Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chemical Plant Control (Ch-306)
Încărcat de
Salim ChohanTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chemical Plant Control (Ch-306)
Încărcat de
Salim ChohanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CHEMICAL PLANT CONTROL (CH-306)
ASSIGNMENT (BASICS TERMS AND DEFINATIONS)
CH-018 TE
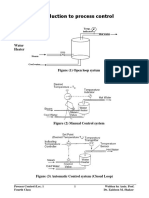
SETPOINT The setpoint is a value for a process variable that is desired to be maintained. For example, if a process temperature needs to kept within 5 C of 100 C, then the set point is 100 C. INPUT VARIABLES Input variables are that which denotes the effect of surrounding on to the chemical process. TYPES: i)MV (Manipulated Var.): Operator can adjust (Fuel flow rate) ii) DV (Disturbance Var.): Decided by external reasons (Feed flow, Fuel Press.) (measured DV and unmeasured DV) OUTPUT VARIABLES Output variables are that which denotes the effect of chemical process on to the surrounding TYPES: CV (Controlled Var.): Decided by the changes in input variables (assumed to be measured) Measured and unmeasured outputs ERROR Error is the difference between the measured variable and the set point and can be either positive or negative. FEED BACK CONTROL In this process control system informations about controlled variable is fed back to the controller and final control elemnt. It uses direct measurement of the controlled variable to adjust values of manipulated variables.It does not measure the disturbance directly. FEED FORWARD CONTROL In this process disturbance are measured in advance and compensate without waiting for a change (disturbance) in control variable . It is used for direct measurement of the disturbance to adjust manipulated variables.
CASCADE CONTROL Cascade control is a control system in which a secondary (slave) control loop is set up to control a variable that is a major source of load disturbance for another primary (master) control loop Proportional (P) Control : The proportional mode adjusts the output signal in direct proportion to the controller input (which is the error signal, e). OR A proportional (P) controller has an output U proportional to its input e , that is, U = Kp e, where K , is a proportionality constant.
THE INTEGRAL (I) CONTROLLER The Integral controller adds the system deviation over time. It integrates the system deviation. OR An integral (I) controller has an output U proportional to the integral of its input e, that is, U = K , / e ( t ) dt, where K , is a proportionality constant
PD .PI AND PID CONTROLLER PD, PI, DI, and PID controllers are combinations of proportional (P), derivative (D), and integral (I) controllers
DEAD TIME It is a delay in the response of a process after some variable is changed, during which no information is known about the new state of the process. It may also be known as the transportation lag or time delay.
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
CHEMICAL PLANT CONTROL (CH-306)
ASSIGNMENT :
TOPIC : FROM : TO : BASICS TERMS AND DEFINATIONS SALEEM CHOHAN CH-018 SIR ZUBAIR AHMED
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- P, I, D, PI, PD, and PID ControlDocument14 paginiP, I, D, PI, PD, and PID ControlArnav KothiyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pid EeeeDocument28 paginiPid Eeeecyprian obotaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pid ThoryDocument24 paginiPid ThoryPravin KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Dynamics & Control: Muhammad Rashed JavedDocument30 paginiProcess Dynamics & Control: Muhammad Rashed JavedTalha ImtiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9.2 - P, I, D, PI, PD, and PID Control - Engineering LibreTextsDocument9 pagini9.2 - P, I, D, PI, PD, and PID Control - Engineering LibreTextsChandrasekar ElankannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Behavior of Feedback Control ProcessesDocument12 paginiDynamic Behavior of Feedback Control ProcessesAubrenica Lopez100% (1)
- Effect Relationship For TheDocument5 paginiEffect Relationship For TheByron MawoyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report ControlDocument33 paginiReport Controlajwadalfatani100% (5)
- CH 4 - Process Control J5800Document49 paginiCH 4 - Process Control J5800mohd_mizanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automation Process ControlDocument39 paginiAutomation Process Controlaw_ae100% (4)
- Pid Controller Tuning: S.no Name of The ChapterDocument35 paginiPid Controller Tuning: S.no Name of The ChapterAmit TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control DynamicDocument10 paginiControl Dynamicكرار نعيم100% (1)
- 2023 PCI360S Introductory ConceptsDocument19 pagini2023 PCI360S Introductory ConceptsSifanele PotwanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3Document11 paginiUnit 3mayuraher9511Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Process Variables-1Document47 paginiChemical Process Variables-1Portia ShilengeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control StrategyDocument44 paginiControl StrategyAyunie FazlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPCDocument15 paginiIPCu can't see meÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp - P8 - Multiprocess TrainerDocument19 paginiExp - P8 - Multiprocess TrainerSiddesh PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 1 Introduction To Process ControlDocument4 paginiLect 1 Introduction To Process ControlZaidoon MohsinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instrumentation Engineering Questions & AnswersDocument10 paginiInstrumentation Engineering Questions & AnswerscontgautamÎncă nu există evaluări
- PID Controller: Control Loop BasicsDocument6 paginiPID Controller: Control Loop Basicsdil17Încă nu există evaluări
- Bcs (Unit 1)Document23 paginiBcs (Unit 1)sivamani CHINNASWAMYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp - P6 - Temperature ControlDocument10 paginiExp - P6 - Temperature ControlSiddesh PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air-Conditioning and Refrigeration Control - 1: Instructor: Eng. Raad Alsaleh Grading SystemDocument92 paginiAir-Conditioning and Refrigeration Control - 1: Instructor: Eng. Raad Alsaleh Grading SystemSunil Varma VeeravalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Process ControlDocument38 paginiBasic Process ControlBoris bryan AletanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Controllers: P, I, D, PI, PD, and PID ControllersDocument5 paginiTypes of Controllers: P, I, D, PI, PD, and PID Controllerspratik chakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slides CPC PDFDocument536 paginiSlides CPC PDFJam imtiaz100% (1)
- Automatic Controllers & Control ModesDocument74 paginiAutomatic Controllers & Control ModesVishal IyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tarea2 Investigacion-Mcca-190090Document13 paginiTarea2 Investigacion-Mcca-190090Christian MendezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contro EngineeringDocument29 paginiContro EngineeringNor AshimyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assistant Professor Dr. Khalaf S Gaeid: Electrical Engineering Department/Tikrit UniversityDocument39 paginiAssistant Professor Dr. Khalaf S Gaeid: Electrical Engineering Department/Tikrit Universityaditee saxenaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ic1352 - Process Control-2 MarksDocument21 paginiIc1352 - Process Control-2 MarksKaushal Kishor100% (1)
- ECNG3004 Control System ApplicationsDocument7 paginiECNG3004 Control System ApplicationsMarlon BoucaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Do We Need Process ControlDocument6 paginiWhy Do We Need Process ControlSebastien PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- CEIC3006 Lec 1Document5 paginiCEIC3006 Lec 1Holly YuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Control CHP 5Document29 paginiProcess Control CHP 5dododoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- EVMS Full Notes PDFDocument78 paginiEVMS Full Notes PDFNaveen DhanurajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5Document39 paginiChapter 5Portia ShilengeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Process Control Basic ConceptsDocument39 paginiIndustrial Process Control Basic Conceptskaezzar10100% (1)
- Chapter - 4 Control Configuration 4.1 Pid ControllerDocument8 paginiChapter - 4 Control Configuration 4.1 Pid ControllerMoorthy ManikandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Controller Principles 2020 NotesDocument17 paginiController Principles 2020 NotesJoseph ChalilÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntroductionDocument39 paginiIntroductionMohd FazliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hitachi Inverter PID Control Users' GuideDocument16 paginiHitachi Inverter PID Control Users' GuideMirinhaeThiago RosárioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary Part MaiDocument8 paginiSummary Part MaiCupa no DensetsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Contrlo PracDocument44 paginiProcess Contrlo PracMvelo PhungulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Control NotesDocument178 paginiProcess Control Notesabdulrhman aljuaydi100% (1)
- A Simple Single-Input-Single-Output (SISO) Feedback Control Loop Consists of FollowingDocument3 paginiA Simple Single-Input-Single-Output (SISO) Feedback Control Loop Consists of FollowingMicahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control SystemsDocument18 paginiControl Systemsgayatri jaltareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 3Document10 paginiChap 3amol76Încă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 06: Study of Process Control-I: Mesbah Ahmad Lecturer Department of Chemical Engineering, BUETDocument18 paginiExperiment 06: Study of Process Control-I: Mesbah Ahmad Lecturer Department of Chemical Engineering, BUETMd Abid AfridiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No 8 IC LabDocument12 paginiExperiment No 8 IC LabAyesha KhurramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Closed Loop Control System (CSL - 04) : Technical Manual FORDocument19 paginiClosed Loop Control System (CSL - 04) : Technical Manual FORAAYUSH KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChE 220LDocument3 paginiChE 220LSweyn BalidoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Control TrainerDocument44 paginiPressure Control TrainerAjeet KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of ControlDocument5 paginiFundamentals of Controltoony reyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temperature Control LabDocument16 paginiTemperature Control Labhoocheeleong234100% (1)
- Instrumentation and Contrrol PPT LessonDocument41 paginiInstrumentation and Contrrol PPT LessonFRANCK DAMSSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microelectronic Systems N2 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesDe la EverandMicroelectronic Systems N2 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesDe la EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hot Work PowerpointDocument18 paginiHot Work PowerpointSalim Chohan100% (1)
- F 44736016Document3 paginiF 44736016Salim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cre Lecture (07-09-2015)Document27 paginiCre Lecture (07-09-2015)Salim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpretation of Batch Reactor DataDocument4 paginiInterpretation of Batch Reactor DataSalim Chohan0% (1)
- Cre Lecture (07-09-2015)Document27 paginiCre Lecture (07-09-2015)Salim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material Selection & Design ConsiderationsDocument21 paginiMaterial Selection & Design ConsiderationsSalim Chohan100% (1)
- Best Practice 12lubricant Selecton For Screw and Recip CompressorsDocument6 paginiBest Practice 12lubricant Selecton For Screw and Recip CompressorsSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 120 PruDocument1 pagină120 PruSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- General ConceptsDocument11 paginiGeneral ConceptsSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 106 MeroxDocument1 pagină106 MeroxSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Troubleshootinh 102-103Document2 paginiTroubleshootinh 102-103Salim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- REPORT 102-103 EditorDocument2 paginiREPORT 102-103 EditorSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schx4004 Mechanical Operations LabDocument23 paginiSchx4004 Mechanical Operations LabsaibapoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numericals 19 PDFDocument8 paginiNumericals 19 PDFSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cre Lecture (07-09-2015)Document27 paginiCre Lecture (07-09-2015)Salim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Description of Process FlowDocument2 paginiDescription of Process FlowSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compressors OperationDocument35 paginiCompressors OperationSalim Chohan100% (1)
- Chemical Engineering Progress (1993) Pag. 53-60Document8 paginiChemical Engineering Progress (1993) Pag. 53-60sharkdude1134100% (1)
- Ethylene Oxide PresentationDocument14 paginiEthylene Oxide PresentationSalim Chohan100% (3)
- Chmiionelect 2Document3 paginiChmiionelect 2kjjkimkmkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaporation: Difference B/W Evaporation & BoilingDocument35 paginiEvaporation: Difference B/W Evaporation & BoilingSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MS Project TutorialDocument36 paginiMS Project TutorialSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cre Lecture (07-09-2015)Document27 paginiCre Lecture (07-09-2015)Salim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 3: PROJECT MANAGEMENT - Suggested Solutions: Question 3.3 Network DrawingDocument3 paginiCHAPTER 3: PROJECT MANAGEMENT - Suggested Solutions: Question 3.3 Network DrawingKoko DandashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Human Resource Management: S. Ali Ammar TaqviDocument9 paginiIntroduction To Human Resource Management: S. Ali Ammar TaqviSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ExtrusionDocument11 paginiExtrusionSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRP ProblemsDocument5 paginiPRP ProblemsSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poly Vinyl ChlorideDocument13 paginiPoly Vinyl ChlorideSalim ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pert CPMDocument33 paginiPert CPMSalim Chohan100% (1)
- CavitationDocument11 paginiCavitationSalim Chohan0% (1)
- InFocus Thunder Speakerphone DatasheetDocument2 paginiInFocus Thunder Speakerphone Datasheetpinke01Încă nu există evaluări
- Music Frequency Cheat SheetDocument1 paginăMusic Frequency Cheat SheetLeonel Molina AlvaradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Usage of D6T-44L - 8L - 1A Thermal SensorDocument23 paginiUsage of D6T-44L - 8L - 1A Thermal SensorEduardo ggÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stainless Steel Wire Mesh and Wire ClothDocument3 paginiStainless Steel Wire Mesh and Wire ClothStela LjevarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bailey HangoutsDocument477 paginiBailey Hangoutsmemes MendezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 3 Submitted by:-YOGESH YADAV ROLL NO. R610215057 SAP ID 500048466Document6 paginiAssignment 3 Submitted by:-YOGESH YADAV ROLL NO. R610215057 SAP ID 500048466Yogesh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2010 Batch (Sem 1 11-12)Document10 pagini2010 Batch (Sem 1 11-12)prateek_7892Încă nu există evaluări
- Truebluepower: Advanced Lithium-Ion Battery TB17Document2 paginiTruebluepower: Advanced Lithium-Ion Battery TB17Milad YadollahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Image Correlation - Tracking With MatlabDocument20 paginiDigital Image Correlation - Tracking With MatlabrajibmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7) Progress PaymentDocument5 pagini7) Progress Paymentkerwin jayÎncă nu există evaluări
- East West Pipe Rack For Piping Project J-80: Sendan International Company LTDDocument25 paginiEast West Pipe Rack For Piping Project J-80: Sendan International Company LTDFarrukh Javed100% (1)
- Mekaniko On The Go: An Online Mechanic Mobile Application: A System Analysis and Design ProjectDocument8 paginiMekaniko On The Go: An Online Mechanic Mobile Application: A System Analysis and Design ProjectMarco MagdaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Assad Abu-Jasser, ECE-iugaza: Electrical Machines (EELE 4350)Document37 paginiDr. Assad Abu-Jasser, ECE-iugaza: Electrical Machines (EELE 4350)MohammedSaadaniHassani67% (6)
- Time of Setting of Hydraulic Cement by Vicat NeedleDocument6 paginiTime of Setting of Hydraulic Cement by Vicat NeedleAbdullah TrwanshyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imp25 PDFDocument8 paginiImp25 PDFEng Marwa ElsherifÎncă nu există evaluări
- OpenSAP Sac1 Week 2 All SlidesDocument17 paginiOpenSAP Sac1 Week 2 All SlidesTheJackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Itw Catalog PDFDocument180 paginiItw Catalog PDFGilbertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 132-LogSat JRC JLN-720 Instruct Manual 1-10-2019Document134 pagini132-LogSat JRC JLN-720 Instruct Manual 1-10-2019Sunil S I ShippingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fast-Recovery Rectifier Diodes: Ru 4Y Ru 4Z RU4 Ru 4A Ru 4B Ru 4CDocument1 paginăFast-Recovery Rectifier Diodes: Ru 4Y Ru 4Z RU4 Ru 4A Ru 4B Ru 4CY. Leonel MolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Data: Convertible Air Handlers 1-1/2 - 5 TonDocument28 paginiProduct Data: Convertible Air Handlers 1-1/2 - 5 TonJonathan CapraÎncă nu există evaluări
- C510WNDocument2 paginiC510WNEdgarDavidDiazCamposÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Ms Pipe:: - (40 MM NB, Class'b'Document4 paginiDesign of Ms Pipe:: - (40 MM NB, Class'b'Kancharla Naga Ratna KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Job Application and Cover LettersDocument1 paginăJob Application and Cover LettersDyah AgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure Tialoc Chemical Resistant Piping Systems: Page 1 of 20Document20 paginiBrochure Tialoc Chemical Resistant Piping Systems: Page 1 of 20Fernando Cesar PérezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0764 Kali LinuxDocument322 pagini0764 Kali LinuxAnonymous wlDp7UrBam0% (2)
- Dtu-30 09 2019 PDFDocument15 paginiDtu-30 09 2019 PDFRameo majumderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case/Duct System (Automobile)Document7 paginiCase/Duct System (Automobile)Tran xuan ThuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- LCD and TV Repair GuideDocument195 paginiLCD and TV Repair GuideUlisesMartin79% (14)
- Unit 5: Extra Practice: KeyDocument1 paginăUnit 5: Extra Practice: KeyMuniz BarbosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FuzzyDocument75 paginiFuzzyvatsalshah24Încă nu există evaluări