Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
The New Generation Computing
Încărcat de
anon_958066741Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
The New Generation Computing
Încărcat de
anon_958066741Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
The new generation computing: Quantum Computing
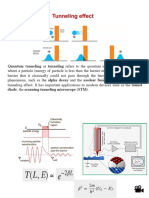
With the invention of computers the processing power has far exceeded the limits of human brain. When computers where invented way back in twentieth century none imagined that a body with transistors embedded on silicon chips could do wonders like a human nor they could act like human. But its a reality. Not surprisingly major concern of research in this field is to improve its performance to ever time highest, i.e. in terms of its speed and memeory.One of the major breakthrough in research was to out leash the power of Quantums in digital technology. We can see in detail about a Quantum Computer through various questions. What is Quantum? The fundamental unit of quantum information is called a quantum bit, or qubit. A qubit is a bit of information represented by a quantum particle, such as the spin of an electron, a property that can be imagined as the spin of a top with its axis pointing either up or down. The up or down spin can correspond to a 0 or 1. But the electron can also be placed in a superposition of states, in which it is both up and down, a 0 and a 1, at the same time. In this situation, an atom or electron or photon takes on strange properties. It can be in two places at once, for example. It behaves in some ways like a wave. But these properties are instantly changed when it interacts with something else, such as when somebody observes it. That is, any two-state system can represent a qubit. This is the difference between a classical and a quantum computer, In an ordinary computer, information is represented in bits, each of which is either a zero or a one. But in a quantum computer, an individual particle can essentially represent a zero and a one at the same time. Making such particles work together, certain kinds of calculations could be done with blazing speed. Which theoretically allows quantum computers to be much more efficient at solving certain types of problems. How do quantum computers work? The exact physical mechanism at work within the quantum computer is somewhat theoretically complex and intuitively disturbing. So to make it simple to understand we will deal only with peripheral ideas of quantum computing.As we have seen in the definition in a quantum computer, an individual particle can essentially represent a zero and a one at the same time. For example If the qubit is in a superposition of the 1 state and the 0 state, and it performed an calculation with another qubit in the same superposition, then one calculation actually obtains 4 results: a 1/1 result, a 1/0 result, a 0/1 result, and a 0/0 result. This is a result of the mathematics applied to a quantum system when in a state of decoherence, which lasts while it is in a superposition of states until it collapses down into one state. The ability of a quantum computer to perform multiple computations in parallel is called quantum parallelism Such a , a quantum computer would be able to perform calculations on a far greater order of magnitude
than traditional computers ... a concept which has serious concerns and applications in the realm of cryptography & encryption. Some fear that a successful & practical quantum computer would devastate the world's financial system by ripping through their computer security encryptions, which are based on factoring large numbers that literally cannot be cracked by traditional computers within the life span of the universe. A quantum computer, on the other hand, could factor the numbers in a reasonable period of time.
Bottleneck in Quantum computing The quantum computer's main drawback is the same as its strength: quantum decoherence. The qubit calculations are performed while the quantum wave function is in a state of superposition between states, which is what allows it to perform the calculations using both 1 & 0 states simultaneously. But this years Nobel Prize has brought in a sigh of relief to this issue. Frenchman Serge Haroche and American David Wineland (both 68) opened the door to new experiments in quantum physics by showing how to observe individual quantum particles while preserving their quantum properties. Working separately, the two scientists developed ingenious laboratory methods that allowed them to manage and measure and control fragile quantum states, said the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. Their ground-breaking methods have enabled this field of research to take the very first steps towards building a new type of superfast computer based on quantum physics, said the academy. The research has also led to the construction of extremely precise clocks that could become the future basis for a new standard of time.
To summarize Quantum computers could radically change peoples lives in the way that classical computers did last century, but a full-scale quantum computer is still decades away, but not too far.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Quantum ComputingDocument26 paginiQuantum ComputingDonald Cade100% (3)
- Quantum Field TheoryDocument16 paginiQuantum Field Theoryrr1819100% (1)
- A K JhaDocument16 paginiA K JhaVirat RohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICT PresentationDocument27 paginiICT PresentationMahleeza NisarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum - Computing (Aditya Raj)Document24 paginiQuantum - Computing (Aditya Raj)Aditya RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Physical Property Interaction QuantizationDocument9 paginiPhysics Physical Property Interaction QuantizationMohammed Abdul RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSE Quantum Computing ReportDocument31 paginiCSE Quantum Computing ReportUtkarshPrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Report On Quantum Computing PDFDocument8 paginiA Report On Quantum Computing PDFVisweswara Rao YedureswarapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Mechanics - BlokinstsevDocument548 paginiQuantum Mechanics - BlokinstsevJulian CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Quantum ComputingDocument20 paginiOn Quantum ComputingAvi KhuranaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum ComputingDocument29 paginiQuantum ComputingVenu PinniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Quantum Computer Technology: Grover's Algorithm Shor's AlgorithmDocument4 paginiIntroduction To Quantum Computer Technology: Grover's Algorithm Shor's AlgorithmsjparidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assembly Languages FinalDocument16 paginiAssembly Languages Finalapi-537257222Încă nu există evaluări
- (FS PPT) (Quantum Computation)Document22 pagini(FS PPT) (Quantum Computation)21IT117 PATEL RAHI PINKALKUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntroductionDocument18 paginiIntroductionSatyabrata MoharanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum ComputingDocument7 paginiQuantum ComputingticÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum ComputingDocument10 paginiQuantum Computingrishu100% (1)
- Seminar report-GOPIDocument10 paginiSeminar report-GOPIGôpínathÎncă nu există evaluări
- DocumentoDocument1 paginăDocumentoNonikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AbstractDocument13 paginiAbstractEnoch HsiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Principles Underpinning Quantum ComputingDocument6 paginiPhysical Principles Underpinning Quantum ComputingAfzaal GhaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-1: What Is Quantum Computing?Document23 paginiChapter-1: What Is Quantum Computing?abhi_430Încă nu există evaluări
- Quantum ComputingDocument12 paginiQuantum Computingapi-26172869Încă nu există evaluări
- Technology Is Defined As The Methods, Systems, and Devices Which Are The Result of Scientific Knowledge Being Used For Practical PurposesDocument4 paginiTechnology Is Defined As The Methods, Systems, and Devices Which Are The Result of Scientific Knowledge Being Used For Practical Purposeskrish kanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum ComputingDocument1 paginăQuantum ComputingSURVEY PROPERTYÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuantumDocument1 paginăQuantumBrian ForteÎncă nu există evaluări
- 42quantum ComputingDocument12 pagini42quantum ComputingNaveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum ComputersDocument21 paginiQuantum Computersshweta_bharti_7Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-1: Quantum ComputingDocument19 paginiChapter-1: Quantum ComputingMahesh ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum ComputingDocument7 paginiQuantum Computingeeshanimajumder7901Încă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Computers: The Future of ComputingDocument14 paginiQuantum Computers: The Future of ComputingSlainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Computing HardwareDocument9 paginiQuantum Computing HardwareSeeron SivashankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Computer SynopsisDocument6 paginiQuantum Computer SynopsisAkshay Diwakar100% (1)
- Zeroes, Ones, and BothDocument4 paginiZeroes, Ones, and BothRavi UpadhayayÎncă nu există evaluări
- ModernphysicsprojectDocument7 paginiModernphysicsprojectAli MakkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SureDocument1 paginăSurerana saadÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuantumDocument12 paginiQuantumSandeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum ComputingDocument17 paginiQuantum ComputingAnkush100% (1)
- Quantum Computing: Memory Bits Qubits Quantum Superposition Qubit StatesDocument3 paginiQuantum Computing: Memory Bits Qubits Quantum Superposition Qubit StatesUtkal ParasarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Quantum ComputingDocument7 paginiIntroduction To Quantum ComputingUmar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Marvels of Quantum Computing Unleashing Unprecedented PowerDocument1 paginăThe Marvels of Quantum Computing Unleashing Unprecedented Powertempuser69Încă nu există evaluări
- Quantum ComputingDocument1 paginăQuantum ComputingAtif SyedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum ComputersDocument23 paginiQuantum ComputersalkagabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Computing - The Limits of Our Technology: Computing Like Never Before - An IntroductionDocument1 paginăQuantum Computing - The Limits of Our Technology: Computing Like Never Before - An IntroductionRausanara FerdoushiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fascinating World of Quantum ComputingDocument2 paginiFascinating World of Quantum ComputingChevroy LindoÎncă nu există evaluări
- About Quantum ComputingDocument1 paginăAbout Quantum ComputingGourav Sarma BiswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Computing 1Document6 paginiQuantum Computing 1chandravinitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- File 52078Document16 paginiFile 52078Kellye CurtisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum ComputingDocument1 paginăQuantum Computingemma abissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- YerchestersDocument1 paginăYerchestersKitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Physics 5Document1 paginăQuantum Physics 5Walid NajjarÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Quantum Computer and Its HistoryDocument3 paginiWhat Is Quantum Computer and Its HistoryAtta Ur Rahman AfridiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum ComputingDocument29 paginiQuantum ComputingNishantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ctext 2Document1 paginăCtext 2LoginÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Computers ExplainedDocument4 paginiQuantum Computers ExplainedthoughtscloudÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review On Quantum ComputingDocument3 paginiA Review On Quantum ComputingRashmi kumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum 3Document7 paginiQuantum 3BRUTAL THORÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Time To Talk About The Ethics of QC Is Now IntroDocument20 paginiThe Time To Talk About The Ethics of QC Is Now IntroNicholas FarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Computing Is A Type of Computing That Uses The Principles of Quantum Mechanics To Perform CalculationsDocument1 paginăQuantum Computing Is A Type of Computing That Uses The Principles of Quantum Mechanics To Perform CalculationsAdriel LousadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Studies of Al-Doped Zno and Ga-Doped Zno Transparent Conducting Oxide Thin FilmsDocument6 paginiComparative Studies of Al-Doped Zno and Ga-Doped Zno Transparent Conducting Oxide Thin FilmsMurtaza SieamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measuring Planck'c Constant Using LEDDocument4 paginiMeasuring Planck'c Constant Using LEDmarkmejia_025Încă nu există evaluări
- ECE 374 - Part - 1c - S2017Document37 paginiECE 374 - Part - 1c - S2017Zakaria ElwalilyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step1:: 1. With Neat Sketches Explain The NMOS and PMOS Fabrication ProcedureDocument6 paginiStep1:: 1. With Neat Sketches Explain The NMOS and PMOS Fabrication ProcedurehghgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Superstrings and Topological Strings at Large NDocument31 paginiSuperstrings and Topological Strings at Large NmlmilleratmitÎncă nu există evaluări
- 300+ Top Power Electronics Questions and Answers PDF - MCQS: Digi-Key EleDocument10 pagini300+ Top Power Electronics Questions and Answers PDF - MCQS: Digi-Key Eleharish nimde100% (1)
- Introduction On SILVACO and MOSFET Simulation Technique PDFDocument18 paginiIntroduction On SILVACO and MOSFET Simulation Technique PDF전다솜[학생](대학원 전자정보융합공학과)Încă nu există evaluări
- Black BodyDocument14 paginiBlack BodyNatheesh TpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ece II Engineering Physics (10phy 22) AssignmentDocument7 paginiEce II Engineering Physics (10phy 22) AssignmentPrakash ShiggaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rigid Rotor Induced DipoleDocument7 paginiRigid Rotor Induced Dipolepero_scribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGFETDocument13 paginiIGFETMariyah AxixÎncă nu există evaluări
- GGNMOS As ESD Protection in Different Nanometer CMOS ProcessDocument2 paginiGGNMOS As ESD Protection in Different Nanometer CMOS ProcessNguyen Van ToanÎncă nu există evaluări
- H2 Quantum Physics - Part 1 Tutorial 2014 - StudentDocument17 paginiH2 Quantum Physics - Part 1 Tutorial 2014 - StudentweinengxxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1-7Document224 paginiChapter 1-7Jackie JonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special Purpose DiodesDocument90 paginiSpecial Purpose DiodesRafi Rebal ShaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Schrodinger Wave Equation: V (X), A X 0Document4 paginiApplications of Schrodinger Wave Equation: V (X), A X 0jasonÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review of Photovoltaic Performance of Organicinorganic SolarDocument53 paginiA Review of Photovoltaic Performance of Organicinorganic SolarChristhy Vanessa Ruiz MadroñeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 9 - Calculating The Pi-Electronic Bond Order and Total Bond OrderDocument9 paginiExercise 9 - Calculating The Pi-Electronic Bond Order and Total Bond Orderapi-235187189Încă nu există evaluări
- Backward Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 paginiBackward Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNIKHILÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solar Cell ReportDocument20 paginiSolar Cell ReportAnkur AnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar MOSFET IRF Series - Tipe KodeDocument2 paginiDaftar MOSFET IRF Series - Tipe KodeDhaniel agungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presented By, Narendra Kuppili, Analog IC Layout EngineerDocument27 paginiPresented By, Narendra Kuppili, Analog IC Layout EngineermanojkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucl - Phys.B v.612Document516 paginiNucl - Phys.B v.612buddy72Încă nu există evaluări
- Preface - 2015 - FinFET Modeling For IC Simulation and DesignDocument2 paginiPreface - 2015 - FinFET Modeling For IC Simulation and Designrakshit yaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics of SemiconductorsDocument62 paginiPhysics of SemiconductorsAlvin Soriano AdduculÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic SanjuDocument42 paginiAtomic Sanjusaptarshi bhattacharyya100% (1)
- Fisika Kuantum 6 1Document16 paginiFisika Kuantum 6 1YudiÎncă nu există evaluări