Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Yearly Form2 2012
Încărcat de
ainarahyuDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Yearly Form2 2012
Încărcat de
ainarahyuDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
WEEK
LEARNING AREA CHAPTER 1: Directed Numbers
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Perform computations involving multiplication and division of integers to solve problems.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Multiply integers. 2. Solve problems involving multiplication of integers. 3. Divide integers. 4. Solve problems involving division of integers. Students will be able to: 1. Perform computations involving combined operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of integers. 2. Solve problems involving combined operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of integers including the use of brackets. Students will be able to: 1. Compare and order decimals. 2. Perform addition, subtraction, multiplication or division on decimals. Students will be able to: 1. Compare and order decimals. 2. Perform addition, subtraction, multiplication or division on decimals. Students will be able to: 1. Perform addition, subtraction, multiplication or division involving two directed numbers. 2. Perform computations involving combination of two or more operations on directed numbers including the use of brackets. 3. Pose and solve problems involving directed numbers.
CCTS
Teaching Aids
1 (04.01.12 06.01.12)
Perform computations involving combined operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of integers to solve problems.
Working out mentally Making inference Translating
10
Coloured chips
10
2 (09.01.12 13.01.12)
Directed Numbers
Extend the concept of integers to fractions to solve problems. Extend the concept of integers to decimals to solve problems. Perform computations involving directed numbers (integers, fractions and decimals).
5 Working out mentally Making inference Translating
10 Coloured chips
10
20
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
LEARNING AREA CHAPTER 2: Squares, squares roots, cubes and cubes roots LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand and use the concept of squares of numbers. LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. State a number multiplied by itself as a number to the power of two and vice-versa. 2. Determine the squares of numbers without using calculators. 3. Estimate the squares of numbers. 4. Determine the squares of numbers using calculators. 5. List perfect squares. 6. Determine if a number is a perfect square. 7. Pose and solve problems involving squares of numbers. Students will be able to: 1. State the square root of a positive number as the number multiplied by itself equals to the given number. 2. Determine the square roots of perfect squares without using calculator. 3. Determine the square roots of numbers without using calculators. 4. Multiply two square roots. 5. Estimate square roots of numbers. 6. Find the square roots of numbers using calculators. 7. Pose and solve problems involving squares and square roots. EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2 Teaching Aids
WEEK
CCTS
3 (16.01.12 20.01.12)
Working out mentally Making inference Translating
Scientific calculator 5 10
Understand and use the concept of square roots of positive numbers.
10
4 5 (30.01.12 03.02.12) Squares, squares roots, cubes and cubes roots
Public Holiday Chinese New Year ( 23.01.2012 27.01.2012 ) Understand and use the Students will be able to: concept of cube of numbers. 1. State a number multiplied by itself twice as a Working out number to the power of three and vice mentally versa. Making 2. Determine cubes of numbers without using inference calculators. Translating 3. Estimate cubes of numbers. 4. Determine cubes of numbers using calculators. 5. Pose and solve problems involving cubes of numbers.
Scientific calculator
10
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
LEARNING AREA Squares, squares roots, cubes and cubes roots LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand and use the concept of cube roots of numbers. LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. State the cube root of a number as the number multiplied by itself twice equals to the given number. 2. Determine the cube roots of integers without using calculators. 3. Determine the cube roots of numbers without using calculators. 4. Estimate cube roots of numbers. 5. Determine cube roots of numbers using calculators. 6. Pose and solve problems involving cubes and cube roots. 7. Perform computations involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and mixed operations on squares, square roots, cubes and cube roots. EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2 Teaching Aids
WEEK
CCTS
5 (30.01.12 03.02.12)
Working out mentally Making inference Translating 5 20
Scientific calculator
6 (06.02.12 10.02.12)
CHAPTER 3: Algebraic Expressions II
Public Holiday Birth of Prophet Muhammad on 5th February 2012 ( Sunday ) Understand the concept of Students will be able to: algebraic terms in two or 1. Identify unknowns in algebraic terms in two more unknowns. or more unknowns. 2. Identify algebraic terms in two or more Interpreting unknowns as the product of the unknowns Classifying with a number. Working out 3. Identify coefficients in given algebraic terms mentally in two or more unknowns. Identifying 4. Identify like and unlike algebraic terms in relations two or more unknowns. Translating 5. State like terms for a given algebraic term. Perform computations involving multiplication and division of two or more terms. Students will be able to: 1. Find the product of two algebraic terms. 2. Find the quotient of two algebraic terms. 3. Perform multiplication and division involving algebraic terms.
Cardboard 5 10
10
School Replacement ( Chinese New Year ) on 11th February 2012 ( Saturday ) Wednesday time table
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
WEEK
LEARNING AREA Algebraic Expressions II
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the concept of algebraic expressions.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Write algebraic expressions for given situations using letter symbols. 2. Recognise algebraic expressions in two or more unknowns. 3. Determine the number of terms in given algebraic expressions in two or more unknowns. 4. Simplify algebraic expressions by collecting like terms. Evaluate expressions by substituting numbers for letters. Students will be able to: 1. Multiply and divide algebraic expressions by a number. 2. Perform a. addition b. subtraction involving two algebraic expressions. 3. Simplify algebraic expressions. Students will be able to: State the relationship between two quantities by using the symbols ' =' or ' ' . Students will be able to: 1. Recognise linear algebraic terms. 2. Recognise linear algebraic expressions. 3. Determine if a given equation is: a. a linear equation b. a linear equation in one unknown. 4. Write linear equations in one unknown for given statements and vice versa. Students will be able to: 1. Determine if a numerical value is a solution of a given linear equation in one unknown. 2. Determine the solution of a linear equation in one unknown by trial and improvement method.
CCTS
Teaching Aids
7 (13.02.12 17.02.12)
Interpreting Classifying Working out mentally Identifying relations Translating
Cardboard 5 10
Perform computations involving algebraic expressions.
20
8 (20.02.12 24.02.12)
CHAPTER 4: Linear Equations
Understand and use the concept of equality. Understand and use the concept of linear equations in one unknown.
5 Interpreting Classifying Working out mentally Identifying relations Translating
5 Balance
10
Understand the concept of solutions of linear equations in one unknown.
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
LEARNING AREA Linear Equations LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the concept of solutions of linear equations in one unknown. LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 3. Determine if a numerical value is a solution of a given linear equation in one unknown. 4. Determine the solution of a linear equation in one unknown by trial and improvement method. 5. Solve equations in the form of: EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2 Teaching Aids
WEEK
CCTS
9 (27.03.12 02.03.12
a. b. c. d.
x+a =b xa =b ax = b x a = b
Interpreting Classifying Working out mentally Identifying relations Translating 10 20
Balance
6.
7. 8.
where a, b, c are integers and x is an unknown. Solve equations in the form of ax + b = c, where a, b, c are integers and x is an unknown. Solve linear equations in one unknown. Pose and solve problems involving linear equations in one unknown.
10 11 (19.03.12 23.03.12) Chapter 5: Ratios, Rates and Proportions
School Replacement ( Chinese New Year ) on 3rd March 2012 ( Saturday ) Thursday time table Discussion and Remedy for the previous lesson Test 1 (05.03.12 09.03.12) Mid Semester One Break ( 10.03.12 18.03.12 ) Understand the concept of Students will be able to: ratio of two quantities. 1. Compare two quantities in the form a : b
a or b .
2.
Understand the concept of proportion to solve problems.
Determine whether given ratios are equivalent ratios. 3. Simplify ratios to the lowest terms. 4. State ratios related to a given ratio. Students will be able to: 1. State whether two pairs of quantities is a proportion. 2. Determine if a quantity is proportional to another quantity given two values of each quantity. 3. Find the value of a quantity given the ratio of the two quantities and the value of another quantity.
Interpreting Classifying Working out mentally Identifying relations Translating
10
Coloured chips Coins
10
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
WEEK
LEARNING AREA Ratios, Rates and Proportions
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the concept of proportion to solve problems.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 4. Find the value of a quantity given the ratio and the sum of the two quantities. 5. Find the sum of two quantities given the ratio of the quantities and the difference between the quantities. 6. Pose and solve problems involving ratios and proportions. Students will be able to: 1. Compare three quantities in the form a: b : c. 2. Determine whether given ratios are equivalent ratios. 3. Simplify ratio of three quantities to the lowest terms. 4. State the ratio of any two quantities given ratio of three quantities. Students will be able to: 1. Identify the hypotenuse of right-angled triangles. 2. Determine the relationship between the lengths of the sides of a right-angled triangle. 3. Find the length of the missing side of a rightangled triangle using the Pythagoras theorem. 4. Find the length of sides of geometric shapes using Pythagoras theorem. 5. Solve problems using the Pythagoras theorem. Students will be able to: 1. Determine whether a triangle is a rightangled triangle. 2. Solve problems involving the converse Pythagoras theorem.
CCTS
Teaching Aids
12 (26.03.12 30.03.12)
Understand and use the concept of ratio of three quantities to solve problems.
Interpreting Classifying Working out mentally Identifying relations Translating
10
Coloured chips Coins
10
13 (02.04.12 06.04.12)
Chapter 6: Pythagoras Theorem
Understand the relationship between the sides of a rightangled triangle.
Arranging sequentially Drawing diagrams
GSP Grid paper Geo-board 5 10
14 (09.04.12 13.04.12)
Pythagoras Theorem
Understand and use the converse of the Pythagoras theorem.
10
School Replacement ( Hari Raya Qurban ) on 14h April 2012 ( Saturday ) Thursday time table
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
WEEK
LEARNING AREA Chapter 7: Geometrical Constructions
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Perform constructions using straight edge (ruler and set square) and compass.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Construct a line segment of given length. 2. Construct a triangle given the length of the sides. 3. Construct: a. perpendicular bisector of a given line segment b. perpendicular to a line passing through a point on the line c. perpendicular to a line passing through a point not on the line. Students will be able to: 4. Construct: a. angle of 60 and 120 b. bisector of an angle. 5. Construct triangles given: a. one side and two angles b. two sides and one angle. 6. Construct: a. parallel lines b. parallelogram given its sides and an angle. Students will be able to: 1. Identify the x-axis, y-axis and the origin on a Cartesian plane. 2. Plot points and state the coordinates of the points given distances from the y-axis and xaxis. 3. Plot points and state the distances of the points from the y-axis and x-axis given coordinates of the points. 4. State the coordinates of points on Cartesian plane.
CCTS
Teaching Aids
15 (16.04.12 20.04.12)
Drawing diagrams Interpreting Identifying relations
Compass Ruler 5 10
16 (23.04.12 27.04.12)
Geometrical Constructions
Perform constructions using straight edge (ruler and set square) and compass.
Drawing diagrams Interpreting Identifying relations
Compass Ruler 5 10
17 (30.04.12 04.05.12)
Chapter 8: Coordinates
Understand and use the concept of coordinates.
Classifying Drawing diagrams Identifying relations
Cartesian plane Geo-board 5 10
Public Holiday Labour Day on 1st May 2012 ( Tuesday )
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
WEEK
LEARNING AREA Coordinates
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand and use the concept of scales for the coordinate axes.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Mark the values on both axes by extending the sequence of given values on the axes. 2. State the scales used in given coordinate axes w here: a. scales for axes are the same b. scales for axes are different. 3. Mark the values on both axes, with reference to the scales given. 4. State the coordinates of a given point with reference to the scales given. 5. Plot points, given the coordinates, with reference to the scales given. 6. Pose and solve problems involving coordinates.
CCTS
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
Teaching Aids
17 (30.04.12 04.05.12)
Classifying Drawing diagrams Identifying relations
Cartesian plane Geo-board 5 10
18 (07.05.12 11.05.12)
Coordinates
Public Holiday Wesak Day on 5th May 20112( Saturday ) State Public Holiday Hol Day of Pahang State on 7th May 2012 ( Monday ) Understand and use the Students will be able to: concept of distance between 1. Find the distance between two points with: two points on a Cartesian a. common y-coordinates plane. Classifying b. common x-coordinates. Drawing 2. Find the distance between two points using diagrams Pythagoras theorem. Identifying 3. Pose and solve problems involving distance relations between two points.
10
Cartesian plane Geo-board
Coordinates
Understand and use the concept of midpoints.
Students will be able to: 1. Identify the midpoint of a straight line joining two points. 2. Find the coordinates of the midpoint of a straight line joining two points with: a. common y-coordinates 3.
5 Classifying Drawing diagrams Identifying relations
10 Cartesian plane Geo-board
b. common x-coordinates. Find the coordinates of the midpoint of the line joining two points. 8
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
4. Pose and solve problems involving midpoints.
WEEK
LEARNING AREA Chapter 9: Loci In Two Dimensions
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the concept of two dimensional loci.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Describe and sketch the locus of a moving object. 2. Determine the locus of points that are of: a. constant distance from a fixed point b. equidistant from two fixed points c. constant distance from a straight line d. Equidistant from two intersecting lines. 3. Construct the locus of a set of all points that satisfies the condition: a. the point is at a constant distance from a fixed point b. the point is at equidistant from two fixed points c. the point is at a constant distance from a straight line d. the point is at equidistant from two intersecting lines Students will be able to: 1. Determine the intersections of two loci by drawing the loci and locating the points that satisfy the conditions of the two loci.
CCTS
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
Teaching Aids
19 (14.05.12 18.05.12)
Classifying Drawing diagrams Identifying relations 5 10
Compass Ruler Pendulum
20 (21.05.12 25.05.12)
Loci In Two Dimensions
Understand the concept of the intersection of two loci.
Classifying Drawing diagrams Identifying relations
10
Compass Ruler Pendulum
First Semester Break (26.05.12 10.06.12) Public Holiday Birthday of Yang Di Pertuan Agong on 2nd June 2012 ( Saturday ) 22 Discussion and Remedy for the previous lesson MID YEAR EXAMINATION ( 11.06.12 15.06.12 )
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
WEEK
LEARNING AREA Chapter 10: Circles
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Recognise and draw parts of a circle.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Identify circle as a set of points equidistant from a fixed point. 2. Identify parts of a circle such as center, radius, chord, circumference, diameter, arc, sector and segment. 3. Draw : a. a circle given the radius and centre b. a circle given the diameter c. a diameter passing through a specific point in a circle given the centre. d. a chord of a given length passing through a point on the circumference e. sector given the size of the angle at the centre and radius of the circle. 4. Determine the center and radius of a given circle by construction. Students will be able to: 1. Estimate the value of . 2. Derive the formula of the circumference of a circle. 3. Find the circumference of a circle, given its diameter or radius. 4. Find the diameter or radius given the circumference of a circle. 5. Solve problems involving circumference of circles. Students will be able to: 1. Derive the formula of the length of an arc. 2. Find the length of arc given the angle at the centre and the radius. 3. Find the angle at the centre given the length of the arc and the radius of a circle.
CCTS
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
Teaching Aids
22 (28.06.12 22.06.12)
Classifying Drawing diagrams Identifying relations 5 10
Compass Ruler Filter paper GSP
Understand and use the concept of circumference to solve problems.
23 (25.06.12 29.06.12)
Circles
Understand and use the concept of arc of a circle to solve problems.
Comparing and contrasting Working out mentally Translating Identifying relations Making inference
10
Compass Ruler Filter paper GSP
10 Compass Ruler Filter paper
10
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
4. 5. Find the length of radius of a circle given the length of the arc and the angle at the centre. Solve problems involving arcs of a circle. GSP
WEEK
LEARNING AREA Circles
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand and use the concept of area of a circle to solve problems.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Derive the formula of the area of a circle. 2. Find the area of a circle given the radius or diameter. 3. Find radius or diameter given the area of a circle. 4. Find the area of a circle given the circumference and vice versa. 5. Solve problems involving area of circles. Students will be able to: 1. Derive the formula of the area of a sector. 2. Find the area of a sector given the radius and angle at the centre. 3. Find the angle at the centre given the radius and area of a sector. 4. Find the radius given the area of a sector and the angle at the centre. 5. Solve problems involving area of sectors and area of circles. Students will be able to: 1. Identify a transformation as a one-to-one correspondence between points in a plane. 2. Identify the object and its image in a given transformation. Students will be able to: 1. Identify a translation. 2. Determine the image of an object under a given translation. 3. Describe a translation: a. by stating the direction and distance of the movement b. in the form(a/b) 4. Determine the properties of translation. 5. Determine the coordinates of:
CCTS
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
Teaching Aids
24 (02.07.12 06.07.12)
25 (09.07.12 13.07.12)
Circles
Understand and use the concept of area of sector of a circle to solve problems.
Comparing and contrasting Working out mentally Translating Identifying relations Making inference
10
10
Compass Ruler Filter paper GSP
10
10
Compass Ruler Filter paper GSP
26 (16.07.12 20.07.12)
Chapter 11: Transformation
Understand the concept of transformations.
Classifying Drawing diagrams Identifying relations Classifying Drawing diagrams Identifying relations
Transformation
Understand and use the concept of translations.
10 Cartesian plane Tracing paper Compass Ruler
11
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
a. b. c. LEARNING AREA Transformation LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand and use the concept of reflections. the image, given the coordinates of the object the object, given the coordinates of the image under a translation. Solve problems involving translations. LEARNING OUTCOMES EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2 Teaching Aids
WEEK
CCTS
27 (23.07.12 27.07.12)
28 29 (06.08.12 10.08.12) Transformation
Students will be able to: 1. Identify a reflection. 2. Determine the image of an object under a reflection on a given line. Classifying 3. Determine the properties of reflections. Drawing 4. Determine: diagrams a. the image of an object, given the axis Identifying of reflection relations b. the axis of reflection, given the object and its image using the method of construction 5. Determine the coordinates of: a. the image, given the coordinates of the object b. the object, given the coordinates of the image under a reflection. 6. Describe a reflection given the object and image. 7. Solve problems involving reflections. Discussion and Remedy for the previous lesson Test 3 (30.07.12 03.08.11) State Public Holiday Nuzul Al Quran Day on 6th August 2012 ( Monday ) Understand and use the Students will be able to: concept of rotations 1. Identify a rotation. 2. Determine the image of an object under a rotation given the centre, the angle and Classifying direction of rotation. Drawing 3. Determine the properties of rotations. diagrams 4. Determine: Identifying a. image of an object, given the centre, relations angle and direction of rotation Translating b. the centre, angle and direction of rotation, given the object and the image using the method of construction 5. Determine the coordinates of a. the image, given the coordinates of the
Cartesian plane Tracing paper Compass Ruler 5 10
10 Cartesian plane Tracing paper Compass Ruler
12
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
object; the object, given the coordinates of the image under a rotation. Describe a rotation given the object and image. Solve problems involving rotation
b.
6. 7. LEARNING AREA Transformation LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand and use the concept of isometry.
WEEK
LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Identify an isometry. 2. Determine whether a given transformation is an isometry. 3. Construct patterns using isometry Students will be able to: 1. Identify if two figures are congruent. 2. Identify congruency between two figures as a property of an isometry. 3. Solve problems involving congruence.
CCTS
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2
Teaching Aids
30 (13.08.12 17.08.12)
Understand and use the concept of congruence.
Classifying Drawing diagrams Identifying relations Translating
Cartesian plane Tracing paper Compass Ruler
31 (27.08.12 31.08.12)
Chapter 12: Solid Geometry II
32 (03.09.12 07.09.12)
Solid Geometry II
Understand and use the Students will be able to: properties of quadrilaterals 1. Determine the properties of quadrilaterals using concept of using reflections and rotations. transformations. MID SEMESTER 2 BREAK ( 18.08.12 26.08.12 ) Public Holiday Hari Raya Puasa on 19th 20th August 2012 (Sunday & Monday) Understand geometric Students will be able to: properties of prisms, 1. State the geometric properties of prisms, Classifying pyramids, cylinders, cones pyramids, cylinders, cones and spheres. Drawing and spheres. diagrams Understand the concept of Students will be able to: Identifying nets. 1. Draw nets for prisms, pyramids, cylinders relations and cones. Translating 2. State the types of solids given their nets. 3. Construct models of solids given their nets. Public Holiday National Day on 31st August 2012 ( Friday ) Understand the concept of Students will be able to: surface area. 1. State the surface areas of prisms, pyramids, cylinders and cones. 2. Find the surface area of prisms, pyramids, Classifying cylinders and cones. Drawing 3. Find the surface area of spheres using the diagrams standard formula. Identifying
Model
10 Model
10 Model
13
ainarahyusmkm2012
FORM TWO MATHEMATICS YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2012
4. Find dimensions length of sides, height, slant height, radius and diameter of a solid given its surface area and other relevant information. Solve problems involving surface areas. LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be able to: 1. Classify data according to those that can be collected by counting and measuring. 2. Collect and record data systematically. Students will be able to: 1. Determine the frequency of data. 2. Determine the data with the highest frequency, the lowest frequency and frequency of a specific value. 3. Organise data by constructing tally charts and frequency tables. 4. Obtain information from frequency tables. relations Translating
5. LEARNING AREA Chapter 13: Statistics Understand the concept of frequency. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the concept of data.
WEEK
CCTS
EXERCISES (Min. Req.) Paper Paper 1 2 5 5
Teaching Aids
33 (10.09.12 14.09.12)
Classifying Drawing diagrams Identifying relations Translating
Microsoft Excel Cartesian plane Newspaper report 5 5
34 (17.09.11 21.09.11)
Statistics
Public Holiday Malaysia Day on 16th September 2012 (Sunday) Represent and interpret data Students will be able to: pictograms 1. Construct pictograms to represent data. bar charts 2. Obtain information from pictograms. line graphs to solve 3. Solve problems involving pictograms. Classifying problems 4. Construct bar charts to represent data. Drawing 5. Obtain information from bar charts. diagrams 6. Solve problems involving bar charts. Identifying 7. Represent data using line graphs. relations 8. Obtain information from line graphs. Translating 9. Solve problems involving line graphs Discussion and Remedy for previous lesson ( 24.09.12 28.09.12 ) Revision and Remedy ( 01.10.12 31.10.12 ) State Public Holiday Birthday of Sultan Pahang on 24th October 2012 ( Wednesday ) Public Holiday Hari Raya Aidil Adha on 26th October 2012 ( Friday ) Final Year Examination ( 29.10.12 12.10.12) Activity after End year exam Final Semester Break from 10th November 2012 - 1st January 2013 Public Holiday Deepavali on 13th November 2012 ( Tuesday ) Public Holiday Awal Muhamarm on 15th November 2012 ( Thursday )
15
15
Microsoft Excel Cartesian plane Newspaper report
35 36 - 38 39 40 - 41 42
14
ainarahyusmkm2012
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Strategy For Improvement of Mathematics Result Class X BY: Academic Support GroupDocument48 paginiStrategy For Improvement of Mathematics Result Class X BY: Academic Support GroupitsankurzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Teaching Plan Maths Form 1 (2011)Document12 paginiYearly Teaching Plan Maths Form 1 (2011)mychris80Încă nu există evaluări
- Data Analysis & Probability - Task & Drill Sheets Gr. 3-5De la EverandData Analysis & Probability - Task & Drill Sheets Gr. 3-5Încă nu există evaluări
- Elementary School ‘Grades 3, 4 & 5: Math – Shape, Space and Measures - Ages 8-11’ eBookDe la EverandElementary School ‘Grades 3, 4 & 5: Math – Shape, Space and Measures - Ages 8-11’ eBookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timss2011 g4 ScienceDocument105 paginiTimss2011 g4 ScienceAnonymous wSeURKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 8 Lesson 1 Fraction Addition and SubtractionDocument8 paginiGrade 8 Lesson 1 Fraction Addition and Subtractionapi-249796897Încă nu există evaluări
- Linear Equations (Inglés) Autor Peter Brown, Michael Evans y David HuntDocument19 paginiLinear Equations (Inglés) Autor Peter Brown, Michael Evans y David HuntMariana GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- GR 10 Term 3 AssignmentDocument3 paginiGR 10 Term 3 AssignmentZuzakhe BonongoiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation Mathematics March 2015 Marking Scheme - FinalDocument14 paginiFoundation Mathematics March 2015 Marking Scheme - FinalpappadutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ridiculously Remarkable RevisionDocument2 paginiRidiculously Remarkable RevisionMathsArkAcademyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATH S5 SB CoreDocument426 paginiMATH S5 SB CoreWycÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workbook PhysicsDocument29 paginiWorkbook PhysicsKemuel De CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCC Education Level 4 and Level 5 March 2015 Exams DatesDocument2 paginiNCC Education Level 4 and Level 5 March 2015 Exams Datesbahadoor22iÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computing Teachers - Resource PackDocument56 paginiComputing Teachers - Resource PackMaxwell Gadget BoatengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teachingpack Geometry Thecircle v2Document28 paginiTeachingpack Geometry Thecircle v2efendy malauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Number Lesson Worksheets and Exams PDFDocument19 paginiNumber Lesson Worksheets and Exams PDFFranklin LirazanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9-1 Geometric Sequences-II - Supplementary MaterialsDocument35 pagini9-1 Geometric Sequences-II - Supplementary MaterialsMa Lourdes MangahasÎncă nu există evaluări
- .Pkdownloadabledownloadsamplesample Id703Document332 pagini.Pkdownloadabledownloadsamplesample Id703Anfaal NaveedÎncă nu există evaluări
- IAL IT Scheme-Of-Work For Unit 4 011019Document34 paginiIAL IT Scheme-Of-Work For Unit 4 011019Anumi JayasingheÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.3.1 Logic GatesDocument55 pagini1.3.1 Logic Gatesmobi 2k17Încă nu există evaluări
- Test Items Working: ColumnDocument21 paginiTest Items Working: Columnriaramdial21Încă nu există evaluări
- 2001 Paper1Document24 pagini2001 Paper1osweewengÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE MATHS PAST PAPER 580 - 2004 - QP - 3Document16 paginiIGCSE MATHS PAST PAPER 580 - 2004 - QP - 3Hassan mahmud100% (3)
- 1 - SCH3U 1.1 Nature of Atoms-2Document38 pagini1 - SCH3U 1.1 Nature of Atoms-2Simon McCabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 1: Mathematics TestDocument24 paginiPaper 1: Mathematics TestLewis LamÎncă nu există evaluări
- FPS U2 SS PDFDocument52 paginiFPS U2 SS PDFAnonymous 4VcUAodJ5Încă nu există evaluări
- Programming Practices and TechniquesDocument12 paginiProgramming Practices and TechniqueswoppaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Physics CIE iGCSE 0625 PPQDocument11 paginiAtomic Physics CIE iGCSE 0625 PPQchelseaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre-Final Igcse Physics Grade 10 Sem 1 2014 Soal - RevisiDocument22 paginiPre-Final Igcse Physics Grade 10 Sem 1 2014 Soal - RevisiJoshuaUntungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Year 9 Science Acid Base AssessmentDocument6 pagini2011 Year 9 Science Acid Base AssessmentvleeeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scotch 3cdmas Mock ExamDocument32 paginiScotch 3cdmas Mock ExamFredÎncă nu există evaluări
- F. Rotation, Reflection, Translation and EnlargementDocument33 paginiF. Rotation, Reflection, Translation and Enlargementthi tar lwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised A LevelDocument180 paginiRevised A LevelmohitadmnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Module IndicesDocument38 paginiChapter 5 Module IndicesCorey LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan ProjectDocument6 paginiLesson Plan Projectapi-608836622100% (1)
- LCM and HCFDocument66 paginiLCM and HCFcoolmagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab ReviewDocument12 paginiLab ReviewAftab SaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Document Production SkillsDocument3 paginiDocument Production SkillsWarnnie MusahÎncă nu există evaluări
- H2 Mathematics Textbook (Choo Yan Min)Document2.228 paginiH2 Mathematics Textbook (Choo Yan Min)Lys NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- FDM September 2015 Examination Marking Scheme - FinalDocument15 paginiFDM September 2015 Examination Marking Scheme - FinalpappadutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Science Coursebook-9-24Document16 paginiComputer Science Coursebook-9-24api-470106119Încă nu există evaluări
- 0417 m17 QP 31Document8 pagini0417 m17 QP 31Popi MastroianniÎncă nu există evaluări
- BTEC Assignment Brief: (For NQF Only)Document2 paginiBTEC Assignment Brief: (For NQF Only)JwsÎncă nu există evaluări
- IB Physics TSMDocument72 paginiIB Physics TSMpeter_yoon_14Încă nu există evaluări
- O Level Physics ATP ReferencesDocument4 paginiO Level Physics ATP ReferencesHassan Ali BhuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BodmasDocument18 paginiBodmasYati GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Science9 ExamDocument16 pagini2011 Science9 Examspyboy99Încă nu există evaluări
- CH-12 Electricity & Circuits PPT-2Document22 paginiCH-12 Electricity & Circuits PPT-2SUHANEERIYAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics PressureDocument35 paginiPhysics Pressuresai yadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan in Grade 8 MathematicsDocument3 paginiLesson Plan in Grade 8 Mathematicschari cruzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADocument20 paginiAShu85Încă nu există evaluări
- Forces and Motion-1Document8 paginiForces and Motion-1api-237070241Încă nu există evaluări
- SMKK Imtiaz Kuala Terengganu Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2012Document12 paginiSMKK Imtiaz Kuala Terengganu Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2012norhasmizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2016Document12 paginiYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2016Mohd Sabri0% (1)
- SMK Tanjung Adang, Gelang Patah, Johor Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2009Document12 paginiSMK Tanjung Adang, Gelang Patah, Johor Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2009Adibah AliasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics Form 2Document18 paginiMathematics Form 2Hilmi Abd GhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
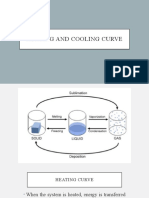
- Heating Cooling Curve SolutionsDocument37 paginiHeating Cooling Curve Solutionspipay vlogsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 116A Whirling Hygrometer - ManualDocument9 pagini116A Whirling Hygrometer - ManualANAND MLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powerplant and Industrial Plant Engineering Problem Solving 1Document3 paginiPowerplant and Industrial Plant Engineering Problem Solving 1jhigs amfufuÎncă nu există evaluări
- MagnetismDocument4 paginiMagnetismTalha MughalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimated Voltage Drop Calculator 1 1 SIEMENSDocument6 paginiEstimated Voltage Drop Calculator 1 1 SIEMENSgvmanoj64Încă nu există evaluări
- InterpretDCNameplate 0702Document2 paginiInterpretDCNameplate 0702Abel OliveiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Conductivity Measurement For Poor Conductor - Lee's DiscDocument17 paginiThermal Conductivity Measurement For Poor Conductor - Lee's Discibnu_iman810% (2)
- Activities: Module 1: Forces and MotionDocument8 paginiActivities: Module 1: Forces and MotionDanica DelarosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sapphire Textile Mills LTD No 2: (70 DENIER)Document19 paginiSapphire Textile Mills LTD No 2: (70 DENIER)Danish NawazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment (7) The Round Turbulent JetDocument5 paginiExperiment (7) The Round Turbulent JetKawar Abid86% (7)
- TLE-Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 10 Quarter 4 Week 8 Install Domestic Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning UnitDocument4 paginiTLE-Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 10 Quarter 4 Week 8 Install Domestic Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning Unitasdfubepruhf asdfubepruhfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics CIE IGCSE 0625 Topic 2 - Forces and MotionDocument10 paginiPhysics CIE IGCSE 0625 Topic 2 - Forces and MotionChris ChinÎncă nu există evaluări
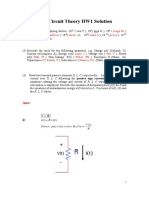
- 1091 Circuit Theory HW1 Solution: Tera T Giga G (Femto FDocument5 pagini1091 Circuit Theory HW1 Solution: Tera T Giga G (Femto F曾燒餅Încă nu există evaluări
- DTnotiDocument49 paginiDTnotiokman17Încă nu există evaluări
- SB5150 THRU SB5200: Schottky Barrier RectifierDocument2 paginiSB5150 THRU SB5200: Schottky Barrier RectifierCube7 GeronimoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Berry 018Document6 paginiBerry 018Hamed Vaziri GoudarziÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYS-2010: General Physics I Course Lecture Notes Section XIIDocument22 paginiPHYS-2010: General Physics I Course Lecture Notes Section XIIReggie DueñasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 Chapter PDFDocument27 pagini14 Chapter PDFsidd rajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material CalculationDocument5 paginiMaterial CalculationRizwan04Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab - 3a - Losses in Pipes and Pipe FittingsDocument13 paginiLab - 3a - Losses in Pipes and Pipe FittingsShehan FernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 14 Kinetics of Particle - Work & EnergyDocument37 paginiChapter 14 Kinetics of Particle - Work & Energyحزيفہ اعظمÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cable Impedance CalculationsDocument4 paginiCable Impedance CalculationsJoseph PoplingerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 5 - Charles LawDocument5 paginiExp 5 - Charles LawSiti Fatimah0% (1)
- Gas Laws Review Sheet Answers RenoDocument2 paginiGas Laws Review Sheet Answers RenoERICA BURNSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 StudentDocument44 paginiChapter 2 StudentSiti ShuhadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Api MPMS 14.5Document8 paginiApi MPMS 14.5JorgeTunÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMU Phys101 Sample Old Exam PapersDocument113 paginiEMU Phys101 Sample Old Exam PapersAli ÖvgünÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review The Article Unified Model For Gas-Liquid Pipe Flow Via Slug DynamicsDocument11 paginiReview The Article Unified Model For Gas-Liquid Pipe Flow Via Slug Dynamicsdimatteoc dimatteocÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHP 2 Electric PotentialDocument21 paginiCHP 2 Electric PotentialSyahshaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- H1 Physics - 8866 - 2013Document19 paginiH1 Physics - 8866 - 2013Deborah MalanumÎncă nu există evaluări