Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Amit Experiment 4
Încărcat de
thesovereignmoonloveDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Amit Experiment 4
Încărcat de
thesovereignmoonloveDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Experiment 4
Aim of the experiment: Employing the exact-charge relationships found in
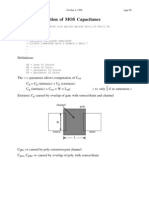
write a MATLAB program that can be used to calculate and plot low frequency C/C0 versus VG characteristics. The program is to calculate C/C0 and the corresponding VG for US=S/(kT/q) stepped in one-unit or less increments from US=UF-21 to UF+21.UF=F/(kT/q) Employ KS= 11.8 and K0= 3.9; Let T =300 K. Only NA and x0 are to be considered input variables. Setting NA =1015/cm3, use your program to plot out the low-frequency C/C0 versus VG curves for x0 =0.1 m, 0.2 m, and 0.3 m
Description of the experiment
Capacitance-voltage plot is used for characterizing mos capacitor. The applied voltage is varied, and the capacitance is measured and plotted as a function of voltage.
Matlab Code
%Low and/or HIGH-frequency p-typeMOS-C C_V CHARACTERISTICS %Subprogram CVintegrad is arun time requirement %INItialization and Input format compact close clear s= menu('choose the desird plot','Low-f C-V','High-f C-V','Both'); NA=input('Please input the bulk doping in /cm3,NA='); xo=input('Please input the oxide thickness in cm,xo='); xmin=input('Specify VGmin(volts),VGmin='); xmax=input('SpecifyVGmax(volts),VGmax='); global UF %Constants and parameters e0 =8.85e-14; q =1.6e-19; k=8.617e-5; KS=11.8; KO=3.9; ni=1.0e10; T=300; kT=k*T; %Computed Constants UF =log(NA/ni); LD =sqrt((kT*KS*e0)/(2*q*ni)); %Gate voltage computation US =UF-21:0.5:UF+21; F=sqrt(exp(UF).*(exp(-US)+US-1)+exp(-UF).*(exp(US)-US-1)); VG= kT*(US+(US./abs(US)).*(KS*xo)/(KO*LD).*F); % low-frequency capacitance computation DENOML=exp(UF).*(1-exp(-US))+exp(-UF).*(exp(US)-1); WL =(US./abs(US)).*LD.*(2*F)./DENOML; cL=1.0./(1+(KO*WL)./(KS*xo)); %High-frequency Capacitance Computation if s~=1, jj=length(US); nn=0; for ii=1:jj, if US(ii)<3, elseif nn==0, INTG=QUAD('CVintgrd',3,US(ii),0.001); nn =1; else INTG =INTG+QUAD('CVintgrd',US(ii-1),US(ii),0.001); end if US(ii)<3, cH(ii)=cL(ii); else
d=(exp(US(ii))-US(ii)-1)./(F(ii).*exp(UF).*INTG); DENOMH=exp(UF).*(1-exp(-US(ii)))+exp(-UF).*((exp(US(ii))1)./(1+d)); WH =LD.*(2*F(ii))./DENOMH; cH(ii)=1.0/(1+(KO*WH)./(KS*xo)); end end else end %plotting the result if s==1, plot(VG,cL); elseif s==2, plot(VG,cH); else plot(VG,cL,'--',VG,cH); text(0.8*xmin,.17,'-Low-f','color',[1,1,0]); text(0.8*xmin,.12,'-High-f','color',[1,0,1]); end axis([xmin,xmax,0,1]); text(0.8*xmin,.27,['NA=',num2str(NA),'/cm3']); text(0.8*xmin,.22,['xo=',num2str(xo),'cm']); xlabel('VG(volts)');ylabel('C/CO');grid
waveforms
Result: Low-frequency C/C0 versus VG curves for x0 =0.1 m, 0.2 m, and 0.3 m was plotted and studied.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Assignment MSSD Kushal 19092024Document9 paginiAssignment MSSD Kushal 19092024Kushal Gangwar M.Tech., Electronics Engineering, IIT(BHU)Încă nu există evaluări
- AC Analysis by MATLABDocument27 paginiAC Analysis by MATLABYaman SoudanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of First and Second Order Circuits in Time and Frequency DomainDocument40 paginiDesign of First and Second Order Circuits in Time and Frequency DomainsravanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMOS Inverter Delay and Power Estimation for RC LoadsDocument4 paginiCMOS Inverter Delay and Power Estimation for RC LoadsTarun PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment all DDDocument35 paginiExperiment all DDFariha shaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tri State InverterDocument18 paginiTri State InverterManasa Upadhyaya100% (1)
- Fourier Analysis On Ti-89Document6 paginiFourier Analysis On Ti-89Jack KennedyÎncă nu există evaluări
- chp5 1Document6 paginichp5 1Harshith GowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steady State Error: Transient ResponseDocument6 paginiSteady State Error: Transient ResponseAshish AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSCAD Model Analysis of 2-Level VSCDocument12 paginiPSCAD Model Analysis of 2-Level VSCErandikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ti89 Power Calculator FunctionsDocument14 paginiTi89 Power Calculator FunctionsJack KennedyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Modelling of Transmission LinesDocument7 pagini5 Modelling of Transmission LinesvirudaianandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Super Buffer Design Driving Large Capacitive Loads: Prepared byDocument14 paginiSuper Buffer Design Driving Large Capacitive Loads: Prepared byTamil SelvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SimlabDocument32 paginiSimlabAkbar AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spice Computation of MOSDocument10 paginiSpice Computation of MOSJaymee LalbhaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psa RecordDocument66 paginiPsa RecordMurugesan ArumugamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design an air-filled circular waveguide for 1 GHz frequency separationDocument12 paginiDesign an air-filled circular waveguide for 1 GHz frequency separationkwizera evaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Series RC Circuit: Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument7 paginiSeries RC Circuit: Electrical and Electronic Engineeringخہٰہٰالہٰد ۦ' ۦ'Încă nu există evaluări
- Anexo: A.1 Modelo de Acelerómetro TorsionalDocument8 paginiAnexo: A.1 Modelo de Acelerómetro Torsionalmartyf777Încă nu există evaluări
- Web For Principle of Communication - B. Tech 4th SemDocument36 paginiWeb For Principle of Communication - B. Tech 4th SemFurqan Ali Khan100% (1)
- AM ModulationDocument8 paginiAM ModulationccoolbraveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Switch CapacitorDocument90 paginiSwitch CapacitorVaibhav Khurana100% (1)
- N Channel MOSFET Level 1Document5 paginiN Channel MOSFET Level 1Kyusang ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 3Document7 paginiLab 3Binod AdhikariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact of MOSFET parameters on parasitic capacitancesDocument5 paginiImpact of MOSFET parameters on parasitic capacitancesNava KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3AE Assignment AN1 2013 SolnsDocument2 pagini3AE Assignment AN1 2013 SolnsAluwani KhomolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pss Scilab ManualDocument21 paginiPss Scilab ManualDse YtÎncă nu există evaluări
- VLSI Design Assignment-2: MOSFET Resistance and Capacitance AnalysisDocument34 paginiVLSI Design Assignment-2: MOSFET Resistance and Capacitance AnalysisDhanvanth MuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modeling and Analysis of DC-DC Converters Under Pulse Skipping ModulationDocument6 paginiModeling and Analysis of DC-DC Converters Under Pulse Skipping ModulationJeba AntonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Study Between Series Resonant Converter and Parallel Resonant ConverterDocument23 paginiComparative Study Between Series Resonant Converter and Parallel Resonant ConverterS.m. FerdousÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation of Short-Circuit IEC 60909Document6 paginiCalculation of Short-Circuit IEC 60909Iuliu Grad86% (7)
- Assignment Load Flow AnalysisDocument23 paginiAssignment Load Flow AnalysisMd Raton AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Updated Simlab ManualDocument46 paginiUpdated Simlab ManualSumanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of CMOS OpAmp For A D/A Converter Buffer by Manraj Singh GujralDocument22 paginiDesign of CMOS OpAmp For A D/A Converter Buffer by Manraj Singh GujralManraj GujralÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment-1: Course:-Analog Communication Systems Laboratory Code:-ECE3001 Slot:-L11+L12Document12 paginiExperiment-1: Course:-Analog Communication Systems Laboratory Code:-ECE3001 Slot:-L11+L12Iyyaasuu YaadataaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 4Document8 paginiLab 4Binod AdhikariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide For Power PredictionDocument11 paginiGuide For Power PredictionpagliasoÎncă nu există evaluări
- E PDFDocument178 paginiE PDFVasu IyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Generalized Direct Matrix ConverterDocument6 paginiNew Generalized Direct Matrix ConverterBhavani PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amplitude ModulationDocument70 paginiAmplitude Modulationhamkane100% (1)
- Mathcad - Opamp 1974Document7 paginiMathcad - Opamp 1974Frank KarthikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimal Design of A Half-Wave Cockroft-Walton Voltage Multiplier With Minimum Total CapacitanceDocument6 paginiOptimal Design of A Half-Wave Cockroft-Walton Voltage Multiplier With Minimum Total CapacitanceFazal AkbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antenna Azimuth and Its Simulation by Lab View Program: School of Electrical and Electronoic EngineeringDocument25 paginiAntenna Azimuth and Its Simulation by Lab View Program: School of Electrical and Electronoic EngineeringKenneth CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric PotentialDocument4 paginiElectric Potentialshreeshivaani28Încă nu există evaluări
- Lopower TutasDocument7 paginiLopower TutasNabil IshamÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANGEN - EN006 Current Transformer Selection For VAMP Series Overcurrent and Differential Relays PDFDocument8 paginiANGEN - EN006 Current Transformer Selection For VAMP Series Overcurrent and Differential Relays PDFRicardo BozoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 2Document3 paginiExercise 2momolololilo4Încă nu există evaluări
- 3.4.2 Output Capacitor: Out C, Max OutDocument14 pagini3.4.2 Output Capacitor: Out C, Max OutReza RzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2performance Evaluation of TRM LinesDocument4 pagini2performance Evaluation of TRM Linesrahul patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE2005 - Tutorial Homework Assignment 9 SolutionDocument6 paginiEE2005 - Tutorial Homework Assignment 9 SolutionKL ChiangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Sheet 5Document2 paginiTutorial Sheet 5Shashank SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- PGCB 2018Document4 paginiPGCB 2018HasibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 9 XDocument11 paginiLab 9 XNandita GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- iNVERTER aSSIGN6 1Document6 paginiiNVERTER aSSIGN6 1Rohan ChopraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regulation of AlternatorDocument6 paginiRegulation of Alternatorkudupudinagesh100% (1)
- RC SeriesDocument8 paginiRC SeriesMoaid BinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 3 Switched Capacitor SimulationDocument28 paginiLab 3 Switched Capacitor SimulationDavid TynanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment-1: IV.2 Understanding Computing Systems ArchitectureDocument2 paginiAssignment-1: IV.2 Understanding Computing Systems ArchitecturethesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diode CirDocument1 paginăDiode CirthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- SyllabusDocument1 paginăSyllabusthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Test-1, Question PaperDocument1 paginăLab Test-1, Question PaperthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inverter NetlistDocument1 paginăInverter NetlistthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital MCQDocument19 paginiDigital MCQthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schedule Oneiros'15Document1 paginăSchedule Oneiros'15thesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Test-1, Question PaperDocument1 paginăClass Test-1, Question PaperthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Objectives - Network AnalysisDocument1 paginăCourse Objectives - Network AnalysisthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEST Question Bank - Digital ElectronicsDocument157 paginiBEST Question Bank - Digital Electronicsabhinav_pundir0% (1)
- PHD Annex 5 Research AssistantshipDocument3 paginiPHD Annex 5 Research AssistantshipthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOP SPEECH PROCESSING BOOKS FOR REFERENCEDocument1 paginăTOP SPEECH PROCESSING BOOKS FOR REFERENCEthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHD Annex 5 Research AssistantshipDocument3 paginiPHD Annex 5 Research AssistantshipthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doctoral Programs (PH.D.) : JIIT, NOIDA: Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument1 paginăDoctoral Programs (PH.D.) : JIIT, NOIDA: Electronics & Communication EngineeringBhanu Partap SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plot Data in MatlabDocument2 paginiPlot Data in MatlabthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inverter NetlistDocument1 paginăInverter NetlistthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best CirDocument1 paginăBest CirthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- A B C A B C: Acropdf - A Quality PDF Writer and PDF Converter To Create Pdf. To Remove The Line, Buy A LicenseDocument1 paginăA B C A B C: Acropdf - A Quality PDF Writer and PDF Converter To Create Pdf. To Remove The Line, Buy A LicensethesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- SROODocument1 paginăSROOthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bulk 32nmDocument4 paginiBulk 32nmthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speaker RecognitionDocument31 paginiSpeaker RecognitionthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- PROOOODocument1 paginăPROOOOthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Experiment 5Document5 paginiLab Experiment 5thesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1: Aim of The Experiment: Construct A Log-Log Plot ofDocument3 paginiExperiment 1: Aim of The Experiment: Construct A Log-Log Plot ofthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Codes for Signal Processing FunctionsDocument12 paginiMatlab Codes for Signal Processing FunctionsthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Experiment - 5: Problem StatementDocument5 paginiLab Experiment - 5: Problem StatementthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 3aDocument4 paginiExp 3athesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Built-in voltage in Si p+/n and n+/p diodesDocument3 paginiBuilt-in voltage in Si p+/n and n+/p diodesthesovereignmoonloveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communication LabDocument9 paginiCommunication Labthesovereignmoonlove100% (1)
- AMP6-BASIC Kit: Bill of Materials (BOM) For Item 43, BOM Rev 1.20Document2 paginiAMP6-BASIC Kit: Bill of Materials (BOM) For Item 43, BOM Rev 1.20harwepinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work Completion Agreement 2010Document1 paginăWork Completion Agreement 2010Md Mehdi HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Reducing ValveDocument3 paginiPressure Reducing ValveSasa JadrovskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmaceutics IntroductionDocument9 paginiPharmaceutics IntroductionVIJAY KUMAR TIRUKKACHIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kettle ReboilersDocument4 paginiKettle ReboilersMuhammad Usman100% (1)
- Practical Data Science With RDocument1 paginăPractical Data Science With RDreamtech Press33% (3)
- Tank Brochure 34 L40 LDocument2 paginiTank Brochure 34 L40 Lmerinoxa1985Încă nu există evaluări
- Winter Snow in The UKDocument5 paginiWinter Snow in The UKmoB0BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 5 Acid Base Titration Vinegar ExperimentDocument3 paginiGroup 5 Acid Base Titration Vinegar ExperimentJan Vincent GoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Specifications Product Specifications: CNT CNT - 195 195 - 1000 1000Document2 paginiProduct Specifications Product Specifications: CNT CNT - 195 195 - 1000 1000sfynksÎncă nu există evaluări
- NOVA Methodology - BY VINOD GANDHIDocument5 paginiNOVA Methodology - BY VINOD GANDHIVinod GandhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tacsa ReportDocument226 paginiTacsa ReportRitu GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- System Inventory Table: Who Qty Price Per Unit Warranty Installation CommentsDocument2 paginiSystem Inventory Table: Who Qty Price Per Unit Warranty Installation Commentskksingh007indiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEMA Grade G10 Glass Epoxy LaminateDocument1 paginăNEMA Grade G10 Glass Epoxy Laminateim4uim4uim4uim4uÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6x6 Phoenix Tipper1Document2 pagini6x6 Phoenix Tipper1vuhuythinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 8 TestDocument2 paginiUnit 8 TestmamazookeeprÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appearances of Human Milk Bright Yellow ColostrumDocument28 paginiAppearances of Human Milk Bright Yellow Colostrumjaish8904100% (3)
- HW 1Document3 paginiHW 1ryan4coug100% (1)
- Account Sales Business Development Executive in San Francisco Bay CA Resume Daniel DelValleDocument1 paginăAccount Sales Business Development Executive in San Francisco Bay CA Resume Daniel DelValleDanielDelValle2Încă nu există evaluări
- LaMotte 7802 Nickel P-54 Octet Comparator Kit InstructionsDocument2 paginiLaMotte 7802 Nickel P-54 Octet Comparator Kit InstructionsPromagEnviro.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eclipse ExtensoJet Model EJ075 Burner SpecsDocument4 paginiEclipse ExtensoJet Model EJ075 Burner SpecszaniluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leventogiannis & Co Interest Form 2012-2013Document4 paginiLeventogiannis & Co Interest Form 2012-2013Aggelos MarkouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Econ 106G Homework 1 Solutions: Dominated Strategies and Best ResponsesDocument2 paginiEcon 106G Homework 1 Solutions: Dominated Strategies and Best ResponsesAmmar DiwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Freeze Dryers - CatalogDocument2 paginiFreeze Dryers - Catalogdéborah_rosalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- B2B Case Study of Sigma TelecomDocument12 paginiB2B Case Study of Sigma TelecomJitendra Kumar100% (1)
- SKD 30 Bridge RectifierDocument3 paginiSKD 30 Bridge RectifierkazishahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bridgman-Stockbarger Technique: CrystallizationDocument2 paginiBridgman-Stockbarger Technique: Crystallizationpippo pappiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Six Sigma DMAICDocument2 paginiSix Sigma DMAICjaviermzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bases For Classification of Retail UnitsDocument8 paginiBases For Classification of Retail UnitsJulian Chacko100% (1)
- CRM in The Pharma IndustryDocument7 paginiCRM in The Pharma Industrysacred54Încă nu există evaluări