Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
TCP IP Quick Guide
Încărcat de
Dinh Truong CongDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
TCP IP Quick Guide
Încărcat de
Dinh Truong CongDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
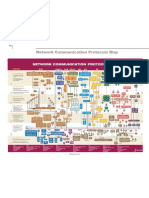
TCP/IP Quick Guide
TCP Services UDP Services IRC Internet Relay Chat DCAP Data Link Switching Client Access Protocol DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol BOOTP Bootstrap Protocol NTP Network Time Protocol TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol ICP Internet Cache Protocol
OSI MODEL
Layer 7: Application Layer
HTTP HyperText Transfer Protocol Gopher TELNET Virtual Terminal
POP3 Post Office Protocol Finger
FTP File Transfer Protocol
SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol IMAP Internet Message Access Protocol
NNTP Network News Transfer Protocol
Defines interface to user processes Provides standardized network services
X Window System X Protocol (X10 X11) CMOT CMIP over TCP/IP
LDAP Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
CLDAP Connectionless LDAP
UDP Encapsulated SNMP SimpleNetwork Mgmt. Protocol v1, v2, v3 RMON I & II Remote Monitoring MIBS
CORBA
IIOP
GIOP
Security
IPX
SLP Service Location Protocol
DNS Domain Name System
AES Advanced Encryption Standard
DES Data Encryption Standard
3DES Triple DES
Layer 6: Presentation Layer
IPSEC
ONC RPC Pemote Procedure Call
Specifies architecture-independent data transfer format Encodes and decodes data; Encrypts and decrypts data; Compresses and decompresses data
LPP Lightweight Presentation Protocol
UDP
TCP
Radius Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service
Kerberos Network Authentication Protocol PPP
TACACS/TACACS+ Terminal Access Controller Access Control System
UDP SLIP
Layer 5: Session Layer
NBSS NetBIOS Session Service ISO TP SMB
NetBEUI
UDP
TCP PPTP Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol L2TP Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol L2F Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol
Frame Relay
Manages user sessions and dialogues Controls establishment and termination of logical links between users
SMB
L2TP
SSHv2 Secure Shell V2 SCPv2 Secure Copy v2
WINS UDP IP
TCP
X.25
NetBIOS
Layer 4: Transport Layer
IPX ISO-DE ISO Development Environment
TCP
GRE Generic Routing Encapsulation
TLS IP in IP SSL IP Encapsulated DIFFSERV Transport Secure Layer in IP Socket Layer Security
NetBIOS DGM IPX IP
Provides reliable and sequential end-to-end packet delivery Provides connectionless oriented packet delivery
TCP Transmission Control Protocol From TCP
UDP User Datagram Protocol
From UDP
Routing Protocol UDP Based RUDP Reliable UDP Cisco HSRP Hot Standby Router RIP Routing Information Protocol
Routing Protocol-TCP Based
Cisco RSRB BGP Border Gateway Remote Source Route Bridging Protocol Protocol Cisco STUN Serial Tunneling of SDLC Header Cisco XOT X.25 Over TCP
Multicast Routing Protocol-TCP Based MSDP Multicast Source Discovery Protocol MBGP Multi-Protocol BGP From TCP Multicast Routing Protocols-IP Based MOSPF Mulitcast OSPF DVMRP Distance Vector Mulitcast Routing Protocol PGM Pragamatic General Mulitcast Protocol PIM-SM Protocol Independant Mulitcast-Sparse Mode PIM-DM Protocol Independant Mulitcast-Dense Mode IGMP Internet Group Management Protocol IP / IPv6 Internet Protocol
IRDP
ICMP Router Discovery Protocol
ICMP/ICMPv6
Internet Control Message Protocol
GDP Gateway Discovery Protocol
Layer 3: Network Layer
Routing Protocol-IP Based EGP NHRP GGP Exterior Gateway Next Hop Gateway-to-Gateway Protocol Resolution Protocol Protocol OSPF RSVP VRRP Open Shortest Resource Reservation Virtual Router Path First Protocol Redundancy Protocol Cisco Protocols IGRP Interior Gateway Routing Protocol E-IGRP Enhanced IGRP
IPSEC Internet IP Security AH Authentication Header ESP Encapsulation Security Payload IP Comp IP Payload Compression IKE Internet Key Exchange
Routes packets according to unigue network addresses
SLIP Serial Line IP
Mobile IP Mobile IPv6
The MPLS signaling protocols are either TCP or UDP based
IPCP/IPv6CP
Layer 2: Data Link Layer
SLE Serial Like Encapsulation
CDP Cisco Discovery Protocol
XTP Xpress Transfer Protocol
ARP SLARP Address Resolution Serial Link ARP Protocol IARP Inverse ARP RARP Reverse ARP
IP Control Protocol IPv6 Control Protocol
CR-LDP LDP TDP Constraint Label Tag Based Distribution Distribution LDP Protocol Protocol
RSVP-TE RSVP Traffic Extension
Defines procedures for operating the communication link Provides framing and sequencing
PPP
ESRP Extreme Standby Router Protocol
CGMP Cisco Group Management Protocol
MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching
Ethernet
Internetwork
Ethernet
IEEE 802.3 CSMA/CD Media Access Control
LAN
Wireless LAN
IEEE 802.11 WLAN Direct Sequence
SNAP Sub Network Access Protocol
802.2 Logical Link Control
Type 1 Connectionless Service Type 2 Connection Service
SMDS Switched Multi-Megabit Data Service
ISO HDLC IBM SDLC High-level Synchronous Data Link Protocol Data Link Protocol PPP Point-to-Point Protocol NCP LCP Link Control Network Control Protocols Protocols ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode Layer
Type 3 ACK w/Connectionless Service
Frame Relay Link Access Procedure for Frame Mode Bearer Services (LAPF)
PPP
IEEE 802.5 Token Passing Ring Media Access Control
FDDI Token Passing Ring Media Access Control
IEEE 802.3 MAC
Layer 1: Physical Layer
FDDI
IEEE 802.3 10 Mbps Ethernet IEEE 802.3u 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Ethernet IEEE 802.11a 54 Mbps IEEE 802.11b 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbps IEEE 802.11g 54 Mbps IEEE 802.11n 100 Mbps - 200 Mbps
MAN
XAUI DWDM
Token Ring
Fiber Optic Shielded Twisted Pair Unshielded Twisted Pair
Defines physical means of sending data over network devices
FDDI Fiber Optic
IEEE 80.16 WiMAX
IEEE 802.3ae 10 Gigabit
DOCSIS Data Over Cable Systems Interface Specification
DSL Digital Subscribe Line
ISDN Q.921 LAPD
SONET/SDH
10GBase-R (LAN) 10GBase-W (WAN) 10GBase-X (WWDM)
WAN
OC-3/STM-1 OC-12/STM-3 OC-48/STM-16 OC-192/STM-64 9.953 Gbps 155.52 Mbps 622.08 Mbps 2.488 Gbps
Javvin Technologies Inc. All rights reserved.
www.javvin.com
IP: Internet Protocol
IPv4: Internet Protocol version 4
IPv4 is dened in IETF RFC 791.
IPv4 Address Format
Extended-Network-Prex 32bit Total length Flags Fragment offset 8 bits 172 . Network-Prex 8 bits 16 . Subnet-Number 8 bits 122 . Host-Number 8 bits 204
IPv4 Packet Format
4 Version 8 IHL 16 Type of service
Identication Time to live Protocol
Header checksum
Source address Destination address Option + Padding Data Version the version of IP (4 for IPv4). IP Header Length (IHL) number of 32-bit words that points to the beginning of the data. It is between 5 (20bytes) to 15 (60 bytes). Type-of-Service indicates the quality of service desired. Type of service Differentiated Services Precedence (000 111) 000 D (1 = minimize delay) 0 T (1 = maximize throughout) 0 R (1 = maximize reliability) 0 C (1 = minimize cost) 1 = ENC capabl x (reserved and set to 0) 1 = congestion experienced Total Length the length of the entire IP packet in bytes. Maximum length is 65,535. Identication an integer that identies the current datagram. Flags a 3-bit eld of which the two low-order bits control fragmentation. X (reserved and set to 0) D (1 = dont fragment) M (1 = more fragment) Fragment Offset indicates the position of the fragments data relative to the beginning of the data in the original datagram. Time-to-Live a counter that gradually decrements down to zero, at which point the datagram is discarded. Protocol - indicates which upper-layer protocol receives incoming packets after IP processing is complete. Some sample protocols: 1 ICMP 2 IGMP 6 TCP 9 IGRP 17 UDP 47 GRE 50 ESP 51 AH 57 SKIP 88 EIGRP 89 OSPF 115 L2TP Header Checksum ensures IP header integrity. Source Address 32 bits eld species the sending node. Bits Class A Class B Class C 31 0 10 110
IPv4 Address Classes
24 Network Network Network 16 Host Host Host 8 0
CIDR
CIDR: Classless and Subnet Address Extensions and Supernetting 31 Network /nn CIDR prex length /1 /2 /3 /4 /5 /6 /7 /8 /9 /10 Dotted Decimal Netmask 128.0.0.0 192.0.0.0 224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 248.0.0.0 252.0.0.0 254.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 255.128.0.0 255.192.0.0 255.224.0.0 255.240.0.0 255.248.0.0 255.252.0.0 255.254.0.0 255.255.0.0 255.255.128.0 255.255.192.0 255.255.224.0 255.255.240.0 255.255.248.0 255.255.252.0 255.255.254.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.128 255.255.255.192 255.255.255.224 255.255.255.240 255.255.255.248 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.254 255.255.255.255 Number of Classfull Networks 128 As 64 As 32 As 16 As 8 As 4 As 2 As 1 A or 256 Bs 128 Bs 64 Bs 32 Bs 16 Bs 8 Bs 4 Bs 2 Bs 1 B or 256 Cs 128 Cs 64 Cs 32 Cs 16 Cs 8 Cs 4 Cs 2 Cs 1C 1/2 C 1/4 C 1/8 C 1/16 C 1/32 C 1/64 C 1/128 C 1/256 C Number of Usable IPs 2,147,483,646 1,073,741,822 536,870,910 268,435,454 134,217,726 67,108,862 33,554,430 16,777,214 8,388,606 4,194,302 2,097,150 1,048,574 524,286 262,142 131,070 65,534 32,766 16,382 8,190 4,094 2,046 1,022 510 254 126 62 30 14 6 2 0 Host 0
Address Class Class A Class B Class C Class D Class E
# Network Bits 8 bits 16 bits 24 bits
# Hosts Bits 24 bits 16 bits 8 bits
Decimal Address Range 1-126 128-191 192-223 224 - 239 240 - 255
Number of Usable IP 16,777,216 (1 A) 1,048,544 (16 B) 65,534 (256 C)
Multicast Experimental
Destination Address 32 bits eld species the receiving node. Options allows IP to support various options. 0 End of option list 1 No operation (PAD) 7 Record route 68 timestamp 131 Loose source route 137 Strict source route Data contains upper-layer information.
/11 /12 /13 /14 /15
IPv6: Internet Protocol version 6
IPv6 is dened in IETF RFC 1883 and RFC 2460.
/16 /17 /18 16bits : aaaa : 16bits aaaa /19 /20 /21 /22 /23 /24 /25 Interface ID (64 bits) /26 /27 /28 Interface ID (64 bits) /29 /30 Interface ID (64 bits) /31 /32
IPv6 Address Format
16bits 16bits 16bits : aaaa : 16bits aaaa : 16bits aaaa : 16bits aaaa
IPv6 Packet Format
4 Version Trafc Class Payload length 12 16 24 Flow label Next header type Hop limit 32 bit
aaaa : aaaa
IPv6 Address Types
IPv6 address is classied in three types: Unicast, Multicast and Anycast. Unicast Address: applied to one network interface. The common global unicast address divisions: Global Routing Prex (N bits) Subnet ID (64-N bits)
Source address (128 bits) Destination address (128 bits) Next header Extension Header Information (optional and variable length) Data (Variable Length) Version Internet Protocol Version number (IPv6 is 6). Trafc class enables a source to identify the desired delivery priority of the packets. Flow label used by a source to label packets for special handling by the IPv6 router. Payload length the length of the data portion of the packet. Next header identies the type of header immediately following the IPv6 header. It is similar to the protocol led in IPv4. Hop limit species the maximum number of routers (hops) through which a packet can traverse before discarded. Source address 128-bit address of the originator of the packet. Destination address 128-bit address of the intended recipient of the packet. Extension Header Information an optional eld (not included in the basic header) with variable length. Routing Fragmentation Authentication Encapsulation Hop-by-Hop Option Destination Options Javvin Technologies Inc. All rights reserved.
Link-local unicast address divisions: 1111111010 (10 bits) 0x000 (54bits)
Site-local unicast address divisions: 1111111011 (10 bits) 0x00 Site Level Aggregation
(Interface ID is based on hardware MAC address.) Multicast Address: applied for multiple network interfaces, and communication is conducted with all hosts with the same address. 0xFF (8 bits) Flag (4 bits) Scope (4 bits) Group ID (112 bits)
IPv4-mapped IPv6 address: 0x000 (80 bits) 0xFFFF (16 bits) IPv4 Address (32 bits)
Anycast Address: applied for multiple network interfaces, but actual communication is conducted with one of them. It has the same format as the Unicast address.
IPv4-competible IPv6 address: 0x000 (80 bits) 0x0000 (16 bits) IPv4 Address (32 bits)
www.javvin.com
IPv4 vs. IPv6
Subjects Address Space Conguration Broadcast / Multicast Anycast support Routing efciency Network Conguration QoS support Security Mobility IPv4 4 Billion Addresses Manual or use DHCP Uses both Not part of the original protocol Need to process Option and Checksum elds by every router Mostly manual and labor intensive ToS using DIFFServ Uses IPsec for Data packet protection Uses Mobile IPv4 IPv6 3.4 x 1038 addresses Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) with or without DHCP No broadcast and has different forms of multicast Explicit support of anycast No checksum; Extended header for options. Facilitate the re-numbering of hosts and routers Flow classes and ow labels IPsec becomes the key technology to protect data and control packets Mobile IPv6 provides fast handover, better router optimization and hierarchical mobility IPv6 Advantages 79 Octillion times the IPv4 address space Lower Operation Expenses and reduce error Better bandwidth efciency Allows new applications in mobility, data center Improved support for extensions and options and better routing efciency. Lower operation expenses and facilitate migration More Granular control of QoS Unied framework for security and more secure computing environment Better efciency and scalability; Work with latest 3G mobile technologies and beyond.
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
TCP is dened by IETF RFC 793.
TCP/IP Utilities
ICMP
ICMP: Internet Message Control Protocol. ICMP for IPv4 is dened in IETF RFC 792 and ICMP for IPv6 is dened in IETF RFC 2463.
TCPDUMP
tcpdump dump trafc on a network tcpdump [-aenStvx] [-c count] [-F le] [-i int] [-r le] [-s snaplen] [-w le] [lter_expression]
TCP Header Format
16 Source port Sequence number Acknowledgement number Offset Rsved U A P R S F Window Urgent pointer 32 bit Destination port
ICMP Header Format. 8 Type Indentier Address mask Type 0 Echo Reply 3 Destination Unreachable Code 0 0 Net Unreachable 1 Host Unreachable 2 Protocol Unreachable 3 Port Unreachable 4 Fragmentation Needed & DF Set 5 Source Route Failed 6 Destination Network Unknown 7 Destination Host Unknown 8 Source Host Isolated 9 Network Administratively Prohibited 10 Host Administratively Prohibited 11 Network Unreachable for TOS 12 Host Unreachable for TOS 13 Communication Administratively Prohibited 4 Source Quench 5 Redirect 0 0 Redirect Datagram for the Network 1 Redirect Datagram for the Host 2 Redirect Datagram for the TOS & Network 3 Redirect Datagram for the TOS & Host 8 Echo 9 Router Advertisement 10 Router Selection 0 0 0 0 Time to Live exceeded in Transit 1 Fragment Reassembly Time Exceeded 0 0 Pointer indicates the error 1 Missing a Required Option 2 Bad Length 13 Timestamp 14 Timestamp Reply 15 Information Request 16 Information Reply 17 Address Mask Request 18 Address Mask Reply 30 Traceroute 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Code 16 Checksum Sequence number 32 bit
Checksum Option + Padding Data
Source port Identies points at which upper-layer source process receives TCP services. Destination port Identies points at which upper-layer Destination process receives TCP services. Sequence number Species the number assigned to the rst byte of data in the current message. Acknowledgment number Contains the sequence number of the next byte of data the sender to receive. Offset Indicates where the data begins. Reserved Reserved for future use. Must be zero. Control bits (Flags) Carry a variety of control information. The control bits may be: U (URG) Urgent pointer eld signicant. A (ACK) Acknowledgment eld signicant. P (PSH) Push function. R (RST) Reset the connection. S (SYN) Synchronize sequence numbers. F (FIN) No more data from sender. Window Species the size of the senders receive window. Checksum Indicates whether the header was damaged in transit. Urgent Pointer Points to the rst urgent data byte in the packet. Option + Padding Species various TCP options. 0 End of Option List 1 No operation (pad) 2 Maximum segment size 3 window scale 4 Selective ACK ok 8 Timestamp Data contains upper-layer information.
-a Convert network and broadcast addresses to names -c Exit after receiving count packets -F Filter expression in le -i Listen on interface -n Dont convert IP addresses to names -r Read packets from le -s Get snaplen bytes from each packet -t Dont print timestamp -v Verbose mode -w Write packets to le -x Display in hex -X Display in hex and ASCII lter_expression Selects which packets will be dumped.
PING
ping - send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to network hosts ping [ -LRUbdfnqrvVaAB] [ -c count] [ -i interval] [ -l preload] [ -p pattern] [ -s packetsize] [ -t ttl] [ -w deadline] [ -F owlabel] [ -I interface] [ -M hint] [ -Q tos] [ -S sndbuf] [ -T timestamp option] [ -W timeout] [ hop ...] destination -a Audible ping. -A Adaptive ping. -b Allow pinging a broadcast address. -B Do not allow ping to change source address. -c count Stop after sending count ECHO_REQUEST packets. -d Set the SO_DEBUG option on the socket being used. -F ow label Allocate 20 bits ow label on echo request packets (Only ping6) -f Flood ping. -i interval Wait interval seconds between sending each packet. -I interface address Set source address to specied interface address. -l preload Sends [preload] packets not waiting for reply. -L Suppress loopback of multicast packets. -n Numeric output only. -p pattern Specify (up to 16) ``pad bytes to ll out the out packet. -Q tos Set Quality of Service -related bits in ICMP datagrams. -q Quiet output. -R Record route. -r Bypass routing tables and send to a host on an attached interface. -s packetsize Specify the number of data bytes to be sent. -S sndbuf Set socket sndbuf. -t ttl Set the IP Time to Live. -T timestamp option Set special IP timestamp options -M hint Select Path MTU Discovery strategy. -U Print full user-to-user latency. -v Verbose output. -V Show version and exit. -w deadline Specify a timeout (seconds) before ping exits. -W timeout Time to wait for a response (seconds).
UDP: User Datagram Protocol
UDP is dened by IETF RFC 768.
11 Time Exceeded
12 Parameter Problem
UDP Header Format
16 Source port Length Data Source port An optional eld indicates the port of the sending process. Destination port Identies points at which upper-layer Destination process receives UDP services. Length The length in octets of the user datagram, including the header and the data (Minimum is 8). Checksum -- Indicates whether the header was damaged in transit. Data Contains upper-level information. Javvin Technologies Inc. All rights reserved. Destination port Checksum 32 bit
www.javvin.com
The Mostly Used TCP/UDP Port Numbers
Port No. 1 2 3 7 13 19 20 21 22 23 25 37 39 42 43 49 53 67 68 69 70 79 80 88 101 102 107 110 111 113 117 118 119 123 135 137 138 139 143 158 161 162 170 179 194 213 389 401 443 445 464 500 513 513 514 514 515 517 Protocol TCP TCP/UDP TCP/UDP TCP/UDP TCP/UDP TCP/UDP TCP TCP TCP TCP TCP TCP/UDP UDP TCP/UDP TCP UDP TCP/UDP UDP UDP UDP TCP TCP/UDP TCP/UDP TCP/UDP TCP TCP TCP TCP TCP/UDP TCP TCP TCP TCP UDP TCP/UDP TCP/UDP UDP TCP TCP TCP UDP UDP TCP TCP TCP UDP TCP TCP/UDP TCP/UDP TCP/UDP TCP/UDP UDP TCP UDP TCP UDP TCP UDP Service Name tcpmux compressnet compressnet echo daytime chargen ftp-data ftp ssh telnet smtp Time RLP nameserver nicname TACACS domain bootps bootps TFTP gopher nger http kerberos hostname iso-tsap rtelnet pop3 sunrpc Auth uucp-path sqlserv nntp ntp epmap netbios-ns netbios-dgm netbios-ssn imap pcmail-srv snmp snmptrap Print-srv BGP irc ipx ldap UPS https CIFS kpasswd isakmp login who cmd syslog printer tals spooler Listens for incoming connections Establishes TCP Connection Copyright 2005 Javvin Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. whod shell ike MCom loc-srv nbname nbdatagram nbsession imap4 repository snmp snmp-trap usenet postofce rpcbind portmap ident tap www, http krb5 hostnames DNS dhcps dhcpc resource name whois mail ttytst source Aliases Comment TCP Port Service Multiplexer Management Utility Compression Process Echo Daytime Character generator File Transfer FTP Control SSH remote login protocol Telnet Simple Mail Transfer Time Resource Location Protocol Host Name Server Who Is TACACS: Login Host Protocol Domain Name Server Bootstrap Protocol Server Bootstrap Protocol Client Trivial File Transfer Protocol Gopher Finger World Wide Web Kerberos NIC Host Name Server ISO-TSAP Class 0 Remote Telnet Service Post Ofce Protocol - Version 3 SUN Remote Procedure Call Authentication Sevice UUCP Path Service SQL Services Network News Transfer Protocol Network Time Protocol DCE endpoint resolution NETBIOS Name Service NETBIOS Datagram Service NETBIOS Session Service Internet Message Access Protocol PC Mail Server SNMP SNMP TRAP Network PostScript Border Gateway Protocol Internet Relay Chat Protocol IPX over IP Lightweight Directory Access Protocol Uninterruptible Power Supply http protocol over TLS/SSL Microsoft-ds (CIFS) Kerberos (v5) Internet Key Exchange (IPSec) Remote Login Database of whos logged on, average load Automatic Authentication Port No. 520 520 521 525 526 530 531 532 533 540 543 544 550 554 556 560 561 636 749 750 1080 1812 1813 Protocol TCP UDP UDP UDP TCP TCP/UDP TCP TCP UDP TCP TCP TCP UDP UDP TCP UDP UDP TCP TCP/UDP UDP TCP/UDP TCP TCP Service Name efs Routing Routing Timed Tempo Courier conference netnews Netwall Uucp Klogin Kshell new-rwho rtsp remotefs rmonitor monitor Ldaps kerberos-adm Kerberos-iv socks RADIUS RADIUS sldap LDAP over TLS/SSL Kerberos administration Kerberos version IV socks RADIUS RADIUS accounting rfs rfs_server rmonitord krcmd new-who uucpd router routed router routed timeserver newdate rpc chat readnews Aliases Comment Extended File Name Server RIPv.1, RIPv.2 RIPng Timeserver Newdate RPC IRC Chat Readnews For emergency broadcasts Uucpd Kerberos login Kerberos remote shell New-who Real Time Stream Control Protocol Rfs Server Rmonitor
TCP/UDP Ports
Process X ... Process Y Processes Sockets IP Addresses
Port N ... UDP datagrams ... Port M ... TCP/UDP TCP/UDP TCP connection IP IP unreliable IP datagrams
Host A
Host B
Well Known Ports: from 0 through 1023 Registered Ports: from 1024 through 49151 Dynamic and/or Private Ports: from 49152 through 65535
ISBN 0-9740945-4-4
Related Products: Network Communication Protocol Map Network Protocols Handbook Packet Analyzer
To order Javvin products: Javvin Technologies, Inc. 13485 Old Oak Way Saratoga CA 95070 USA www.javvin.com help@javvin.com 1-408-872-3881
Javvin Technologies Inc. All rights reserved.
www.javvin.com
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Ethernet Quick Guide SecuredDocument4 paginiEthernet Quick Guide SecuredDương Ngọc Sơn100% (1)
- Poster - RADCOM - ProtocolDocument1 paginăPoster - RADCOM - ProtocolSang Tae JoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProtocolsDocument1 paginăProtocolsJorge LangleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protocols For Print5Document1 paginăProtocols For Print5gynaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World of Protocols - Todos (Quase) Protocolos Do MundoDocument1 paginăThe World of Protocols - Todos (Quase) Protocolos Do Mundosaulo-95100% (1)
- Netwoking ProtocolsDocument1 paginăNetwoking ProtocolsOmar AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- VOIP SecureDocument6 paginiVOIP Securedeadpoint123Încă nu există evaluări
- VMware - A Guide for New Admins - CLI: VMware Admin Series, #2De la EverandVMware - A Guide for New Admins - CLI: VMware Admin Series, #2Încă nu există evaluări
- TCP/IPDocument286 paginiTCP/IPbobdxcool100% (12)
- OSI Layers Model Network AssociatesDocument1 paginăOSI Layers Model Network Associatesacademy100% (15)
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) SecurityDe la EverandVoice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) SecurityÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Software Defined Networking (SDN) Is Going To Change Your World Forever: The Revolution In Network Design And How It Affects YouDe la EverandHow Software Defined Networking (SDN) Is Going To Change Your World Forever: The Revolution In Network Design And How It Affects YouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Windows Server 2012 Unified Remote Access Planning and DeploymentDe la EverandWindows Server 2012 Unified Remote Access Planning and DeploymentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementing 802.11, 802.16, and 802.20 Wireless Networks: Planning, Troubleshooting, and OperationsDe la EverandImplementing 802.11, 802.16, and 802.20 Wireless Networks: Planning, Troubleshooting, and OperationsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- SpamAssassin: A practical guide to integration and configurationDe la EverandSpamAssassin: A practical guide to integration and configurationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireshark Basics Self StudyDocument51 paginiWireshark Basics Self StudymzyptÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nmap in the Enterprise: Your Guide to Network ScanningDe la EverandNmap in the Enterprise: Your Guide to Network ScanningÎncă nu există evaluări
- VMware Certified Professional 6 Exam Guide (Exam #2V0-642): Comprehensive guide right from basics to advanced VMware Network Virtualization concepts (English Edition)De la EverandVMware Certified Professional 6 Exam Guide (Exam #2V0-642): Comprehensive guide right from basics to advanced VMware Network Virtualization concepts (English Edition)Încă nu există evaluări
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager 8: Expert Administration CookbookDe la EverandCisco Unified Communications Manager 8: Expert Administration CookbookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Windows PowerShell for .NET Developers - Second EditionDe la EverandWindows PowerShell for .NET Developers - Second EditionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- SIP Extensions For The IP Multimedia Subsystem A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDe la EverandSIP Extensions For The IP Multimedia Subsystem A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethernet Quick GuideDocument4 paginiEthernet Quick GuideTelekom FilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networking Fundamentals: Develop the networking skills required to pass the Microsoft MTA Networking Fundamentals Exam 98-366De la EverandNetworking Fundamentals: Develop the networking skills required to pass the Microsoft MTA Networking Fundamentals Exam 98-366Încă nu există evaluări
- IPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet v1.3 PDFDocument1 paginăIPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet v1.3 PDFIsaque ProfetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Versatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSDe la EverandVersatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Routing: Algorithms, Protocols, and ArchitecturesDe la EverandNetwork Routing: Algorithms, Protocols, and ArchitecturesÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPv6 Tech MapDocument1 paginăIPv6 Tech Map장운호Încă nu există evaluări
- WireShark Complete Users GuideDocument223 paginiWireShark Complete Users GuideSpyDr ByTe100% (3)
- Wireshark TutorialDocument24 paginiWireshark TutorialAbdullah M. Saleh50% (2)
- Network Poster HD 2009Document1 paginăNetwork Poster HD 2009Tito Ramirez100% (1)
- Protocol PosterDocument1 paginăProtocol Posterapi-3806249100% (4)
- Mindmap OSPFDocument1 paginăMindmap OSPFmohanraj_ponnusamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCP/IPDocument6 paginiTCP/IPJennifer100% (5)
- TCP-IP Unleashed, Third EditionDocument1.117 paginiTCP-IP Unleashed, Third Editiongopi_merugu100% (4)
- IOS Interior Routing ProtocolsDocument1 paginăIOS Interior Routing ProtocolsPotosi LoleteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Troubleshooting With Wireshark PDFDocument450 paginiTroubleshooting With Wireshark PDFMeliko ian100% (6)
- VoIP and H.323Document38 paginiVoIP and H.323Khiz JabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SkyEdge II ExtendDocument2 paginiSkyEdge II ExtendkjingarÎncă nu există evaluări
- By - Megha Thirki Aditya Sy BSC ItDocument30 paginiBy - Megha Thirki Aditya Sy BSC Itmegha thirkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CST7206-wk02 SLIDESDocument51 paginiCST7206-wk02 SLIDESSaifÎncă nu există evaluări
- SURPASS+HiT+7070 +presentation 031114Document80 paginiSURPASS+HiT+7070 +presentation 031114dogar99pk83% (6)
- PRTG Report 96693 - Report - (2019-09-25 00-00 - 2019-09-28 00-00) UTCDocument9 paginiPRTG Report 96693 - Report - (2019-09-25 00-00 - 2019-09-28 00-00) UTCHarizi BassemÎncă nu există evaluări
- ulsSysSpecRel2 1 2Ed01It01Document202 paginiulsSysSpecRel2 1 2Ed01It01mandar LawandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 3.0 Network ManagementDocument70 paginiTopic 3.0 Network Managementabinissri rajamuniswaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quidway CX200D Metro Services Platform Product SpecificationDocument4 paginiQuidway CX200D Metro Services Platform Product Specificationneerajkamra07Încă nu există evaluări
- Bootp and DHCPDocument3 paginiBootp and DHCPankitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Date Version Description Drafted byDocument9 paginiDate Version Description Drafted bySamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- KBiVMS Client User Manual 20170701Document245 paginiKBiVMS Client User Manual 20170701AlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Basic HTTP Session - HTTP - MDNDocument4 paginiA Basic HTTP Session - HTTP - MDNintel4winÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methodology For Firewall Penetration and PrecautionDocument9 paginiMethodology For Firewall Penetration and PrecautionLofty N AmahÎncă nu există evaluări
- List ExampleDocument2 paginiList ExamplejoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature Review Asterisk - EditedDocument17 paginiLiterature Review Asterisk - EditedMuhammad JunaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Video Conferencing Systems Cisco Telepresence 1700 Cts 1700 k9 RFDocument6 pagini1 Video Conferencing Systems Cisco Telepresence 1700 Cts 1700 k9 RFjuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding BGP Path Selection - Technical Documentation - Support - Juniper NetworksDocument3 paginiUnderstanding BGP Path Selection - Technical Documentation - Support - Juniper NetworksManoj Kumar PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCSP RDL 6000 Mod 2 ENB Overview Config R1.3.2 V1.3Document64 paginiRCSP RDL 6000 Mod 2 ENB Overview Config R1.3.2 V1.3Tommy AsselinÎncă nu există evaluări
- VMware-NSX-VSphere Content Pack DescriptionDocument12 paginiVMware-NSX-VSphere Content Pack DescriptionCalin Damian TanaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- PMP100,400 PTP 100,200 SolutionsUserGuideIssue1Document534 paginiPMP100,400 PTP 100,200 SolutionsUserGuideIssue1MiguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- BRKETI-2003 - Understanding Multicluster Kubernetes Connectivity OptionsDocument73 paginiBRKETI-2003 - Understanding Multicluster Kubernetes Connectivity OptionsmorpheusnaakÎncă nu există evaluări
- MOXA Industrial Secure Router Installation GuideDocument18 paginiMOXA Industrial Secure Router Installation GuideguguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rfc6349 WP Tfs TM AeDocument8 paginiRfc6349 WP Tfs TM AecpeanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- VoIP Performance Management and OptimizationDocument49 paginiVoIP Performance Management and OptimizationVanioRamos100% (1)
- JBoss AMQ 7 Deep DiveDocument35 paginiJBoss AMQ 7 Deep DiveJohn ArcherÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODUL VOIP 2 ROUTER (AutoRecovered)Document4 paginiMODUL VOIP 2 ROUTER (AutoRecovered)RuslanUBhel'zÎncă nu există evaluări
- Remote Connection Data SheetDocument7 paginiRemote Connection Data SheetJulio CubillasÎncă nu există evaluări
- E45 User Manual For UT300R2UDocument40 paginiE45 User Manual For UT300R2UDhanya VancheeswaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9Ch NMEA (Serial) Ethernet GatewayDocument16 pagini9Ch NMEA (Serial) Ethernet GatewayEvgeny YudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nor Azimah Khalid FSKM, Uitm Shah AlamDocument39 paginiNor Azimah Khalid FSKM, Uitm Shah AlamNOl ShAnahÎncă nu există evaluări