Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
ELE3103
Încărcat de
Nur Syazwani KhamisDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ELE3103
Încărcat de
Nur Syazwani KhamisDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cg Mohd Ridzuan al-Kindy (PISMP-MT IPG KDRI 2010)
ELE3103 English for Language Teachers Topic 1: Language and Communication Definition of Language The way chosen for communicates with others such that the meaning / thinking can be delivered to others. Pearson Education Limited (2000) - "System of communication by written or spoken word, which is used by the people of a particular country or area." Sets of rules in language: o Phonology study of sound system o Morphology study of morpheme & allomorph o Syntax study on how he word combined o Semantics study of meaning o Lexicon study of set of words and idiom Language and Culture Culture factor that affects the language: o Religion o Social traits o Geography boundary o Different activities of people o Borrowed words (e.g.: Candy from Sanskrit) Function of Language Informative essentially, the communication of information o Affirms or denies propositions (facts) o To describe or reason about something o Have truth value Expressive reports feeling or attitudes o Related to poetry & literature o Two main aspects evoking certain feeling & expressing feelings Directive the purposes of causing (or preventing) o Found in command & requests o Not considered as true or false o E.g.: Close the windows. Uses of the Language Ceremonial not simply mix expressive & directive language function because perfomative aspects are included Performative Utterance language which performs the action it reports (e.g.: I do) Phatic language street-corner conversations (e.g.: Hi) Form of Language (Types of Sentences) Sentence Types Assertion / Declarative Usual / Function Informative The room is cool. Expressive I had a nice time Directive I would like some coffee.
Question / But isnt this Isnt that Dont you want Interrogative Gymnasium? great? to help me? Command / Read the Have a nice Shut the Imperative notes for test. day. windows. Exclamation / The universe Im really Its late! Exclamatory is bounded! glad! Non-verbal Communication Includes facial expressions, eye contact, tone of voice, body posture and motions & positioning within groups. Categories & features (G.W. Porter): o Physical personal type of communication (e.g.: facial expressions, tone of voice, sense of touch, sense of smell & body motion) o Aesthetics types of communication through creative expression (e.g.: play instrumental music, dancing, painting & sculpting) o Signs mechanical types of communication (e.g.: signal flags, sirens, horns) o Symbolic types of communication that make uses of religious, status or ego-building symbols Static Features (by Argyle) Dynamic Static Features o Distance standing (sign of attraction to other people) o Orientation present ourselves to others (face-to-face, side-to-side or back-to-back) o Posture convey the degree of formality or relaxation o Physical contact shaking hand, touching, holding, embracing, pushing or patting on the back. It reflect intimacy or feeling Dynamic Features o Facial expressions smile, frown, raised eyebrow, yawn & sneer. It continually changes during interaction & monitored constantly by audience. o Gestures hand and body part movement o Looking major feature in communication. It convey emotion signal when to talk or finish or aversion. Tortoriello, Blott & DeWine defined non-verbal communication as: the exchange of messages primarily through non-linguistics means, including: kinaesthetic, facial expressions and eye contact, tactile communication, space and territory, environment, paralanguage (vocal but non-linguistics cues), the use of silence & time o Kinaesthetic Forward & backward
Cg Mohd Ridzuan al-Kindy (PISMP-MT IPG KDRI 2010)
Vertical movement Side-to-side movement o Facial expression o Eye contact o Tactile communication o Personal Space o Environment o Paralanguage o Silence & Time Speech and Writing Definition of Speech o The faculty or act of speaking o The faculty or act of expressing or describing thoughts, feelings, or perceptions by the articulation of words o Something spoken; an utterance o Vocal communication; conversation o A talk or public address: "The best impromptu speeches are the ones written well in advance" (Ruth Gordon) o A printed copy of such an address o One's habitual manner or style of speaking o The language or dialect of a nation or region: American speech Features of Speech o Speech is a dynamic, ephemeral behavior distributed in time; it proceeds continuously. o It has many features of continuous movements o Whole interaction between speaker and listener is dependent on the situation (context) o Speech is a resource available for all normally equipped human beings across different social groups and cultures Definition of Writing o The act of one who writes. o Written form: Put it in writing. o Handwriting; penmanship. o Something written, especially: Meaningful letters or characters that constitute readable matter. A written work, especially a literary composition. o The occupation or style of a writer. Features of Writing o It has the character of objects o Written text is made up of discrete symbols o Organized in certain regular spatial patterns (according to syntactic rules) o Lacks an immediate context reader must properly understand a written text o Acquisition of the ability to read and write is quite
different from learning to speak and understand speech.
English Language in Malaysia Malaysian English (MyE), formally known as Malaysian Standard English (MySE) o Form of English used and spoken in Malaysia as a second language Features: o Malaysian English is generally non-rhotic English o Originates from British English (Colonial era) o Post-colonial influence by American English There are 3 level of categories of English in Malaysia o Acrolect near natives o Mesolect used daily in interaction (mostly used by professionals ) o Basilect street language English Language Teaching Policy in Primary Schools. To equip pupils with the basic skills and knowledge of the English language so as to enable them to communicate, both orally and in writing, in and out of the school. o Aims: Listen to and understand simple spoken English in certain given contexts Speak and respond clearly and appropriately in familiar situations using simple language Read and understand different kinds of texts for enjoyment and information Write for different purposes and in different forms using simple language
Cg Mohd Ridzuan al-Kindy (PISMP-MT IPG KDRI 2010)
Level Lower primary ( Year 1 3) Upper primary ( Year 4 6) Secondary school (Form 1 5) Form 6 (MUET) Matriculation
Time Period 330 minutes / week 120 minutes / week (National-type Chinese and Tamil) 300 minutes / week 120 minutes / week (national-type Chinese and Tamil) 280 minutes/ week
Manglish Got or not? Sure ah? Like dat cannot la! O.K. wat? (OK what?) ..is it?
English Did that happen? or Do you have it? Are you sure? I cannot accept it this way or in this condition Isn't this good enough? or This should be acceptable, isn't it? Is this/that correct? or Is the statement true?
400 minutes / week 6 hours / week
English Language in School (Issues) o Focused on the literary skills (writing and reading) o Lack of exposed on the orally skills (listening and speaking) o Exam orientated o Not enough English teachers. o Introduced the teaching and learning mathematics and science in English (2005) and will be drop on 2012. o Malaysia English also create their own words which come from a variety of influences. Malaysian British / American Handphone (often abbreviated to HP) Slippers Mobile phone or Cell phone Flip-flop (not to be confused with slip-on night-time footwear) Means both 'at work out of town' or less frequently 'at work overseas / abroad' Sick note Noodles
Topic 2: Introduction to Phonology Speech Organs Speech organ produce the many sounds needed for language (articulators) The organs of speech:
Outstation
The articulator and the sound produced:
MC (medical certificate) Mee
Malaysian Colloquial English which is famously known as MANGLISH or Street English o Using mixing grammar and words that don't belong together can be done quite spontaneously and be quite amusing. o The local language (Malay) terms, intonations, exclamations and grammar are fused with English o The changing the pronunciation, intonation, over-simplifying the grammar to express the words.
Cg Mohd Ridzuan al-Kindy (PISMP-MT IPG KDRI 2010)
o Bilabial with two lips (/b/, /p/, /m/, /w/) o Labiodental upper teeth & inner lower lip (/f/, /v/) o Dental tongue near / on inner surface of upper teeth (//, //) o Alveolar tongue tip near / on tooth ridge (/t/, /d/, /s/, /z/, /n/, /l/) o Palatal tongue blade or body near tooth ridge (//, //, /t /, /d/, /r/, /y/) o Velar tongue body near / on soft palate / velum (/g/, /k/, //) o Glottal by air passing windpipe through vocal cord (/h/) Vowel Sound It is an open sound. It is produced by not blocking the breath with the lips, teeth, or tongue. It is the shape of your mouth that decides which vowel sound comes out. It is always voiced (VD Front Seat /iy/ High Sit /I/ Say /ey/ Mid Met /e/ Low Cat /ae/ My /ay/ Ball Now /aw/ Up // Book /U/ No /ow/ Central Back Do /uw/
g h j k l m n p q r s t v w x y z) 25 Consonant Sound /b/ as in bib /g/ as in dig /k/ as in king /n/ as in pen /s/ as in sent /w/ as in window /ch/ as in chip // as in the // as in thing /d/ as in pond /h/ as in hop /l/ as in hall /p/ as in pop /t/ as in tent /y/ as in yell /sh/ as in sheep /ng/ as in ring /f/ as in laugh /j/ as in jam /m/ as in thumb /r/ as in car /v/ as in hive /z/ as in zip /zh/ as in Asia /hw/ wheat
Diphthong Sound A vowel sound that starts near the articulatory position for one vowel and moves toward the position for another, as (oi) in boil or () in fine o Proper diphthong coalition or union of two vowel sounds pronounced in one syllable; as, ou in out, oi in noise o Improper diphthong vowel digraph; a union of two vowels in the same syllable, only one of them being sounded; as, ai in rain, eo in people Consonant Sound Produce sounds more consistent and easier to identify than vowels Can be voiceless (VL) or voiced (VD) Work should be done on identifying beginning consonant sounds (e.g.: t-t-t tulip) After that, activities can focus on identifying final consonant sounds (e.g.: cat ends with the t-t-t sound) Sound produced by stopping the air flowing freely through the mouth; a letter representing a sound thus defined (b c d f
Topic 3: Morphology Morpheme The smallest meaningful unit in the grammar of a language o s (affix to show plural) o And o ed (affix to show past tense) Types of morpheme: o Bound morphemes : morpheme cannot appear on their own (dependent) o Free morphemes : morpheme can appear on their own (independent) want free morpheme wanted -ed bound morpheme Derivational Morpheme The morpheme that added with affixes such that it change the meaning of words or the part of speech or both. Root Word + Derivational Root Word Affixes Morpheme Able Possible Full (adj.) Hard (adj.) Un + able Im + possible Full + ly Hard + er Unable Impossible Fully (adv.) Harder (adv.)
Inflectional Morpheme The morpheme that can only be suffix and create a change in the function of word. Types of inflectional morpheme:
Cg Mohd Ridzuan al-Kindy (PISMP-MT IPG KDRI 2010)
o Noun inflectional morpheme 1. Plural Noun (-s, -es, -ies, -en) Singular Apple Bus Tomato Cherry Child Mother-in-law Plural Apples Buses Tomatoes Cherries Children Mothers-in-law Suffix -s -es -es -ies -en -s
1. Comparative (-er)
A
Adjective Big
C
Example Suffix -er Suffix -er -er
Shape A is bigger than shape B Comparative Harder Earlier
Adverb Hard Early Suffix s 2. Superlative Adjective
2. Possessive Form (s and ) Used for Singular / plural nouns not ending in -s Nouns ending with -s Compound noun The second name if two names are joined by and Plural nouns ending in -s Example Johns coat Womens club Franciss tools Fishermans catch Ahmad and Muhammads father The girls shoes The birds nest
Example Shape A is biggest Comparative Hardest Earliest
Suffix -est Suffix -est -est
Big Adverb
s Hard s Early
o Verb inflectional morpheme 1. Present Tense (-s, -es) Example He walks to school She washes her skirt. 2. Past Tense (-ed) He walked to school She washed her skirt. 3. Past Participle (-en, -ed) Awaken Talked 4. Present Participle Walking -ing -en -ed -ed -ed Suffix -s -es
Allomorph A unit of meaning that can vary in sound (phonologically) without changing meaning o Past tense allomorph Walk walked Want wanted Weep wept Shake shook o Plural allomorph noun ends in an alveolar / alveo-palatal sibilant /s/, /z/, //, /t / - lances, mazes, fishes, badges, beaches noun ends in a non-strident voiceless consonant /p/, /t/, /k/, /f/, // e.g. cups, leeks, carts, laughs, moths /-z/ elsewhere (all vowels and /b/, /d/, /g/, /m/, /n/, /l/, /r/, /w/, /j/), e.g. bards, mugs, rooms, keys, shoes Word Structure The way in which a word is constructed, the elements of which it is made, is an important building block in our understanding of our language. The admissible arrangement of sounds in words.
o Adjective and adverb inflectional morpheme
Cg Mohd Ridzuan al-Kindy (PISMP-MT IPG KDRI 2010)
Affixes
exin-
from, out not in, into between wrong after back beneath, under across not
exclude include
Prefix an affix that is added to the begin of a word e.g.: unable
Infix an affix that is added to the middle of a word (in some languages)
Suffix an affix that is added to the end of a word e.g.: fully
inintermispostresubtransun-
internet misconception post-graduate restart subtopic transnational unknown
Combining Vowels o Link the root to the suffix or the root to another root. Words Combination o pancreat is the root (pancreas) o itis is the suffix Since itis begins with a vowel, we do not need to add a combining vowel. pneum is the root (lung), o is the combining vowel, encephal is the second root which does start with a vowel (so we KEEP the combining vowel), o is the second combining vowel, graphy is the suffix (test.)
10 common suffixes: Suffix -able / -ible -ance / -ence -ate -ful -ity -less -ly -ment -ness -tion / -ion / -sion Meaning Capable of being The act of Making / applying Full of The state of being Without In a certain way The result of being The state of being The act of / the state of being Powerful Complexity Wireless Fully Statement Awareness Promotion Example Changeable Compatible Endurance Conference
pancreatitis
pneumoence phalography
Combining Forms o Made up of a root plus the combining vowel. hemat is the root (blood), o is the combining vowel, logy is the suffix (study of), the combining form is hemat /o
hematology
Word Formation Process Processes for creating new words in a language. Process consists of a combination of morphemes that are rule-governed (a new word is formed). Major Word Formation Process: o Affixation Forming words by adding affixes to morphemes 15 common prefixes: Prefix adcircumcomdedisMeaning to, toward around, about with, together away from, off away, apart decomposition disable Example AdSense circumference
o Compounding Process that forms new words from two or more independent words. e.g.: girl + friend = girlfriend o Reduplicating Process of forming new words either by doubling an entire word (total reduplication) or part of a word (partial reduplication). Total reduplicating: e.g.: bye - bye Partial reduplicating: e.g.: hunny-bunny
Cg Mohd Ridzuan al-Kindy (PISMP-MT IPG KDRI 2010)
o Suppletion Relationship between forms of a word wherein one form cannot be phonologically or morphologically derived from the other (this process is rare). e.g.: am vs was Minor Word Formation Process: o Acronym Words that are formed from the initials of several words. e.g.: RAM = Random Access Memory o Blending Process of creating a new word by combining the parts of two different words, usually the beginning of one word and the end of another. e.g.: camera + recorder = camcorder o Clipping Process of creating new words by shortening parts of a longer word. e.g.: doctor doc
o Can be constructed using: Present participle e.g.: Singing out of tones, the singer was booed off the stage. Past participle e.g.: Frightened by the strange noises, Patricia woke her mother up.
Topic 4: Syntax Definition of Syntax From Greek word meaning order or arrangement Study of the principles and rules for constructing sentences in natural languages. Types of Phrases Noun Phrase o Can be used: In opposition to a noun e.g.: Ahmad, Ali cousins will come to visit Terengganu As subject e.g.: Jogging thrice a week can maintain the healthy. As object of a verb e.g.: Hairi bought a new motorcycle.
Adverbial Phrase o Adverbial phrase of manner Answer the question how? e.g.: The prince loved her with all his heart. o Adverbial phrase of reason Answer the question why? e.g.: He opens the door to let his father enter. Prepositional Phrase o Group of words that begins with a preposition and does not have verb. e.g.: I put the books on the table. Phrase Structure Rule (Tree Diagram) A way to describe a given language's syntax. e.g.:
Verb Phrase
Transformational Rule (Operations) Relates two phrase markers in the course of a derivation from the deep to the surface syntactic representation of a sentence, as by reordering, inserting, or deleting elements. Types of transformation: o Declarative Interrogative o Active Passive o Aux-movement
Cg Mohd Ridzuan al-Kindy (PISMP-MT IPG KDRI 2010)
o -wh-movement o There sentences o PP preposition Examples of Transformation Rule o Declarative Interrogative
Object of the verb e.g.: She asks Saiful why she was fuming Object of preposition e.g.: Is there any login in what he just saying? o Adjective Clause (AdjC) o Adverb Clause (AdvC) begins with when, while, before, until Adverbial clause of manner begin with as, just as, as if, as though, just like e.g.: You look as if you had seen a spirit. Adverbial clause of reason begin with because, as, since, for e.g.: The baby cried because he was hungry. Adverbial clause of purpose begin with so that, in order that, in case e.g.: I bought along an umbrella in case it rained. Adverbial clause of result begin with so that, that, so e.g.: It was so hot that the chocolate melted. Adverbial clause of comparison begin with as, than e.g.: Ahmad cant run as fast as Borhan. Sentence Patterns Structure of Sentences o Simple sentence Contains only one clause e.g.: The ice melts quickly o Compound sentence Create a sense of balance or contrast between two (or more) equally-important pieces of information e.g.: I want like to eat strawberry cake but I prefer to eat chocolate cake today. o Complex sentence contains one independent clause and at least one dependent clause e.g.: Although my friend invited me to a party, I do not want to go Types of Sentences o Declarative sentence Express possibility, a probability or impossibility. e.g.: I might not be able to meet you now. Commands & question. e.g.: You are not going funfair with us? o Interrogative sentence Yes / No Interrogative need Yes or No answer e.g.: Are you married? Wh- Interrogative Wh-question
o -wh-movement
Clause Types Clause group of words that contain a subject and a verb, but which is usually only part of a sentence. Main clause or Can stand alone. Its meaning is independent clause very clear; e.g. I know. Subordinate clause or dependent clause Main Clause or Independent Clause 1. I know 2. You must read 3. I do not know 4. It is cold Cannot stand alone. It depends on the main clause for its full meaning; e.g. what he wants. Subordinate clause or Dependent Clause what he wants. if you want to learn. why he went out. when it rains.
Types of dependent clause: o Noun Clause (NC) begin with that, where, who, what Subject of a verb e.g.: What I do is for your own good.
Cg Mohd Ridzuan al-Kindy (PISMP-MT IPG KDRI 2010)
e.g.: What are you doing? o Exclamatory sentence Express strong & sudden feeling e.g.: How awful its look! o Imperative sentence Express commands e.g.: Go into the room now. Warning e.g.: You had better stop crying. Direction e.g.: Go straight. Instruction e.g.: Cut the orange. Prohibitions e.g.: No littering. Advice e.g.: Do not wonder too far away. Offers e.g.: Have some watermelon. Sentences Patterns o Subject + Intransitive Verb e.g.:The students listened to the professor discuss the five sentence patterns. o Subject + Intransitive Linking Verb + Subject Complement e.g.:The English professor is a man who wants to help his students.. o Subject + transitive verb + direct object e.g.: Barack Obama picked Joe Biden for his vice president. o Subject + transitive verb + indirect object + direct object e.g.: Barack Obama offered Joe Biden the vice presidency o Subject + transitive verb + direct object + object complement e.g.: In November of 2008, the American people elected Barack Obama president
Topic 5: Semantics Definition of Semantics & Pragmatics Semantics o The study of language which focuses on meaning. e.g.: My father is the driver Words Semantics My (i) pronouns (ii) human (iii) those who say (i) human (ii) Men (iii) Adult (iv) the father of child (i) human (ii) to bring vehicle
father
driver
Pragmatic o Area of language function that embraces the use of language in social context. o Pragmatics skills Knowing that you have to answer when a question has been asked. Being able to participate in a conversation by taking it in turn with other speakers. Awareness that you have to introduce a topic conversation in order for listener to fully understand. The ability to maintain a topic. The ability to maintain appropriate eye contact (not too much staring and not too much looking away) during a conversation. Knowing which words or what sort of sentence type to use when initiating a conversation or responding to something someone has said. The ability to distinguish how to talk and behave towards different communicative partners. The ability to notice and respond to the non-verbal aspects of language. Denotative & Connotative Meaning Denotative meaning o The meaning of a symbol that is shared by a group of people and work for communication o Lateral meaning (direct meaning) Connotative meaning o The meaning of a symbol that is personal to an individual and not shared o Not lateral meaning (indirect direct)
Cg Mohd Ridzuan al-Kindy (PISMP-MT IPG KDRI 2010)
Word Mother Cat
Denotative Meaning a female parent a carnivorous mammal, domesticated as a rat catcher or pet
Home
a place where one lives; a residence Rose a red rose with a green stem Sense & References Polysemy (or polysemia) o An intimidating compound noun for a basic language feature. e.g.: paper comes from Greek papyrus Synonymy o Word or phrase meaning same the same as another in the same language. e.g.: Postpone means Put off Hyponymy o Inclusive relationship where some lexemes are co-hyponyms of another that includes them. e.g.: Rose, Hibiscus, Morning glory hyponym of flower Antonymy o Word opposite in meaning to another. o Gradable antonymy e.g.: Tall vs short taller, shorter o Ungradable antonymy e.g.: married vs not married taller, shorter e.g.: half dead, barely alive, more dead than alive, quite pregnant Figurative Expressions Make communication a bit more hazardous, increasing the risk of misunderstandings. o Allegory - a symbolic representation e.g.: The blindfolded figure with scales is an allegory of justice. o Alliteration - the repetition of the initial consonant. There should be at least two repetitions in a row. e.g.: Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers. o Allusion A reference to a famous person or event in life or literature. e.g.: She is as pretty as the Mona Lisa. o Assonance - the repetition of similar vowel sounds in a sentence.
Connotative Meaning love and security graceful motion, affectionate playfulness, noble reserve and admirable self sufficiency a place of security, comfort, and family passion and love
o Foreshadowing - hints of what is to come in the action of a play or a story o Hyperbole - a figure of speech involving exaggeration. o Metaphor - A comparison in which one thing is said to be another. e.g.: The cat's eyes were jewels, gleaming in the darkness. o Onomatopoeia - the use of words to imitate the sounds they describe. e.g.: The burning wood crackled and hissed. o Oxymoron - putting two contradictory words together. e.g.: bittersweet, jumbo shrimp, and act naturally o Personification - is giving human qualities to animals or objects. e.g.: The daffodils nodded their yellow heads. o Pun - A word is used which has two meanings at the same time, which results in humor. o Simile - figure of speech involving a comparison between unlike things using like, as, or as though.
Compiled by, Mohd Ridzuan bin Mohd Taib PISMP Mathematics Semester 5, 2010 Credit: The notes from friends PISMP Mathematics Semester 5, 2010
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Daily Lesson Plan English Year3 ©syazwanikhamis: Stages Activities ResourcesDocument3 paginiDaily Lesson Plan English Year3 ©syazwanikhamis: Stages Activities ResourcesNur Syazwani KhamisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction: Assessment of Speaking and Listening Skills in English (Asl)Document37 paginiIntroduction: Assessment of Speaking and Listening Skills in English (Asl)Sai NathÎncă nu există evaluări
- 27 ASL For Teacher S BookDocument28 pagini27 ASL For Teacher S BookNur Syazwani KhamisÎncă nu există evaluări
- TEACHING & ASSESSING READINGDocument13 paginiTEACHING & ASSESSING READINGNur Syazwani KhamisÎncă nu există evaluări
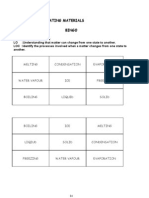
- State of Matter Topic Sains Year 5Document19 paginiState of Matter Topic Sains Year 5usemyknow.blogspot.com100% (1)
- The Teaching and Assessing of Reading SkillsDocument22 paginiThe Teaching and Assessing of Reading Skillspopopino13Încă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Week 1: Children'S Learning in ScienceDocument1 paginăTutorial Week 1: Children'S Learning in ScienceNur Syazwani KhamisÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Gengo Style Guide for English TranslationsDocument10 paginiGengo Style Guide for English TranslationsCissyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smallgroup Lesson PlanDocument7 paginiSmallgroup Lesson PlanJuanita Castro BarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7th Grade English Course Unit 1 Curriculum DocumentDocument12 pagini7th Grade English Course Unit 1 Curriculum Documentapi-401345105Încă nu există evaluări
- Magic Beans Story ComprehensionDocument43 paginiMagic Beans Story Comprehensionsai ramxeroxÎncă nu există evaluări
- For The Gas and Electricity Industries: Paul DummettDocument8 paginiFor The Gas and Electricity Industries: Paul DummettTrainPrinterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why teach speaking skillsDocument7 paginiWhy teach speaking skillsAnh VanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bucto LDMDocument22 paginiBucto LDMJackie Lou ElviniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eng. II MapDocument31 paginiEng. II MapAlan FlorenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparative Study On Language Curriculum Models in The Philippines and Hong KongDocument8 paginiA Comparative Study On Language Curriculum Models in The Philippines and Hong KongInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLE2023 Registered Papers 1Document24 paginiSLE2023 Registered Papers 1Silvija Austėja GudelytėÎncă nu există evaluări
- ED6 - Unit 1Document10 paginiED6 - Unit 1Mai Bich HanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- EN8LC-Ia-5.1:: Lesson Plan For Grade 8 English DATE: June 10, 2019 I. Objectives/ Learning OutcomesDocument2 paginiEN8LC-Ia-5.1:: Lesson Plan For Grade 8 English DATE: June 10, 2019 I. Objectives/ Learning OutcomesMaryknol AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIABIF 131 Notes (Complete)Document20 paginiBIABIF 131 Notes (Complete)Ngobe COLLETEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pourochnye Plany Excel 6Document236 paginiPourochnye Plany Excel 6Jadira ZinullaevnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0057 E2L Primary ProgressionGrid tcm142-592563Document28 pagini0057 E2L Primary ProgressionGrid tcm142-592563Sophee SophiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Needs of English Language Skills Among Receptionists at Boutique Hotels in BangkokDocument70 paginiThe Needs of English Language Skills Among Receptionists at Boutique Hotels in BangkokHamza ZorakÎncă nu există evaluări
- FREE English To Hindi Translation - Instant Hindi TranslationDocument1 paginăFREE English To Hindi Translation - Instant Hindi TranslationAKshay PareekkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 11 English Study GuideDocument3 paginiGrade 11 English Study GuideTyler50% (2)
- Language Hub Student's Book Answer KeyDocument38 paginiLanguage Hub Student's Book Answer Keyteste 123Încă nu există evaluări
- There Are Heaps of Lists Online. What Is The Purpose of This List?Document7 paginiThere Are Heaps of Lists Online. What Is The Purpose of This List?Matt GemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- What's in the picture? English vocabulary for kidsDocument47 paginiWhat's in the picture? English vocabulary for kidsAgus supriyadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Origins of Basque, Europ - Rangi RanganathDocument313 paginiIndian Origins of Basque, Europ - Rangi Ranganatharjuna45Încă nu există evaluări
- This Book Uses Some Grammar Words in English: Noun Verb Adjective Adverb PrepositionDocument9 paginiThis Book Uses Some Grammar Words in English: Noun Verb Adjective Adverb Prepositioncarnalle19Încă nu există evaluări
- End-Of-Course Test Grammar, Vocabulary, Pronunciation, and Practical English ADocument9 paginiEnd-Of-Course Test Grammar, Vocabulary, Pronunciation, and Practical English APaty LeónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Íñigo, IsabelDocument127 paginiÍñigo, IsabelBrendaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESP FOR SPECIFIC PURPOSESDocument10 paginiESP FOR SPECIFIC PURPOSESMuhammad Shofyan IskandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Subject Teachers' Perceptions and Strategies in Managing Large Classes: A Case Study of NepalDocument9 paginiEnglish Subject Teachers' Perceptions and Strategies in Managing Large Classes: A Case Study of NepalLinguistic Forum - A Journal of LinguisticsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Note Speakers: Rita InderawatiDocument4 paginiKey Note Speakers: Rita InderawatiMuhammad KholisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 RazredDocument17 pagini2 RazredKatarina CrnkovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- English For Everyone - Level 1 - Beginner, Practice Book - Dorling KindersleyDocument176 paginiEnglish For Everyone - Level 1 - Beginner, Practice Book - Dorling Kindersleyadrieledrica souza100% (3)