Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Air Density Uncertainty
Încărcat de
jrlr65Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Air Density Uncertainty
Încărcat de
jrlr65Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
AIR DENSITY AND ITS
AIR DENSITY AND ITS
UNCERTAINTY
UNCERTAINTY
Manuel Salazar Manuel Salazar
Maria Vega Maria Vega
CONTENTS
CONTENTS
Air and its composition
Air and its composition
Ways to calculate the air density
Ways to calculate the air density
Chart
Chart
CIPM Equation
CIPM Equation
Approximate equation
Approximate equation
Uncertainty
Uncertainty
Air and its composition
Air and its composition
The air is a mixture of several gases dry air, and water in steam
form. Troposphere is the inferior layer of the terrestrial atmosphere,
terrestrial surface altitude of 6 to 18 kilometers, the air we breathed is
concentrated there.
The dry air as the water steam behaves like ideal gases. They have been
developed to empirical laws that relate the macroscopic values, in ideal
gases, these values include pressure (p), volume (V) and temperature (T)
Ley de Charles Ley de Gay-Lussac Ley de Boyle
IDEAL GAS LAW
It It is is constituted by a nitrogen constituted by a nitrogen
mixture and of oxygen like mixture and of oxygen like
basic element (99%) and the basic element (99%) and the
rest like noble gases. The rest like noble gases. The
composition is similar around composition is similar around
the world. the world.
Water Steam (0 Water Steam (0- -5%), Carbon 5%), Carbon
dioxide, hydrocarbons, tars, dioxide, hydrocarbons, tars,
ashes, dust and SO2. ashes, dust and SO2.
Electrical delivery form Electrical delivery form C2H2, C2H2,
H202, 03, NO3H, NH3, H202, 03, NO3H, NH3,
NO3NH4. NO3NH4.
4 10 4 10
- -5 5
1 10 1 10
- -5 5
Xen Xen n n
0,35 10 0,35 10
- -5 5
5 10 5 10
- -5 5
Hidrogeno Hidrogeno
3 10 3 10
- -4 4
1 10 1 10
- -4 4
Cript Cript n n
0,7 10 0,7 10
- -4 4
5 10 5 10
- -4 4
Helio Helio
1 10 1 10
- -3 3
1,5 10 1,5 10
- -3 3
Ne Ne n n
0,3 0,3 0,94 0,94 Arg Arg n n
23,1 23,1 20,92 20,92 Oxigeno Oxigeno
75,6 75,6 78,14 78,14 Nitr Nitr geno geno
en peso en peso en volumen en volumen Elemento Elemento
Proporci Proporci n n Proporci Proporci n n
COMPOSICION DEL AIRE COMPOSICION DEL AIRE
PURO PURO
Air and its composition
Air and its composition
Ways to calculate the air
Ways to calculate the air
density
density
Density defined in a qualitative manner as the measure of the
relative mass of objects with a constant volume
Hypothesis de Avogadro Two gases same volume (same pressure and
temperature) contain the same number of particles, or molecules
Standard Law gases
P.V = n . R . T n = m/Mr
As function of altitude
As function of altitude
Using a
Using a
refractometer
refractometer
Air buoyancy artefacts methods
Air buoyancy artefacts methods
Equation CIPM /81
Equation CIPM /81
Approximate equation
Approximate equation
Ways to calculate the air
Ways to calculate the air
density
density
Atmospheric pressure drops Atmospheric pressure drops
about about or about 1.1 mbar ( or about 1.1 mbar (kPa kPa) )
for each 100 meters. for each 100 meters. Density Density
decreases decreases
Ways to calculate the
Ways to calculate the
air density
air density
AS FUNCTION OF ALTITUDE
L = L = 6,5 6,5 temperature lapse rate, deg K/km temperature lapse rate, deg K/km
H = H = geopotencial geopotencial altitude altitude
Z = geometrical altitude Z = geometrical altitude
To = Temperature K To = Temperature K
Po = Atmospheric Pressure Po = Atmospheric Pressure
Ways to calculate the air density
Ways to calculate the air density
AS FUNCTION OF ALTITUDE
Changes in air density can be determined with good precision usi Changes in air density can be determined with good precision using ng
an optical method based on the high correlation between air an optical method based on the high correlation between air
density and air index of refraction. density and air index of refraction.
R R specific refraction or the specific refraction or the refractional refractional invariant in unction composition of air and invariant in unction composition of air and
the local atmospheric conditions the local atmospheric conditions
n n is is determined by a simple ratio of laser frequencies: determined by a simple ratio of laser frequencies:
laser frequency locked to one transmission peak o laser frequency locked to one transmission peak of the interferometer under vacuum f the interferometer under vacuum
the frequency locked to the same peak of the interferometer plac the frequency locked to the same peak of the interferometer placed in air ed in air. .
vacio
Ways to calculate the air density
Ways to calculate the air density
REFRACTROMETRY
aire
vacio
n
=
aire
The method is based on the weighing of two artefacts having the The method is based on the weighing of two artefacts having the same same
nominal mass and the same surface area but with very different nominal mass and the same surface area but with very different
volumes. Two weightings are necessary to determine the air densi volumes. Two weightings are necessary to determine the air density , ty ,
one in air and one in vacuum one in air and one in vacuum
I I
1 1
e I e I
2 2
balance readings in air balance readings in air mass mass
1 1
and and mass mass
2 2
V V
m1 m1
e e V V
m2 m2
volume of m volume of m
1 1
y m y m
2 2
air density air density
I I
3 3
e I e I
4 4
the balance readings in vacuum the balance readings in vacuum mass mass
1 1
y mass y mass
2 2
S the difference in surface area between the two artefacts and S the difference in surface area between the two artefacts and
mass of adsorption per unit area. mass of adsorption per unit area.
Ways to calculate the air density
Ways to calculate the air density
AIR BUOYANCY ARTEFACTS METHODS
) (
2 1 2 1 m m aire
V V I I m + =
4 3
I I m
vaco
=
S m m
vacio aire
+ =
2 1
2 1 4 3
) (
m m
V V
S I I I I
Ways to calculate the air density
Ways to calculate the air density
FORMULA CIPM
From the equation of state of a non-ideal gas and the experimental
conditions the density of moist air
Where
P pressure
T thermodynamic temperature 273,15 + t
Mv molar mass of the water
Z compressibility factor
R molar gases constant
| |
1 3
10 * ) 0004 , 0 ( 011 , 12 9635 , 28
2
+ = kgmol x M
co a
p
t p
t p hf x
sv
v
) (
) , ( =
From
From
BIPM
BIPM
formula we obtain one
formula we obtain one
numerical approximate equation :
numerical approximate equation :
Ways to calculate the air density
Ways to calculate the air density
APPROXIMATE EQUATION
t
e h p
t
r
a
+
=
15 , 273
* * 009024 , 0 * 34848 , 0
* 0612 , 0
Thermodynamic properties of mixtures of gas with Thermodynamic properties of mixtures of gas with vapor vapor. saturation . saturation
pressure and temperature of dew, Indexes of humidity, Volume, he pressure and temperature of dew, Indexes of humidity, Volume, heat at
and humid enthalpy, temperature of saturation adiabatic and wet and humid enthalpy, temperature of saturation adiabatic and wet
thermometer thermometer. .
Some definitions: Some definitions:
Relative Humidity. Relative Humidity. The relative humidity is the percent of The relative humidity is the percent of saturation saturation
humidity humidity, generally calculated in relation to saturated , generally calculated in relation to saturated vapor vapor density, in density, in
(%): (%):
HR = 100 HR = 100 Pv Pv/Ps (%) /Ps (%)
Temperature of adiabatic saturation, Temperature of adiabatic saturation, Th Th , is the ideal temperature of , is the ideal temperature of
equilibrium will have the air non saturated after undergoing an equilibrium will have the air non saturated after undergoing an adiabatic adiabatic
and isobaric process ( and isobaric process (iso iso enthalpic enthalpic), that it takes it temperature to the ), that it takes it temperature to the
saturation by means of liquid evaporation of water to this. saturation by means of liquid evaporation of water to this.
Temperature of wet thermometer is Temperature of wet thermometer is the temperature the temperature that it reaches a that it reaches a
thermometer covered with a wet cloth that is exposed to an airfl thermometer covered with a wet cloth that is exposed to an airflow ow
without saturating that it flows at speeds near 5 without saturating that it flows at speeds near 5 m/s m/s
Dew point Dew point is the temperature, at which the moisture content in the air wi is the temperature, at which the moisture content in the air will ll
saturate saturate the air the air , , If the air is cooled further, some of the moisture will If the air is cooled further, some of the moisture will
condense condense . .
Ways to calculate the
Ways to calculate the
air density
air density
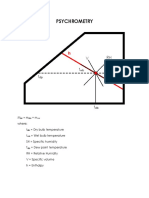
PSYCHROMETRY
Variation of Variation of
electrical electrical
properties properties
Hygrometer digital Hygrometer digital
Gravimetric Gravimetric
Hygrometer of Chemist Hygrometer of Chemist
absorption absorption
Condensation Condensation
Hygrometer of dew Hygrometer of dew
point point
Hygroscopic Hygroscopic
hygrometer hygrometer of hair or of hair or
others materials others materials
Thermodynamic Thermodynamic psychrometer psychrometer
METHOD METHOD ARTEFACT ARTEFACT
To mesure the humidity :
Ways to calculate the air density
Ways to calculate the air density
PSYCHROMETRY
Ways to calculate the
Ways to calculate the
air density
air density
PSYCHROMETRY
Psychrometer and aspiro
psychrometer Consist two
thermometers, one normal
(dry) and another with their
bulb permanently humidified
thanks to a cloth or wet gauze
that it recovers it.
The humidity can be measured
between both starting from
the difference of temperature
apparatuses
Diagram Carrier. Diagram Carrier.
- - The T represents (C) in the The T represents (C) in the
abscissa axis (axis x) and the abscissa axis (axis x) and the
mixture reason or humidity (X, in mixture reason or humidity (X, in
kg of water/kg of dry air) in the kg of water/kg of dry air) in the
axis of orderly (axis and, to the axis of orderly (axis and, to the
right). right).
- - The saturation curve (HR = 100%) The saturation curve (HR = 100%)
it ascends toward the right and it it ascends toward the right and it
represents the end of the represents the end of the
diagram. In this curve the diagram. In this curve the
temperatures of humid temperatures of humid
thermometer and the thermometer and the
temperatures of dew are located. temperatures of dew are located.
- - - - The curves of humidity relative The curves of humidity relative
constant are similar to that of constant are similar to that of
saturation, advancing down (lying saturation, advancing down (lying
down more) as it diminishes the down more) as it diminishes the
humidity of the air. humidity of the air.
Ways to calculate the
Ways to calculate the
air density
air density
PSYCHROMETRY
CHART
600 610 620 630 640 650 660 670 680 690 700
0.7
0.71
0.72
0.73
0.74
0.75
0.76
0.77
0.78
0.79
0.8
.8
0.7
a
19 40 % . p . ( )
a
20 40 % . p . ( )
a
21 40 % . p . ( )
a
24 40 % . p . ( )
700 600 p
Air density evaluated with
Relative humidity 40 %,
temperature 19 C 24 C,
pressure 600 mbar 700 mbar
660 694 728 762 796 830 864 898 932 966 1000
0.8
0.84
0.88
0.92
0.96
1
1.04
1.08
1.12
1.16
1.2
1.2
0.8
a
19 50% . p . ( )
a
20 50% . p . ( )
a
21 50% . p . ( )
a
24 50% . p . ( )
1000 660 p
Air density with evaluated with
Relative humidity 50 %,
temperature 19 C 24 C,
pressure 660 mbar 1000 mbar
Ways to calculate the
Ways to calculate the
air density
air density
CHART
Air density evaluated with
Relative humidity 40 % - 60 %,
temperature 20 C ,
pressure 600 mbar 1000 mbar
40 42 44 46 48 50 52 54 56 58 60
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
1.05
1.1
1.15
1.2
1.185
0.7
a
20 h
r
. 1000 .
( )
a
20 h
r
. 800 .
( )
a
20 h
r
. 700 .
( )
a
20 h
r
. 600 .
( )
60 40 h
r
Ways to calculate the
Ways to calculate the
air density
air density
CHART
Air density evaluated with
Relative humidity 40 %,
temperature 19 C 25 C,
pressure 800 mbar 1000 mbar
19 19.6 20.2 20.8 21.4 22 22.6 23.2 23.8 24.4 25
0.9
0.93
0.96
0.99
1.02
1.05
1.08
1.11
1.14
1.17
1.2
1.189
0.929
a
t 40 . 1000 . ( )
a
t 40 . 800 . ( )
25 19 t
Ways to calculate the
Ways to calculate the
air density
air density
CALCULATION OF THE AIR DENSITY
CIPM
Where:
p Pressure of air in Pa.
M
a
molar mass of dry air.
Z Compressibility factor
R Universal constant of ideal gases
T Temperature of air in K
X
v
molar fraction of water steam
M
v
molar mass of water
|
|
.
|
\
|
a
v
v
a
M
M
x
ZRT
pM
1 1
Molar mass of dry air, Ma
Molar mass of dry air, Ma
If it considers constant of air component
If it considers constant of air component
M
M
a a
= 0,028963 512440 kg mol
= 0,028963 512440 kg mol
- -1 1
If it can measure the concentration of CO
If it can measure the concentration of CO
2 2
M
M
a a
= [28,9635 + 12,011 (
= [28,9635 + 12,011 (
X
X
CO2 CO2
.
.
-
-
0,0004)]* 10
0,0004)]* 10
- -3 3
kg
kg
mol
mol
- -1 1
Compressibility factor, Z Compressibility factor, Z
Where: Where:
p p Air pressure in Pa Air pressure in Pa
T T Air temperature in K Air temperature in K
t t Environmental temperature in Environmental temperature in
o o
C C
a a
0 0
1, 581 23 1, 581 23 X X 10 10
- -6 6
K Pa K Pa
- -1 1
a a
1 1
- -2,9331 x 10 2,9331 x 10
- -8 8
Pa Pa
- -1 1
a a
2 2
1,1043 x 10 1,1043 x 10
- -10 10
K K
- -1 1
Pa Pa
- -1 1
b b
0 0
5,707 x 10 5,707 x 10
- -6 6
K Pa K Pa
- -1 1
b b
1 1
- -2,051 X 10 2,051 X 10
- -8 8
Pa Pa
- -1 1
C C
0 0
1.9898 x 10 1.9898 x 10
- -4 4
K Pa K Pa
- -1 1
C C
1 1
- - 2,376 x 10 2,376 x 10
- -6 6
Pa Pa
- -1 1
d d 1,83 x 10 1,83 x 10- -11K 11K
2 2
Pa Pa
- -2 2
e e - -0,765 x 10 0,765 x 10
- -8 8
K K
2 2
Pa Pa
- -2 2
( ) ( ) | | ( )
2
2
2
2
1 0 1 0
2
2 1 0
1
v v v
ex d
T
p
x t c c x t b b t a t a a
T
p
Z + + + + + + + + =
Universal Constant of ideal gases, R Universal Constant of ideal gases, R
R = 8.314510 8,4 x R = 8.314510 8,4 x lO lO- -6 J . mol 6 J . mol
- -1 1
. K . K
- -1 1
Molar fraction of water steam, Xv Molar fraction of water steam, Xv
In function of relative humidity, h In function of relative humidity, h
In function of temperature of dew point, tr
Where:
Relative humidity
Pressure of saturated steam
Fugacity factor
p
t p
t p hf x
sv
v
) (
) , ( =
p
t p
t p f X
r sv
r v
) (
) , ( =
sv
p
sv
p
h
sv
p
) , (
r
t p f
Enhancement factor f f(p,t
r
)
Where:
2
t p f + + =
p
T
1,000 62
3.14 x 10
-8
Pa
-1
5,6 x 10
-7
K
-2
Air pressure in Pa
Air temperature in
O
C or dew point
temperature (t
r
) in
O
C
Pressure of saturated steam, p
sv
Where:
+ + + =
T
D
C BT AT Pax p
sv
2
exp 1
A 1,237 884 7 x 10-5 K-2
B -1,912 131 6 x 10-2 K-1
C 33,937 110 47
D -6,343 164 5 x 103 K
T Air temperature in K or dew point
temperature (Tr) in K
UNCERTAINTY OF AIR DENSITY
SOURCES OF UNCERTAINTY
Atmospheric temperature
Calibration of barometric
Resolution of barometric
Variation of
atmospheric pressure
during calibration
2
3
2
2
2
1 p p p
u u u up + + =
k
U
u
B
p
=
1
12
2
B
p
d
u =
24
3
+
=
p p
up
Environmental conditions
Calibration of thermometer
Resolution of instrument
Variation of temperature
during calibration
k
U
u
t
t
=
1
12
2
t
t
d
u =
24
3
+
=
t t
u
t
2
3
2
2
2
1 t t t t
u u u u + + =
Relative humidity of air
Calibration of hygrometer
Resolution of hygrometer
Variation of the air relative
humidity during calibration
2
3
2
2
2
1 h h h h
u u u u + + =
k
U
u
h
h
=
1
12
2
h
h
d
u =
24
3
+
=
h h
u
h
Constant R of ideal gases
Equation adjustment for the determination of
air density
u
R
= 84x 10
-7
J mol
-1
K
-1
3 5 4
10 50 , 9 ) 9495 , 0 )( 10 1 (
= = kgm x x u
ec
Sensitivity Coefficient
Pressure
Temperature
Relative humidity.
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
p
a v
v
a v
v
a v
v
a a a
p
Xv
Xv p
f
f
X
X p
X
X
Z
Z p
f
f
X
X
Z
Z p
Z
Z p
c
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
=
t
T
T
P
P
X
X t
f
f
X
X t
T
T
t
T
T
P
P
X
X
Z
Z t
f
f
X
X
Z
Z t
Z
Z t
T
T
Z
Z
ct
sv
sv
v
v
a v
v
a a
sv
sv
v
v
a v
v
a a a
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
=
h
X
X h
X
X
Z
Z
C
v
v
a v
v
h
a
Where:
1 =
t
T
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+ + + =
2
2
2 exp
T
D
B AT
T
D
C BT AT
T
P
sv
1 8
10 14 , 3
= =
Pa x
p
f
t
t
f
2 =
p
fP
h
X
sv v
=
p
hP
f
x
sv v
=
2
p
hfP
p
xv
sv
p
hf
P
X
sv
v
=
( ) | | ( )
2
2
2
1 0 1 0
2
2 1 0
2
) (
1
v v v
ex d
T
p
X t C C X t b b t a t a a
T p
Z
+ + + + + + + +
( ) ( ) | | ( )
2
3
2
2 1 1 0
2
2 1 0
2
2
v
ex d
T
p
Xv t C C X t b b t a t a a
T
p
T
Z
o v
+ + + + + + + =
( )
2
1 2 1
1 2
v v
X c X b t a a
T
p
t
Z
+ + +
( )
2
1 1 0
2 2
2 2
T
eX p
tx c x c t b b
T
p
X
Z
v
v v o
v
+ + + +
Constant R
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
Ma
Mv
Xv
ZRT
Ma
p
1 1
a
v
v
a
M
M
x
RT Z
pM
Z
1 1
2
|
|
.
|
\
|
a
v
v
a
M
M
X
ZRT
pM
T
1 1
2
|
|
.
|
\
|
a
v a
v
M
M
ZRT
pM
X
1
|
|
.
|
\
|
a
v a
M
M
Xv
T ZR
pM
R
1
2
|
.
|
\
|
=
R
C
a
R
molK j kgm CR
1 3
114203618 , 0
=
Equation
Uncertainty evalation
Degrees of freedom
Expanded uncertainty
1 =
ec
C
( ) | |
2
=
t
i i p
x u c u
ec
ec
R
R
h
h
t
t
p
p
n
t
t
xt
ef
v
u
v
u
v
u
v
u
v
u
u
v
u
u
v
4 4 4 4
4
4
4
4
+ + + +
= =
p
u k U =
:
Where :
( )
( )
( )( )
( ) ( ) p s t s
p p t t
n n
p t r
n
k
k k
=
=
1
1
1
,
( )
( )
( )( )
( ) ( ) h s t s
h h t t
n n
h t r
n
k
k k
=
=
1
1
1
,
( )
( )
( )( )
( ) ( ) h s p s
h h p p
n n
h p r
n
k
k k
=
=
1
1
1
,
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
( )
= +
+ =
1
1 1
2
, 2
N
i
N
i j
j i j i j i
i
i i p
x x r x u x u c c x u c u
Consider that the atmospheric pressure, temperature and
relative humidity are correlated, its uncertainty:
Reference
Reference
Estimacin
Estimacin
de la incertidumbre en la
de la incertidumbre en la
determinacin
determinacin
de la
de la
densidad del aire, Luis Omar Becerra Santiago y
densidad del aire, Luis Omar Becerra Santiago y
mara
mara
Elena
Elena
Guardado
Guardado
gonzlez
gonzlez
, CENAM , Abril 2003.
, CENAM , Abril 2003.
Equation
Equation
for
for
the
the
determination
determination
of
of
the
the
density
density
of
of
Moir
Moir
Air
Air
,
,
R.S
R.S
.
.
Davis
Davis
,
,
Metrologia
Metrologia
1992,29,67
1992,29,67
-
-
70.
70.
Equation
Equation
for
for
the
the
dertimination
dertimination
of
of
the
the
density
density
of
of
moist
moist
air
air
, P.
, P.
giacomo.Metrologia
giacomo.Metrologia
18,33
18,33
-
-
40 1982.
40 1982.
Three
Three
methods
methods
of
of
determining
determining
the
the
density
density
of
of
moist
moist
air
air
during
during
mass
mass
comparisons
comparisons
, A.
, A.
Picard
Picard
y
y
h. Fang. Metrologia 2002, 39,
h. Fang. Metrologia 2002, 39,
31
31
-
-
40.
40.
Discrepancies
Discrepancies
in
in
air
air
density
density
determination
determination
between
between
the
the
thermodynamic
thermodynamic
formula
formula
and
and
a
a
gravimetric
gravimetric
method
method
:
:
evidence
evidence
for
for
a
a
new
new
value
value
of
of
the
the
mole
mole
fraction
fraction
of
of
argon
argon
in
in
air
air
, A
, A
Picard
Picard
,
,
H.
H.
Fang
Fang
,
,
Metrologia
Metrologia
41, 396
41, 396
-
-
400
400
Thanks for the
attention
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Recommended Reference Materials for Realization of Physicochemical Properties: Pressure–Volume–Temperature RelationshipsDe la EverandRecommended Reference Materials for Realization of Physicochemical Properties: Pressure–Volume–Temperature RelationshipsE. F. G. HeringtonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Air Density and Its Uncertainty - Manuel Salazar & Maria VegaDocument37 pagini01 Air Density and Its Uncertainty - Manuel Salazar & Maria VegamoxlindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dissolved Gas Concentration in Water: Computation as Functions of Temperature, Salinity and PressureDe la EverandDissolved Gas Concentration in Water: Computation as Functions of Temperature, Salinity and PressureÎncă nu există evaluări
- DENSIDAD DEL AIRE Y SU INCERTIDUMBRE InglesDocument19 paginiDENSIDAD DEL AIRE Y SU INCERTIDUMBRE InglesRicarditoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air ConditioningDocument68 paginiAir ConditioningCharan Reddy AbbadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air-Conditioning System and Its Psychrometric Processes and ApplicationDocument34 paginiAir-Conditioning System and Its Psychrometric Processes and ApplicationAlvin LoocÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 314 1.2 PsychrometryDocument10 paginiCE 314 1.2 PsychrometryRajid MobajidÎncă nu există evaluări
- PsychrometryDocument7 paginiPsychrometryVirma Anne CorpuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychrometry AND Psychrometric Chart: Dr. Mohammed Osama El-SamadonyDocument33 paginiPsychrometry AND Psychrometric Chart: Dr. Mohammed Osama El-SamadonyMedo HamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Vapour Effects in Mass MeasurementDocument4 paginiWater Vapour Effects in Mass MeasurementaldesanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Humidification and DehumidificationDocument37 paginiLecture Humidification and DehumidificationUsman Khan0% (1)
- Chapter 3 (Humidity and Solubility)Document39 paginiChapter 3 (Humidity and Solubility)Riham Fuad Bazkhan Al ZadjaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- PsychrometryDocument76 paginiPsychrometrybansodevhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moist Air Properties and Conditioning ProcessesDocument94 paginiMoist Air Properties and Conditioning Processespamsanchezmd100% (1)
- 1.0 Introduction Properties of AirDocument86 pagini1.0 Introduction Properties of AirMuhd ShazanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Humidity in AirDocument6 paginiHumidity in AirJeffÎncă nu există evaluări
- PsychrometricsDocument13 paginiPsychrometricssuirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Lecture Conditioning)Document31 pagini4 Lecture Conditioning)Rehan AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 9 - CE 433Document21 paginiLecture 9 - CE 433SEEMA NIHALANIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presented By: Aishwarya Deopujari Prerana Das Nishtha Duggal Vasundhra Singh SrideviDocument110 paginiPresented By: Aishwarya Deopujari Prerana Das Nishtha Duggal Vasundhra Singh Sridevikothat82Încă nu există evaluări
- 16Air conditioning1Document14 pagini16Air conditioning1bharathd911Încă nu există evaluări
- DryingDocument24 paginiDryingramnareshretneniÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIR CHEMISTRY and HVAC TypesDocument6 paginiAIR CHEMISTRY and HVAC Typeskesavaganesan58Încă nu există evaluări
- Air Density CalculatorDocument3 paginiAir Density CalculatorcaturskÎncă nu există evaluări
- % Outdoor Air CalculationDocument6 pagini% Outdoor Air Calculationamirin_kingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psych Rome TryDocument13 paginiPsych Rome TryAmira BagumbaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- ETD Chapter 5Document14 paginiETD Chapter 5Vasantha SeelanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Me Lab ReportDocument15 paginiFinal Me Lab ReportMigelle Jose BarlisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpe Notes - Unit IIDocument4 paginiCpe Notes - Unit IIdhananivethaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Properties-Psycometric ChartsDocument6 paginiAir Properties-Psycometric Chartsa_j_sanyal259Încă nu există evaluări
- Psych Rome TryDocument62 paginiPsych Rome TryMohd Hafiz Ahmad100% (1)
- Experiment No. 5 1Document6 paginiExperiment No. 5 1JunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measurement of HumidityDocument5 paginiMeasurement of HumidityJerico LlovidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relative Density of Gases Lab ReportDocument10 paginiRelative Density of Gases Lab ReportAnusha AnuÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT II Air-ConditioningDocument12 paginiUNIT II Air-ConditioningiamgeniousÎncă nu există evaluări
- Humidification and Cooling Towers FullDocument114 paginiHumidification and Cooling Towers FullHoorish NiaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- EntalpiDocument5 paginiEntalpiOnur KaplanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSYCHROMETRYDocument10 paginiPSYCHROMETRYGopinath DhamodaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- RacDocument3 paginiRacofficial vrÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2Document4 pagini2xpuraw21Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 Psychrometry PDFDocument24 pagini2 Psychrometry PDFFaiz FauziÎncă nu există evaluări
- PsychrometricsDocument9 paginiPsychrometricsSeptimiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Density of Moist AirDocument4 paginiDensity of Moist AirChristian MavarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3-Emission Monitoring and SamplingDocument77 pagini3-Emission Monitoring and SamplingFarah SyaheyraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Materials in Incompressible FlowDocument42 paginiReview Materials in Incompressible FlowAviation Review MaterialsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychrometrics Chart GuideDocument8 paginiPsychrometrics Chart GuideFaruk HosenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Conditioning PDFDocument74 paginiAir Conditioning PDFDatu JonathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychometric Chart (0-91899 - En)Document44 paginiPsychometric Chart (0-91899 - En)Anonymous 7z6OzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- I. What Is Air Conditioning?Document9 paginiI. What Is Air Conditioning?Christian Aquino FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide On Air PropertiesDocument22 paginiGuide On Air PropertiesTusshar KÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To Air Density and Density Altitude CalculationsDocument28 paginiAn Introduction To Air Density and Density Altitude Calculationsblowmeasshole1911Încă nu există evaluări
- Thermo L10Document26 paginiThermo L10Pronto P ChirinkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychrometry: V RH T T SHDocument13 paginiPsychrometry: V RH T T SHKAL ELÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning (Meng 4711) : PsychrometryDocument58 paginiRefrigeration and Air-Conditioning (Meng 4711) : PsychrometryaddisudagneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 7-Properties of Gas and Vapor MixturesDocument5 paginiLesson 7-Properties of Gas and Vapor MixturesOrley G Fadriquel0% (1)
- Air Dispersion Formulas GuideDocument14 paginiAir Dispersion Formulas GuidebenfildÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Density and Density Altitude CalculationsDocument20 paginiAir Density and Density Altitude CalculationsNeelesh Kumar MuthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychrometric Processes of Air ConditioningDocument37 paginiPsychrometric Processes of Air ConditioningEphraim MekonnenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air ConditioningDocument72 paginiAir ConditioningNIKÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Mean Free Path in Air: (Receioed 5 May and in Final Form JanuaryDocument8 paginiThe Mean Free Path in Air: (Receioed 5 May and in Final Form JanuaryKaren JahairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hoklas SC 02Document60 paginiHoklas SC 02jrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- 67 Uscs ClasificDocument28 pagini67 Uscs ClasificLuis ValensÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensor Guide MicrochipDocument22 paginiSensor Guide MicrochipLeonardo Solís VásquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Notes: The Use of LuxmetersDocument4 paginiLab Notes: The Use of Luxmetersjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- D 4356 Â " 84 R02 RDQZNTY - PDFDocument13 paginiD 4356 Â " 84 R02 RDQZNTY - PDFluis_may22Încă nu există evaluări
- D21222 PDFDocument4 paginiD21222 PDFjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- A2LA Policy On Measurement TraceabilityDocument9 paginiA2LA Policy On Measurement Traceabilityjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- How Sensors Work - Load CellsDocument7 paginiHow Sensors Work - Load Cellsjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- PT Provider ProceduresDocument13 paginiPT Provider Proceduresjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- D21222 PDFDocument4 paginiD21222 PDFjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- Determination of Elmendorf Tearing Resistance: Product Testing Apparatus Product Testing ApparatusDocument3 paginiDetermination of Elmendorf Tearing Resistance: Product Testing Apparatus Product Testing Apparatusjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- Toward A Standard Thermistor Calibration Method: Data Correction SpreadsheetsDocument7 paginiToward A Standard Thermistor Calibration Method: Data Correction Spreadsheetsjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- Lista de No Conformidades 17025Document29 paginiLista de No Conformidades 17025jrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- Mejora OshasDocument237 paginiMejora Oshasjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- R051-1-E06 Calibracion MasasDocument83 paginiR051-1-E06 Calibracion MasasdjfreditoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Milligram MassDocument10 paginiMilligram Massjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- 2013 Apr PH Meters PDFDocument4 pagini2013 Apr PH Meters PDFAshfaq AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Measurement Technology For Temperature: Assurance Through Precision - Versatility Through Data Transmission by RadioDocument10 paginiNew Measurement Technology For Temperature: Assurance Through Precision - Versatility Through Data Transmission by Radiojrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- PID Control Technical Notes: GeneralDocument6 paginiPID Control Technical Notes: GeneralSatya Sai Babu YeletiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NIST Stopwatch & Timer Calibrations 2009Document82 paginiNIST Stopwatch & Timer Calibrations 2009ririmonir100% (1)
- ISO/TS 12913-2:2018 Soundscape - Part 2: Data Collection and Reporting Requirements - What's It All About?Document3 paginiISO/TS 12913-2:2018 Soundscape - Part 2: Data Collection and Reporting Requirements - What's It All About?jrlr65100% (1)
- T21P Defender 2000 Indicator ESDocument104 paginiT21P Defender 2000 Indicator ESNorberto Martinez100% (1)
- Catalogo PHDocument8 paginiCatalogo PHjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- Mettler Toledo Microbalance PDFDocument82 paginiMettler Toledo Microbalance PDFjrlr650% (1)
- Design and Construction of A Gallium Fixed-Point Blackbody at CENAMDocument3 paginiDesign and Construction of A Gallium Fixed-Point Blackbody at CENAMjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- Measurement Uncertainty StrategiesDocument3 paginiMeasurement Uncertainty Strategiesjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- Astm E2857Document5 paginiAstm E2857jrlr65100% (2)
- Pharma WeighDocument57 paginiPharma WeighSagi Nguyen100% (2)
- USP BalancesDocument4 paginiUSP Balancesjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- AL-Series Analytical and Toploading Balances: Operation ManualDocument23 paginiAL-Series Analytical and Toploading Balances: Operation Manualjrlr65Încă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Properties of Matter PDFDocument4 paginiThermal Properties of Matter PDFgakphysics9Încă nu există evaluări
- ACMV DESIGN: Sample Heat Load Calculation For General Office Meeting RoomDocument5 paginiACMV DESIGN: Sample Heat Load Calculation For General Office Meeting RoomVenkates Adhinarayanan50% (2)
- Dreyer Analysis 1988Document349 paginiDreyer Analysis 1988Yutt WattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wire Wound Fin Tubes-Concept EngineeringDocument2 paginiWire Wound Fin Tubes-Concept EngineeringProcess TiglobalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tom Durkin, Senior Partner Sims-Durkin Associates Indianapolis, IN Tom Durkin, Senior Partner Sims-Durkin Associates Indianapolis, INDocument13 paginiTom Durkin, Senior Partner Sims-Durkin Associates Indianapolis, IN Tom Durkin, Senior Partner Sims-Durkin Associates Indianapolis, INCarlos SamaniegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LabDocument7 paginiLabshriraam asokumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topside - Cold Blowdown ChartDocument1 paginăTopside - Cold Blowdown ChartNKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expansion Valves - Working PrincipleDocument3 paginiExpansion Valves - Working PrinciplePradeep Sukumaran100% (1)
- TIR100-2 Instruction ManualDocument20 paginiTIR100-2 Instruction ManualEmil CalilovÎncă nu există evaluări
- EnergyPlus Weather Converter V7.1.0.010 Statistics for AhmedabadDocument35 paginiEnergyPlus Weather Converter V7.1.0.010 Statistics for Ahmedabadnikita chawlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inorganic Compounds Refrigerants Group 4Document4 paginiInorganic Compounds Refrigerants Group 4HANS PAULO LAYSONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 - Ideal Gas and Specific HeatDocument16 paginiModule 3 - Ideal Gas and Specific Heatclark100% (1)
- Thermal elongation brass liner diameter increase problemDocument20 paginiThermal elongation brass liner diameter increase problemmaria katherine pantojaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPhO 2010 Theo Problem 2Document4 paginiIPhO 2010 Theo Problem 2Cretu NicolaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entropy Examples and EquationsDocument2 paginiEntropy Examples and EquationsRome BautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set 9Document2 paginiSet 9Carlos Alberto Huamaní GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Performance Assessment of Hvac SystemsDocument4 paginiEnergy Performance Assessment of Hvac SystemsBudihardjo Sarwo SastrosudiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparing Filmwise and Dropwise Condensation EfficiencyDocument16 paginiComparing Filmwise and Dropwise Condensation EfficiencyElvin GarashliÎncă nu există evaluări
- JEE Physics AalneDocument1 paginăJEE Physics AalneJUBIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Conditioning Processes and Cycles: Ir. Dr. Sam C. M. HuiDocument36 paginiAir Conditioning Processes and Cycles: Ir. Dr. Sam C. M. HuiMarcelo RibeiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bitzer CompressorDocument40 paginiBitzer CompressorMamdooh Abdallah75% (4)
- Chapter 14 Chemical EquilibriumDocument83 paginiChapter 14 Chemical Equilibriumroxy8marie8chanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HjjooDocument28 paginiHjjooJohn Patrick DagleÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.pressure Volume Work, Reversible Work, Irreversible WorkDocument3 pagini2.pressure Volume Work, Reversible Work, Irreversible WorkKABHISHKA BALAMURUGAN (RA2311043010117)Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Basic Air Conditioner SystemsDocument7 paginiLesson Basic Air Conditioner Systemsmister pogiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChE 110A Problem Set No. 6 Thermodynamic CalculationsDocument2 paginiChE 110A Problem Set No. 6 Thermodynamic CalculationsYodhi PratamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atmospheric Water Vapour ProcessesDocument6 paginiAtmospheric Water Vapour ProcessesBrian chunguliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engg MCQDocument12 paginiMechanical Engg MCQEknath Talele100% (2)
- Thermoelectric EffectsDocument43 paginiThermoelectric EffectsLIAKMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rockhounding for Beginners: Your Comprehensive Guide to Finding and Collecting Precious Minerals, Gems, Geodes, & MoreDe la EverandRockhounding for Beginners: Your Comprehensive Guide to Finding and Collecting Precious Minerals, Gems, Geodes, & MoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Finest Hours: The True Story of the U.S. Coast Guard's Most Daring Sea RescueDe la EverandThe Finest Hours: The True Story of the U.S. Coast Guard's Most Daring Sea RescueEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (21)
- A Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeDe la EverandA Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- When the Earth Had Two Moons: Cannibal Planets, Icy Giants, Dirty Comets, Dreadful Orbits, and the Origins of the Night SkyDe la EverandWhen the Earth Had Two Moons: Cannibal Planets, Icy Giants, Dirty Comets, Dreadful Orbits, and the Origins of the Night SkyEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (7)
- The Fourth Phase of Water: Beyond Solid, Liquid, and VaporDe la EverandThe Fourth Phase of Water: Beyond Solid, Liquid, and VaporEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (8)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeDe la EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (5)
- A Short History of Planet Earth: Mountains, Mammals, Fire, and IceDe la EverandA Short History of Planet Earth: Mountains, Mammals, Fire, and IceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (10)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastDe la EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (31)
- A Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersDe la EverandA Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (111)
- The Water Kingdom: A Secret History of ChinaDe la EverandThe Water Kingdom: A Secret History of ChinaEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (19)
- The Story of Stuff: How Our Obsession with Stuff is Trashing the Planet, Our Communities, and Our Health-and a Vision for ChangeDe la EverandThe Story of Stuff: How Our Obsession with Stuff is Trashing the Planet, Our Communities, and Our Health-and a Vision for ChangeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (37)
- Zondervan Essential Atlas of the BibleDe la EverandZondervan Essential Atlas of the BibleEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (9)
- The Man Who Caught the Storm: The Life of Legendary Tornado Chaser Tim SamarasDe la EverandThe Man Who Caught the Storm: The Life of Legendary Tornado Chaser Tim SamarasEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (21)
- The Witch's Yearbook: Spells, Stones, Tools and Rituals for a Year of Modern MagicDe la EverandThe Witch's Yearbook: Spells, Stones, Tools and Rituals for a Year of Modern MagicEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableDe la EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (22)
- When Life Nearly Died: The Greatest Mass Extinction of All TimeDe la EverandWhen Life Nearly Died: The Greatest Mass Extinction of All TimeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)