Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Breaker
Încărcat de
Yudo Heru PribadiDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Breaker
Încărcat de
Yudo Heru PribadiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
A.
CIRCUIT BREAKER Is a device : - to open and close a circuit by non-automatic means - to open the circuit automatically on a predetermined overload of current or during faults without damage to itself when properly applied within its rating. - When the transformer primary reference current is equal or greater than 45 amperes or when there is more than one transformer in a substation, the protection will be by a power circuit breaker........................IEC
I. Capacity for medium Voltage EMBED Word.Picture.8
II. Capacity for High Voltage III. Capacity for Extra High Voltage
B. BREAKER RATINGS 1. Voltage Rating (Rated Maximum Voltage)
* the highest rms(root mean square) voltage, above nominal system voltage, for which the circuit breaker is designed, and is the upper limit of operation. * 15 kV, 72.5 kV, 145 kV, 245 kV 2.Continuous Current Rating (Rated Continuous Current) * Rated Continuous Current * the designated limit of current in rms amperes at rated frequency w/c it shall be required to carry continuously without exceeding any of the limitations/conditions in a specified ambient temperature. * Ambient temp. from -30 deg. C to 40 deg. C * Altitude is not above 3300 ft (1000m) 3.KAIC Rating (Rated Short Circuit Current, K=1) * Kilo-Ampere Interrupting Capacity (KAIC) * the maximum amount of symmetrical current that the breaker can safely interrupt at rated maximum voltage -without injuring or damaging itself. * KAIC = k X Rated Short-Circuit Current where: k = is the ratio of rated maximum voltage to the lower limit of the range of operating voltage. = Vmax / Vmin Modern Circuit Breakers, k = 1.0 KAIC = k X Rated Short Circuit Current = Rated Short Circuit Current Old Circuit Breakers, k>1.0 Condition 1: If RMV > OV > (1/k) x RMV then, KAIC = Rated Isc x (Rated Maximum Voltage / Operating Voltage) Condition 2: If OV < (1/k) x RMV then, KAIC is limited to Rated Isc x k KAIC = Rated Isc x k Example: Consider an indoor oilless circuit breaker having a rated short-circuit current of 37,000 A at rated maximum voltage of 15kV and K = 1.30. What is the symmetrical interrupting capability at an operating voltage at a.)13.2 kV? b.)11.5 kV? C. BREAKER SIZING E/X Simplified Method
- E/X simplified procedure result may be compared with 100% of the circuit breaker KAIC rating where X/R < 15 (X1/R1 for 3-phase faults) ((2X1 + Xo)/(2R1 + Ro) for SLG-faults) - If X/R is unknown, the E/X does not exceed 80% of the KAIC rating of the breaker. - For SLG Faults, where it is greater than the 3-Phase Faults or Xo less than X1
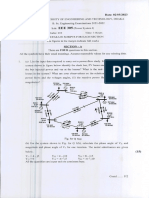
I. SAMPLE PROBLEM
A SUBSTATION
1. Solve for the maximum fault duties at the 3-phase fault points. 2. Specify the Voltage Ratings, Continuous Current Ratings & KAIC Ratings of the circuit breakers. A. Gb Fault Current at position I ( Primary side )
B. Gb Fault Current at position II ( Secondary side )
C. Table of Capacity circuit breaker rating
D. Diagram of current Fault at Primary Unit Substation
E. Diagram Fault current at Point 1
F. Diagram Fault current at Point II
G. Table of capacity Circuit Breaker rating
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Building Design PDFDocument6 paginiBuilding Design PDFYudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- ASQ Presentation FCG November 2017Document131 paginiASQ Presentation FCG November 2017SaemundrSigfussonÎncă nu există evaluări
- FullPaperSNI2004 Hardi N-EvaluasiSisProteksiSDHDocument8 paginiFullPaperSNI2004 Hardi N-EvaluasiSisProteksiSDHYudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Manual Kalkulasi Voltage Drop P-At.A (Panel Atap Tower A) : Sheet 4 OF 4Document4 paginiManual Kalkulasi Voltage Drop P-At.A (Panel Atap Tower A) : Sheet 4 OF 4Yudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Construction PlanDocument223 paginiConstruction PlanYudo Heru Pribadi100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Universal Teleprotection: Test CertificateDocument7 paginiUniversal Teleprotection: Test CertificateYudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Shielding of Power CablesDocument6 paginiShielding of Power CablesYudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Tray and Ladder Practice GuideDocument73 paginiTray and Ladder Practice GuidemariusrotaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Dahandbook Section 08p07 Protection of HV Transformers 757288 EnaDocument36 paginiDahandbook Section 08p07 Protection of HV Transformers 757288 EnarajanarsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- CSR Bradford Acoustic Design GuideDocument80 paginiCSR Bradford Acoustic Design Guideambiencea100% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Cable Installation ManualDocument95 paginiCable Installation Manualjohnnybe510% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Diesel Electric Generating PlantsDocument104 paginiDiesel Electric Generating Plantsnavinchopra1986100% (3)
- Cable Installation ManualDocument95 paginiCable Installation Manualjohnnybe510% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Catalog Practical Advices Surge Arrestors by SchneiderDocument15 paginiCatalog Practical Advices Surge Arrestors by SchneiderYudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Short Circuit CalculationDocument46 paginiShort Circuit Calculationratnesh_xp1Încă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- 3.1 Turbine and GoverningDocument90 pagini3.1 Turbine and GoverningYudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Arc Busbar in SwitchboardDocument11 paginiArc Busbar in SwitchboardYudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical CheckListDocument33 paginiElectrical CheckListYudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide To Selection of Electrical CableDocument46 paginiA Guide To Selection of Electrical Cableapi-3808029100% (7)
- Short Circuit CalculationDocument42 paginiShort Circuit Calculationgraduadoesime100% (17)
- Practical Introduction To Power System Protection & ControlDocument94 paginiPractical Introduction To Power System Protection & Controlriogomes73% (11)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Basics of ElectricityDocument88 paginiBasics of Electricitysavannah78Încă nu există evaluări
- Methods of Estimating Steam ConsumptionDocument23 paginiMethods of Estimating Steam ConsumptionYudo Heru Pribadi75% (4)
- Test & Commisioning Super ConductorDocument168 paginiTest & Commisioning Super ConductorYudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Recovery of Switching CapacitorDocument4 paginiRecovery of Switching CapacitorYudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineer Manual - Engineer and Design Liquid Process Piping - ReviewDocument245 paginiEngineer Manual - Engineer and Design Liquid Process Piping - ReviewSyedFAkharAbbas100% (5)
- Installation Wiring HomeDocument50 paginiInstallation Wiring HomeYudo Heru Pribadi100% (1)
- Systems, Structure and ControlDocument188 paginiSystems, Structure and ControlYudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Short Circuit AnalysisDocument5 paginiShort Circuit AnalysisYudo Heru PribadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview QuestionsDocument2 paginiInterview QuestionsBala SubramaniyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IWCF Kick SheetDocument3 paginiIWCF Kick SheetKathryn SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pertemuan 7. Unit Protection (T. DAVIES) Protection of Industrial Power SystemsDocument24 paginiPertemuan 7. Unit Protection (T. DAVIES) Protection of Industrial Power Systemswijayaroni363Încă nu există evaluări
- Bin WuDocument44 paginiBin WuYennifer AlcainoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gee 1993Document9 paginiGee 1993DIEGO JUAN POZO REYNAGAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordinación de Protecciones SiemensDocument9 paginiCoordinación de Protecciones SiemensivanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SJP - 220kv KPTCL - Busbar - 2bba1 & 2bba2Document56 paginiSJP - 220kv KPTCL - Busbar - 2bba1 & 2bba2kalinath41100% (1)
- Study of BUET Power Plant and Sub-Stations: EEE 306 Experiment 5Document4 paginiStudy of BUET Power Plant and Sub-Stations: EEE 306 Experiment 5সামিন জাওয়াদ100% (1)
- Control Cable - Trafo BayDocument25 paginiControl Cable - Trafo BayAnupam0103Încă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Approach To Estimate Feeder AccommodatiDocument16 paginiAnalytical Approach To Estimate Feeder AccommodatiCleberton ReizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- PartsOfSection - Alternator - Generator Part ListingDocument3 paginiPartsOfSection - Alternator - Generator Part ListingAndi RifkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Guide ABB MV-Protection (EN) - 1VCP000280Document52 paginiTechnical Guide ABB MV-Protection (EN) - 1VCP000280Cesar VenturoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logic SelectivityDocument6 paginiLogic SelectivitymoosuhaibÎncă nu există evaluări
- L-3ff - lIEEE Date: 02/05/2023: Toomw 200MW 20 Mvar 9 Mvar Bus 2Document26 paginiL-3ff - lIEEE Date: 02/05/2023: Toomw 200MW 20 Mvar 9 Mvar Bus 2mahiyanintesirprethuprethuÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Single Line Diagram: Sajad 1Document3 paginiGeneral Single Line Diagram: Sajad 1Mahyar MashayekhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radial, Loop Double and Grid Form SystemsDocument29 paginiRadial, Loop Double and Grid Form SystemsHamid RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types and Applications of Overcurrent Relay 1Document10 paginiTypes and Applications of Overcurrent Relay 1Alfredo RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uni M Size 9E and 10 Inverter and Rectifier Sheet Issue 3 (0478-0115-03) - ApprovedDocument7 paginiUni M Size 9E and 10 Inverter and Rectifier Sheet Issue 3 (0478-0115-03) - ApprovedDave CárdenasÎncă nu există evaluări
- L&T Electrical & Automation: (+VE) (-VE) (+VE) (-VE)Document1 paginăL&T Electrical & Automation: (+VE) (-VE) (+VE) (-VE)Sivachandran RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prathama Solarconnect Energy Private Limited: Short Circuit Study ReportDocument18 paginiPrathama Solarconnect Energy Private Limited: Short Circuit Study Reportramesh cuppuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distance Principles - Basic PrincipleDocument76 paginiDistance Principles - Basic Principlemanu2020100% (1)
- FG Wilson Product - Rating - SummaryDocument8 paginiFG Wilson Product - Rating - Summaryre marÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buchholz Relay For Transformer ProtectionDocument5 paginiBuchholz Relay For Transformer ProtectionAhmed Said GhonimyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 800MW DPR - Electrical CommentsDocument2 pagini800MW DPR - Electrical CommentsrukmagoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Substation EquipmentsDocument62 paginiSubstation Equipmentskarikalan1100% (5)
- GensetDocument6 paginiGensetMark Moldez0% (1)
- Dimo ReportDocument51 paginiDimo ReportKASUN DILANGAÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Difference Between Earthing and Grounding?: 45 AnswersDocument1 paginăWhat Is The Difference Between Earthing and Grounding?: 45 Answersrod8silvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Well Control Kill Sheet (Low Angle Wells) : (BBLS) Drillstring Volume Annular Volume (BBLS)Document2 paginiWell Control Kill Sheet (Low Angle Wells) : (BBLS) Drillstring Volume Annular Volume (BBLS)scrbdgharaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Good Presentation On Power TransformersDocument38 paginiGood Presentation On Power TransformersAdetunji TaiwoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationDe la EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Enhanced Oil Recovery Handout: A Focus on WaterfloodingDe la EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery Handout: A Focus on WaterfloodingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataDe la EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (22)
- Case Studies of Material Corrosion Prevention for Oil and Gas ValvesDe la EverandCase Studies of Material Corrosion Prevention for Oil and Gas ValvesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsDe la EverandGas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)