Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Index (Ceftriaxone)
Încărcat de
Fildehl Janice Bomediano CatipayDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Index (Ceftriaxone)
Încărcat de
Fildehl Janice Bomediano CatipayDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CEFTRIAXONE Rocephin CLASSIFICATION(S): Ther. Class: anti-infectives Pharm.
Class: third-generation cephalosporins INDICATIONS Treatment of: o Skin and skin structure infections o Septicemia o Bone and joint infections o Meningitis o Urinary and gynecologic infections including o Perioperative prophylaxis gonorrhea or respiratory tract infections o Single-dose treatment of acute bacterial otitis media o Intra-abdominal infections o Lyme disease. ACTION Bind to the bacterial cell wall membrane, causing cell death. Therapeutic Effects: o Bactericidal action against susceptible bacteria. Spectrum: o Similar to that of second-generation cephalosporins, but activity against staphylococci is less, whereas activity against gram-negative pathogens is greater, even for organisms resistant to first- and second-generation agents o Notable is increased action against o Enterobacter o Klebsiella o Serratia o Haemophilus pneumoniae o Moraxella influenzae o Neisseria catarrhalis o Escherichia coli o Proteus o Borrelia o Providencia burgdorferi o Some activity against anaerobes, including Bacteroides fragilis. PHARMACOKINETICS Absorption: Well absorbed after IM administration.
Distribution: Widely distributed. Cross the placenta; enter breast milk in low concentrations. CSF penetration better than with first- and second-generation agents. Protein Binding: 90%. Metabolism and Excretion: Partly metabolized and partly excreted in the urine. Half-life: ceftriaxone348522 min CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS Contraindicated in: Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins Serious hypersensitivity to penicillins Use Cautiously in: Combined severe hepatic and renal impairment (dosage reduction/increased dosing interval recommended for ceftriaxone) History of GI disease, especially colitis Geriatric patients (dosage adjustment due to age-related decrease in renal function may be necessary) Pregnancy and lactation (have been used safely). ADVERSE REACTIONS AND SIDE EFFECTS* *CAPITALS indicate life threatening; underlines indicate most frequent. CNS: SEIZURES(high doses). GI: PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS COLITIS, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, cramps, pseudolithiasis (ceftriaxone). Derm: rashes, urticaria. Hemat: bleeding (increased with cefoperazone), blood dyscrasias, hemolytic anemia. Local: painat IM site, phlebitisat IV site. Misc: allergic reactions includingANAPHYLAXIS andSERUM SICKNESS, superinfection. INTERACTIONS Drug-Drug: Ingestion of alcohol within 4872 hr of cefoperazone may result in a disulfiram-like reaction Concurrent use of large doses of cephalosporins and NSAIDs may increase the risk of bleeding Concurrent use of loop diuretics ornephrotoxic agents including aminoglycosidesmay increase the risk of nephrotoxicity ROUTE AND DOSAGE
Ceftriaxone IM, IV (Adults): Most infections0.51 g q 12 hr or 12 g q 24 hr. Gonorrhea250 mg IM. Meningitis2 g q 12 hr. IM, IV (Children): Most infections2537.5 mg/kg q 12 hr. Meningitis100 mg/kg q 24 hr or 50 mg/kg q 12 hr. Skin/softtissue infections5075 mg/kg q 24 hr. Acute otitis media50 mg/kg IM single dose. AVAILABILITY o Ceftriaxone Powder for injection: 250 mgRx, 500 mgRx, 1 gRx, 2 gRx, 10 gRx Premixed containers: 1 g/50 mlRx, 2 g/50 mlRx. TIME/ACTION PROFILE ONSET Ceftriaxone IM Ceftriaxone IV rapid rapid PEAK 12 hr end of infusion DURATION 1224 hr 1224 hr
NURSING IMPLICATIONS ASSESSMENT Assess patient for infection (vital signs; appearance of wound, sputum, urine, and stool; WBC) at beginning of and throughout therapy. Before initiating therapy, obtain a history to determine previous use of and reactions to penicillins or cephalosporins. Persons with a negative history of penicillin sensitivity may still have an allergic response. Obtain specimens for culture and sensitivity before initiating therapy. First dose may be given before receiving results. Observe patient for signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis (rash, pruritus, laryngeal edema, wheezing). Discontinue the drug and notify the physician or other health care professional immediately if these symptoms occur. Keep epinephrine, an antihistamine, and resuscitation equipment close by in the event of an anaphylactic reaction. Lab Test Considerations: May cause positive results for Coombs' test in patients receiving high doses or in neonates whose mothers were given cephalosporins before delivery. o May cause increased serum AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, LDH, BUN, and creatinine.
May rarely cause leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, lymphocytosis, and thrombocytosis. POTENTIAL NURSING DIAGNOSES Infection, risk for (Indications, Side Effects). Diarrhea (Adverse Reactions). Knowledge deficit, related to medication regimen (Patient/Family Teaching). IMPLEMENTATION o PO: Administer around the clock. May be administered on full or empty stomach. Administration with food may minimize GI irritation. Shake oral suspension well before administering. IM: Reconstitute IM doses with sterile or bacteriostatic water for injection or 0.9% NaCl for injection. May be diluted with lidocaine to minimize injection discomfort. o Inject deep into a well-developed muscle mass; massage well. IV: Monitor injection site frequently for phlebitis (pain, redness, swelling). Change sites every 4872 hr to prevent phlebitis. o If aminoglycosides are administered concurrently, administer in separate sites, if possible, at least 1 hr apart. If second site is unavailable, flush lines between medications. Direct IV: Dilute in at least 1 g/10 ml. Avoid direct IV administration of ceftriaxone. Do not use preparations containing benzyl alcohol for neonates. Rate: Administer slowly over 35 min. Ceftriaxone Intermittent Infusion: Reconstitute each 250-mg vial with 2.4 ml, each 500-mg vial with 4.8 ml, each 1-g vial with 9.6 ml, and each 2-g vial with 19.2 ml of sterile water for injection, 0.9% NaCl, or D5W for a concentration of 100 mg/ml. Solution may be further diluted in 50100 ml of 0.9% NaCl, D5W, D10W, D5/0.45% NaCl, or LR. Solution may appear light yellow to amber. Solution is stable for 3 days at room temperature. Rate: Administer over 1530 min in adults and 1030 min in newborns or children. Y-Site Compatibility: o acyclovir o aztreonam o foscarnet o heparin o allopurinol o diltiazem o gatifloxacin o linezolid o amifostine o fludarabine o granisetron o melphalan
o o o o
meperidine methotrexate morphine paclitaxel
o o o
propofol remifentanil sargramostim
o o o
sodium bicarbonate tacrolimus teniposide
o o o
theophylline thiotepa zidovudine
Y-Site Incompatibility: o alatrovafloxacin o fluconazole o pentamidine o vinorelbine. o filgrastim o labetalol o vancomycin PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING Instruct patient to take medication at evenly spaced times and to finish the medication completely, even if feeling better. Missed doses should be taken as soon as possible unless almost time for next dose; do not double doses. Advise patient that sharing of this medication may be dangerous. Advise patient to report signs of superinfection (furry overgrowth on the tongue, vaginal itching or discharge, loose or foulsmelling stools) and allergy. Instruct patient to notify health care professional if fever and diarrhea develop, especially if stool contains blood, pus, or mucus. Advise patient not to treat diarrhea without consulting health care professional. Cefditoren: Inform female patients that cefditoren can be taken concomitantly with hormonal contraceptives. EVALUATION Clinical response to therapy can be evaluated by: Resolution of the signs and symptoms of infection. Length of time for complete resolution depends on the organism and site of infection Decreased incidence of infection when used for prophylaxis.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Adults and Children 15 Y Pediatric 6 - 14 YDocument2 paginiAdults and Children 15 Y Pediatric 6 - 14 YFildehl Janice Bomediano Catipay100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument15 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of The BrainFildehl Janice Bomediano CatipayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bad Effects of E-Gadgets On Health and Safety UseDocument19 paginiBad Effects of E-Gadgets On Health and Safety UseFildehl Janice Bomediano CatipayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification (S) Therapeutic: Anti-Infectives Pharmacologic: FluoroquinolonesDocument9 paginiClassification (S) Therapeutic: Anti-Infectives Pharmacologic: FluoroquinolonesFildehl Janice Bomediano CatipayÎncă nu există evaluări
- SalbutamolDocument5 paginiSalbutamolFildehl Janice Bomediano CatipayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zinc SulfateDocument2 paginiZinc SulfateFildehl Janice Bomediano CatipayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Martin Buber: BiographyDocument4 paginiMartin Buber: BiographyFildehl Janice Bomediano CatipayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- A. Classification and Characteristics of Diabetes MellitusDocument6 paginiA. Classification and Characteristics of Diabetes MellitusNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3AÎncă nu există evaluări
- City Government of Kabankalan: State Protect TheDocument2 paginiCity Government of Kabankalan: State Protect ThefortunecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Test - Mid TermDocument2 paginiPractice Test - Mid Termngaanhc2ngtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relapse PreventionDocument10 paginiRelapse PreventionDawn FarmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scheme of Work - Form 4: Week (1 - 3)Document7 paginiScheme of Work - Form 4: Week (1 - 3)honeym694576Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 Positive Psychology Module 1Document7 pagini1 Positive Psychology Module 1diether780Încă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal InternasionalDocument110 paginiJurnal InternasionalRafi DevianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UL WP Final Using Leading and Lagging Safety Indicators To Manage Workplace Health and Safety Risk V7 LR1Document10 paginiUL WP Final Using Leading and Lagging Safety Indicators To Manage Workplace Health and Safety Risk V7 LR1Nhut NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument22 paginiUntitledBenjamin Swami100% (7)
- Ngan 2018Document9 paginiNgan 2018rafaelaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- HematuriaDocument15 paginiHematurianisaw_2Încă nu există evaluări
- GATS 2 FactSheetDocument4 paginiGATS 2 FactSheetAsmi MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Toxicity TestingDocument4 paginiHistory of Toxicity TestingIja Nur100% (1)
- Esoterrorists GM ReferenceDocument1 paginăEsoterrorists GM ReferenceAlisa NakdontreeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compliance in Adolescents With Chronic Diseases: A ReviewDocument10 paginiCompliance in Adolescents With Chronic Diseases: A ReviewMaggy GarcíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 Areas of Assessment Pedia DutyDocument3 pagini13 Areas of Assessment Pedia DutyJoshua MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ PebcDocument7 paginiMCQ Pebcshamram20050% (1)
- Family DeclarationDocument5 paginiFamily DeclarationVanlal MuanpuiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epoch Elder Care Provides High Quality Assisted Living HomesDocument17 paginiEpoch Elder Care Provides High Quality Assisted Living HomesMahesh MahtoliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asynchronous Activities IE 533Document34 paginiAsynchronous Activities IE 533Ryanne TeñosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pe9 Week3 Pe9pf Le H 41Document17 paginiPe9 Week3 Pe9pf Le H 41Edeli Faith PatrocinioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitchell H. Katz-Evaluating Clinical and Public Health Interventions - A Practical Guide To Study Design and Statistics (2010)Document176 paginiMitchell H. Katz-Evaluating Clinical and Public Health Interventions - A Practical Guide To Study Design and Statistics (2010)Lakshmi SethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No 1 bt502 SeminarDocument15 paginiAssignment No 1 bt502 SeminarMashal WakeelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irene Gee Regidor BSED-English Conditions of Developmental Delay 1. Mental RetardationDocument3 paginiIrene Gee Regidor BSED-English Conditions of Developmental Delay 1. Mental RetardationAliana CabalunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Customer Is Always Right Right? Is That Not What Companies Always Claim?Document6 paginiThe Customer Is Always Right Right? Is That Not What Companies Always Claim?faith mutsambiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- ! Food Futures in Education and Society (2023)Document321 pagini! Food Futures in Education and Society (2023)SaboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerobic Exercise Dos and DontsDocument2 paginiAerobic Exercise Dos and DontsSandy NodadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social Causation and Social ConstructionDocument6 paginiSocial Causation and Social Constructionhuberpadilla100% (1)
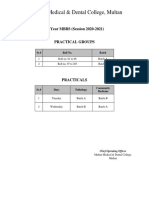
- 4th Year MBBS Batches & GroupsDocument2 pagini4th Year MBBS Batches & GroupsSohail Abbas KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reaction Paper#5 (Santos, Allysa Mhay V.)Document2 paginiReaction Paper#5 (Santos, Allysa Mhay V.)Allysa Mhay SantosÎncă nu există evaluări