Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Junior Big Ideas
Încărcat de
api-202207322Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Junior Big Ideas
Încărcat de
api-202207322Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Junior Division - Big Ideas
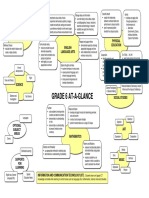
Grade 4 The Arts Dance Elements of dance, focus on time and energy Narrative form Elements of dance, focus on relationship Call-and-response form Elements of dance, focus on body, space, time, energy and relationship Guided improvisation Role-play Elements of drama Use research skills to expand their understanding of different kinds of problems and to help them nd solutions Further aspects of standard notation Create and perform a variety of compositions Think critically about the music they hear and perform Provide constructive feedback regarding their own and others efforts Concepts introduced in Grades 1-5 All elements of design Principles of design, focus on balance Grade 5 Grade 6
Drama
Role-play Elements of drama Select appropriate symbols, manipulative story elements, and experiment with various techniques to create different effects for different audiences
Music
Read standard notation in the treble clef Sing or play music in two parts Create simple rhythms and melodies as accompaniments How music is organized
Sing and/or play from standard music notation and other forms of notation Use key signatures Create compositions in a variety of forms using notational software Key inuences affecting music in our past and present cultures Concepts introduced in Grades 1-4 All elements of design Principles of design, focus on proportion
Visual Arts
Concepts introduced in Grades 1-3 All elements of design Principles of design, focus on emphasis
Physical Education Active Living Active Participation Participation in program activities, behaviours showing readiness Enjoyment of activity (individual, small-group, and leadup activities) Factors that motivate or challenge participation (in and outside of school) DPA - sustained, moderate to vigorous activity, 20 min. per day, including warmup and cool-down Physical activity and health-related tness Exertion, self-assessment, intrinsic, extrinsic factors Developing and acting on personal physical activity goals Behaviour and procedures that maximize safety of self and others Prevention of accidents and injuries DPA - sustained, moderate to vigorous activity, 20 min. per day, including warm-up and cool-down Physical activity and health-related tness Assessment and monitoring of health-related tness Developing and implementing personal tness plans
Physical Fitness
Safety
Behaviour and procedures that maximize safety of self and others Minimizing environmental health risks
Behaviour and procedures that maximize safety of self and others Treating minor injuries
Movement Competence Skills and Concepts Stability: static balance; jumping, hopping and landing Locomotion: movement combinations Manipulation: sending and receiving; retaining objects Stability: static and dynamic balance; jumping, hopping and landing Locomotion: movement combinations Manipulation: sending and receiving; retaining objects Stability: static and dynamic balance; locomotion Manipulation: sending and receiving; retaining objects
Strategies
Activity components - variety of lead-up, recreational, tness, and dance activities Categories of games and activities - common features and strategies Tactical solutions to increase success in activities
Healthy Living Understanding Health Concepts Making Healthy Choices Making Connections for Healthy Living Healthy Eating: Nutrients, food choices, healthy eating goals Personal Safety & Injury Prevention: Safe use of technology, bullying and abuse, decision making - assessing goals Substance Use, Addictions, and Related Behaviours: Tobacco use Healthy Eating: Nutrition facts tables, food labels; media inuences Personal Safety & Injury Prevention: Threats to personal safety; actions, selfconcept Substance Use, Addictions, and Related Behaviours: Alcohol use Healthy Eating: Inuences on healthy eating, eating cues and guidelines, benets of healthy eating/active living Personal Safety & Injury Prevention: Safe and positive social interaction, conict management; responsibilities, risks - care for self and others, safety practices Substance Use, Addictions, and Related Behaviours: Cannabis, illicit drugs; supports; strategies, safe-choices, inuences
Language Arts Oral Communication Listening to Understand: Purpose, Active Listening Strategies, Comprehension Strategies, Demonstrating Understanding, Making Inferences/Interpreting Texts, Extending Understanding, Analysing Texts, Point of View, Presentation Strategies Speaking to Communicate: Purpose, Interactive Strategies, Clarity and Coherence, Appropriate Language, Vocal Skills and Strategies, Non-Verbal Cues, Visual Aids Reecting on Oral Communication Skills and Strategies: Metacognition and Interconnected Skills
Junior Division - Big Ideas
Grade 4 Reading Grade 5 Grade 6 Reading for Meaning: Variety of texts, Purpose, Comprehension Strategies, Demonstrating Understanding, Making Inferences/Interpreting Texts, Extending Understanding, Analyzing Texts, Responding to and Evaluating Texts, Point of View Understanding Form and Style: Text Forms, Text Patterns, Text Features, Elements of Style Reading With Fluency: Reading Familiar Words, Reading Unfamiliar Words, Reading Fluently Reecting on Reading Skills and Strategies: Metacognition and Interconnected Skills Text Forms: Diary or journal Elements of Style: alliteration, descriptive adjective and adverbs Text Forms: Short stories Elements of Style: word choice, and the use of similes, personication, comparative adjectives Text Forms: Myth Elements of Style: word choice, and the use of hyperbole, strong verbs, dialogue and complex, sentences
Writing
Developing and Organizing Content: Purpose and Audience, Developing Ideas, Research, Classifying Ideas, Organizing Ideas, Review Using Knowledge of Form and Style in Writing: Form, Voice, Word Choice, Sentence Fluency, Point of View, Preparing for Revision, Revision, Producing Drafts Applying Knowledge of Language Conventions and Presenting Written Work Effectively: Spelling Familiar Words, Spelling Unfamiliar Words, Vocabulary, Punctuation, Grammar, Proofreading, Publishing, Producing Finished Works Reecting on Writing Skills and Strategies: Metacognition, Interconnected Skills and Portfolio Organizing Ideas: Summaries with graphic organizers Voice: Words and stylistic elements that convey a specic mood Punctuation: Apostrophe and quotation marks Grammar: Common and proper nouns; verbs in the simple present, past and future tenses; adjectives and adverbs; subject/verb agreements; prepositions; and conjunctions Organizing Ideas: Several linked paragraphs Voice: Modifying language and tone to suit different circumstances and audiences Sentence Fluency: Conjunctions and pronouns Punctuation: Commas before and or but in compound sentences to join principal clauses; quotation marks; and the placement of commas, question marks, and exclamation marks inside quotation marks in direct speech Grammar: Common nouns; collective nouns; adjectives, including comparative adjectives; the helping verb; adverbs modifying verbs; comparative adverbs Organizing Ideas: Structured, multiparagraph piece of writing Preparing for Revision: Focus on supporting details and precise language Punctuation: Commas to separate words in a list or after an introductory word or phrase; quotation marks in dialogue; and some uses of the colon, semi-colon, and brackets Grammar: Personal subject and object pronouns, indenite pronouns; conjunctions; subordinate clauses; adverb phrases; and present, past and future verb tenses
Media Literacy
Understanding Media Texts: Purpose and Audience, Making Inferences/Interpreting Texts, Responding to and Evaluating Texts, Audience Responses, Point of View, Production Perspectives Understanding Media Forms, Conventions and Techniques: Form, Conventions and Techniques Creating Media Texts: Purpose and Audience, Form, Conventions and Techniques, Producing Media Texts Reecting on Media Literacy Skills and Strategies: Metacognition and Interconnected Skills
Mathematics Number Sense and Numeration Quantity Operational sense Relationships Representation Proportional reasoning Addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of single and multidigit whole numbers Addition and subtraction of decimal numbers to tenths and money amounts Whole-number unit rates Whole numbers to 10,000 Decimal numbers to tenths Simple fractions Money amounts to $100 Magnitude: counting forwards and backwards by 0.1 and by fractional amounts Length, perimeter, area, mass, capacity, volume, and elapsed time Relationships among units and measurable attributes, including area and perimeter of rectangles Multiplication and division of multidigit whole numbers Addition and subtraction of decimal numbers to hundredths Whole-number rates Whole numbers to 100,000 Decimal numbers to hundredths Proper and improper fractions Mixed numbers Magnitude: counting forward and backward by 0.01 Multiplication and division of whole numbers Addition and subtraction of decimal numbers to thousandths Percent, ratio, and unit rate Whole numbers to 1 000 000 Decimal numbers to thousandths Proper and improper fractions Mixed numbers
Measurement Attributes, units and measurement sense Measurement relationships
Perimeter, area, temperature change, and elapsed time) Relationships among units and measurable attributes, including area of a rectangle and volume of a rectangular prism) Side and angle properties of 2D shapes Nets of prisms and pyramids Locations of objects, using the cardinal directions Translate 2D shapes
Metric quantities Relationships among units and measurable attributes, including area of a parallelogram, area of a triangle, and the volume of a triangular prism)
Geometry and Spatial Sense Properties of 2D shapes and 3D gures Geometric relationships Location and movement
Geometric properties and angles of quadrilaterals and 3D gures Construct 3D gures, using 2D shapes Locations of an object, using a grid map Reect 2D shapes
Polygons and angles Sketch 3D gures, and construct 3D gures from drawing Locations of objects in the rst quadrant of a coordinate system Rotate 2D shapes Growing and shrinking patterns (where the terms are whole numbers) Repeating patterns involving rotations Variables in simple algebraic expressions and equations
Patterning and Algebra Patterns and relationships Variables, expressions and equations
Predict numeric and geometric patterns Repeating patterns involving reections Equality between pairs of expressions, using addition, subtraction and multiplication
Growing and shrinking patterns (table of values) Repeating patterns involving translations Variables in equations
Junior Division - Big Ideas
Grade 4 Data Management and Probability Collection and organization of data Data relationships Probability Collect and organize discrete primary data and display the data using charts and graphs, including stem-and-leaf plots and double bar graphs Read, describe, and interpret primary data and secondary data presented in charts and graphs, including stem-andleaf plots and double bar graphs Predict the results of a simple probability experiment, then conduct the experiment and compare the prediction to the results Grade 5 Collect and organize discrete or continuous primary data and secondary data and display the data using charts and graphs, including broken-line graphs Read, describe, and interpret primary data and secondary data presented in charts and graphs, including broken-line graphs Represent as a fraction the probability that a specic outcome will occur in a simple probability experiment, using systematic lists and area models Grade 6 Collect and organize discrete or continuous primary data and secondary data and display the data using charts and graphs, including continuous line graphs Read, describe, and interpret data, and explain relationships between sets of data Determine the theoretical probability of an outcome in a probability experiment, and use it to predict the frequency of the outcome
Science and Technology Understanding Life Systems Habitats and Communities Systems and Interactions: plants and animals are interdependent and are adapted to meet their needs from the resources available in their particular habitats Sustainability and Stewardship: changes to habitats can affect plants and animals and the relationships between them Society relies on plants and animals Human Organ Systems Systems and Interactions: Organ systems are components of a larger system (the body) and, as such, work together and affect one another Structure and Function: Organ structures are linked to their functions Systems in the human body work together to meet our basic needs Choices we make affect our organ systems and, in turn, our overall health Biodiversity Systems and Interactions: Biodiversity includes diversity of individuals, species, and ecosystems. Sustainability and Stewardship: Classication of the components within a diverse system is a beginning point for understanding the interrelationships among the components. Because all living things are connected, maintaining diversity is critical to the health of the planet. Humans make choices that can have an impact on biodiversity. Flight Structure and Function: Flight occurs when the characteristics of structures take advantage of certain properties of air. Matter: Air has many properties that can be used for ight and for other purposes.
Understanding Structures and Mechanisms
Pulleys and Gears Systems and Interactions: Pulleys and gears change the speed, direction, and motion of, and force exerted on, moving objects Energy: Pulleys and gears make it possible for a small input force to generate a large output force Gears are specialized wheels and axles that are used daily in many machines
Forces Acting on Structures and Mechanisms Structure and Function: Structures and mechanisms throughout our environment have forces that act on and within them We can measure forces in order to determine how they affect structures and mechanisms. This information can be used to guide the design of new structures and mechanisms. Forces that result from natural phenomena have an effect on society and the environment. Properties of and Changes in Matter Matter: There are three states of matter Energy: Matter that changes state is still the same matter. Sustainability and Stewardship: Physical change refers to the fact that a substance can be changed from one form to another Chemical change implies the formation of a new substance The properties of materials determine their use and may have an effect on society and the environment Conservation of Energy and Resources Energy: Energy sources are either renewable or non-renewable Sustainability and Stewardship: Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but it can be transformed Choices about using energy and resources have both immediate and long-term impacts Conservation (reducing our use of energy and resources) is one way of reducing the impacts of using energy and resources.
Understanding Matter and Energy
Light and Sound Energy: Light and sound are forms of energy with specic properties Sound is created by vibrations Light is required to see Technological innovations involving light and sound have an impact on the environment
Electricity and Electrical Devices Energy: Electrical energy can be transformed into other forms of energy. Systems and Interactions: Other forms of energy can be transformed into electrical energy. Sustainability and Stewardship: Electrical energy plays a signicant role in society, and its production has an impact on the environment. Society must nd ways to minimize the impact of energy production on the environment. Space Systems and Interactions: Earth is a part of a large interrelated system. Technological and scientic advances that enable humans to study space affect our lives.
Understanding Earth and Space Systems
Rocks and Minerals Change and Continuity: Rocks and minerals have unique characteristics and properties that are a result of how they were formed Sustainability and Stewardship: The properties of rocks and minerals determine societys possible uses for them Structure and Function: Our use of rocks and minerals affects the environment
Social Studies
Junior Division - Big Ideas
Grade 4 Heritage and Citizenship Medieval Times Major features of daily life in medieval European societies Major events and inuences of the era and how they shaped medieval society Compare communities in medieval times with their own communities today Grade 5 Early Civilizations Inuence of natural environment on the development of various early civilizations around the world Changes in the ways human needs were met as a result of technological advances Signicant innovations of early civilization and continuing relevance to modern society Grade 6 First Nation Peoples and European Explorers Main characteristics of North American First Nation cultures, including their close relationship with the natural environment Motivating factors for early European exploration and the prevailing attitudes of the explorers Positive and negative effects of interactions between European and First Nation peoples from rst Viking contact to the time of permanent European settlement in the early 17th century Canadas Links to the World Canadas economic, political, social, and physical links with the US and other regions of the world Importance of international connections for Canadas well-being and inuence in the world Current international issues that concern Canada and Canadas response to them
Canada and World Connections
Canadas Provinces, Territories and Regions Physical and political divisions of Canada How physical characteristics inuence the economy and culture of Ontario and the other provinces and territories Use maps, graphics, and print materials Economic and cultural relationships that connect communities throughout the country
Aspects of Citizenship and Government in Canada Structure and function of the three levels of government in Canada and how they relate to one another Rights of groups and individuals and the responsibilities of citizenship in Canada Ways in which government and the responsibilities of citizenship directly affect their own lives
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Grade 3 Curriculum OverviewDocument15 paginiGrade 3 Curriculum Overviewapi-277609697Încă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10Document8 paginiGrade 10agha zahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- GR 3 ViewDocument15 paginiGR 3 Viewapi-250252817Încă nu există evaluări
- 11 Big Ideas in Curriculum A DurdanDocument5 pagini11 Big Ideas in Curriculum A Durdanapi-251923771Încă nu există evaluări
- Typical Course of Study: Grade 6: Language ArtsDocument8 paginiTypical Course of Study: Grade 6: Language Artsagha zahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 1 Curriculumoverview 20102011Document4 paginiGrade 1 Curriculumoverview 20102011api-239513595Încă nu există evaluări
- Audience AnalysisDocument12 paginiAudience AnalysisMulla AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Currsum4 13Document2 paginiCurrsum4 13api-259906596Încă nu există evaluări
- Communication Skills: - Nonverbal Communication - Oral Communication - Written CommunicationDocument73 paginiCommunication Skills: - Nonverbal Communication - Oral Communication - Written Communicationretailer72Încă nu există evaluări
- 8 CommunicationDocument29 pagini8 CommunicationAditya KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 4 (Four) Subject Description The ArtsDocument8 paginiGrade 4 (Four) Subject Description The Artsapi-273242824Încă nu există evaluări
- Skills and Competencies Needed For Successful SpeechmakingDocument33 paginiSkills and Competencies Needed For Successful SpeechmakingNiña CaracenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 3, English Teaching MethodsDocument46 paginiSession 3, English Teaching MethodsĐỗ Quỳnh TrangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Suggestions For Teaching Critical Listening and Story ComprehensionDocument24 paginiSuggestions For Teaching Critical Listening and Story ComprehensionHazwan AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Managing CommunicationDocument31 pagini8 Managing CommunicationkirsurkulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Life Skills: 2A: Tools/Techniques UsedDocument18 paginiAssessment of Life Skills: 2A: Tools/Techniques Usedspirit571Încă nu există evaluări
- Core CompetenciesDocument2 paginiCore Competenciesapi-476501990Încă nu există evaluări
- EthicsDocument5 paginiEthicsNeon AbrahamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Skills and Entrepreneurship DevelopmentDocument34 paginiGeneric Skills and Entrepreneurship DevelopmentDSKS EducationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speaking Theories PDFDocument32 paginiSpeaking Theories PDFAnonymous ZMLlQvBop100% (3)
- Lva1 App6891Document23 paginiLva1 App6891saidikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1 Developing Listening and Speaking SkillsDocument30 paginiTopic 1 Developing Listening and Speaking SkillsKoshla SegaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Typical Course of Study: Grade 7: Language ArtsDocument8 paginiTypical Course of Study: Grade 7: Language Artsagha zahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- MoralDocument31 paginiMoralKharl Ashley PastorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cognitive Communicative and Alternative Treatment ApproachesDocument51 paginiCognitive Communicative and Alternative Treatment ApproachesKrithikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 02Document15 paginiLecture 02Salman NisarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spoken EnglishDocument15 paginiSpoken Englisharjitkashyap5Încă nu există evaluări
- Applying Learning Theories To Healthcare PracticeDocument47 paginiApplying Learning Theories To Healthcare PracticeDylan VallartaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct File Topic DownloadDocument27 paginiDirect File Topic DownloadJass SidhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Strategies: Maria Azela L.Tamayo, PH.DDocument28 paginiReading Strategies: Maria Azela L.Tamayo, PH.DMarionette Asendido MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diass ReviewerDocument4 paginiDiass ReviewerClaire CleofasÎncă nu există evaluări
- P 21 SkillsmetDocument4 paginiP 21 Skillsmetapi-302204887Încă nu există evaluări
- Artificial IneleganceDocument42 paginiArtificial IneleganceNAGAVARDHAN 7CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading SkillsDocument35 paginiReading SkillsNivedita PatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Program PsychologyDocument3 paginiProgram PsychologyToni D.Încă nu există evaluări
- Teaching Listening & Speaking: Prepared by DR Sabariah MD RashidDocument23 paginiTeaching Listening & Speaking: Prepared by DR Sabariah MD RashidAysel SafarzadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 12Document8 paginiGrade 12agha zahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 6 at A GlanceDocument2 paginiGrade 6 at A Glanceapi-335724826100% (1)
- Kindergarten Curriculum Overview 091510Document5 paginiKindergarten Curriculum Overview 091510sonu621Încă nu există evaluări
- Core-Competencies Engelie Lara-Faure 1Document2 paginiCore-Competencies Engelie Lara-Faure 1api-691702370Încă nu există evaluări
- Special EducationDocument113 paginiSpecial EducationJudessa Abetona MalasagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designing Effective Training ProgramsparticipantsversionDocument20 paginiDesigning Effective Training ProgramsparticipantsversionKool BhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To IsDocument17 paginiIntroduction To IsAadil KakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eng3c SyllabusDocument4 paginiEng3c Syllabusapi-100040718Încă nu există evaluări
- Division 4 Curriculum OverviewDocument10 paginiDivision 4 Curriculum OverviewtuckwoodmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engl 158 - 3-Lecture 3 - Writing As A ProcessDocument37 paginiEngl 158 - 3-Lecture 3 - Writing As A ProcessAma Serwaa YeboahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Employability Skills 2001Document1 paginăEmployability Skills 2001api-235006458Încă nu există evaluări
- Speakout Upper-Intermediate PDFDocument48 paginiSpeakout Upper-Intermediate PDFLucia DominguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speakout Upper-Intermediate PDFDocument48 paginiSpeakout Upper-Intermediate PDFLucia DominguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growing With Groups 2023 1Document69 paginiGrowing With Groups 2023 1api-401672390Încă nu există evaluări
- Holland PresentationDocument27 paginiHolland Presentationapi-330710955Încă nu există evaluări
- Teaching ListeningDocument49 paginiTeaching ListeningmonicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exhibition Student Handbook Acs EnglandDocument19 paginiExhibition Student Handbook Acs Englandapi-279213766100% (5)
- 21st Century Report Card - ParentsDocument9 pagini21st Century Report Card - Parentsapi-371680417Încă nu există evaluări
- Principle of Teaching: Donald P. LlenoDocument85 paginiPrinciple of Teaching: Donald P. LlenoDonald LlenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3 - Writing As A ProcessDocument37 paginiLecture 3 - Writing As A ProcessSeyram AdomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Collection Tools in Qualitative Method-1Document44 paginiData Collection Tools in Qualitative Method-1Shristi DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- LET Reviewer Developmental ReadingDocument6 paginiLET Reviewer Developmental ReadingLois Jade TaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Portfolio Rubric - BlankDocument1 paginăPortfolio Rubric - Blankapi-202207322Încă nu există evaluări
- Advent Prayer Service - Presider VersionDocument4 paginiAdvent Prayer Service - Presider Versionapi-202207322Încă nu există evaluări
- Shared Reading - DiagramDocument2 paginiShared Reading - Diagramapi-202207322Încă nu există evaluări
- Problem SolvingDocument19 paginiProblem Solvingapi-202207322100% (1)
- g6 Integrated Ss LaDocument4 paginig6 Integrated Ss Laapi-202207322Încă nu există evaluări
- Dana - BrochureDocument2 paginiDana - Brochureapi-202207322Încă nu există evaluări
- Conference and Banqueting.Document14 paginiConference and Banqueting.john mwangiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test AaDocument55 paginiTest AaKaye PatanindagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Different Committees in The HospitalDocument8 paginiDifferent Committees in The HospitalShehnaz SheikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- PARS 19 - Slide PDFDocument23 paginiPARS 19 - Slide PDFNorsyaliza Abd Razak100% (1)
- Discuss Any Four Challenges Faced by Ovc and Their Intervention StrategiesDocument5 paginiDiscuss Any Four Challenges Faced by Ovc and Their Intervention StrategiesJohn MugabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MiraMate Light Pad InstructionsDocument8 paginiMiraMate Light Pad InstructionsLaurentMartinonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpretation: LPL - PSC Chandigarh Sector 19-D Booth No:-3, Sector:-19-D ChandigarhDocument5 paginiInterpretation: LPL - PSC Chandigarh Sector 19-D Booth No:-3, Sector:-19-D ChandigarhSanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prescribing For Transgender Patients ELHEDocument4 paginiPrescribing For Transgender Patients ELHEGe YgayÎncă nu există evaluări
- الصحة PDFDocument17 paginiالصحة PDFGamal MansourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Health Psychology Biopsychosocial Interactions 9th Edition Edward P Sarafino Timothy W SmithDocument37 paginiTest Bank For Health Psychology Biopsychosocial Interactions 9th Edition Edward P Sarafino Timothy W Smithsequelundam6h17s100% (13)
- Food StampsDocument80 paginiFood StampsAnvitaRamachandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- DebateDocument12 paginiDebate•Kai yiii•Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanDocument3 paginiLab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanGiacen100% (3)
- V-Gel Cleaning & User GuideDocument3 paginiV-Gel Cleaning & User GuideInstrulife OostkampÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predicting and Controlling Influenza Outbreaks - Published Article - IJERSTE - Vol.12 Issue 2, Feb 2023Document4 paginiPredicting and Controlling Influenza Outbreaks - Published Article - IJERSTE - Vol.12 Issue 2, Feb 2023dimple kharwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Back Pain During PregnancyDocument3 paginiBack Pain During PregnancyDr. Sadhana KalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Food Surety - Food Fraud Prevention Checklist (3p)Document3 paginiFood Surety - Food Fraud Prevention Checklist (3p)Mark KwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Influence of Music in Horror Games (Final Draft)Document7 paginiThe Influence of Music in Horror Games (Final Draft)Panther LenoXÎncă nu există evaluări
- EFT GuideDocument11 paginiEFT Guidenokaion19% (26)
- Misericordia LetterDocument2 paginiMisericordia LetterKatie DangerfieldÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5e-Schneider 2302 Chapter 7 MainDocument16 pagini5e-Schneider 2302 Chapter 7 MainMeni GeorgopoulouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Musculoskeletal Clinical Translation FrameworkDocument1 paginăMusculoskeletal Clinical Translation FrameworkRafaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pengaruh Metode Pengeringan Terhadap Karakter Mutu Fisik Dan Kimia Serbuk Minuman Instan Kulit Buah NagaDocument9 paginiPengaruh Metode Pengeringan Terhadap Karakter Mutu Fisik Dan Kimia Serbuk Minuman Instan Kulit Buah NagaHadi Yusuf FaturochmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uti StudiesDocument10 paginiUti Studiesapi-302840362Încă nu există evaluări
- Covid-19 RT-PCR Test Report & Certification: Certificate IssuedDocument1 paginăCovid-19 RT-PCR Test Report & Certification: Certificate IssuedJerome OliverosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Azibact MMDocument37 paginiAzibact MMરહીમ હુદ્દાÎncă nu există evaluări
- FNCP - Problem 3 HTNDocument3 paginiFNCP - Problem 3 HTNteuuuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma Case StudyDocument39 paginiAsthma Case StudyDimitris TasiouÎncă nu există evaluări
- DR Daniel Samadi MD PC - Pediatric ENT NJDocument7 paginiDR Daniel Samadi MD PC - Pediatric ENT NJPediatric ENT NJ by Dr Daniel SamadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study (Aub)Document16 paginiCase Study (Aub)Lucila Lugo0% (2)