Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Unit-1 Control System Analysis and Components
Încărcat de
Brooke HollandDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Unit-1 Control System Analysis and Components
Încărcat de
Brooke HollandDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Subject-Control System Engineering
VIT-EAST
Class-ECE, 6th Sem
UNIT-1 CONTROL SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND COMPONENTS
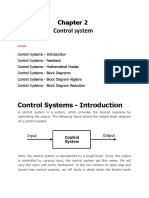
OVERVIEW OF CONTROL SYSTEM:Control System An interconnection of components forming a system configuration that will provide a desired response & minimize the Errors at their output.The comtrol system is used to controlloing the response of the system. The term "control system" may be applied to the essentially manual controls that allow an operator, for example, to close and open a hydraulic press, perhaps including logic so that it cannot be moved unless safety guards are in place. Process The device, plant, or system under control. The input and output relationship represents the cause-and-effect relationship of the process.
Open and closed loop systems:
When the output quentity of a control system is not feedback to the input quentaty.the control system is called openloop control system. In the open loop control system in which the control action does not depend on the output.
Block Diagram of Open Loop System
Prapered By-J.P Mishra
Subject-Control System Engineering
VIT-EAST
Class-ECE, 6th Sem
Closed-Loop Control Systems :Utilizes feedback to compare the actual output to the desired output response. In a closed loop control the system includes a sensor to measure the output and uses feedback of the sensed value to influence the control input variables.
Block Diagram of Close Loop System
Example of Close Loop Control System: Automatic Iron Box
Heating Element
Power Supply
Output
(Temperature)
(Sensor) ON-Off System
Response Signal
Prapered By-J.P Mishra
Subject-Control System Engineering
VIT-EAST
Class-ECE, 6th Sem
Multivariable Control System: There are usually at least two control loops.Systems with more than one control loop are known as multi-input multi-output (MIMO) or multivariable systems. In this System such input is independently considered.
Multivariable Control System
Example of Multivariable Control System: Driving a Vehicle with Speed Control Wind+traffic Disturbance Desired Speed
BRAIN
Acclerator Pedal ENGIN
Actual Speed
Hands (Sterring Control)
Actual Direction
Desired Direction
Speed Meter
Prapered By-J.P Mishra
Subject-Control System Engineering
VIT-EAST
Class-ECE, 6th Sem
Digital Control System:-A digital controller is usually cascaded with the plant in a feedback system. The rest of the system can either be digital or analog. Typically, a digital controller requires:
A/D conversion to convert analog inputs to machine readable (digital) format. D/A conversion to convert digital outputs to a form that can be input to a plant (analog) A program that relates the outputs to the inputs
Digital Control System
Prapered By-J.P Mishra
Subject-Control System Engineering
VIT-EAST
Class-ECE, 6th Sem
Block Diagram Reduction Techniques: It is a representation of the control system giving the inter-relation between the transfer function of various components. The block diagram is obtained after obtaining the differential equation & Transfer function of all components of a control system. The arrow head pointing towards the block indicates the i/p & pointing away from the block indicates the o/p.
If G(s) is TF (Transfer Function), G(S)= C(S)/R(S) After obtaining the block diagram for each & every component, all blocks are combined to obtain a complete representation. It is then reduced to a simple form with the help of block diagram algebra. The following block diagram reduction algebra is used, when 1.Block in cascade (series) 2. Combining blocks in parallel 3. Eliminating a feedback loop 4. Moving a take-off point Before a block 5. Moving a take-off point After of a block
Prapered By-J.P Mishra
Subject-Control System Engineering
VIT-EAST
Class-ECE, 6th Sem
BLOCK DIAGRAMS REDUCTION OFCONTROL SYSTEMS
Prapered By-J.P Mishra
Subject-Control System Engineering Signal Flow Graph Techniques:
VIT-EAST
Class-ECE, 6th Sem
Signal Flow Diagrams are another method for visually representing a system. Signal Flow Diagrams are especially useful, because they allow for particular methods of analysis, such as Mason's Gain Formula. Signal flow diagrams typically use curved lines to represent wires and systems, instead of using lines at right-angles, and boxes, respectively. Every curved line is considered to have a multiplier value, which can be a constant gain value, or an entire transfer function. Signals travel from one end of a line to the other, and lines that are placed in series with one another have their total multiplier values multiplied together (just like in block diagrams). Signal flow diagrams help us to identify structures called "loops" in a system, which can be analyzed individually to determine the complete response of the system
Mason's Gain Formula
Mason's rule is a rule for determining the gain of a system. Mason's rule can be used with block diagrams, but it is most commonly (and most easily) used with signal flow diagrams.
Forward Paths
A forward path is a path in the signal flow diagram that connects the input (Source Point) to the output (Sink Point) without touching any single node or path more than once. A single system can have multiple forward paths.
Loops
A loop is a structure in a signal flow diagram that leads back to itself. A loop does not contain the beginning and ending points, and the end of the loop is the same node as the beginning of a loop. Loops are said to touch if they share a node or a line in common. The Loop gain is the total gain of the loop, as you travel from one point, around the loop, back to the starting point. Mason's Gain Formula is Given by as Follows
Prapered By-J.P Mishra
Subject-Control System Engineering
VIT-EAST
Class-ECE, 6th Sem
Where: T=Overall Transmittance OR Gain =Forward Path Gain of Kth Forward Path =1-(Sum of all loop transmittance which are not touching to the Kth Forward Path) =Graph Transmittance =1- (Sum of all individual loop transmittance) + (Sum of loop gain products of all possible pairs of non touching loops)- (Sum of loop gain products of all possible Triplets of non touching loops)
Signal Flow Graph Representation:Example-(i)
Prapered By-J.P Mishra
Subject-Control System Engineering
VIT-EAST
Class-ECE, 6th Sem
Example-(ii)
Prapered By-J.P Mishra
Subject-Control System Engineering
VIT-EAST
Class-ECE, 6th Sem
Example-(iii)
10
Prapered By-J.P Mishra
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Control Systems NotesDocument152 paginiControl Systems Notesdarlachantisaideepthi450Încă nu există evaluări
- Autotronics and Vehicle Intelligence : Aeng6205Document25 paginiAutotronics and Vehicle Intelligence : Aeng6205Abubaker MuzayinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Control System DeceDocument7 paginiLinear Control System Decepardeep4372Încă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Control Systems in 40 CharactersDocument23 paginiFundamentals of Control Systems in 40 CharactersSona LavaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AUTOMATIC - CONTROL - SYSTEM - UNIT - 1 - For MergeDocument45 paginiAUTOMATIC - CONTROL - SYSTEM - UNIT - 1 - For MergemanishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS Two MarksDocument7 paginiCS Two MarkssivaeinfoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control SystemsDocument12 paginiControl Systemsoyebowale.emmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems NotesDocument133 paginiControl Systems Noteseee limatÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE2253 Control Systems NotesDocument124 paginiEE2253 Control Systems NotesrameshsmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems NotesDocument50 paginiControl Systems NotesEEE CRRÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSE Termwork-2018 - ALV - 2150909Document71 paginiCSE Termwork-2018 - ALV - 2150909Milan ModhawadiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems Typed NotesDocument129 paginiControl Systems Typed Notesta003744Încă nu există evaluări
- J.B. Institute Control Systems Lecture NotesDocument135 paginiJ.B. Institute Control Systems Lecture Notessugunasri UÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit IDocument7 paginiUnit IanandhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Program: Automated Vehicle Control SystemsDocument12 paginiProgram: Automated Vehicle Control SystemsKalakriti IITIÎncă nu există evaluări
- LESSON1 IntroToControlSystemDocument10 paginiLESSON1 IntroToControlSystemalexancog456Încă nu există evaluări
- CE Unit 1Document84 paginiCE Unit 1P POORNA CHANDRA REDDYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automatic Control Lecture OverviewDocument56 paginiAutomatic Control Lecture OverviewGGAP LASTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Loop and Close Loop Control SystemDocument10 paginiOpen Loop and Close Loop Control SystemAmrit SinghaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 Buku NelsonDocument6 paginiChapter 7 Buku Nelsoncatia asdosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control SystemsDocument8 paginiControl Systemsmohammed zaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study, Analysis and Evaluation of Block Diagram Reduction Name: University of Polytechnic/college ofDocument10 paginiStudy, Analysis and Evaluation of Block Diagram Reduction Name: University of Polytechnic/college ofTana AzeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechatronics NotesDocument90 paginiMechatronics NotesSanskar AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System Engineering PPT by ShemsudinDocument42 paginiControl System Engineering PPT by ShemsudinShemsudin AhmedteibÎncă nu există evaluări
- 58077-13950-IC1251 IV Sem Control System 2-MARKSDocument15 pagini58077-13950-IC1251 IV Sem Control System 2-MARKSMarilyn PrascillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Closed-Loop Control FundamentalsDocument8 paginiClosed-Loop Control FundamentalsavenashaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System Engineering (15A02303) : Lecture Note B.TechDocument126 paginiControl System Engineering (15A02303) : Lecture Note B.TechNAZMUS SAKIBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems Lecture NotesDocument70 paginiControl Systems Lecture NotesPrathamraj ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-I: Concept of Control SystemDocument129 paginiUnit-I: Concept of Control SystemPavitra Murugesan100% (1)
- 1. Chapter 1_Transfer FunctionDocument52 pagini1. Chapter 1_Transfer FunctionNahome NigussieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems Notes DEE M2 JuneDocument34 paginiControl Systems Notes DEE M2 JuneThairu MuiruriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 2. Matemethical Modelling of Control Systems V1Document13 paginiTopic 2. Matemethical Modelling of Control Systems V1xREDCivicCometxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System Unit-1Document29 paginiControl System Unit-1Tanishq SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems NotesDocument74 paginiControl Systems NotesNirjal RanipaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Control System: Presented by Imran Basha SyedDocument35 paginiLinear Control System: Presented by Imran Basha SyedSyed Imran BashaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LCS R19 - Unit-1Document8 paginiLCS R19 - Unit-1Gowtham DhanarasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System Engineering 2 MarksDocument18 paginiControl System Engineering 2 MarksSeenu CnuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems - NotesDocument61 paginiControl Systems - NotesNarasimha Murthy YayavaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE2253 NotesDocument124 paginiEE2253 NotesSiva Kathikeyan100% (1)
- Draw and Explain Closed Loop System: AssignmentDocument3 paginiDraw and Explain Closed Loop System: AssignmentSameer ArifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Engineering: Closed-Loop Poles Are The Positions of The Poles (OrDocument9 paginiControl Engineering: Closed-Loop Poles Are The Positions of The Poles (OrWanambwa SilagiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Closed-Loop Control Systems ExplainedDocument9 paginiClosed-Loop Control Systems ExplainedBhimsen ShresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control TheoryDocument10 paginiControl TheoryAnonymous E4Rbo2sÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING – BCS – SHORT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ON BIOLOGICAL CONTROL SYSTEMSDocument15 paginiBIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING – BCS – SHORT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ON BIOLOGICAL CONTROL SYSTEMSNoor AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control SystemDocument16 paginiControl SystemChuThếHuânÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC6405 Syllabus Control Systems Engineering Class III EEEDocument16 paginiEC6405 Syllabus Control Systems Engineering Class III EEEAruna ChandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Closed-Loop System and Closed-Loop Control SystemsDocument9 paginiClosed-Loop System and Closed-Loop Control SystemsfwefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control TheoryDocument12 paginiControl TheorymCmAlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Closed Loop Control System ExplainedDocument6 paginiClosed Loop Control System ExplainedMUHAMMAD AKRAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS Unit-1Document42 paginiCS Unit-1auchthram143Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Control SystemsDocument36 paginiIntroduction to Control Systemsmary mutungaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System EngineeringDocument125 paginiControl System Engineeringcüneyt şanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulink Basics TutorialDocument143 paginiSimulink Basics TutorialHiếu HuỳnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block DiagramsDocument26 paginiBlock Diagramsmanoj walekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3Document13 paginiLecture 3Abdullah Mohammed AlsaadouniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Engineering Instructional Module LecturesDocument13 paginiControl Engineering Instructional Module LecturesJohn Kenneth Santiago PaulinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpe 315 Feedback Control System LessonsDocument28 paginiCpe 315 Feedback Control System Lessonskeny amigableÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Engineering: Types of Control SystemsDocument26 paginiControl Engineering: Types of Control SystemsGilbert SigalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nonlinear Control Feedback Linearization Sliding Mode ControlDe la EverandNonlinear Control Feedback Linearization Sliding Mode ControlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imageprograf Ipf780 SM Rev3 022717Document320 paginiImageprograf Ipf780 SM Rev3 022717Rick_IngersollÎncă nu există evaluări
- Citroenforum hr-MIRASCRIPT PDFDocument6 paginiCitroenforum hr-MIRASCRIPT PDFNemanja BoricÎncă nu există evaluări
- Secret Clickbank Domination Blueprint: Ritoban Chakrabarti'sDocument12 paginiSecret Clickbank Domination Blueprint: Ritoban Chakrabarti'sKarteekking RÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - How To Create A Personal Access Token in GitHubDocument4 pagini2 - How To Create A Personal Access Token in GitHubKashif KamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 153A Joystick Poscon - DNV CertificateDocument2 pagini153A Joystick Poscon - DNV Certificatehansin desvirgensenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix 63 RISDocument1 paginăAppendix 63 RISRafael AlcasidÎncă nu există evaluări
- OCI Foundations IZ0-1085Document10 paginiOCI Foundations IZ0-1085Min Min20% (5)
- 0Document1.370 pagini0Linda HamiltonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial For RobotitoDocument323 paginiTutorial For RobotitoLuciano RabassaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICONICS Suite Resolved Issues 1097Document19 paginiICONICS Suite Resolved Issues 1097Hồ PhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Manual For PileGroupDocument120 paginiUser Manual For PileGroupmyplaxisÎncă nu există evaluări
- TBL-31-E-GMA - ED80-DL-113-EN-1-Wiring and Interconnection Diagram-Waste Water Central Monitoring BasinDocument6 paginiTBL-31-E-GMA - ED80-DL-113-EN-1-Wiring and Interconnection Diagram-Waste Water Central Monitoring BasinAjeng InsaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equipment List For Flexi BSCDocument47 paginiEquipment List For Flexi BSCgalal0% (1)
- Ovation To Abb SystemDocument2 paginiOvation To Abb SystemAnderson Pisconte SoteloÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is New in PTV Vissim/Viswalk 11Document20 paginiWhat Is New in PTV Vissim/Viswalk 11Billy BrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Vision AssignmentDocument5 paginiComputer Vision AssignmentMOHIT KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Posiflex OPOS Driver Installation V13xxDocument11 paginiPosiflex OPOS Driver Installation V13xxelbakri abd elhakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview Questions Topic Wise PDFDocument7 paginiInterview Questions Topic Wise PDFBalaji KommaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZigZag Transformer in ATPDocument10 paginiZigZag Transformer in ATPCesar ZamudioÎncă nu există evaluări
- NET201 Lab Experiment # 5 - Configuring IPv6 Static and Default RoutesDocument19 paginiNET201 Lab Experiment # 5 - Configuring IPv6 Static and Default RoutesJasmin Cez MabilanganÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP User ClassificationDocument4 paginiSAP User ClassificationPadmanabhan100% (3)
- GSM Location Update Sequence DiagramDocument4 paginiGSM Location Update Sequence DiagramYogesh BindwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obr ReportDocument9 paginiObr ReportSujitKGoudarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 17 - Software Testing StrategiesDocument38 paginiChapter 17 - Software Testing Strategiesmalik assadÎncă nu există evaluări
- WitBlox Young InventorDocument10 paginiWitBlox Young InventorvivektonapiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThreadX User GuideDocument362 paginiThreadX User GuidetrungvbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Analytics: Enhancing Decision Making Association Analytics: A Mining ApproachDocument30 paginiBusiness Analytics: Enhancing Decision Making Association Analytics: A Mining ApproachManvendra SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passport Automation System-Varsh.88Document8 paginiPassport Automation System-Varsh.88Bandaru PriyankaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 Introduction RoboticsDocument49 paginiLecture 1 Introduction RoboticshoangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Install PostgreSQL 10 With Repmgr On CentOS 7Document5 paginiInstall PostgreSQL 10 With Repmgr On CentOS 7AymenÎncă nu există evaluări