Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Prevent Platelet Plugs.: Never IM
Încărcat de
dekspeerTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Prevent Platelet Plugs.: Never IM
Încărcat de
dekspeerDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
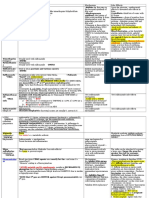
Anticoagulants Heparin Warfarin Low-molecular-weight Inhibit action or formation of clotting factors. Prevent clot formation. prolong bld time.
Monitored by activated Monitored by prothrombin Longer duration of action partial thromboplastin time (PT) and INR (PT-INR) than that of heparin. More times (aPTTs). stable response. Pt can give own injections at home. Drug of choice preventing DVT following surgery. Antagonist: Protamine Antagonist: Vitamin K More predictable response sulfate Doesnt require frequent lab monitoring because Parenteral or subcu (never Given orally only they are dose related to IM). Short half-life (1 to 2 May be started while the the pts weight. Given SC hrs) patient is still on heparin Comes in a pre-filled SC doses should be given in until PT-INR levels indicate syringe. Pt may go home areas of deep subcu fat adequate anticoagulation on injections such as the abdomen Full therapeutic effect Ensure that SC doses are unless ordered otherwise, takes several days & sites rotated. Dont give Monitor Prothrombin time given SC, not IM (SC action takes up to 1 hour) SC doses /in 2 of: PT -normal range is 11 to SC doses should be given in umbilicus, incisions, open 13 seconds, therapeutic wounds, scars, drainage should be one to two times areas of deep subcutaneous fat such as tubes, or stomas. the patients normal value the abdomen unless Do not aspirate or massage International normalized ordered otherwise, and & injection site (May cause ratio (INR) - 2.0 to 3.5 are sites rotated hematoma formation). therapeutic. IV dose- bolus or infusions Teach: balance of vitamin K Do not give SC doses within 2 inches of: (onset of act immediate) foods, keep lab appts. The umbilicus, abdominal Lab values are done daily incisions, or open wounds, to monitor coag effects scars, drainage tubes, (aPTT), (normal values ranging from 25 to 40 seconds). stomas Therapeutic Do not aspirate SC anticoagulation the aPTT injections or massage should be one to two times injection site the pts baseline. AE: blding (risk ^ w/ ^ dosages) may be localized or systemic, N/V, abdominal cramps, thrombocytopenia. N con: Assess-VS, lab values, existence of underlying renal or hepatic disorders. Teach: Report burning, stinging, warmth, excessive bruising, pain or swelling at IV site. Take warfarin same time each day, avoid hazardous activities. Report: nosebleeds, excessive menstrual flow, bleeding gums, or bruising, limit garlic intake, use soft bristle tooth brush & electric razor, hold pressure on cuts 20 minutes. 2RN check.
Antiplatelet Inhibit platelet aggregation Prevent platelet plugs. interfering with the various aspects of platelet function (platelet aggregation)
Aspirin (OTC) Potent medication Effect of single dose may persist for as long as a week. Do not use with other anticoagulants unless prescribed by MD. Used to prevent stroke (CVA) & MI. Can be given concurrently with anticoagulants (what for ^ risk of bleeding) Puncture IV sites or cuts may require increased pressure applied to stop the bleeding Monitor for ecchymoses
Thrombolytic Lyse, or breakdown, existing clots. Dissolve. Goal to restore bld flow o tissue served by blocked vessel. Used in: Acute MI Pulmonary embolism Acute ischemic stroke (CVA), o rDVT Best to be administered within 4 hrs. Can cause severe bleeding (stop transfusion if occurs) Monitor VS continuously. Administered in the critical care area or ER. Conditions that exclude pt from receiving thrombolytics: Recent trauma, sx or biopsies, arterial emboli, cerebral embolism, hemorrhage, thrombocytopenia. septic thrombophlebitis. & child birth within 10 days. Obtain baseline coagulation tests (aPTT, bleeding time, PT, and/or INR); hematocrit, hemoglobin and platelet count.
Antifibrinolytic Promote blood coagulation. Action opposite to anticoagulant, shorten bleeding time
Indications Prevention & tx of excessive bleeding (Hyperfibrinolysis, surgical complications, excessive oozing from surgical sites such as chest tubes, reducing total blood loss and duration of bleeding in the postoperative period)
N.C: mon for blding with trauma or surgery. Aspirin can cause gastritis or GI bleeding, may cause nausea or GI upset (administer with food)
Monitor LOC, check neurological status Observe for dysrhythmias Only given IV.never IM
NC: Monitor peripheral pulses. Monitor for paresthesias, Chest pain or SOB. Monitor for pulmonary thrombus or embolus
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Pediatric Cardiology and Pulmonology: A Practically Painless ReviewDe la EverandPediatric Cardiology and Pulmonology: A Practically Painless ReviewÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 Fun Facts About Your Heart: Educational VersionDe la Everand14 Fun Facts About Your Heart: Educational VersionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs For Diabetes MellitusDocument3 paginiDrugs For Diabetes MellitusGerardLum100% (1)
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Document1 paginăBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument2 paginiAntihypertensive DrugsJillary LlagunoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFDocument25 paginiDrugclasses Pharmacologypart 1 PDFSutanya100% (2)
- SUMMARY Drugs Used Primarily For Gastrointestinal ConditionsDocument3 paginiSUMMARY Drugs Used Primarily For Gastrointestinal ConditionsXylex Dave AndresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal Swelling + AscitesDocument29 paginiAbdominal Swelling + AscitesDevina CiayadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charting Examples For Physical AssessmentDocument16 paginiCharting Examples For Physical Assessmentim3in1Încă nu există evaluări
- IMG EmpAposterDocument1 paginăIMG EmpAposterChiu LeoÎncă nu există evaluări
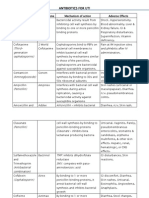
- ANTIBIOTICS FOR UTI (CephalosporinsDocument16 paginiANTIBIOTICS FOR UTI (CephalosporinsSunil BasnetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Cheat SheetDocument3 paginiRenal Cheat Sheetkad ourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anticoagulation PharmacologyDocument36 paginiAnticoagulation PharmacologyaymenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument2 paginiChemotherapeutic AgentsmajÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionDocument7 pagini3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Family Names of DrugsDocument1 paginăFamily Names of DrugsangelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre-op Evaluation SummaryDocument1 paginăPre-op Evaluation Summarysabbo morsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti-Arrhythmic Agents For Pharmacy PDFDocument41 paginiAnti-Arrhythmic Agents For Pharmacy PDFKelvinTMaikanaÎncă nu există evaluări
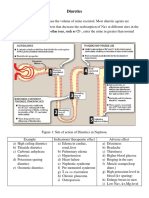
- DiureticsDocument4 paginiDiureticsNazmul Islam AbirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common MedicationsDocument4 paginiCommon MedicationsFatima CarricoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDocument3 paginiPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotic GuideDocument6 paginiAntibiotic GuideAnnTran100% (1)
- Cell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of ActionDocument3 paginiCell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of Actionyanks1120Încă nu există evaluări
- Common Medications UsedDocument3 paginiCommon Medications UsedRay Michael CasupananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart Failure: Signs, Causes, TreatmentsDocument1 paginăHeart Failure: Signs, Causes, TreatmentsTrisha VergaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- DrugsDocument155 paginiDrugsAkankshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharm Expansion 17 NDFDocument1 paginăPharm Expansion 17 NDFNokz M. Raki-inÎncă nu există evaluări
- (CV2) Pharmacology of AnticoagulantsDocument6 pagini(CV2) Pharmacology of AnticoagulantsHanifa Shereen B. AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diuretics TabulationDocument3 paginiDiuretics TabulationAna Rika Javier HarderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uworld JournalDocument3 paginiUworld JournalJayÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINAL Hypertension Medication Summary SSDocument1 paginăFINAL Hypertension Medication Summary SSronique reidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotics 9Document11 paginiAntibiotics 9Beth Morales100% (1)
- EAR First AidDocument4 paginiEAR First Aidr_lakshmi2722Încă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotics Chart 2Document10 paginiAntibiotics Chart 2Vee MendÎncă nu există evaluări
- CarafateDocument1 paginăCarafateAdrianne BazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluids Electrolytes Visual NotesDocument8 paginiFluids Electrolytes Visual NotesVin Lorenzo CampbellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Moa PK Use Se Ci Blood Coagulation: AnticoagulantsDocument4 paginiDrug Moa PK Use Se Ci Blood Coagulation: AnticoagulantsYusoff RamdzanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CholestyramineDocument1 paginăCholestyramineKatie McPeekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of ActionDocument13 paginiGeneric Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of Actionangel3424Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab Values and Vital SignsDocument4 paginiLab Values and Vital SignsWole Olaluwoye100% (1)
- Pharmacology A - NSAIDSDocument14 paginiPharmacology A - NSAIDSselflessdoctorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of MurmursDocument2 paginiClassification of MurmursNazneen SiddiquiÎncă nu există evaluări
- History and Physical Exam SkillsDocument7 paginiHistory and Physical Exam SkillsAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Name FurosemideDocument1 paginăGeneric Name FurosemideChristopher LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Examinations Crib Sheet v7Document36 paginiClinical Examinations Crib Sheet v7aparish10100% (1)
- Primary Care Antibiotic Guideline FINAL May 2015Document10 paginiPrimary Care Antibiotic Guideline FINAL May 2015Atta Muhammad MemonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDocument8 paginiApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conduction System: Rhythm Identification and TreatmentDocument12 paginiConduction System: Rhythm Identification and Treatmenthops23Încă nu există evaluări
- PorphyriaDocument4 paginiPorphyriaHimalaya AggarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- AntimicrobialsDocument1 paginăAntimicrobialsRomaine Barrett100% (1)
- Ecg Crit - CareDocument55 paginiEcg Crit - CarekrismatactayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFDocument21 paginiReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFAndres F. TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106Document47 paginiPharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106sean liyanageÎncă nu există evaluări
- LasixDocument1 paginăLasixKatie McPeek100% (2)
- V V V V Nonpurulent: Keflex (Cephalexin) or Cefadroxil V Purulent: I & D Gold Standard If Systemic MRSA CoverageDocument1 paginăV V V V Nonpurulent: Keflex (Cephalexin) or Cefadroxil V Purulent: I & D Gold Standard If Systemic MRSA CoverageCyndiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inflamed Trachea, (Tracheitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandInflamed Trachea, (Tracheitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs Affecting Coagulation ObjectivesDocument14 paginiDrugs Affecting Coagulation ObjectiveslouradelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anticoagulation Protocol For PostDocument8 paginiAnticoagulation Protocol For PostMohammed IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treatment Protocol of Snake Bite: Kaushik.H.M 080201388Document23 paginiTreatment Protocol of Snake Bite: Kaushik.H.M 080201388tiruchanurÎncă nu există evaluări
- NHS Lanarkshire Major Haemorrhage GuideDocument3 paginiNHS Lanarkshire Major Haemorrhage GuideleicesterbugÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Exchanger Sodium SilicateDocument2 paginiHeat Exchanger Sodium SilicateChristopher BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retail Management PPT1Document14 paginiRetail Management PPT1Srilekha GubbalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- M-LVDT: Microminiature Displacement SensorDocument2 paginiM-LVDT: Microminiature Displacement Sensormahdi mohammadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System Packet BDocument5 paginiCirculatory System Packet BLouise SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1. Pharmacological Therapeutics. 2.2. Basic Cardiac Life Support (BCLS) and Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) in Neonates and ChildDocument3 pagini2.1. Pharmacological Therapeutics. 2.2. Basic Cardiac Life Support (BCLS) and Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) in Neonates and Childclint xavier odangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AZ ATTR Concept Test Clean SCREENERDocument9 paginiAZ ATTR Concept Test Clean SCREENEREdwin BennyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analisis Dampak Reklamasi Teluk Banten Terhadap Kondisi Lingkungan Dan Sosial EkonomiDocument10 paginiAnalisis Dampak Reklamasi Teluk Banten Terhadap Kondisi Lingkungan Dan Sosial EkonomiSYIFA ABIYU SAGITA 08211840000099Încă nu există evaluări
- wch13 01 Rms 20230817Document24 paginiwch13 01 Rms 20230817halcieeschÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio-Tank Guidelines for Indian RailwayDocument51 paginiBio-Tank Guidelines for Indian Railwayravi100% (2)
- Sarthak WorksheetDocument15 paginiSarthak Worksheetcyber forensicÎncă nu există evaluări
- RA8485 Animal Welfare Act (Carabao Slaughter)Document2 paginiRA8485 Animal Welfare Act (Carabao Slaughter)Jazreth Gaile100% (1)
- Erapol EHP95ADocument2 paginiErapol EHP95AMohammad Doost MohammadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Life Sciences Part 1 CSIR JRF NET GATE DBT PDFDocument132 paginiLife Sciences Part 1 CSIR JRF NET GATE DBT PDFPavani Reddy68% (22)
- Species Diversity in Lentic and Lotic Systems of Lake Tamblyn and The Mcintyre RiverDocument21 paginiSpecies Diversity in Lentic and Lotic Systems of Lake Tamblyn and The Mcintyre Riverapi-393048315Încă nu există evaluări
- ASR1201D ASR1201D-D: Slim Water-Proof RFID ReaderDocument1 paginăASR1201D ASR1201D-D: Slim Water-Proof RFID ReaderCatalin BailescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infinite & Finite Slope1Document38 paginiInfinite & Finite Slope1CHUKKALA LEELA RAVALIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABSCESSDocument35 paginiABSCESSlax prajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scaffolding Control & MeasuresDocument3 paginiScaffolding Control & Measuresviswamanoj100% (1)
- SVIMS-No Que-2Document1 paginăSVIMS-No Que-2LikhithaReddy100% (1)
- Endocrown Review 1Document9 paginiEndocrown Review 1Anjali SatsangiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Placenta Previa Case StudyDocument59 paginiPlacenta Previa Case StudySiergs Smith GervacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition During PregnancyDocument8 paginiNutrition During PregnancyHalliahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 4 Summary - KEY PDFDocument3 paginiExercise 4 Summary - KEY PDFFrida Olea100% (1)
- General Specifications: Detail ADocument1 paginăGeneral Specifications: Detail AJeniel PascualÎncă nu există evaluări
- Book 1Document94 paginiBook 1JOHNÎncă nu există evaluări
- UMR Introduction 2023Document110 paginiUMR Introduction 2023tu reves mon filsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap 716 PDFDocument150 paginiCap 716 PDFjanhaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natural Resources in PakistanDocument5 paginiNatural Resources in PakistanSohaib EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cot 1 Vital SignsDocument22 paginiCot 1 Vital Signscristine g. magatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valvula de Leve MasterDocument20 paginiValvula de Leve Masterguillermo trejosÎncă nu există evaluări