Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Engineering Mathematics1
Încărcat de
bkpooja03Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Engineering Mathematics1
Încărcat de
bkpooja03Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
*4161101*
Seat No.
[4161] 101
F.E. Semester I Examination, 2012 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS I (2008 Pattern)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
Instructions : I) Attempt Q. 1 or Q. 2, Q. 3 or Q. 4, Q. 5 or Q. 6 from Section I and Q. 7 or Q. 8, Q. 9 or Q. 10, Q. 11 or Q. 12 from Section II. II) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books. III) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary. IV) Black figures to the right indicate full marks. V) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed. VI) Assume suitable data, if necessary. SECTION I 1. A) Define Rank of the matrix. Find the rank of matrix A by reducing it to its normal form.
1 1 1 0 A = 1 1 2 1 3 1 0 1
B) Show that the system 3x + 4y + 5z = 4x + 5y + 6z = 5x + 6y + 7z = is consistent only when , , are in geometric progression.
P.T.O.
[4161] 101
-2-
*4161101*
C) Verify Cayley Hamilton theorem for the matrix
1 2 2 A = 0 2 1 and hence find A1. 1 2 2
OR 2. A) Find Eigen values and Eigen vectors for the matrix
2 2 0 A = 2 2 0 0 0 1
B) Examine whether the following vectors are linearly dependent. If so find the relation between them x1 = (1, 1, 1, 3), x2 = (1, 2, 3, 4), x 3 = (2, 3, 4, 7). C) Given the transformation
1 x1 4 5 3 Y= 1 2 x 2 1 4 1 x 3
Find the co-ordinates (x1, x2, x3) corresponding to (2, 9, 5) in Y. 3. A) Prove that
1+ cos + i sin i 2 e . = cot 1 cos + i sin 2
B) Solve the equation x7 x4 + x3 1 = 0 by using De Moivres theorem.
*4161101*
-3-
[4161] 101
C) Prove that
1 1 log = log cosec i 1 e 2 + i . 2 2 2
OR 4. A) If z1, z2 and origin represent vertices of an equilateral triangle on the Argand diagram, show that
1 1 1 + 2 = 2 z1 z2 z1z2 B) If cosec + ix = u + iv then prove that 4
(u2 + v2)2 = 2(u2 v2). C) If a = ei, b = ei , c = ei then prove that
(a + b)(b + c)(c + a) = 8 cos . cos . cos . abc 2 2 2
5. A) If y =
1 (x 2)(x 1)2
then find nth order differential coefficient of y w.r.t. x. B) If x = tan (log y) prove that, (1 + x2)yn + 2 + [2(n + 1) x 1]yn + 1 + [n2 n 2]yn = 0.
[4161] 101
-4-
*4161101*
C) Test convergence of the series (any one) : 1)
1 1 1 1 + + + + ..... 2 9 28 65
1 1 3 2 1.3.5 3 2) 2 x + 2 . 4 x + 2.4.6 x + .....
OR 6. A) Find nth order differential coefficient of y w.r.t. x
1+ x2 1 y = tan x
1
B) If y = (sin1x)2 then prove that (1 x2) yn + 2 (2n + 1)xyn + 1 n2yn = 0. C) Test convergence of the series (any one) : 1) 2)
1 2 3 4 + + ..... 2 5 10 17
5 6
n=1
2nn! nn
SECTION II 7. A) Using Taylors theorem express (x 2) 3(x 2) + 4(x 2) + 5 in powers of x. B) Expand (1 + sin x)
1 2
4 3 2
5 5
upto x .
*4161101*
-5-
[4161] 101
C) Solve any one :
sinh x lim 1) Evaluate x0 x
1 x2
2) Evaluate lim 1
x 2
cos2 x e2x 2xe
OR
x x x2 x4 = 1 + + ... 8. A) Show that x 2 12 720 e 1
B) Expand tan x in powers of (x 1) as far as the term in (x 1)3. C) Solve any one :
sin x. sin1 x x 2 lim 1) Evaluate x0 x6 a cos x a + bx2 1 lim = 2) Find a and b if x0 4 12 x
5 6
9. Attempt any two : A) If f(x, y) =
1 1 log x log y + + then prove that 2 2xy x x2 + y2
16
xfx + yfy + 2f = 0 .
B) If x = r cosh , y = r sinh then show that (x y) (zx zy) = rzr z
[4161] 101
-6-
*4161101*
C) If u = log (x3 + y3 x2y xy2) prove that uxx + 2uxy + uyy =
4 (x + y)2
OR 10. Solve any two : A) If x = u tan v, y = u sec v prove that (ux)y (vx)y = (uy)x (vy)x. B) If u = f(x2 y2, y2 z2, z2 x2) show that
1 1 1 ux + uy + uz = 0 . x y z
16
C) If xm + y m = bm then prove that
d2 y xm2 = (m 1)bm 2m1 dx 2 y
11. A) If u = x + y + z, uv = y + z, uvw = z, show that
(x, y, z) = u2v (u, v, w)
6 6
B) Discuss the maxima and minima of f(x, y) = x3 + y3 3 axy. C) Examine for functional dependence u =
1 1 x+y , v = tan x + tan y . Find the relation 1 xy between them if functionally dependent.
OR
*4161101*
-7-
[4161] 101
12. A) For the transformation x = u(1 v), y = uv prove that
(x, y) (u, v) . = 1. (u, v ) (x, y)
B) Divide 120 into three parts so that the sum of their products taken two at a time shall be maximum. C) Find the percentage error in the area of an ellipse when the errors of 2% and 3% are made in measuring its major and minor axis respectively.
B/I/12/21,445
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- s201 Mathematics IDocument2 paginis201 Mathematics IbhkedarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics IIDDocument2 paginiMathematics IIDSreejan ShrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- r05010102 Mathematics IDocument8 paginir05010102 Mathematics ITarun HanchateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Page 1Document3.035 paginiPage 1Dinesh PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics - I MDocument3 paginiMathematics - I MSitesh SilÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMA2891-Homework 1: Due On March 25th, 2013, Monday On ClassDocument1 paginăAMA2891-Homework 1: Due On March 25th, 2013, Monday On ClassYiu HahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anna University Maths Question BankDocument8 paginiAnna University Maths Question Bankcadburyz_sin935040Încă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Further TransDocument4 paginiTutorial Further TransGileShopping CrewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Mathematics-1-2008 PatternDocument7 paginiEngineering Mathematics-1-2008 PatternPravin SawantÎncă nu există evaluări
- c1bs02 - c1902 MathematicsDocument2 paginic1bs02 - c1902 MathematicsbhkedarÎncă nu există evaluări
- M1211 PDFDocument31 paginiM1211 PDFYogaisan RamasawmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PENANG 2013 STPM TRIAL PAPERS For Mathematics T TERM 2Document8 paginiPENANG 2013 STPM TRIAL PAPERS For Mathematics T TERM 2SK100% (3)
- Anna University Maths Question BankDocument56 paginiAnna University Maths Question BankabhynayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- M 2Document9 paginiM 2raviteja1840Încă nu există evaluări
- 20 11 2023 Linear Algebra ExercisesDocument11 pagini20 11 2023 Linear Algebra Exercisesnshimiyimanac53Încă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Mathematics II Model Question Paper StudyhauntersDocument3 paginiEngineering Mathematics II Model Question Paper StudyhauntersSriram JÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engg. Mathematics I (MAT - 101) RCSDocument2 paginiEngg. Mathematics I (MAT - 101) RCSArun D PaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time: 3 Hours 06 - Mathematics - July 2008 Marks: 100 PG - 1Document6 paginiTime: 3 Hours 06 - Mathematics - July 2008 Marks: 100 PG - 1SURAJ SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- t1102-t2102 Math I 31 12 13Document3 paginit1102-t2102 Math I 31 12 13api-275877530Încă nu există evaluări
- MSC Mas6002, Introductory Material Block C Mathematical Methods ExercisesDocument11 paginiMSC Mas6002, Introductory Material Block C Mathematical Methods ExercisesCourtney WilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quadratic EquationsDocument17 paginiQuadratic EquationsCgzam ZamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09a1bs01 Mathematics 1Document5 pagini09a1bs01 Mathematics 1Ansh PratapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tulsiramji Gaikwad-Patil College of Engineering & Technology Department of Computer Science & Engineering Session 2012-2013 Question BankDocument11 paginiTulsiramji Gaikwad-Patil College of Engineering & Technology Department of Computer Science & Engineering Session 2012-2013 Question BankMinhaz AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Et 101 (A)Document4 paginiEt 101 (A)murugan_collegemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Paper of 2Nd Year Mathematics: UNDER THE SUPERVISION of Professors & LecturersDocument2 paginiStudy Paper of 2Nd Year Mathematics: UNDER THE SUPERVISION of Professors & LecturersDanish Naeem BhattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ques. Bank E Maths-III PDFDocument8 paginiQues. Bank E Maths-III PDFPrakharGuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Engineering Mathematics I SemDocument2 paginiIntroduction To Engineering Mathematics I Semshubhambani45Încă nu există evaluări
- c1bs01 Mathematics I Set1Document2 paginic1bs01 Mathematics I Set1bhkedarÎncă nu există evaluări
- MA2111 M1 May 2009 QP PDFDocument4 paginiMA2111 M1 May 2009 QP PDFSriram JÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATH015 Autumn2015 Assignments Final Exam Practice QuestionsDocument17 paginiMATH015 Autumn2015 Assignments Final Exam Practice QuestionsMohamadFadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- M 2 QuestionBankDocument10 paginiM 2 QuestionBankGiridhar Every TimeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Question Paper Subject: Mathematics Class: Senior Secondary Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100Document22 paginiSample Question Paper Subject: Mathematics Class: Senior Secondary Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100Amar KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat NoDocument9 pagini3 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat Nokaran11deshmukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ma2161 QBDocument10 paginiMa2161 QBRaj MygameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics-I, Sem-I Practice Questions On All ModulesDocument12 paginiMathematics-I, Sem-I Practice Questions On All Modulesaditya2189rdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quadratic EquationsDocument18 paginiQuadratic EquationsErwani KamaruddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructions: Answer ALL Questions by Placing A Thick Horizontal Line OnDocument4 paginiInstructions: Answer ALL Questions by Placing A Thick Horizontal Line OnMillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalyst Academy Mathematics XII PaperDocument3 paginiCatalyst Academy Mathematics XII PaperMohan LalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monitoring Exam Preparation Questions / 8th GradesDocument9 paginiMonitoring Exam Preparation Questions / 8th GradesUali IztoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- bt1R0721 21 11 09rahulDocument23 paginibt1R0721 21 11 09rahulVilluri SudheerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics March 2008 EngDocument7 paginiMathematics March 2008 EngPrasad C MÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Puc Question Papers of Mathematics 1997-2010Document65 pagini2nd Puc Question Papers of Mathematics 1997-2010Mohan Kumar PÎncă nu există evaluări
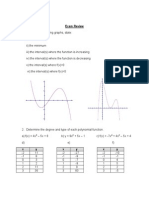
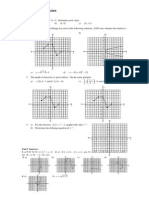
- Exam ReviewDocument8 paginiExam ReviewvasdevharishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Question Paper - Applied Mathematics-12054Document4 paginiSample Question Paper - Applied Mathematics-12054Jackson Anthony100% (1)
- Assignment#01. CalculusDocument3 paginiAssignment#01. CalculusAbdul Rehman AkmalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Code: 9ABS301 II B.Tech I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, November 2011Document4 paginiCode: 9ABS301 II B.Tech I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, November 2011sivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 1Document4 paginiProblem Set 1Ray Fellix GanardiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cse-III-Engineering Mathematics - III (10mat31) - Question PaperDocument4 paginiCse-III-Engineering Mathematics - III (10mat31) - Question PaperVenkatesh Prasad0% (1)
- Maths j11Document4 paginiMaths j11jayantsingh13Încă nu există evaluări
- Exam Review 11 Q&ADocument5 paginiExam Review 11 Q&Aesn_kÎncă nu există evaluări
- c1301 Mathematics IDocument2 paginic1301 Mathematics ISrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- C-16 C-102 Sbtet-Mar2018Document3 paginiC-16 C-102 Sbtet-Mar2018DrGudimella Vrk SagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.SC (Maths)Document32 paginiB.SC (Maths)vrsafeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quadratic Equation: WorksheetDocument3 paginiQuadratic Equation: WorksheetHarsha PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03004-03006-03007 S1-Complex Analysis and Numerical Methods-QPDocument3 pagini03004-03006-03007 S1-Complex Analysis and Numerical Methods-QPARAV PRAJAPATIÎncă nu există evaluări
- April 2006Document90 paginiApril 2006செபா செல்வாÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)De la EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Încă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsDe la EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageDe la EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesDe la EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q. Marks. 1. 2. 3. Total : Minor Examination PYL556Document7 paginiQ. Marks. 1. 2. 3. Total : Minor Examination PYL556asdfghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elementary Linear AlgebraDocument20 paginiElementary Linear AlgebraArviena JasmineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vector Matrix Tensor ReviewDocument13 paginiVector Matrix Tensor ReviewmuradbashirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors That Affect Gas PressureDocument5 paginiFactors That Affect Gas PressureYing FlaviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 4: Conservation of Momentum: P P M V +M V M V +M VDocument4 paginiLab 4: Conservation of Momentum: P P M V +M V M V +M VMark Carr0% (1)
- Atkin 12001 Molekular Spectroscopy 003Document5 paginiAtkin 12001 Molekular Spectroscopy 003Nikke ArdilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 19 A2 Questions Name .. /40 1.: (Total 6 Marks)Document4 paginiWeek 19 A2 Questions Name .. /40 1.: (Total 6 Marks)Solace HusseinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-Vi Multi Degree of Freedom SystemsDocument37 paginiChapter-Vi Multi Degree of Freedom SystemsAHMEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 - Mechanical Vibration - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument13 paginiUnit 4 - Mechanical Vibration - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inJitendar SahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schedule 325Document3 paginiSchedule 325Samuel Alfred ForemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matrices PDFDocument24 paginiMatrices PDFJOHN CHARLASÎncă nu există evaluări
- De Adv - Math Set BDocument5 paginiDe Adv - Math Set BDEATH WISHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Vampire: Collapse-Free Action at A Distance by The Photon Annihilation OperatorDocument4 paginiQuantum Vampire: Collapse-Free Action at A Distance by The Photon Annihilation Operatorsad100% (1)
- Operator Theory On Hilbert SpacesDocument24 paginiOperator Theory On Hilbert SpacesFUN FactorÎncă nu există evaluări
- An A Fun BibDocument4 paginiAn A Fun BibJuan Ricardo PradaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q. Mechanics Problem SolutionDocument2 paginiQ. Mechanics Problem SolutionAtif ImamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resta Lecture NotesDocument112 paginiResta Lecture NotesArnabAdhikaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathieu EquationDocument69 paginiMathieu EquationVivek SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Mechanics NET-JRF June 2011 - June 2014Document32 paginiQuantum Mechanics NET-JRF June 2011 - June 2014Abhishek UpadhyayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nassim Haramein Answers His CriticsDocument7 paginiNassim Haramein Answers His Criticsr.viola9101Încă nu există evaluări
- Chamseddine, Ali Consani, Caterina Higson, Nigel Khalkhali, Masoud Moscovici, Henri Yu, Guoliang (2019) - Advances in Noncommutative GeometryDocument753 paginiChamseddine, Ali Consani, Caterina Higson, Nigel Khalkhali, Masoud Moscovici, Henri Yu, Guoliang (2019) - Advances in Noncommutative GeometryTomás CampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spivak Solucionario 2Document12 paginiSpivak Solucionario 2diego2193Încă nu există evaluări
- t13 PDFDocument8 paginit13 PDFMaroshia MajeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional Analysis - Eigenfunctions of The Helmholtz Equation in Toroidal Geometry - Mathematics Stack ExchangeDocument3 paginiFunctional Analysis - Eigenfunctions of The Helmholtz Equation in Toroidal Geometry - Mathematics Stack ExchangewongkiyuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7.3 Vertical CurvesDocument8 pagini7.3 Vertical CurvesJB RSNJNÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Darwin LagrangianDocument4 paginiOn Darwin LagrangianManu SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Robotics and Automation ME-465 Lec 3: Dr. Sara AliDocument58 paginiRobotics and Automation ME-465 Lec 3: Dr. Sara Alimuhammad usamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Ii : Mit OpencoursewareDocument5 pagini5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Ii : Mit Opencoursewaresanskarid94Încă nu există evaluări
- How To Solve A Linear System of Equations Using A Quantum ComputerDocument35 paginiHow To Solve A Linear System of Equations Using A Quantum ComputerMuhammad Adnan KhalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classical Mechanics Notes (4 of 10)Document30 paginiClassical Mechanics Notes (4 of 10)OmegaUserÎncă nu există evaluări