Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
BIO1 - Plantlike Protists
Încărcat de
dacspinlacDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
BIO1 - Plantlike Protists
Încărcat de
dacspinlacDrepturi de autor:
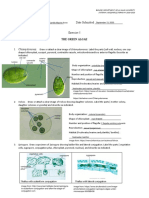
PLANTLIKE PROTISTS The Unicellular Algae
Euglenophyta Pyrrophyta Chrysophyta Bacillariophyta Ecology of Unicellular Algae
Chlorophyll & Accessory Pigments
Why plantlike?
Most contain chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis May be used to classify unicellular algae
Chlorophyll & Accessory Pigments
Water vs. light absorption
Sunlight passes through H2O, E absorbed by H2O depth dimmer, bluer light
Chlorophyll & Accessory Pigments
Chlorophyll a
Found in plants Captures red & violet light Other forms (b, c) absorb different l of light
Chlorophyll & Accessory Pigments
Accessory pigments
Absorb light at different l than chlorophyll Gives algae wide range of colors Carotenoids yellow-orange Xanthophylls brownish Phycobilins red, blue
PHYLUM EUGLENOPHYTA (~800 spp.) Euglenophytes/Euglenoids
Predominantly green: chl a, chl b, carotenoids, xanthophylls Genus Euglena
Habitat: freshwater Size: 50 mm Nutrition: photoautroph/ heterotroph
Why is it advantageous for Euglena to be flexible in its mode of nutrition?
PHYLUM EUGLENOPHYTA (~800 spp.) Euglenophytes/Euglenoids
Parts of Euglena:
Flagella Spins Euglena through H2O Eyespot Reddish pigment Detects sunlight Paramylon bodies Stores surplus food Pellicle CM folded into ribbonlike ridges w/ microtubules
PHYLUM EUGLENOPHYTA (~800 spp.) Euglenophytes/Euglenoids
Parts of Euglena:
Flagella Spins Euglena through H2O Eyespot Reddish pigment Detects sunlight Paramylon bodies Stores surplus food Pellicle CM folded into ribbonlike ridges w/ microtubules
Phacus
Why is it advantageous for Euglena to have a tough & flexible pellicle?
PHYLUM EUGLENOPHYTA (~800 spp.) Euglenophytes/Euglenoids
Parts of Euglena:
Flagella Spins Euglena through H2O Eyespot Reddish pigment Detects sunlight Paramylon bodies Stores surplus food Pellicle CM folded into ribbonlike ridges w/ microtubules
Why is it advantageous for Euglena to have a tough & flexible pellicle?
PHYLUM EUGLENOPHYTA (~800 spp.) Euglenophytes/Euglenoids
Reproduction
Binary fission
PHYLUM PYRROPHYTA (~1,100 spp.) Dinoflagellates
Predominantly brown: chl a, chl c, carotenoids, xanthophylls (fucoxanthin) Habitat
Marine, freshwater
Nutrition
Some photosynthetic, some heterotrophic Store food as starch
Reproduction
Binary fission
Gonyaulax Causative agent of red tide
PHYLUM PYRROPHYTA (~1,100 spp.) Dinoflagellates
Parts
CW Two thick plates Cellulose Flagella Wrapped in grooves of plates Causes spinning movement Gr. dinos, whirling
Gonyaulax Causative agent of red tide
PHYLUM PYRROPHYTA (~1,100 spp.) Dinoflagellates
Unique characteristics
Bioluminescent When agitated Pyrrophyta, fire plants No histones The only eukaryotes w/o histones
Noctilluca scintillans, sea sparkle
PHYLUM CHRYSOPHYTA (~850 spp.)
Yellow-Green and Golden-Brown Algae
Predominantly golden olive: chl a, chl c, carotenoids, xanthophylls
Gr. chrysos, golden; Chrysophyta, golden plants
Dinobryon
PHYLUM CHRYSOPHYTA (~850 spp.)
Yellow-Green and Golden-Brown Algae
Habitat
Mostly freshwater
Nutrition
Photoautotroph/ heterotroph Store food as laminarin
Reproduction
Most asexual, some sexual
Synura
PHYLUM BACILLARIOPHYTA (~10,000 spp.) Diatoms
Among the most abundant organisms on Earth
PHYLUM BACILLARIOPHYTA (~10,000 spp.) Diatoms
Predominantly olive brown: chl a, chl c, carotenoids, xanthophylls Habitat
Marine, freshwater
Nutrition
Store food as oil, sometimes as leucosin (CH2O)
Reproduction
Binary fission
PHYLUM BACILLARIOPHYTA (~10,000 spp.) Diatoms
Cell wall
Thin, delicate, rich in SiO2 (main ingredient of glass) Shaped like two sides of a Petri dish W/ fine lines and patterns
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Phytoplankton
Microscopic, photosynthetic organisms that float near the surface of oceans, ponds, lakes
Gr. planktos, wandering
Most unicellular algae Base of food chain; allows diversity of aquatic life Carries out ~1/2 of the photosynthesis on Earth
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Phytoplankton
Microscopic, photosynthetic organisms that float near the surface of oceans, ponds, lakes
Gr. planktos, wandering
Most unicellular algae Base of food chain; allows diversity of aquatic life
Carries out ~1/2 of the photosynthesis on Earth
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Phytoplankton
Microscopic, photosynthetic organisms that float near the surface of oceans, ponds, lakes
Gr. planktos, wandering
Ceratium
Most unicellular algae Base of food chain; allows diversity of aquatic life
Arachnodiscus
Carries out ~1/2 of the photosynthesis on Earth
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Phytoplankton
Microscopic, photosynthetic organisms that float near the surface of oceans, ponds, lakes
Gr. planktos, wandering
Most unicellular algae Base of food chain; allows diversity of aquatic life
Triceratium
Carries out ~1/2 of the photosynthesis on Earth
Actinocyclus
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Phytoplankton
Microscopic, photosynthetic organisms that float near the surface of oceans, ponds, lakes
Gr. planktos, wandering
Most unicellular algae Base of food chain; allows diversity of aquatic life
Baltic chain diatoms
Melosira
Carries out ~1/2 of the photosynthesis on Earth
Auliscisculptus ovalis
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Phytoplankton
Microscopic, photosynthetic organisms that float near the surface of oceans, ponds, lakes
Gr. planktos, wandering
Pleurosigma
Most unicellular algae Base of food chain; allows diversity of aquatic life
Carries out ~1/2 of the photosynthesis on Earth
Plagiogramma oblongata
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Phytoplankton
Microscopic, photosynthetic organisms that float near the surface of oceans, ponds, lakes
Gr. planktos, wandering
Navicula
Most unicellular algae Base of food chain; allows diversity of aquatic life
Navicula
Carries out ~1/2 of the photosynthesis on Earth
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Symbiotic Algae
Some corals have intercellular dinoflagellates
Dinoflagellates feed on waste products of corals, then serve as main food source for reef communities Coral bleaching
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Symbiotic Algae
Some corals have intercellular dinoflagellates
Dinoflagellates feed on waste products of corals, then serve as main food source for reef communities Coral bleaching
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Symbiotic Algae
Tridacna gigas, giant clam
Mantle populated by photosynthetic dinoflagellates
with zooxanthellae
Tridacna gigas
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Algal blooms
Sewage discharge Rapid heterotroph growth
Good: Recycles sewage and other waste material May be used as an indicator sp. of organic pollution Bad: Algal bloom Depletes water of nutrients Decomposition depletes DO
What does indicator species mean?
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Algal blooms
Pyrodinium bahamense
var compressum
Causative agent of red tide Produces dangerous toxin Shellfish (clam, oysters, etc.) experience biomagnification Eating infected shellfish causes serious illness, paralysis, death Not all are toxic
Why red tide?
ECOLOGY OF UNICELLULAR ALGAE Algal blooms
Pyrodinium bahamense
var compressum
Causative agent of red tide Produces dangerous toxin Shellfish (clam, oysters, etc.) experience biomagnification Eating infected shellfish causes serious illness, paralysis, death Not all are toxic
Why red tide?
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- BIO1 - MolluscaDocument22 paginiBIO1 - MolluscadacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO1 - ArthropodaDocument19 paginiBIO1 - ArthropodadacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO1 - EchinodermataDocument22 paginiBIO1 - EchinodermatadacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO3 - EnzymesDocument11 paginiBIO3 - EnzymesdacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO3 - DNA ReplicationDocument9 paginiBIO3 - DNA ReplicationdacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO1 - Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, AnnelidaDocument15 paginiBIO1 - Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, AnnelidadacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO3 - Transcription and TranslationDocument6 paginiBIO3 - Transcription and TranslationdacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omnis Cellula e CellulaDocument9 paginiOmnis Cellula e CelluladacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genes and ChromosomesDocument7 paginiGenes and ChromosomesdacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incomplete Dominance, Codominance, Multiple Alleles, Polygenic InheritanceDocument7 paginiIncomplete Dominance, Codominance, Multiple Alleles, Polygenic InheritancedacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW: Keywords For Cell ReproductionDocument1 paginăHW: Keywords For Cell ReproductiondacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Discussed in Campbell Biology, 9 EdDocument5 paginiAs Discussed in Campbell Biology, 9 Eddacspinlac0% (1)
- As Discussed in Campbell Biology, 9 Ed. and in Essentials of Genetics (Klug and Cummings), 3 EdDocument20 paginiAs Discussed in Campbell Biology, 9 Ed. and in Essentials of Genetics (Klug and Cummings), 3 EddacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio3 Guidelines SY2012-2013Document2 paginiBio3 Guidelines SY2012-2013dacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument39 paginiCell Structure & Functiondacspinlac100% (9)
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument44 paginiClassification of Living ThingsdacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio1 Guidelines SY2012-2013 PDFDocument3 paginiBio1 Guidelines SY2012-2013 PDFdacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio1 1stQtr Outline SY12-13Document1 paginăBio1 1stQtr Outline SY12-13dacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historical Development of Evolutionary ThoughtDocument33 paginiHistorical Development of Evolutionary Thoughtdacspinlac100% (1)
- Development of The Cell TheoryDocument8 paginiDevelopment of The Cell Theorydacspinlac100% (1)
- Darwin's Theory of EvolutionDocument42 paginiDarwin's Theory of Evolutiondacspinlac100% (1)
- Modern Evolutionary TheoryDocument18 paginiModern Evolutionary TheorydacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evidences of EvolutionDocument31 paginiEvidences of EvolutiondacspinlacÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Biotechnology Assignment 1Document6 paginiBiotechnology Assignment 1Audrey LeonnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mass Cultivation of Freshwater MicroalgaeDocument13 paginiMass Cultivation of Freshwater MicroalgaeIemazh Sakinah100% (1)
- Enterpenurship ProjectDocument21 paginiEnterpenurship ProjectMoater ImranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protein Contents of Edible Algae in Upper MyanmarDocument38 paginiProtein Contents of Edible Algae in Upper MyanmarA MNyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Whittaker 1969Document11 paginiWhittaker 1969Cole LufaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Kingdom FlowchartDocument11 paginiPlant Kingdom FlowchartVaibhav Chauhan100% (1)
- Formulir AlgaeDocument70 paginiFormulir AlgaeFaiz HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kerala +1 Botany Focus Area Question Bank - Plant KingdomDocument2 paginiKerala +1 Botany Focus Area Question Bank - Plant KingdomMolly KuttyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cyanophyceae by Dr. S.N. SureshDocument4 paginiCyanophyceae by Dr. S.N. SureshdrsnsureshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eucheuma Denticulatum PDFDocument2 paginiEucheuma Denticulatum PDFMatthewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spirulina Cultivation: A Review: January 2012Document16 paginiSpirulina Cultivation: A Review: January 2012sakalidhasavasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- FAO Report Global Seaweed 2018Document125 paginiFAO Report Global Seaweed 2018Cynthia DewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protists and FungiDocument25 paginiProtists and Fungichasing catÎncă nu există evaluări
- G GopakumarDocument11 paginiG GopakumarStalinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alage Biomass - Characetrisics and Application (Katarzyna)Document146 paginiAlage Biomass - Characetrisics and Application (Katarzyna)Eu Be Rahat100% (1)
- Gast Caron 2001 Photosymbiotic Associations Planktic Forams RadiolariaDocument7 paginiGast Caron 2001 Photosymbiotic Associations Planktic Forams RadiolariaforaminsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument8 paginiKingdom PlantaeSurbhi GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- West, G.S. The British Freshwater AlgaeDocument391 paginiWest, G.S. The British Freshwater Algaeshelfedge100% (1)
- Studies On The Occurrence of Phytoplankton Near TheDocument6 paginiStudies On The Occurrence of Phytoplankton Near TheInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Do We Classify The Living WorldDocument5 paginiHow Do We Classify The Living WorldAnonymous HXLczq3Încă nu există evaluări
- Borowitzka Et Al 2016 The Physiology of Microalgae, The Cell Cycle of MicroalgaeDocument44 paginiBorowitzka Et Al 2016 The Physiology of Microalgae, The Cell Cycle of MicroalgaeKarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algae, Fungi and ProtozoaDocument53 paginiAlgae, Fungi and ProtozoaMirza Salman BaigÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9Document3 pagini9Ali Ghahreman67% (3)
- Important Questions For NEET Biology 2023 - Plant KingdomDocument15 paginiImportant Questions For NEET Biology 2023 - Plant Kingdomnekmohammadkhan10Încă nu există evaluări
- AKU EB - Biology - XI - Paper I - 2013 - MayDocument8 paginiAKU EB - Biology - XI - Paper I - 2013 - MayAnas FaheemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pemanfaatan Copepoda Oithona SP SebagaiDocument386 paginiPemanfaatan Copepoda Oithona SP SebagaihajijojonÎncă nu există evaluări
- NAME - Date SubmittedDocument3 paginiNAME - Date SubmittedvlajeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monitoring Pond Water Quality To Improve Shrimp and Fish ProductionDocument3 paginiMonitoring Pond Water Quality To Improve Shrimp and Fish ProductionInternational Aquafeed magazineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control and Monitor Algae With The MPC-BuoyDocument12 paginiControl and Monitor Algae With The MPC-BuoyLulzim LumiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam in Fishery Arts 3Document4 paginiExam in Fishery Arts 3Paul Espinosa100% (5)