Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Neurological Disorders
Încărcat de
marc_encinaresDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Neurological Disorders
Încărcat de
marc_encinaresDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
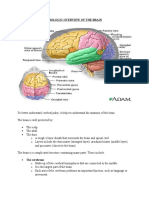
Neurological Disorders (Diagnostic Studies) Prepared by: Nancy P. Gariando, Ed. D.
,RN Jan 2, 2013 Learning Outcomes Discuss the various diagnostic studies used in clients with neurological problems
Diagnostic Studies A. X-ray of the skull and spine - used to rule out fractures, dislocations and curvatures of the spine 1. Preprocedure: explain the purpose of the procedure; instruct the client to lie still 2. Post procedure: no follow up is needed B. Lumbar Puncture (LP) - insertion of a spinal needle through the L3-L4 into the subarachonoid space to obtain cerebrospinal fluid for laboratory analysis to measurepressure or instill medications 1. Preprocedure: Obtain a written consent Instruct the client to empty the bladder Instruct the client to lie still during the procedure 2. Procedure: Assist the client to assume a lateral recumbent position with knees flexed 3. Post procedure: Instruct the client to lie flat, generally 4-8 hrs. to prevent spinal headache Encourage fluids Monitor the puncture site for leakage of CSF and hematoma C. Cerebral Angiography (CA) - the x-ray study of the cerebral vascular system following an injection of contrast medium into the femoral artery
1. Preprocedure: Explain the procedure Obtain a written consent Assess for allergies t iodine NPO for 8-12 hrs Inform the client that a warm sensation may be experienced with injection of the dye Instruct the client to lie still during the procedure Inform the client that groin discomfort may be felt when the groin puncture is made 2. Procedure: Administer sedation as prescribed 3. Postprocedure: Maintain the client on bed rest generally 8-12 hrs Monitor the puncture dressing Monitor the VS Apply pressure to the puncture site with a sandbag Encourage fluids Assess the extremity for skin color, temperature, and capillary refill assess the area distal to the injection site. D. Myelogaphy -air contrast or water contrast X-ray study inserted into the subarachnoid space of the spine. 1. Preprocedure: explain the procedure obtain written consent assess allergies to iodine NPO for 2-4 hrs instruct the client that a warm sensation may be felt with the injection of the dye instruct the client to void instruct the client to lie still during the procedure inform the client that during the procedure the table will be titled up and down to the facilitae injection of the dye hold phenothiazines for tricyclic antidepressant, which may lower the seizure threshold. 2. Procedure: Administer sedation as prescribed
3. Postprocedure: elevate the head of the bed 60 degrees if a water-soluble agent was used, otherwise 30 to 45 degrees. monitor the client for headaches, fever, still neck, or photophobia, which may indicate meningitis wait 48 hrs before restarting phenothiazine or tricyclic antidepressant maintain the client on bed rest generally for 8-12 hrs Encourage fluids Monitor urine output E. Positron emission tomography (PET) -Nuclear scan that has an advantage over the Ct or MRI because it not only provides information on the blood flow, oxygen uptake, glucose transport, but also information on the function of the brain. 1. Pre procedure: explain the procedure instruct the client t void assess for allergy to iodine instruct the client to lie still during the procedure instruct the client to avoid caffeine, smoking an alcohol for 24 hrs. obtain baseline VS and neurological assessment. 2. Procedure: administer sedation as prescribed may offer relaxation tapes or mental relaxation exercised to facilitate lying still. 3. Postprocedure: instruct the client to wash hands after voiding and bowel movement because radionucleic is excreted in urine and feces encourage fluids F. MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) - non- invasive scanning test that has the advantage over CT scanning because it relies on the interaction between the bodys chemistry and a magnetic field. 1. Pre-procedure: Explain the procedure. Obtain a written consent. Reassure the client that there is no radiation exposure. Remove any hairpins, glasses, jewelry, watch and other metal objects. Offer the client earplugs for the loud knocking and thumping noises.
Instruct the client to lie still during the procedure. Assess the client for a pacemaker, cerebral aneurysm clips, or other metal objects that would be affected by a magnetic field. Instruct the client to void.
2. Procedure: Administer sedation as prescribed.
3. Post-procedure: No special procedural care.
G. COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY (CT) SCAN - computerized analysis of tomographic x-rays providing three-dimensional cross sections of tissue structures of the brain. 1. Pre-procedure: Explain the procedure. Obtain a written consent. NPO for 4 hours Remove hairpins, wigs and all hair accessories. Assess for allergy to Iodine. Instruct the client to lie still during the procedure.
2. Procedure: Administer sedation as prescribed. Place the clients head in a holding device. Start an intravenous line. Xenon and oxygen mix may be administered by neck or endotracheal tube.
3. Post-procedure: Encourage fluids. Monitor the client for adverse reactions of Xenon gas.
H. ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY (EEG) - non-invasive study that evaluates the electrical activity of the brain. 1. Pre-procedure: Explain the procedure. Inform the client to avoid fasting which may result in hypoglycemia and adversely affect the results.
Instruct the client to wash the hair the night before the procedure. Avoid hairsprays, oils or hairpins the day of the procedure. Instruct the adult client to sleep no more than 5-7 hours the night before. If prescribed, consult the physician before administering an anticonvulsant. Instruct the client to lie still during the procedure. Instruct the client to avoid caffeine-containing products, alcohol or illegal drugs.
2. Procedure: Assist the client to reclining chair or bed. Attach the electrodes to the scalp with electrode gel. Reinforce lying still with the eyes closed. Monitor the client for seizure activity. If prescribed, instruct the client to deeply breathe 20 times in a 3-minute period to induce hyperventilation, producing cerebral vasoconstriction a alkalosis, which may result in seizure activity. If prescribed, place a bright light infront of client and perform 1 to 20 flashes of light per second with the eyes first open then closed (photic stimulation-seizures are light sensitive) If prescribed, sleep may be induced with oral or intravenous sedation that may induce brain waves, indicating certain types of epilepsy (frontal lobe epilepsy)
3. Postprocedure: Remove the electrode gel from the clients scalp Offer the client shampoo to wash the hair Inform the client who has a sleep EEG to have someone else drive him home Monitor the client for seizure activity
Nursing Diagnoses 1. Risk for aspiration 2. Anticipatory Grieving 3. Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion 4. Ineffective Airway clearance 5. Impaired Physical Mobility 6. Impaired Verbal Communication 7. Risk for injury 8. Ineffective Therapeutic Regimen Management 9. Risk for impaired skin integrity 10. Impaired Urinary Elimination Pattern 11. Impaired Nutrition: Less than Body Requirements
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Histology of Respiratory System Conducting PortionDocument2 paginiHistology of Respiratory System Conducting PortionFarahh ArshadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kuliah 4 Oedem Paru PulmonaryedemaDocument43 paginiKuliah 4 Oedem Paru PulmonaryedematrianaamaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIT ExaminationDocument7 paginiGIT ExaminationVineeth Reddy100% (1)
- TongueDocument9 paginiTongueseety2Încă nu există evaluări
- True Undescened TestesDocument42 paginiTrue Undescened TestesSahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDocument14 paginiEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- Answers & Solutions: NEET (UG) - 2019Document35 paginiAnswers & Solutions: NEET (UG) - 2019Gowri ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOEFL 1 BookDocument78 paginiTOEFL 1 BookMarleni Lagos GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ace3 Unit4 TestDocument3 paginiAce3 Unit4 Testnatacha67% (3)
- Retention and RelapseDocument59 paginiRetention and RelapseAshwin ThejaswiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dwitya To TrityaDocument34 paginiDwitya To TrityaAsh GamejiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi-Analyte ELISArrayDocument1 paginăMulti-Analyte ELISArrayShi Jie PangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomic and Physiologic Overview of The BrainDocument5 paginiAnatomic and Physiologic Overview of The BrainIlona Rosabel Bitalac0% (1)
- UtiDocument41 paginiUtiKetaks MooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bites and StingsDocument23 paginiBites and StingsAngela PabloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain Stem Death: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 paginiBrain Stem Death: Learning ObjectivesFarizÎncă nu există evaluări
- MorantDocument11 paginiMorantkrymisÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Waking Dark by Robin WassermanDocument52 paginiThe Waking Dark by Robin WassermanRandom House Teens100% (1)
- Annotated BibliographyDocument19 paginiAnnotated Bibliographyapi-455648185Încă nu există evaluări
- Giovanni Maciocia Menorrhagia NotesDocument22 paginiGiovanni Maciocia Menorrhagia Noteshihi12100% (5)
- Chest X Ray Made SimpleDocument103 paginiChest X Ray Made SimpleMayer Rosenberg100% (18)
- Lecture Notes Eye DiseasesDocument52 paginiLecture Notes Eye DiseasesHaseeb Islam100% (2)
- Factors Influencing ToxicityDocument7 paginiFactors Influencing ToxicityderrickÎncă nu există evaluări
- STEAM INHALATION RELIEFDocument4 paginiSTEAM INHALATION RELIEFDani PhilipÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Backyard Dairy BookDocument84 paginiThe Backyard Dairy Bookseagypsy04100% (1)
- IDJ Vol 4 7Document5 paginiIDJ Vol 4 7Saatvik AtriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision On EquipmentsDocument32 paginiRevision On EquipmentsDr Atef HadedyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Terminology 2Document32 paginiMedical Terminology 2Nisya Andesita HÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ode of The Jade Dragon Yu Long Fu PDFDocument10 paginiOde of The Jade Dragon Yu Long Fu PDFAikido EurogetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cloze Passage Reading ComprehensionDocument15 paginiCloze Passage Reading ComprehensionkiluÎncă nu există evaluări