Engleza Capitolul 3 Si 4Document7 paginiLimba Engleza Capitolul 3 Si 4DimaNooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject: Physics AS (Unit 2) Topic: Waves: Made By: Moustafa Mohamed Ahmed Ewis Adham Ibrahim Youssef BedairDocument7 paginiSubject: Physics AS (Unit 2) Topic: Waves: Made By: Moustafa Mohamed Ahmed Ewis Adham Ibrahim Youssef BedairAhmed Mohamed EwisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 Exam #3 Study GuideDocument7 pagini2014 Exam #3 Study Guidehairey947594Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is Electromagnetic Wave?Document3 paginiWhat Is Electromagnetic Wave?Lance Aaron LapuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communication Systems/Wave Propagation: Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument6 paginiCommunication Systems/Wave Propagation: Electromagnetic SpectrumFarshad GanjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Utilities 3: Lecture 1 - Waves and Sound WavesDocument120 paginiBuilding Utilities 3: Lecture 1 - Waves and Sound WavesJann BayotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diffraction TextDocument1 paginăDiffraction TextBunty MitraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physic Note Chpter 1Document10 paginiPhysic Note Chpter 1fadzilahvazeerulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waves - Lecture 1Document45 paginiWaves - Lecture 1Hisham MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fysica NOTA 2 PAG: 124 - 150Document4 paginiFysica NOTA 2 PAG: 124 - 150camilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysing Diffraction of WavesDocument20 paginiAnalysing Diffraction of WavesAshley AngÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.5 Diffraction of Waves 2021Document53 pagini5.5 Diffraction of Waves 2021PNAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Print - Sound WavesDocument9 paginiPrint - Sound WavesantonellidejanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ocean Waves: "Like" HTTPS://WWW - Facebook.Com/Cornelloceanography "Follow" @cuoceanographyDocument43 paginiOcean Waves: "Like" HTTPS://WWW - Facebook.Com/Cornelloceanography "Follow" @cuoceanographytrollingandstalkingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thunder and LightningDocument3 paginiThunder and LightningGabriel Cortez MercadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constructive Interference: - Two Waves That Combine To Create A Larger AmplitudeDocument12 paginiConstructive Interference: - Two Waves That Combine To Create A Larger Amplitudeapi-236506403Încă nu există evaluări
- Waves: Ivan L. Saligumba Institute of Education and Teacher TrainingDocument40 paginiWaves: Ivan L. Saligumba Institute of Education and Teacher TrainingGellirose S. Bantayan100% (1)
- Chapter 17 NotesDocument72 paginiChapter 17 Notesapi-30718309Încă nu există evaluări
- Oscillation: Online Learning Resources For Malaysia StudentsDocument0 paginiOscillation: Online Learning Resources For Malaysia StudentsJia HuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waves IiDocument48 paginiWaves IiKisaka GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary Notes - Topic 4 Edexcel Physics GCSEDocument4 paginiSummary Notes - Topic 4 Edexcel Physics GCSEtrical27 tricalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 - Student HandoutDocument19 paginiLecture 1 - Student HandoutJeric LumantasÎncă nu există evaluări
- WavesDocument3 paginiWavesPREM OfFiCiAlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Term Paper TopicsDocument12 paginiTerm Paper TopicsAnuj RautelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary NotesDocument4 paginiSummary Notesspicy chicken sandwichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 2: Sounding: Madam Nazirah Md. TarmiziDocument62 paginiTopic 2: Sounding: Madam Nazirah Md. TarmizihakimiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sound in Water: Water Encyclopedia: Physics and Chemistry, Pp. 569-571Document3 paginiSound in Water: Water Encyclopedia: Physics and Chemistry, Pp. 569-571meliaminorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waves PowerpointDocument68 paginiWaves PowerpointMadana R naikÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 WavesDocument4 pagini4 WavessophiederryÎncă nu există evaluări
- TUGAS07 Pengetahuan Fisik LautDocument7 paginiTUGAS07 Pengetahuan Fisik LautRizaldi CaesarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7021 Chap02Document31 pagini7021 Chap02Gerry RobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 105 10awaves1introductionDocument43 pagini105 10awaves1introductionNguyễn Hoàng ThànhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Things U Should Know About WavesDocument2 paginiThings U Should Know About WavesShahrul AnisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conductor Parameters-SI UnitsDocument17 paginiConductor Parameters-SI UnitsMunesu Innocent Dizamuhupe0% (1)
- Atmospheric AerosolsDocument24 paginiAtmospheric Aerosolsh_guthrieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aashto T 19m-t 19-14Document2 paginiAashto T 19m-t 19-14Ajesh SohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- One Read-S-0039-1685126Document4 paginiOne Read-S-0039-1685126soelmasry6Încă nu există evaluări
- Final ProjectDocument22 paginiFinal ProjectDevil KingÎncă nu există evaluări
- PT FLASH CALCULATION (Using Peng Robinson EOS) : Chemical Engineer's GuideDocument88 paginiPT FLASH CALCULATION (Using Peng Robinson EOS) : Chemical Engineer's GuideDaniel Marcelo Velasquez100% (1)
- Einstein, Perrin, and The Reality of Atoms PDFDocument4 paginiEinstein, Perrin, and The Reality of Atoms PDFDiego PachecoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Press Force SensorDocument4 paginiPress Force SensortivakornÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natural Gas Sweetening by Monoethanolamine ProcessDocument22 paginiNatural Gas Sweetening by Monoethanolamine Processasamad54Încă nu există evaluări
- ENGR451 Notes 1 Winter 2019 PDFDocument158 paginiENGR451 Notes 1 Winter 2019 PDFWeixian LanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esas Ayuda 3Document7 paginiEsas Ayuda 3Friendrich FriedchickenÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Experimental Study of The Orientation Effect On Fatigue Crack Propagation in Rolled AZ31B Magnesium AlloyDocument10 paginiAn Experimental Study of The Orientation Effect On Fatigue Crack Propagation in Rolled AZ31B Magnesium AlloyFrancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Quantum Field Theory Roberto CasalbuoniDocument261 paginiAdvanced Quantum Field Theory Roberto Casalbuoniapi-3797403100% (1)
- Oil Absorption and Surface Area RelationshipDocument2 paginiOil Absorption and Surface Area RelationshipMarjorie Dulay DumolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q13&14Document2 paginiQ13&14Izzah HzmhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer Test ProtocolsDocument9 paginiMethyl Red and Voges-Proskauer Test Protocolsemily zavaleta zavaletaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CORAGUM C-80 179129 Technical SpecificationDocument1 paginăCORAGUM C-80 179129 Technical SpecificationpippoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrophoresis Lecture Ricki PPT 10 (Compatibility Mode)Document9 paginiElectrophoresis Lecture Ricki PPT 10 (Compatibility Mode)lordniklausÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial - 4 and Solution Feb 2 2017 FinalDocument2 paginiTutorial - 4 and Solution Feb 2 2017 FinalRounak MajumdarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active Ingredients in Pain RelieverDocument13 paginiActive Ingredients in Pain RelieverkatrinaarnaizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Information Sheet 6: Revision 2: 2012Document8 paginiTechnical Information Sheet 6: Revision 2: 2012anon_260328012Încă nu există evaluări
- Microencapsulation 1Document25 paginiMicroencapsulation 1Gowtham GloreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Testing of Welded JointsDocument41 paginiMechanical Testing of Welded JointsSanadÎncă nu există evaluări