Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Untitled 1
Încărcat de
Mychal Dillan VeedorDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Untitled 1
Încărcat de
Mychal Dillan VeedorDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
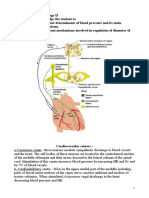
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Central Nervous System Medulla Oblongata; relays motor and sensory impulses between other
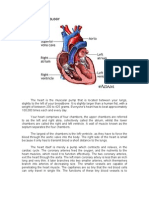
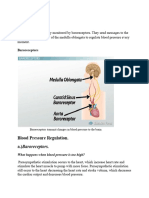
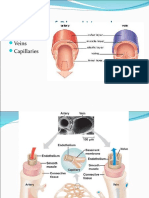
parts of the brain and the spinal cord. Reticular formation (also in pons, midbrain, and diencephalon) functions in consciousness and arousal. Vital centers regulate heartbeat, breathing (together with pons) and blood vessel diameter. Hypothalamus; controls and intergrates activities of the autonomic nervous system and pituitary gland. Regulates emotional and behavioral patterns and circadian rhythms. Controls body temperature and regulates eating and drinking behavior. Helps maintain the waking state and establishes patterns of sleep. Produces the hormones oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone. Cardiovascular System Baroreceptor, pressure-sensitive sensory receptors, are located in the aorta, internal carotid arteries, and other large arteries in the neck and chest. They send impulses to the cardiovascular center in the medulla oblongata to help regulate blood pressure. The two most important baroreceptor reflexes are the carotid sinus reflex and the aortic reflex. Chemoreceptors, sensory receptors that monitor the xhemical composition of blood, are located close to the baroreceptors of the carotid sinus and the arch of the aorta in small structures called carotid bodies and aortic bodies, respectively. These chemoreceptors detect changes in blood level of O2, CO2, and H+. Renal System Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone system. When blood volume falls or blood flow to the kidneys decreases, juxtaglomerular cells in the kidneys secrete renin into the bloodstream. In sequence, renin and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) act on their substrates to produce the active hormone angiotensin II, which raises blood pressure in two ways. First, angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor; it raises blood pressure by increasing systemic vascular resistance. Second, it stimulates secretion of aldosterone, which increases reabsorption of sodium ions and water by the kidneys. The water reabsorption increases total blood volume, which increases blood pressure. Antidiuretic hormone. ADH is produced by the hypothalamus and released from the posterior pituitary in response to dehydration or decreased blood volume. Among other actions, ADH causes vasoconstriction, which increases blood pressure. Atrial Natriuretic Peptide. Released by cells in the atria of the heart, ANP lowers blood pressure by causing vasodilation and by promoting the loss of salt and water in the urine, which reduces blood volume.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System - RAASDocument3 paginiThe Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System - RAASrienz nicnic peraltaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone SystemDocument3 paginiRenin Angiotensin Aldosterone SystemDivya Ranasaria100% (1)
- Renin - Angiotensin System RAS Renin - Angiotensin-Aldosterone System RaasDocument3 paginiRenin - Angiotensin System RAS Renin - Angiotensin-Aldosterone System RaasReynaKatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocument15 paginiCardiovascular DrugsMeilynne Gem C. SonjacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVS Lect 6 Blood Pressure, PathophysiologyDocument13 paginiCVS Lect 6 Blood Pressure, PathophysiologySherwan R Shal100% (5)
- Indian Horse QuestionsDocument2 paginiIndian Horse Questionslee0% (1)
- Test Bank Endocrine PDFDocument29 paginiTest Bank Endocrine PDFWenzy Cruz100% (3)
- Essentials of Understanding Psychology 10th Edition Feldman Solutions Manual 1Document23 paginiEssentials of Understanding Psychology 10th Edition Feldman Solutions Manual 1patricia100% (36)
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument6 paginiCardiovascular PhysiologyatefmaboodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orthostatic Hypotension: Causes, Tests, and Treatment OptionsDe la EverandOrthostatic Hypotension: Causes, Tests, and Treatment OptionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Free Knitted ToysDocument20 pagini5 Free Knitted ToysMihaiCamelia0% (2)
- Brioche Cat Hat by Natasha SillsDocument4 paginiBrioche Cat Hat by Natasha SillsMythili SHIVKUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology of Blood PressureDocument4 paginiPhysiology of Blood PressureNoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy&Physiology, Pathophysiology (Julie)Document6 paginiAnatomy&Physiology, Pathophysiology (Julie)Camille Diane AgoncilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peer TutorialDocument11 paginiPeer Tutorialmashe1Încă nu există evaluări
- Blood Pressure Physio AssigmentDocument16 paginiBlood Pressure Physio AssigmentNoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Pressure PhysiologyDocument15 paginiBlood Pressure PhysiologyNoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 5-14 Notes 3 (Dragged) 2Document1 paginăWeek 5-14 Notes 3 (Dragged) 2navkkirangillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baroreceptors and Therefore The Sympathetic SystemDocument5 paginiBaroreceptors and Therefore The Sympathetic SystemS GÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVS 5Document6 paginiCVS 5MayankÎncă nu există evaluări
- KMBDocument22 paginiKMBAnjelia NovrianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Pressure SummaryDocument7 paginiBlood Pressure SummaryNancy You100% (1)
- Special Circulation - UnpriDocument44 paginiSpecial Circulation - UnpriAnnisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Secretion of Potassium Ions Into The NephronDocument1 paginăSecretion of Potassium Ions Into The NephronDoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angiotensin II: Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument2 paginiAngiotensin II: Autonomic Nervous SystemRafael AhumadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regulation of Blood PressureDocument5 paginiRegulation of Blood PressureKing kakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANP 1105 Blood VesselsDocument72 paginiANP 1105 Blood VesselsMathios TigerosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology Cardiovascular System The HeartDocument6 paginiAnatomy and Physiology Cardiovascular System The Heartmark OrpillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs Acting On Cardiovascular System-FinalsDocument125 paginiDrugs Acting On Cardiovascular System-FinalsPrincess C. SultanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood GlucoseDocument8 paginiBlood GlucoseT SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy & Physiologyc: Y CC CC CC C C CCC CCCCC C CDocument4 paginiAnatomy & Physiologyc: Y CC CC CC C C CCC CCCCC C CroothanngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharma Notes 17-18Document4 paginiPharma Notes 17-18flixiexpressÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Pressure RegulationDocument4 paginiBlood Pressure Regulationmutisya.mathuvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- .SHOCK, Alice - 1704638750000Document12 pagini.SHOCK, Alice - 1704638750000Nakintu AliceÎncă nu există evaluări
- GroupWorkSOLERANTOQUEPLAZA MCNSG3Document4 paginiGroupWorkSOLERANTOQUEPLAZA MCNSG3Leah AntoqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gland (Or Hypophysis), A Bean-Sized Organ Suspended From It by A Stem CalledDocument3 paginiGland (Or Hypophysis), A Bean-Sized Organ Suspended From It by A Stem CalledJoyce Ann CumlatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 79ed041a-a32f-4b59-809c-e28fe2bc77e1Document89 pagini79ed041a-a32f-4b59-809c-e28fe2bc77e1NKAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 24 Sistem Homeostatis Jantung DR - NiaDocument22 pagini24 Sistem Homeostatis Jantung DR - NiaSurya ArhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Pressure RegulationDocument3 paginiBlood Pressure RegulationiMaibelle BelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homeostasis: Homoios - "The Same" Stasis - "Standing" Homeostasis - "Standing or Staying The Same"Document6 paginiHomeostasis: Homoios - "The Same" Stasis - "Standing" Homeostasis - "Standing or Staying The Same"Jayrelle D. SafranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thirst - Group 4Document15 paginiThirst - Group 4carmelalouis.trinidadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart FailureDocument42 paginiHeart FailureParsa EbrahimpourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short-Term Regulation of Blood PressureDocument5 paginiShort-Term Regulation of Blood PressureRae OkonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular Regulatory MechanismDocument34 paginiCardiovascular Regulatory Mechanismhia natasyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology HeartDocument11 paginiAnatomy and Physiology HeartKier_John_Kora_9076Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 8 - Lecture Notes For StudentsDocument22 paginiWeek 8 - Lecture Notes For StudentsLoren SarigumbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cvs Regulation Part 2Document57 paginiCvs Regulation Part 2NyamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)Document4 pagini10 Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)saleem9242ssÎncă nu există evaluări
- L14Document2 paginiL14MilenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 2 Blpressoureoduph - 20 Februari 2012week 2 Blpressoureoduph - 20 Februari 2012Document43 paginiWeek 2 Blpressoureoduph - 20 Februari 2012week 2 Blpressoureoduph - 20 Februari 2012Maria Dini AdmiratiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec-5 The Posterior Pituitary GlandDocument39 paginiLec-5 The Posterior Pituitary GlandMowlidAbdirahman Ali madaaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 Blood As A Transport MediumDocument43 paginiUnit 3 Blood As A Transport MediumKemoy FrancisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 25circulation Part 3Document15 pagini25circulation Part 3Jaydave PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood PressureDocument26 paginiBlood PressureEniola DaramolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument78 paginiAntihypertensive DrugsOsannah Irish InsongÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVS PharmacologyDocument19 paginiCVS Pharmacologymug ashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control of Blood Flow: After Reading This Chapter You Should Be Able ToDocument12 paginiControl of Blood Flow: After Reading This Chapter You Should Be Able ToDrbee10Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 33 HypertensionDocument5 paginiChapter 33 HypertensiongytmbiuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BioA430 Chapter 2 Vs RGDocument65 paginiBioA430 Chapter 2 Vs RGIbrahim MarmalÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Endocrine SystemDocument13 paginiThe Endocrine SystemThenmozhi SivajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Introduction To HypertensionDocument14 paginiGeneral Introduction To HypertensionpragnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Biology PPT Darryl Arcillas & Dency TuastumbanDocument14 paginiGeneral Biology PPT Darryl Arcillas & Dency TuastumbanApril Rose Caquilala GalauraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood PressureDocument15 paginiBlood PressureKiran DeviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Project FinalDocument68 paginiBio Project Finalsourajit royÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular Control: Marinette Rumusud-Jambaro, MD Diplomate in Internal MedicineDocument48 paginiCardiovascular Control: Marinette Rumusud-Jambaro, MD Diplomate in Internal MedicineVerlette Roselle Aguisanda LizardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osteomyelitis IntroDocument2 paginiOsteomyelitis IntroMychal Dillan VeedorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructor's Guide To Table Tennis PDFDocument36 paginiInstructor's Guide To Table Tennis PDFKhanh TranÎncă nu există evaluări
- CiprofloxacinDocument3 paginiCiprofloxacinapi-3797941Încă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument4 paginiDrug StudyMychal Dillan VeedorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economiczoology 170604183247Document142 paginiEconomiczoology 170604183247aimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Nervous SystemDocument11 paginiAnatomy of Nervous SystemGrace CosmodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For Combi-OvensDocument9 paginiGuidelines For Combi-OvensDavid BradleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20084222614756Document24 pagini20084222614756masoodaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7th Grade Considering Cockroaches Text - QuestionsDocument3 pagini7th Grade Considering Cockroaches Text - QuestionsSubhash_iimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gayatri Mantra MudraDocument3 paginiGayatri Mantra Mudradineshgomber100% (1)
- Mechanism of BreathingDocument2 paginiMechanism of BreathingMonikita PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Silkewormes and Their Flies by Thomas Moffat ("T.M.") @1599Document107 paginiThe Silkewormes and Their Flies by Thomas Moffat ("T.M.") @1599TerryandAlanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cupcake English Proj ChartsDocument3 paginiCupcake English Proj Chartsapi-315759858Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Basic Principles of Animal Form and FunctionDocument44 paginiChapter 4 Basic Principles of Animal Form and FunctionPrince VillacrusisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 8: Lola The Animal Helper: Name: . Class: DateDocument12 paginiUnit 8: Lola The Animal Helper: Name: . Class: DatehoangavÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Marketing Plan For 2014 PETLAN CompanyDocument18 paginiThe Marketing Plan For 2014 PETLAN CompanyJared Atanerwitzy M100% (1)
- Burn Shock and Resuscitation RevisedDocument70 paginiBurn Shock and Resuscitation RevisedsalmanhabeebekÎncă nu există evaluări
- WFRP 4E Modified Fumbles and MiscastsDocument7 paginiWFRP 4E Modified Fumbles and MiscastsVinie CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESL Trivia Game - Beginner 2 PDFDocument1 paginăESL Trivia Game - Beginner 2 PDFjoshuabaezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zoology PDFDocument734 paginiZoology PDFJames SoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolutionary Relationship in Kingdom Plantae: Dependence of Gametophyte and Sporophyte Water Dependence in FertilizationDocument4 paginiEvolutionary Relationship in Kingdom Plantae: Dependence of Gametophyte and Sporophyte Water Dependence in FertilizationAida AisyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section A Look at The Picture. Rearrange The Words To Form Correct Sentences. (10 Marks)Document5 paginiSection A Look at The Picture. Rearrange The Words To Form Correct Sentences. (10 Marks)Hassan BachaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modern Bio II - Nutrition Plant and AnimalsDocument77 paginiModern Bio II - Nutrition Plant and AnimalsLavander BlushÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdenoiditisDocument4 paginiAdenoiditisApurbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Korea NoDocument51 paginiKorea NoAlejandro MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exchange Surfaces 1 QPDocument12 paginiExchange Surfaces 1 QPSaaleh AbanurÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7912 ALL TutorialsDocument41 pagini7912 ALL TutorialsHenok BayuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dog Bite Attorney EncinoDocument6 paginiDog Bite Attorney Encinostephensmith1Încă nu există evaluări
- HumanbodyDocument190 paginiHumanbodyapi-431347330Încă nu există evaluări