Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Yearly Plan Science Form 2
Încărcat de
PaRimala DeviTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Yearly Plan Science Form 2
Încărcat de
PaRimala DeviDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Created by CDC SZA SMKN
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FORM 2
SCIENCE
SCIENCE PANEL OF SMKIS 2013
Created by CDC SZA 10
TABLE OF CONTENTS
THEMES & LEARNING AREAS THEME 1 : MANAGEMENT AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE Learning Area: 1. World through our senses Learning Area: 2. Nutrition THEME 2 : MAN AND THE VARIETY OF LIVING THINGS Learning Area: 1. Biodiversity Learning Area: 2. Interdependence among living organisms and the environment THEME 3 : MATTER IN NATURE Learning Area: 1. Water and Solution Learning Area: 2. Air Pressure THEME 4 : FORCE AND MOTION Learning Area: 1. Dynamics Learning Area: 2. Support and Movement THEME 5 : TECHNOLOGICAL AND INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT IN SOCIETY Learning Area: 1. Stability Learning Area: 2. Simple Machine
Page 2-4 4-6 6 7-10 10-15 16-17 15-16 17 18 19
Created by CDC SZA 12
THEME: MANAGEMENT AND CONTINUITY OF LIFE LEARNING AREA: 1. THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES
Week & date Chapters & Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) SPS (Science Process Skills) Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Being thankful to God. Being objective. Being responsible about the safety of oneself, others, and environment Observing Realising that science is a means to understand nature. The structures of the receptors are not required. Notes
1st Sem. 1 2-4/1/13
CHAPTER 1 : THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES LO1 Sensory organs The five senses, the sensory organs and the stimuli. The pathway from stimulus to response Stimulus Sensory organs Nerves Brain Nerves Response Activity 1.1 textbook v.1 (Relate daily activities & senses that involved) Discussion of what happens in our body after a stimulus is detected.
Characteris e Correlate Visualising Generalise
Observing Inferring
2 7 11/1/13
LO2
Sense of touch The structure of the human skin involved in stimuli detection, The sensitivity of the skin at different parts of the body towards stimuli. Discuss the sensitivity of the skin in daily life
Using models, charts, computer software and other teaching aids. Carry out activity to compare the sensitivity of different parts of the body towards touch Discussion of connection to the following situations such as receiving an injection, using Braille
Characteris e Correlate Analyse Conclude
Interpreting data
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills)
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Being thankful to God. Being objective. Being responsible about the safety of oneself, others, and environment
Notes
1st Sem. 1 2-4/1/13
CHAPTER 1 : THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES LO1 Sensory organs The five senses, the sensory organs and the stimuli. The pathway from stimulus to response Stimulus Sensory organs Nerves Brain Nerves Response Activity 1.1 textbook v.1 (Relate daily activities & senses that involved) Discussion of what happens in our body after a stimulus is detected.
Characteris e Correlate Visualising Generalise
Observing Inferring
2 7 11/1/13
LO3 Sense of smell Identify the structure of the nose, Identify the position of the sensory cells in the detection of smell.
Using models, charts, computer software and other teaching aids.
Characteris e Correlate Visualising
Observing Inferring Being responsible about the safety of oneself, others, and environment Being thankful to God
2 7 11/1/13
LO4 Sense of taste. The different areas of the tongue that respond to different taste, Relate the sense of taste with the sense of smell.
Carry out activities to detect the different areas of the tongue that respond to different tastes. Carry out activities to find how taste is related to smell.
Compare & differentiat e Correlate Conclude
Classify Inferring Interpreting data
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills)
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Being thankful to God. Being objective. Being responsible about the safety of oneself, others, and environment
Notes
1st Sem. 1 2-4/1/13
CHAPTER 1 : THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES LO1 Sensory organs The five senses, the sensory organs and the stimuli. The pathway from stimulus to response Stimulus Sensory organs Nerves Brain Nerves Response Activity 1.1 textbook v.1 (Relate daily activities & senses that involved) Discussion of what happens in our body after a stimulus is detected.
Characteris e Correlate Visualising Generalise
Observing Inferring
3 14 18/1/13
LO5 Sense of hearing The structure of the human ear, The function of the different parts of the ear, Mechanism of hearing.
Computer simulation to illustrate the hearing mechanism. Discussion of the hearing mechanism.
Characteris e Visualising
Observing
Being responsible about the safety of oneself, others, and environment Being objective. Being thankful to God.
3 14 18/1/13
LO6 Sense of sight. Identify the structure of the human eye, Explain the functions of different parts of the eye, Describe how we see.
Examine the cows eye or model of a human eye. Collect information on structure and function of each part of the eye. Discuss of sight mechanism
Characteris e Visualising
Observing
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills)
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Being thankful to God. Being objective. Being responsible about the safety of oneself, others, and environment
Notes
1st Sem. 1 2-4/1/13
CHAPTER 1 : THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES LO1 Sensory organs The five senses, the sensory organs and the stimuli. The pathway from stimulus to response Stimulus Sensory organs Nerves Brain Nerves Response Activity 1.1 textbook v.1 (Relate daily activities & senses that involved) Discussion of what happens in our body after a stimulus is detected.
Characteris e Correlate Visualising Generalise
Observing Inferring
4 21/1 25/1/13
LO7 Light and sight. Describe the properties of light i.e. Reflection, refraction. State the various defects of vision, Ways to correct vision defects, The limitations of sight, Stereoscopic and monocular visions with the survival of animals, The appropriate device to
Carry out activities to study: reflection of light & b) refraction of light between two mediums of different density. Collect information about the types of defects of vision and the contribution/use of technology to rectify them. Carry out activities to show what short sightedness and long sightedness are and how to correct them. Discuss what astigmatism is and the way to correct it. Carry out activities to investigate a) optical illusion, b) blind-spot.
Visualising Compare & differentiat e Analyse Correlate Making analogy by stating and give examples Compare &
Defining operationall y Classifying Measuring and using numbers Inferring Defining operationall y Communica ting
Relate the properties of Being light to natural honest and phenomena and accurate in daily usage. recording Angles of and incidence, validating reflection, data. refraction and normal are not Appreciating required. the Astigmatism, contribution optical illusions, of science blind-spot, and monocular and technology. stereoscopic visions should Thinking be introduced. rationally. Microscope,
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills)
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Being thankful to God. Being objective. Being responsible about the safety of oneself, others, and environment
Notes
1st Sem. 1 2-4/1/13
CHAPTER 1 : THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES LO1 Sensory organs The five senses, the sensory organs and the stimuli. The pathway from stimulus to response Stimulus Sensory organs Nerves Brain Nerves Response Activity 1.1 textbook v.1 (Relate daily activities & senses that involved) Discussion of what happens in our body after a stimulus is detected.
Characteris e Correlate Visualising Generalise
Observing Inferring
overcome the limitations of sight.
Discuss the connection between stereoscopic vision and monocular vision with the survival of animals. Gather information about the device to overcome the limitation of sight.
contrast by connecting Generate ideas by identifying
magnifying glass, telescope, binoculars, ultrasound scanning device, X-ray, periscope should be included. Defining operationall y Predicting Appreciating the contribution of science and technology. Thinking . Included devices such as hearing aids and stethoscope.
5 28/1 1/2/13
LO8 Sound and hearing. Describe the properties of sound, The reflection and absorption of sound, Explain the defects of hearing,
Discuss the limitations of hearing and ways of improving it. Carry out activities to investigate the need for stereophonic hearing in determining the direction of sound.
Correlate Visualising Relating
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills)
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Being thankful to God. Being objective. Being responsible about the safety of oneself, others, and environment rationally.
Notes
1st Sem. 1 2-4/1/13
CHAPTER 1 : THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES LO1 Sensory organs The five senses, the sensory organs and the stimuli. The pathway from stimulus to response Stimulus Sensory organs Nerves Brain Nerves Response Activity 1.1 textbook v.1 (Relate daily activities & senses that involved) Discussion of what happens in our body after a stimulus is detected.
Characteris e Correlate Visualising Generalise
Observing Inferring
Ways of rectifying the defects in hearing, The limitations of hearing, The device used to overcome the limitations of hearing, Explain stereophonic hearing. 5 28/1 1/2/13 LO9 The stimuli and responses in plants. The stimuli that cause response in plants, The parts of plants sensitive to specific stimulus, Relate the response in plants to their survival. Carry out experiments to investigate: a) stimuli detected by plants, b) identify the parts of the plants sensitive to specific stimulus. Discuss in what ways the response of plants towards stimuli are important for their survival. Analyse Synthesizin g Differentiat e Conclude Sequencing Characteris e Experiment ing
Being accurate in recording data. Being systematic. Having critical and
Observing Inferring
Responses in plants should include phototropism, geotropism, hydrotropism, nastic movement, thigmotropism.
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills)
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Being thankful to God. Being objective. Being responsible about the safety of oneself, others, and environment analytical thinking.
Notes
1st Sem. 1 2-4/1/13
CHAPTER 1 : THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES LO1 Sensory organs The five senses, the sensory organs and the stimuli. The pathway from stimulus to response Stimulus Sensory organs Nerves Brain Nerves Response Activity 1.1 textbook v.1 (Relate daily activities & senses that involved) Discussion of what happens in our body after a stimulus is detected.
Characteris e Correlate Visualising Generalise
Observing Inferring
Correlate
LEARNING AREA:
6 4 -8/2/13
2. NUTRITION
Realising that science is tools to understan d nature Being kindhearted Only the major vitamins [ A, B, C, D, E and K ] & minerals [calcium, sodium, iron, iodine, phosphorus and potassium ] are required . Vitamin B need not be classified into B1, B2 and so on. Introduce alcohol-
CHAPTER 2 :NUTRITION LO1 The classes of food. Explain through the classes of food, State the function of each class of food, Test for starch, glucose, protein and fats. Discuss the classes of food i.e. carbohydrate, protein, fats, vitamins, minerals, fibre and water and state their functions. Carry out activities to test for starch (iodine solution), glucose (Benedicts solution), protein (Millons reagent) and fats (alcoholemulsion test). Characteris e Compare & contrast Correlate Visualising Making analogy Observing Classifyin g Defining operation ally
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills)
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Being thankful to God. Being objective. Being responsible about the safety of oneself, others, and environment
Notes
1st Sem. 1 2-4/1/13
CHAPTER 1 : THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES LO1 Sensory organs The five senses, the sensory organs and the stimuli. The pathway from stimulus to response Stimulus Sensory organs Nerves Brain Nerves Response Activity 1.1 textbook v.1 (Relate daily activities & senses that involved) Discussion of what happens in our body after a stimulus is detected.
Characteris e Correlate Visualising Generalise
Observing Inferring
emulsion test for fat. CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Compare & contrast Correlate Analyse Generalise Correlate Compare & contrast SPS (Science Process Skills) Measuring and using numbers Communica ting Inferring Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Being cooperative. Appreciating and practising clean and healthy living. Notes
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
6 4 -8/2/13
LO2 The importance of a balanced diet. Meaning of a balanced diet is, The factors that must be considered when planning a balanced diet, Explain how the factors affect a balanced diet,
Discuss: a) what a balanced diet is, b) the factors that determine a persons balanced diet: age, size, sex, job, climate, state of health. Collect food wrappers that show calorific value of food and make a list to show the calorific value for
The unit of energy in food can be measured either in joules or calories.
10
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes The quantity of energy in each gram of carbohydrate, protein and fats, Estimate the calories of food taken in a meal, Plan a balanced diet.
Suggested Learning Activities each type of food. Discuss to estimate the calories of food taken in a meal. Plan a balanced diet for a day (breakfast, lunch and dinner).
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Characterise
SPS (Science Process Skills) Observing
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values
Notes
8 18 22/2/13
LO3 The digestive system in man. Explain what digestion is, The parts of the digestive system, The flow of food particles in the alimentary canal, The functions of the organs in the digestive system, The process of digestion in the alimentary canal, End products of digestion of carbohydrate, protein and fats.
Discuss that digestion is the breakdown of large food molecules into smaller soluble molecules that can be readily absorbed by the body. Identify parts of the digestive system and the flow of food particles in the alimentary canal using model/chart/CD ROM. Discuss the functions of the various organs in the digestive system and the enzymes found. Carry out activities to show the action of the enzyme in the saliva on starch.
Characterise Compare & contrast by identifying Analyse Visualising Correlate Compare & contrast Sequencing Prioritising Generalise
Observing
Practising healthy living. Being objective. Being cooperative.
Defining operationall y Inferring Communica ting
Enzymes should only include amylase, protease and lipase.
8 18 22/2/13
LO4 The process of absorption of digested food. The process of absorption of the products of digestion, The absorption of glucose
Discuss the process of absorption of the products of digestion in the small intestine. Carry out an experiment to show the absorption of glucose through
Correlate Compare & contrast Analyse Making analogy
Inferring Defining operationall y
Thinking rationally. Being cooperative.
The structure of vilus is not required. Need only mention vilus increases the surface area
11
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes through a Visking tube.
Suggested Learning Activities a Visking tube.
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills)
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values
Notes
for absorption.
9 25/2 1/3/13
LO5 The re-absorption of water and defecation. Water reabsorption in the large intestine, Defecation, The problem of defecation with eating habits. LO6 The habits of healthy eating. The importance of eating nutritious food, Practice good eating habits, The generous distribution of food to the underprivileged / needy, The dining culture of different people conforming to sensitivities and religious beliefs.
Discuss the reabsorption of water by the large intestine and the process of defecation. Discuss the importance of good eating habits to avoid constipation.
Correlate Compare & contrast Analyse Making analogy
Inferring Defining operationall y
Thinking rationally. Being cooperative
Plan and carry out a healthy eating habit. Discuss the following topics : a) practicing good eating habits i.e. eating nutritious food and eating in moderation, b) the generous distribution of food to the underprivileged / needy, c) cultural practices in dining conforming to sensitivities and religious beliefs.
Correlate Compare & contrast Relating Visualising
Inferring Predicting
9 25/2 1/3/13
Appreciating and practicing clean and healthy living. Being kindhearted and caring.
THEME: MAN AND THE VARIETY OF LIVING THINGS LEARNING AREA: 1. BIODIVERSITY
12
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Correlate Compare & contrast Characteris e Compare & differentiat e Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
SPS (Science Process Skills) Inferring
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Having an interest and curiosity towards the environme nt. Being systematic. Having critical and analytical thinking.
Notes
10 25/2 1/3/13 10 4 8/3/13
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY LO1 The variety of living organisms and their classification. Explain the diversity of living organisms in a habitat, Classify various animals based on common characteristics, Classify various plants based on common characteristics, Explain the importance of biodiversity to the environment.
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of living organisms. Collect and classify various plants and animals into a system based on common characteristics. a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish, bird, amphibian, reptile. b) Plant: Flowering plant, nonflowering plant, monocotyledon, dicotyledon. c) Build a concept map on living organisms based on the classification above. Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
Observing Classifying Communica ting
. Basic concept on variety of living organisms has been introduced in primary science. Emphasize only on the classification in the suggested learning activities. Malaysia is one of the twelve megabiodiversity countries in the world should be highlighted
LEARNING AREA:
11 11 15/3/13
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
Having critical and analytical thinking Basic concept of prey predator and competition has been taught in primary school. Refer all to local issues like the crow problem in Klang. Basic concept of habitat has been
CHAPTER 4: THE INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS. LO1 The inter-dependence among living organisms Species, population and community are, Habitat and ecosystem Various habitats in one Carry out a field work to study species, habitat, population, community in an ecosystem. Characteris e Form mental image Analyse Observing Classify
Realising that science is a means to understan
13
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Correlate Compare & contrast Characteris e Compare & differentiat e Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
SPS (Science Process Skills) Inferring
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Having an interest and curiosity towards the environme nt. Being systematic. Having critical and analytical thinking.
Notes
10 25/2 1/3/13 10 4 8/3/13
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY LO1 The variety of living organisms and their classification. Explain the diversity of living organisms in a habitat, Classify various animals based on common characteristics, Classify various plants based on common characteristics, Explain the importance of biodiversity to the environment.
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of living organisms. Collect and classify various plants and animals into a system based on common characteristics. a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish, bird, amphibian, reptile. b) Plant: Flowering plant, nonflowering plant, monocotyledon, dicotyledon. c) Build a concept map on living organisms based on the classification above. Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
Observing Classifying Communica ting
. Basic concept on variety of living organisms has been introduced in primary science. Emphasize only on the classification in the suggested learning activities. Malaysia is one of the twelve megabiodiversity countries in the world should be highlighted
LEARNING AREA:
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
Carry out a discussion on interdependence among living organisms and the environment to create a balanced ecosystem. Correlate by explaining through examples
ecosystem, The interdependence among living organisms and the environment to create a balanced ecosystem,
d nature..
Appreciatin g the balance of nature.
introduced in primary school. During the field work the concept of ecology will be constructed through contextual learning.
14
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Correlate Compare & contrast Characteris e Compare & differentiat e Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
SPS (Science Process Skills) Inferring
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Having an interest and curiosity towards the environme nt. Being systematic. Having critical and analytical thinking.
Notes
10 25/2 1/3/13 10 4 8/3/13
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY LO1 The variety of living organisms and their classification. Explain the diversity of living organisms in a habitat, Classify various animals based on common characteristics, Classify various plants based on common characteristics, Explain the importance of biodiversity to the environment.
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of living organisms. Collect and classify various plants and animals into a system based on common characteristics. a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish, bird, amphibian, reptile. b) Plant: Flowering plant, nonflowering plant, monocotyledon, dicotyledon. c) Build a concept map on living organisms based on the classification above. Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
Observing Classifying Communica ting
. Basic concept on variety of living organisms has been introduced in primary science. Emphasize only on the classification in the suggested learning activities. Malaysia is one of the twelve megabiodiversity countries in the world should be highlighted
LEARNING AREA:
11 11 15/3/13
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
Collect and interpret data on the types of interactions as follows: a) prey-predator, b) symbiosis: commensalism, mutualism and parasitism e.g. remora and shark, algae and fungi, tape worm and man, c) competition. Conduct an activity to show the importance of the interaction between organisms and the environment. Characteris e Conclude by explaining with examples Compile & differentiat e Analyse by Observing Interpreting data Classifying Inferring Defining operationall y Realising that science is a means to understand nature.
LO2 The interaction between living organisms. The types of interactions between living organisms, The interactions between living organisms, The importance of interaction between living organisms and the environment,
15
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Correlate Compare & contrast Characteris e Compare & differentiat e Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
SPS (Science Process Skills) Inferring
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Having an interest and curiosity towards the environme nt. Being systematic. Having critical and analytical thinking.
Notes
10 25/2 1/3/13 10 4 8/3/13
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY LO1 The variety of living organisms and their classification. Explain the diversity of living organisms in a habitat, Classify various animals based on common characteristics, Classify various plants based on common characteristics, Explain the importance of biodiversity to the environment.
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of living organisms. Collect and classify various plants and animals into a system based on common characteristics. a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish, bird, amphibian, reptile. b) Plant: Flowering plant, nonflowering plant, monocotyledon, dicotyledon. c) Build a concept map on living organisms based on the classification above. Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
Observing Classifying Communica ting
. Basic concept on variety of living organisms has been introduced in primary science. Emphasize only on the classification in the suggested learning activities. Malaysia is one of the twelve megabiodiversity countries in the world should be highlighted
LEARNING AREA:
11 11 15/3/13 LO3
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
Collect and interpret data on the producer, consumer, decomposer and pyramid number. Construct a food web from a few food chains and identify the producer, consumer and decomposer. Discuss the energy flow in the food web constructed. Characteris e Conclude by identifying & constructin g Visualising Correlate Observing Interpreting data Having critical and analytical thinking. Being cooperativ e Being Food chain has been taught in primary science
The food web. Meanings of producers, consumers and decomposers Combination of a few food chains to construct a food web,. The producer, consumer and decomposer in a food web,
Predicting Communica ting
Refer to the crown of thorn problem in the coral reef in the marine park
16
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Correlate Compare & contrast Characteris e Compare & differentiat e Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
SPS (Science Process Skills) Inferring
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Having an interest and curiosity towards the environme nt. Being systematic. Having critical and analytical thinking.
Notes
10 25/2 1/3/13 10 4 8/3/13
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY LO1 The variety of living organisms and their classification. Explain the diversity of living organisms in a habitat, Classify various animals based on common characteristics, Classify various plants based on common characteristics, Explain the importance of biodiversity to the environment.
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of living organisms. Collect and classify various plants and animals into a system based on common characteristics. a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish, bird, amphibian, reptile. b) Plant: Flowering plant, nonflowering plant, monocotyledon, dicotyledon. c) Build a concept map on living organisms based on the classification above. Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
Observing Classifying Communica ting
. Basic concept on variety of living organisms has been introduced in primary science. Emphasize only on the classification in the suggested learning activities. Malaysia is one of the twelve megabiodiversity countries in the world should be highlighted
LEARNING AREA:
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
Conduct a game to show the effects of an increase or decrease in the number of organisms in a pyramid number. Discuss the consequences if a component of living organisms in an ecosystem is missing Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude Forecasting Predicting honest .
Pyramid number from a food chain, Relate the food web and the pyramid number to energy flow. Predict the consequences if a certain component of living organisms in the ecosystem is missing
17
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Correlate Compare & contrast Characteris e Compare & differentiat e Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
SPS (Science Process Skills) Inferring
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Having an interest and curiosity towards the environme nt. Being systematic. Having critical and analytical thinking.
Notes
10 25/2 1/3/13 10 4 8/3/13
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY LO1 The variety of living organisms and their classification. Explain the diversity of living organisms in a habitat, Classify various animals based on common characteristics, Classify various plants based on common characteristics, Explain the importance of biodiversity to the environment.
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of living organisms. Collect and classify various plants and animals into a system based on common characteristics. a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish, bird, amphibian, reptile. b) Plant: Flowering plant, nonflowering plant, monocotyledon, dicotyledon. c) Build a concept map on living organisms based on the classification above. Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
Observing Classifying Communica ting
. Basic concept on variety of living organisms has been introduced in primary science. Emphasize only on the classification in the suggested learning activities. Malaysia is one of the twelve megabiodiversity countries in the world should be highlighted
LEARNING AREA:
12 18/3 22/3/13
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
Carry out discussion on what photosynthesis is. Carry out experiments to determine the factors needed for photosynthesis i.e. carbon dioxide, water, light and chlorophyll. Discuss the importance of photosynthesis in maintaining a balanced ecosystem. Characteris e Hypothesisi ng Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude Synthesisin g Communica ting Experiment ing Being honest and accurate in recording and validating data. Being responsible of the environme nt. The carbon and oxygen cycle should be included.
LO4 Photosynthesis. Meaning of photosynthesis The factors required for photosynthesis, State the products of photosynthesis, The variables that are required for photosynthesis,
Hypothesisi ng Inferring
18
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Correlate Compare & contrast Characteris e Compare & differentiat e Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
SPS (Science Process Skills) Inferring
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Having an interest and curiosity towards the environme nt. Being systematic. Having critical and analytical thinking.
Notes
10 25/2 1/3/13 10 4 8/3/13
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY LO1 The variety of living organisms and their classification. Explain the diversity of living organisms in a habitat, Classify various animals based on common characteristics, Classify various plants based on common characteristics, Explain the importance of biodiversity to the environment.
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of living organisms. Collect and classify various plants and animals into a system based on common characteristics. a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish, bird, amphibian, reptile. b) Plant: Flowering plant, nonflowering plant, monocotyledon, dicotyledon. c) Build a concept map on living organisms based on the classification above. Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
Observing Classifying Communica ting
. Basic concept on variety of living organisms has been introduced in primary science. Emphasize only on the classification in the suggested learning activities. Malaysia is one of the twelve megabiodiversity countries in the world should be highlighted
LEARNING AREA:
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL PERTAMA 23 MAC 2013 31 MAC 2013
13 1 5/4/13
LO5 The importance of conservation and preservation of living organisms. Explain what conservation and preservation are,
Collect and interpret data on the conservation and preservation of living organisms. Carry out a field work in a natural forest reserve (wetlands, highland forest or tropical rain forest) or an animal sanctuary to study the conservation and preservation of
Conclude Compare & contrast Generate ideas Analyse Generalise
Interpreting data Inferring Communica ting
Being cooperativ e.
The role of man in conservation and preservation has been highlighted in primary school. Forest is also home to some indigenous
Appreciatin g the
19
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Correlate Compare & contrast Characteris e Compare & differentiat e Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
SPS (Science Process Skills) Inferring
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Having an interest and curiosity towards the environme nt. Being systematic. Having critical and analytical thinking.
Notes
10 25/2 1/3/13 10 4 8/3/13
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY LO1 The variety of living organisms and their classification. Explain the diversity of living organisms in a habitat, Classify various animals based on common characteristics, Classify various plants based on common characteristics, Explain the importance of biodiversity to the environment.
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of living organisms. Collect and classify various plants and animals into a system based on common characteristics. a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish, bird, amphibian, reptile. b) Plant: Flowering plant, nonflowering plant, monocotyledon, dicotyledon. c) Build a concept map on living organisms based on the classification above. Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
Observing Classifying Communica ting
. Basic concept on variety of living organisms has been introduced in primary science. Emphasize only on the classification in the suggested learning activities. Malaysia is one of the twelve megabiodiversity countries in the world should be highlighted
LEARNING AREA:
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
living organisms. Discussion on how the improvement in science and technology helps in the conservation and preservation of living organisms. Run a campaign to stress on the importance of conservation and preservation / Carry out a role play involving the parties concerned in solving problems related to the conservation and preservation of Conclude balance of nature. people should be included.
Explain the steps taken to preserve and conserve living organisms, Justify the importance of conservation and preservation of living organisms, Support activities organised by various parties to preserve and conserve the living organisms.
Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
Communica ting
Having critical and analytical thinking.
20
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Correlate Compare & contrast Characteris e Compare & differentiat e Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
SPS (Science Process Skills) Inferring
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Having an interest and curiosity towards the environme nt. Being systematic. Having critical and analytical thinking.
Notes
10 25/2 1/3/13 10 4 8/3/13
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY LO1 The variety of living organisms and their classification. Explain the diversity of living organisms in a habitat, Classify various animals based on common characteristics, Classify various plants based on common characteristics, Explain the importance of biodiversity to the environment.
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of living organisms. Collect and classify various plants and animals into a system based on common characteristics. a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish, bird, amphibian, reptile. b) Plant: Flowering plant, nonflowering plant, monocotyledon, dicotyledon. c) Build a concept map on living organisms based on the classification above. Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
Observing Classifying Communica ting
. Basic concept on variety of living organisms has been introduced in primary science. Emphasize only on the classification in the suggested learning activities. Malaysia is one of the twelve megabiodiversity countries in the world should be highlighted
LEARNING AREA:
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
living organisms.
21
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Correlate Compare & contrast Characteris e Compare & differentiat e Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
SPS (Science Process Skills) Inferring
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Having an interest and curiosity towards the environme nt. Being systematic. Having critical and analytical thinking.
Notes
10 25/2 1/3/13 10 4 8/3/13
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY LO1 The variety of living organisms and their classification. Explain the diversity of living organisms in a habitat, Classify various animals based on common characteristics, Classify various plants based on common characteristics, Explain the importance of biodiversity to the environment.
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of living organisms. Collect and classify various plants and animals into a system based on common characteristics. a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish, bird, amphibian, reptile. b) Plant: Flowering plant, nonflowering plant, monocotyledon, dicotyledon. c) Build a concept map on living organisms based on the classification above. Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
Observing Classifying Communica ting
. Basic concept on variety of living organisms has been introduced in primary science. Emphasize only on the classification in the suggested learning activities. Malaysia is one of the twelve megabiodiversity countries in the world should be highlighted
LEARNING AREA:
14 8 12/4/13 LO6
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
Carry out a brainstorming session to discuss the environmental issues affecting the balance in nature and how to solve it. Carry out a discussion to justify that man needs stable and productive ecosystem to ascertain a harmonious life. Being respectful and wellmannered. Being flexible and openminded. Daring to Example of environmental Issues: Global climate change, habitat destruction, species extinction, air, soil and water pollution, loss of wetlands, solid waste management, deforestation, land overuse, over fishing, toxin in the
The role of man in maintaining the balance in nature. The effects of human activities on the balance in nature, How man solve problems related to environment, Human need a stable,
Correlate Analyse
Inferring
Generate ideas (justify)
Communica ting
22
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Correlate Compare & contrast Characteris e Compare & differentiat e Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
SPS (Science Process Skills) Inferring
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Having an interest and curiosity towards the environme nt. Being systematic. Having critical and analytical thinking.
Notes
10 25/2 1/3/13 10 4 8/3/13
CHAPTER 3 : BIODIVERSITY LO1 The variety of living organisms and their classification. Explain the diversity of living organisms in a habitat, Classify various animals based on common characteristics, Classify various plants based on common characteristics, Explain the importance of biodiversity to the environment.
Discuss the diversity in the general characteristics of living organisms. Collect and classify various plants and animals into a system based on common characteristics. a) Animal: Invertebrate, vertebrate, mammal, fish, bird, amphibian, reptile. b) Plant: Flowering plant, nonflowering plant, monocotyledon, dicotyledon. c) Build a concept map on living organisms based on the classification above. Discuss the importance of maintaining the biological diversity as one of the countrys natural heritage.
Observing Classifying Communica ting
. Basic concept on variety of living organisms has been introduced in primary science. Emphasize only on the classification in the suggested learning activities. Malaysia is one of the twelve megabiodiversity countries in the world should be highlighted
LEARNING AREA:
2. INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
try. environment.
productive and balanced ecosystem.
23
Created by CDC SZA 12
THEME: MATTER IN NATURE LEARNING AREA: 1. WATER AND SOLUTION
Week & date CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) SPS (Science Process Skills) Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Being honest and accurate in recording and validating data Notes
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CHAPTER 5 : WATER & SOLUTION 15 16 19/4/13 LO1 The physical characteristics of water. State the meaning of the freezing point of water, The meaning of the boiling point of water, The physical characteristics of water, Explain through example the effects of impurities on the physical characteristics of water. Carry out activities to determine the following: a) the freezing point of water, b) the boiling point of water. Characteri se Observing
The kinetic Theory should be introduced. Relate the freezing and boiling point of water to the kinetic Theory.
Correlate Carry out an activity to observe the effects of impurities on the physical characteristics of water. Conclude
Defining operational ly Interpretin g data
24
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Characteri se
SPS (Science Process Skills) Observing Inferring Defining operational ly
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Having critical and analytical thinking
Notes
16 22 26/4/13
LO2
The composition of water. Determine the composition of water, Test the presence of hydrogen and oxygen. Carry out an electrolysis to determine the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen in a molecule of water.
Analyse Visualisin g
The ionic theory on electrolysis is not needed. Understand ng that hydrogen is discharge at the cathode and oxygen at the anode is adequate. The ratio of gases is required.
17 29/4 3/5/13
LO3 The process of evaporation of water. Meaning of evaporation Examples the factors that affect the rate of evaporation of water with reference to the kinetic theory, Compare and contrast between evaporation and boiling, The application of the evaporation of water in daily life.
Carry out experiments to study the factors affecting the rate of evaporation of water i.e. humidity, the temperature of the surrounding, surface area and the movement of air. Discuss the factors affecting the rate of evaporation in relation to the kinetic theory. Discuss the similarities and differences between evaporation and boiling. Gather information on evaporation process and its application in daily life i.e. drying of clothes, preservation of agricultural products and processing of food.
Characteri se Compare & contrast Generate ideas Analyse Generalis e Conclude Correlate Compile & differentia te
Observing Measuring and using numbers Experimen ting Interpretin g data Defining operational ly Spacingtime relationshi p Inferring
Being honest and accurate in recording and validating data
Appreciating the balance of nature
25
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills)
SPS (Science Process Skills) Classifying
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values
Notes
18 6 10/5/13 19 13/5 17/5/13
LO4
Solution and solubility. Meanings of solute, solvent and solution Contrast and compare between dilute solution, concentrated and saturated solution, Explain what suspension is, Explain what solubility is, Explain the factors affecting the solubility of solutes in water, Explain the importance of water as a universal solvent in life, Give examples on the uses of organic solvents in our everyday life.
Discuss the differences between solute, solvent and solution. Carry out activities to prepare a dilute solution, a concentrated solution and a saturated solution. Discuss the similarities and differences between dilute solution, concentrated solution and saturated solution. Carry out activities to illustrate the differences between a solution and a suspension. Carry out experiments to determine the factors affecting the solubility of a solute. a) Nature of solvent, b) Nature of solute, c) Temperature. Carry out experiment to determine the factors affecting the rate of dissolving: temperature, rate of stirring,
Characteri se Compare, Compile , differentia te & contrast Visualisin g Correlate
Observing Classifying
Having critical and analytical thinking Appreciating the contribution of science and technology Daring to try Being honest and accurate in recording and validating data.
Introduce insoluble sediments are known as residue.
Defining operational ly Inferring Communic ating
20 20/524/5
Compare & contrast Generate ideas Analyse Synthesisi ng Generalis e Conclude Forecastin
Experimen ting Spacingtime relationshi p
26
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
size of solute particle. Discuss the importance of water as a universal solvent in life. Gather information on the application of organic solvents in daily life. CUTI PERTENGAHAN TAHUN 25 MEI 2013 9 JUN 2013 LO5 21 10 14/6/13 Acid and alkali. Identify the properties of acid, identify the properties of alkali, State that acid and alkali only show their properties in the presence of water, Explain through examples the definition of acid and alkali, Identify the substances which are acidic or alkaline in everyday life, State the uses of acid and alkali in daily life, Explain the meaning of neutralisation, Write an equation in words to Carry out activities to study: a) the properties of acid in terms of pH value, taste, corrosive nature, effect on litmus paper, reaction with metals such as magnesium and zinc, b) the characteristics of alkali in terms of pH value, taste, corrosive nature, effect on litmus paper, c) carry out a discussion to define acid and alkali operationally. Carry out activities to determine the acidic and alkaline substances in daily life. Gather information on the usage of acid and alkali in everyday life such as in agriculture and industry. Discuss on the meaning of neutralisation. Carry out an activity to show
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) g
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values
Notes
Observing Characteri se Compile & differentia te Correlate Making analogy Compare & contrast Generate ideas Analyse Synthesisi ng Generalis e Conclude Forecastin g Classifying Interpretin g data Defining operational ly Communic ating Appreciating the contribution of science and technology Having critical and analytical thinking Appreciating the balance of nature
Caution: Chemicals in the laboratory should not be tasted. Use only dilute acid and dilute alkali. Do not use active metal such as potassium and sodium in the reaction with acid.
27
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills)
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values
Notes
describe the neutralisation process, Explain through examples the uses of neutralization in daily life.
neutralisation using the hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide of the same concentration. Discuss the application of neutralization in daily life e.g. using shampoo and conditioner and, insect bite.
22 17 21/6/13
LO6 The methods of water purification. List the natural sources of water, State the reasons for water purification, Describe the various types of water purification,
Make a visit to a water purification site. Brainstorming on the following: natural resources of water, the reasons for water purification. Discuss the various types of water purification such as filtration, boiling, chlorination and distillation. Carry out activities to study the
Generate ideas Analyse Generalis e Conclude
Communic ating Defining operational ly Classifying
Appreciating and practicing clean and healthy living Appreciating the contribution of science and technology
The latest development in water purifications e.g. ultraviolet treatment can be discussed.
Compile &
28
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
Compare the strengths and weaknesses of the various types of water purification.
various types of water purification such as filtration, boiling and distillation. Pupils present their findings to discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the various types of water purification. Make a visit to a water processing plant to study the water supply system and stages involved in water purification. Discuss the ways to save water. Do a project on how much water the average household uses. Collect and interpret data on types of water pollutants which include: a) industrial waste such as chemical and radioactive residues, b) domestic waste such as garbage and sewage, c) chemicals from the agricultural activities such as fertilisers and pesticides, d) siltation caused by constructions and deforestation, e) accidental spillage from tankers. Conduct discussion on the effect of water pollution on living things. Generate ideas on ways to control
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) differentia te
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Being thankful to God.
Notes
22 17 21/6/13
LO7 The water supply system. Describe how the water supply system works, Explain ways to save water.
Generate ideas Analyse Generalis e Conclude Compile & differentia te Characteri se Conclude Generate ideas Analyse Generalis e Conclude Relating
Communic ating
Having an interest and curiosity towards the environment.
Interpretin g data Classifying Observing Interpretin g data Communic ating Inferring Being objective Having an interest and curiosity towards the environment. Appreciating and practicing clean and healthy living.
22 17/6 21/6/13
LO8 The preservation of water quality. Give examples of water pollutants, Explain the effect of water pollution on living things, Explain ways to control water pollution, Explain ways to preserve water and its quality.
Predicting
29
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
water pollution. Discuss ways to conserve and preserve water and its quality. Run a campaign on Love Our Rivers.
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Visualisin g
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values
Notes
THEME: MATTER IN NATURE LEARNING AREA: 2. AIR PRESSURE
Week & date Chapters & Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Characterise Analyse Visualising Generate ideas Generalise Conclude SPS (Science Process Skills) Observing Inferring Defining operationall y Communica ting Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Notes
23 24 28/6/13
CHAPTER 6 : AIR PREESURE LO1 Air pressure. Explain the existence of air pressure with reference to the Kinetic Theory, Explain the factors affecting air pressure.
Carry out an activity to discuss the kinetic theory of gases. Carry out an activity to show that air exerts pressure. Carry out activities to show the factors affecting air pressure, i.e. volume and temperature.
Realising that science is a mean to understand nature. Having critical and analytical thinking
30
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Characterise Conclude Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude Correlate
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Appreciating the contribution of science and Technology. Having critical and analytical thinking. Being cooperative.
Notes
23 24 28/6/13
LO2 The principle of air pressure in daily life. Explain with examples things that use the principle of air pressure, Generate ideas to solve problems using the principle of air pressure,
Caution: Do not place tank containing gas under high pressure near heat.
Collect and interpret data on appliances that use the principle of air pressure. Gather information and discuss the application of air pressure in syringe, siphon, spraying pump and drinking straw. Discuss ways of using the principle of air pressure to solve daily problems such as blockage in sinks and pouring condensed milk from a can. *Teachers can design some activities. Gather information on how a gas tank containing gas under high pressure works. Discuss the safety precautions taken when using gas under high pressure.
Observing Interpreting data Communica ting
Inferring
Relate the safety measures taken when using gas under high pressure.
PENTAKSIRAN PUSAT 24 - 27
THEME: FORCE AND MOTION LEARNING AREA: 1. DYNAMICS
31
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
28 29/7 2/8/13 28 29/7 2/8/13
CHAPTER 7 : DYNAMICS LO1 Force. State that a force is a push or a pull, Explain the effects of forces, Explain the various types of forces. Carry out activities to show pushing and pulling are forces. Carry out activities to show the effects of force (changes in shape, position, speed and direction). Carry out activities to show different types of forces (frictional, gravitational, electrostatic and magnetic force).
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Characterise Visualising Sequencing Compile & differentiate Generate ideas Analyse Synthesising Generalise
SPS (Science Process Skills) Observing Defining operationally Using time spacerelationship Classifying Communicat ing
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values
Notes
Rational and objective in thinking. Being cooperative Appreciating the contribution of science and technology. Being honest and accurate in recording and validating data. Being systematic. Appreciating the contribution of science and technology. Having critical
29 5 6/8/13
LO2 The measurement of force. State the unit of force. Principle of a spring balance works. The magnitude of force.
Discuss the unit of force and the principle of a spring balance. Carry out activity to measure the magnitude of force.
Characterise Correlate Conclude
Observing Measuring and using numbers Interpreting data
30 19 23/8/13
LO3 Application of frictional force. Explain with example the existence of frictional force, State the direction and the magnitude of frictional force, Carry out an experiment to show how different types of Discuss with examples to show the existence of frictional force. Carry out activities to identify the direction of frictional force and measure the magnitude of the force.
Characterise Correlate Conclude Visualising
Observing Measuring and using numbers Interpreting data
Ignore static frictional force
32
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes surfaces affects frictional force, Explain the advantages and disadvantages of friction, Explain ways to increase friction. Explain ways to reduce friction, Explain with examples the application of friction in daily life.
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Compile & differentiate Generate ideas Analyse Synthesising Conclude Generalise
SPS (Science Process Skills) Defining operationally Experimenti ng Communicat ing
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values and analytical thinking.
Notes
Carry out an experiment to show how different types of surfaces affect the magnitude of frictional force. Gather information and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of friction. Carry out activities on ways to increase friction, reduce friction. Discuss the application of increasing and decreasing friction in our daily life.
Being cooperative.
31 26 30/8/13
LO4 Application of work. Explain with examples how work is done, State the unit for work, Calculate the work done.
Discuss with examples to show work done when an object is moved by a force. Carry out activities to determine the work done by using: Work (J) = Force (N) X Distance (m)
Compile & differentiate Correlate Generate ideas Analyse Synthesising Conclude Generalise
Communicat ing Measuring and using numbers
Being cooperative.
Having critical and analytical thinking.
Interpreting data 31 26 LO5 Application of power. State the meaning of power, Carry out activities to determine power by using: Power (W) = Work (J) Visualising Defining operationally Being honest and accurate in recording
33
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date 30/8/13
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities Time (s)
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Correlate Conclude
SPS (Science Process Skills) Measuring and using numbers Interpreting data
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values and validating data. Being systematic.
Notes
State the unit for power, Calculate power on the work done.
32 2 6/9/13
LO6 The importance of force in life. Describe life if force does not exist.
Create an activity to show how life would be without force, e.g. in a poster, a sketch or skit.
Characterise Generate ideas Analyse Synthesising Generalise
Observing Communicat ing
Appreciating the contribution of science and technology.
THEME: FORCE AND MOTION LEARNING AREA: 2. SUPPPORT AND MOVEMENT
Week & date Chapters & Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Characterise Gather information and discuss the various support systems in a) land and aquatic vertebrates, b) land and aquatic invertebrates. . Compile & differentiate Classifying Visualising SPS (Science Process Skills) Observing Defining operationall y Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Interest and inquisitive. Realising that science is a means to understand nature. Notes
33 9 13/9/13
CHAPTER 8 : SUPPORT & MOVEMNT LO1 The support system in animals. Explain the various support systems in vertebrates and invertebrates, Compare and contrast the support system between land and aquatic vertebrates, Compare and contrast the
For invertebrates introduce exoskeleton endoskeleton, hydrostatic skeleton
34
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes support system between land and aquatic invertebrates.
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills)
SPS (Science Process Skills)
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values
Notes
33 913/9/13
LO2 The support system in plants. Explain the various support systems in plants, in woody and non-woody plants Classify plants based on their support systems.
Carry out activities to study the various support systems in plants. Carry out activities to classify plants based on their support systems.
Characterise Visualising Compile & differentiate
Observing Defining operationall y Classifying
Interest and inquisitive. Having an interest and curiosity towards the environment.
Features that help non-woody plants include tendrils, thorns, air sacs in aquatic plants.
34 17 20/9/13
LO3 Appreciating the support system in living things. Justify the important of the support system to living things
Discuss issues i.e.: a) inability of whales to move back to the sea after being washed to shore, b) a crippled person using crutches for support.
Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude Visualising
Communica ting Being thankful to God.
Defining operationall y
THEME: TECHNOLOGICAL AND INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT IN SOCIETY
35
Created by CDC SZA 12
LEARNING AREA:
Week & date
1. STABILITY
Suggested Learning Activities CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Characterise Correlate Compile & differentiate Visualising SPS (Science Process Skills) Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Notes
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
35 23 27/9/13
CHAPTER 9 : STABILITY LO1 Factors affecting the stability Determine the point of equilibrium in regular and irregular shapes, Relate the point of equilibrium as the centre of gravity of objects, Relate the centre of gravity to the stability of objects.
Carry out activities to find the point of equilibrium in regular and irregular shapes. Carry out an experiment to find out how the centre of gravity affects the stability of an object by manipulating the height, base area. Discuss the relationship between the centre of gravity to stability.
Observing Inferring Classifying Defining operationall y
Being cooperative. Having critical and analytical thinking.
36 30/9 4/10/13
37 7 11/10/13
LO2 Appreciating the importance of stability. Ways to improve the stability of objects around them, Explain with examples the application of stability in life.
Carry out a brain storming session on ways to improve stability. Carry out activities like projects or games to build models by applying the concept of stability.
Characterise Correlate by suggesting Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude Visualising
Observing Inferring Communica ting
Appreciating the contribution of science and technology.
Defining operationall y
36
Created by CDC SZA 12
THEME: TECHNOLOGICAL AND INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT IN SOCIETY LEARNING AREA: 2. SIMPLE MACHINE
Week & date Chapters & Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Characterise Discuss that the lever enables us to: a) change a small force into a big force, b) change a small movement into a large movement, c) state that the moment of force = force X perpendicular distance from pivot to force. Make an observation to identify the load, force and fulcrum then classify them into first, second and third class levers. Carry out an activity to show the relationship between moment and the product of force and distance. Solving problems related to levers using the following formulae: Load (N) X distance of the load from fulcrum (m) = Force (N) X distance of the force from the fulcrum (m) Correlate Making analogy Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude Compile & differentiate Correlate SPS (Science Process Skills) Observing Inferring Defining operationally Communicati ng When we open the door or use a wrench to loosen a nut, we are applying a force that causes a turning effect to accomplish the desired task. The turning effect is called the moment of a force. Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values Ability to think critically and analytically. Notes
38 14 18/10/13 39 21 25/10/13
CHAPTER 10 : SIMPLE MACHINE LO1 Levers. List things around them that use the principle of the lever, State what a lever can do, Identify load, force and fulcrum in the lever, Classify levers, Explain what is meant by the moment of a force, Solve problems related to levers.
Classifying Measuring and using numbers.
37
Created by CDC SZA 12
Week & date
Chapters & Learning Outcomes
Suggested Learning Activities
CCTS (Critical & creative thinking skills) Characterise
SPS (Science Process Skills) Observing Measuring and using numbers Communicati ng
Scientific Attitudes & Noble Values
Notes
40-41 28/10 8/11/13
LO2 Appreciating the innovative efforts in the design of machine to simplify work. Design or improvise a device using the principle of a lever.
Carry out a project to build a device using the principles of a lever.
Correlate Generate ideas Analyse Generalise Conclude
Appreciating the contribution of science and technology.
42
Kemaskini fail peribadi pelajar sains tingkatan 2 2013.
38
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Uhv & Pe Unit 1 & 2Document20 paginiUhv & Pe Unit 1 & 2JAGRITI AWASTHIÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Analysis of Students' Logical Thinking Ability and Adversity Quotient, and It Is Reviewed From Cognitive StyleDocument9 paginiThe Analysis of Students' Logical Thinking Ability and Adversity Quotient, and It Is Reviewed From Cognitive StyleBunmamp Tran Minh PhucÎncă nu există evaluări
- Get Rid of The Performance Review! - WSJDocument8 paginiGet Rid of The Performance Review! - WSJSourav Basu100% (1)
- Mabruroh - 2017 - J. - Phys. - Conf. - Ser. - 812 - 012056Document7 paginiMabruroh - 2017 - J. - Phys. - Conf. - Ser. - 812 - 012056Sekarwuni YhudantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embodiment and Language Comprehension ReV PDFDocument6 paginiEmbodiment and Language Comprehension ReV PDFDiletta GullottaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hans Jonas, L. E. Long (Editor) - Philosophical Essays - From Ancient Creed To Technological Man-Atropos Press (2010) PDFDocument374 paginiHans Jonas, L. E. Long (Editor) - Philosophical Essays - From Ancient Creed To Technological Man-Atropos Press (2010) PDFmarko1234100% (1)
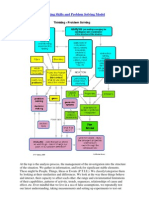
- Thinking Skills and Problem Solving ModelDocument4 paginiThinking Skills and Problem Solving ModelJohn Evans100% (3)
- Magic Lessons (Magick The Occult Imagination Will)Document41 paginiMagic Lessons (Magick The Occult Imagination Will)magicalpathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tarot Readers Black BookDocument42 paginiTarot Readers Black BookAlessandro Balossini100% (2)
- Beyond The Attractor Factor - Workbook PDFDocument21 paginiBeyond The Attractor Factor - Workbook PDFjohnsonkk125100% (2)
- The Career State Inventory As Intentional AssessmentDocument15 paginiThe Career State Inventory As Intentional Assessmentranti faqothÎncă nu există evaluări
- Think Big Take Small Steps and Build The Future You WantDocument282 paginiThink Big Take Small Steps and Build The Future You WantRhuthshana Shanker100% (3)
- Karl Mannheim by David Kettler, Volker Meja, Nico StehrDocument167 paginiKarl Mannheim by David Kettler, Volker Meja, Nico StehrLuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- English-10 SLM Q1 M7 L1 CC V2.0 Released26Oct21Document21 paginiEnglish-10 SLM Q1 M7 L1 CC V2.0 Released26Oct21Jheff DomingoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barsalou - 2015 - SITUATED CONCEPTUALIZATIONDocument17 paginiBarsalou - 2015 - SITUATED CONCEPTUALIZATIONДарья БарашеваÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adolescents Musical Relaxation Understanding Related Affective ProcessingDocument15 paginiAdolescents Musical Relaxation Understanding Related Affective ProcessingEsun RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Symbolic InteractionismDocument37 paginiLesson Symbolic InteractionismCandys Demeterio Bati100% (3)
- Social 8 Renaissance Unit PlanDocument12 paginiSocial 8 Renaissance Unit Planapi-242289205Încă nu există evaluări
- Social Cognition: Learning OutcomesDocument6 paginiSocial Cognition: Learning OutcomesmelchieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding How Asperger Children and Adolescents Think and LearnDocument122 paginiUnderstanding How Asperger Children and Adolescents Think and LearnOliver Tabag100% (5)
- Purity of Thought self-analysisDocument2 paginiPurity of Thought self-analysisAgung SuryaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Ideation TechniquesDocument3 paginiKey Ideation TechniquesSocrates FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pyschological First AidDocument26 paginiPyschological First AidVhenn Francis SaysonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Game SenseDocument7 paginiGame Senseapi-357871401Încă nu există evaluări
- Thinking Skills and Ict Kemahiran Berfikir Dalam IctDocument11 paginiThinking Skills and Ict Kemahiran Berfikir Dalam Ictapi-299111428Încă nu există evaluări
- The Sosuave Guide To Women and DatingDocument45 paginiThe Sosuave Guide To Women and DatingPaulo BarrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 GE005 UTSDocument12 paginiModule 3 GE005 UTSpaubosnagmailkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quarter 1 - Module 2: Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument22 paginiQuarter 1 - Module 2: Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDarylCrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Paper Sample Middle SchoolDocument5 paginiResearch Paper Sample Middle Schoolfys1q18y100% (1)
- Who A Zettelkasten Is For (Especially An Analog One) - Zettelkasten ForumDocument14 paginiWho A Zettelkasten Is For (Especially An Analog One) - Zettelkasten Forumzentropia100% (1)